Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Key Ideas
Uploaded by
api-261372832Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Key Ideas
Uploaded by
api-261372832Copyright:
Available Formats
Matter
Section 2
Key Ideas
Why are color, volume, and density classified as
physical properties?
Why are flammability and reactivity classified as
chemical properties?
Matter
Section 2
Bellringer
Physical properties are characteristics of a substance that
can be observed without changing the composition of the
substance. Physical properties are often used to separate
a mixture into its original components. Imagine that you
have been given a mixture of sand, sugar, pieces of cork,
and iron filings.
Think about how you can use the physical properties of
the sand, sugar, cork, and iron filings in order to separate
them out of the mixture.
Matter
Section 2
Bellringer, continued
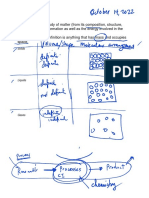
1. What do you separate in the first step?
How?
2. What is separated out in the second
step? How?
3. What happens in the third step?
Matter
Section 2
Physical Properties
Why are color, volume, and density classified as
physical properties?
Physical properties are characteristics that can
be observed without changing the identity of the
substance. Name 5 of these
Matter
Section 2
Physical Properties, continued
Physical properties can help identify substances. In fact we
classify almost all matter based on its physical properties
Physical properties can be observed or measured.
Examples: shape, color, odor, texture, state, melting
point, boiling point, strength, hardness, magnetism, the
ability to conduct electricity or heat
melting point: the temperature and pressure at which a solid
becomes a liquid
boiling point: the temperature and pressure at which a liquid
becomes a gas
Physical properties help determine uses. EX Construction
Matter
Section 2
Visual Concept: Solid, Liquid and Gas
Matter
Section 2
Physical Properties, continued
Density is a physical property.
Question: What has more mass, a ton of feathers or a ton of
bricks?
Which takes up more space? Which is more dense?
mass
m
density
, or D
volume
V
density: the ratio of the mass of a substance to the volume
of the substance
common unit of density is g/cm 3
Density is different from weight.
Matter
Section 2
Low and High Density Objects
Matter
Section 2
Math Skills
WS: Rearanging algebraic equations
Density
If 10.0 cm3 of ice has a mass of 9.17 g, what is the
density of ice?
1. List the given and unknown values.
Given: mass, m = 9.17 g
volume, V = 10.0 cm3
Unknown: density, D = ? g/cm3
Matter
Section 2
Math Skills, continued
2. Write the equation for density.
density = mass/volume, or D = m/V
3. Insert the known values into the equation, and
solve.
m
D
V
9.17 g
D
10.0 cm3
D = 0.917 g/cm3
Matter
Section 2
Chemical Properties
Why are flammability and reactivity classified
as chemical properties?
A chemical property describes how a substance
changes into a new substance, either by
combining with other elements or by breaking
apart into new substances.
Matter
Section 2
Chemical Properties, continued
Flammability is a chemical property.
flammability: the ability to burn
Reactivity is a chemical property.
reactivity: the capacity of a substance to combine chemically
with another substance creating different substances as a
result.
Matter
Section 2
Chemical Properties, continued
Physical and chemical properties are different.
Physical properties can be observed without changing
the identity of a substance.
EX: measuring mass, feeling texture, density, odor
Chemical properties can be observed only in situations
in which the identity of the substance changes.
EX: Flammibility, reactivity
Matter
Section 2
Reactions vary in speed
Slow
Iron rusting (oxidizing)
Matter
Section 2
Reactions vary in speed
Fast
Baking soda and vinegar
Matter
Section 2
Reactions vary in speed
Very Fast
Alkali metals (Sodium, etc) and water
Alkali Reactions
Matter
Section 2
Visual Concept: Comparing Physical and
Chemical Properties
You might also like
- Interactive Textbook1 2 Pproperties of MatterDocument7 pagesInteractive Textbook1 2 Pproperties of Matterapi-240094705No ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument10 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesGerald CatiponNo ratings yet
- W1 - Matter and Separation TechniquesDocument28 pagesW1 - Matter and Separation TechniquesLouie BarrientosNo ratings yet
- What Are Physical Properties of Matter?Document32 pagesWhat Are Physical Properties of Matter?Tomasian100% (1)
- Chem 1 L1 W1Document51 pagesChem 1 L1 W1Desire JoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Properties of MatterDocument36 pagesChapter 2 - Properties of MatterAlberto Armas100% (1)
- Gen - Chem 1-Week 1 and 2Document13 pagesGen - Chem 1-Week 1 and 2Mishal NoroñaNo ratings yet
- Percentage Composition: Juliusleo M. Martin Teacher IIIDocument26 pagesPercentage Composition: Juliusleo M. Martin Teacher IIIjuliusleo martin100% (1)
- Gen Chem 1 Q1Mod1Document23 pagesGen Chem 1 Q1Mod1Joselito UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Local Media8006898687101183011Document26 pagesLocal Media8006898687101183011Aryan Francis LampitocNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science VIDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science VILim Torres100% (9)
- General Chemistry 1: Quarter 3 - WEEK 1Document24 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Quarter 3 - WEEK 1RODEL AZARESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Classification of MatterDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Classification of MatterPatrice Francisco100% (1)
- Local Media7711445783592677217Document33 pagesLocal Media7711445783592677217katNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Jeannie QuillanoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Describing MatterDocument16 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Describing MatterJohn Paul Recopuerto ParachaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 LM General Chemistry1 Module1Document13 pagesGrade 11 LM General Chemistry1 Module1Micaela Jhane GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 and 2: Properties of Matter: Rbi Script: General Chemistry 1 Prepared By: Donnafe M. AganonDocument2 pagesLesson 1 and 2: Properties of Matter: Rbi Script: General Chemistry 1 Prepared By: Donnafe M. Aganonbenjie panlicanNo ratings yet
- Mark Ace Lardera - (Template) Learning Activity Sheet Grade 12 STEM General Chemistry 1 Week 1Document8 pagesMark Ace Lardera - (Template) Learning Activity Sheet Grade 12 STEM General Chemistry 1 Week 1Zyrus Dizon MondiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Physical Vs Chemical PropertiesDocument21 pagesLesson 1 Physical Vs Chemical PropertiesHey IsabelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.04 Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesLesson 1.04 Chemistry Notescamaron123No ratings yet
- Chem. Lesson 1Document31 pagesChem. Lesson 1Ashlee Talento100% (1)
- week-1-2-Properties-of-Matter (2) NOTESDocument5 pagesweek-1-2-Properties-of-Matter (2) NOTESJerome SarsonasNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - General Chemistry 1 (Final)Document7 pagesModule 1 - General Chemistry 1 (Final)Mutsumi JingujiNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Properties of MatterDocument16 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Properties of MatterLovely Trixie D. DandalNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDocument17 pagesScience 6 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterLharize CastroNo ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument12 pagesProperties of MatterKriz ZiaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chemistry 1-Task 1Document4 pagesGen Chemistry 1-Task 1khlneNo ratings yet
- Hubilla, Neil Jhon - Chemistry M1L1Document7 pagesHubilla, Neil Jhon - Chemistry M1L1Neil Jhon HubillaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Mathematics, Science, and TechnologyDocument3 pagesModule 5 Mathematics, Science, and TechnologyMarianne Bag-aoNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1 W1Document7 pagesGen Chem 1 W1Kenken GenotivaNo ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument73 pagesProperties of Matterkimsioco02No ratings yet
- Bulk Properties of MatterDocument11 pagesBulk Properties of Matterstock hackNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Section 5.1 - Chemical and Physical ChangeDocument4 pagesLesson 1 - Section 5.1 - Chemical and Physical ChangeshanlbyNo ratings yet
- Merged Lectures Chem 140 Sem2 2022-2023 Chap 1-12Document375 pagesMerged Lectures Chem 140 Sem2 2022-2023 Chap 1-12haitham101297No ratings yet
- Properties of Matter Lesson 1Document39 pagesProperties of Matter Lesson 1mika3laac0sta14No ratings yet
- p4.3.1 - Year 9 Physics Study Pack States of Matter Work 1Document2 pagesp4.3.1 - Year 9 Physics Study Pack States of Matter Work 1ChickenNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry For NEET 2023 - Free PDF DownloadDocument13 pagesRevision Notes On Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry For NEET 2023 - Free PDF Downloaddoctor188001No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Matter PropertiesDocument32 pagesLecture 1 Matter PropertiesAhmed FouadNo ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument34 pagesProperties of MatterElmas ChiongNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1Document60 pagesModule 1 Lesson 107 JAVIER LLYOD GENELSON B.No ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument4 pagesREVIEWERKim RonaldNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Jelou LumakinNo ratings yet
- Module1 MeasurementDocument73 pagesModule1 MeasurementGelacio Masgong IIINo ratings yet
- (Week 1, Week 2 - Module 1 - Module 2... ) Science8-Q3-Slm1Document35 pages(Week 1, Week 2 - Module 1 - Module 2... ) Science8-Q3-Slm1Ron FamilaranNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem1-Week1Document58 pagesGen Chem1-Week1llamasballsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Notes FilledDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Notes FilledlizschNo ratings yet
- PS - 6 Chapter 02Document98 pagesPS - 6 Chapter 02taekang JeonNo ratings yet
- GeneralChemistry1 - Quarter1 - Week 1-4Document81 pagesGeneralChemistry1 - Quarter1 - Week 1-4Aze Mamalayan100% (1)
- Questions 8/8/2011: Write 4 Questions Here About THE Information On This PageDocument5 pagesQuestions 8/8/2011: Write 4 Questions Here About THE Information On This PageYhena ChanNo ratings yet
- PROPERTIES OF SUBSTANCES - PPTDocument8 pagesPROPERTIES OF SUBSTANCES - PPTDarko TrajanovNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Concepts Classification and States of MatterDocument40 pagesUnit 2 Concepts Classification and States of Matterapi-327076063No ratings yet
- Special andDocument16 pagesSpecial andapi-271064836No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Matter and Its PropertiesDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Matter and Its PropertiesJennelyn BaylonNo ratings yet
- Special andDocument16 pagesSpecial andapi-271036545No ratings yet
- ModuleDocument7 pagesModuleapi-353861615100% (1)
- Teacher-Made Learner's Home Task: S7MT-ib-c-3 S7MT-id-e-2Document4 pagesTeacher-Made Learner's Home Task: S7MT-ib-c-3 S7MT-id-e-2Carissa Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- 1 Chemistry For Engineers Chemistry and Measurement 2023Document38 pages1 Chemistry For Engineers Chemistry and Measurement 2023Hanzly AurellanoNo ratings yet
- Diffun Campus: Laboratory HighschoolDocument4 pagesDiffun Campus: Laboratory HighschoolhaydeeNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 (Grade 11-STEM) : The Study of MatterDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 (Grade 11-STEM) : The Study of MatterRafael MalonzoNo ratings yet
- 01 The Study of Chemistry and MeasurementsDocument6 pages01 The Study of Chemistry and MeasurementsJoshua HernandezNo ratings yet
- Week 12Document1 pageWeek 12api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 13Document1 pageWeek 13api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 13Document1 pageWeek 13api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 11Document1 pageWeek 11api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 12Document1 pageWeek 12api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 10Document1 pageWeek 10api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 10Document1 pageWeek 10api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 6Document1 pageWeek 6api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 9Document1 pageWeek 9api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 8Document1 pageWeek 8api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 7Document1 pageWeek 7api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 6Document1 pageWeek 6api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 9Document1 pageWeek 9api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 8Document1 pageWeek 8api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 9Document1 pageWeek 9api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 8Document1 pageWeek 8api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 7Document1 pageWeek 7api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 6Document1 pageWeek 6api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 5Document1 pageWeek 5api-261372832No ratings yet
- Week 5Document1 pageWeek 5api-261372832No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Analytical Chemistry PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - Analytical Chemistry PDFImanghhNo ratings yet
- APTET Syllabus Paper IIDocument15 pagesAPTET Syllabus Paper IIrajendra kumar devarapalliNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: I. II. Iii. IV. A. BDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: I. II. Iii. IV. A. BLuz Marie CorveraNo ratings yet
- Nature of MatterDocument39 pagesNature of MatterChaela GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Aqua Regia - WikipediaDocument34 pagesAqua Regia - WikipediaLựuLiềuLìNo ratings yet
- Emission Management Process Walkthrough 20170308-1Document67 pagesEmission Management Process Walkthrough 20170308-1heyravikumarNo ratings yet
- Otto Channel - 10 Đề chuyên HCM - Happy new year 2021Document65 pagesOtto Channel - 10 Đề chuyên HCM - Happy new year 2021Cỏ May Mắn100% (1)
- Power Puffcorns Lab ExperimentDocument13 pagesPower Puffcorns Lab ExperimentJonas Tristan Del MundoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Chemical EngineerDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Chemical EngineerJose Antonio Fermin JimenezNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED Inoganic BookDocument490 pagesADVANCED Inoganic BookHassan Haider100% (1)
- Organ System ReviewerDocument31 pagesOrgan System ReviewerDronio Arao L-saNo ratings yet
- October 2013 - Part 1 of 2Document721 pagesOctober 2013 - Part 1 of 2SonjaWaltersNo ratings yet
- Science 5 (Part1 - Worksheets) - 1st QuarterDocument10 pagesScience 5 (Part1 - Worksheets) - 1st QuarterROMENo ratings yet
- Science: First Quarter - Module 3 Mixtures and SubstancesDocument26 pagesScience: First Quarter - Module 3 Mixtures and SubstancesFatulousNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions - Class XIIDocument58 pagesChemical Reactions - Class XIImsujoyNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Specification FOR Ready Mixed Paint, Dipping, Fire ResistingDocument13 pagesIndian Standard: Specification FOR Ready Mixed Paint, Dipping, Fire ResistingDevapradatta NathNo ratings yet
- Amo MaxDocument2 pagesAmo MaxamitiffcoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lecture Part 1Document49 pagesModule 1 Lecture Part 1Princess joy De RuedaNo ratings yet
- Purifier and Its FunctionDocument23 pagesPurifier and Its FunctionDim lordwin HacutinaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry+Final+Exam+Practice+Problems,+Set+I+ (Dec +2022)Document4 pagesChemistry+Final+Exam+Practice+Problems,+Set+I+ (Dec +2022)srinath parvatine100% (1)
- Karbon Aktif ProsesDocument23 pagesKarbon Aktif ProsesUlil AmbriNo ratings yet
- CDTX PatentDocument16 pagesCDTX PatentCharles GrossNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering For Non-Chemical Engineers - AIChEDocument2 pagesChemical Engineering For Non-Chemical Engineers - AIChEKajer quemar50% (2)
- Lab Report 3Document3 pagesLab Report 3Nayli QistinaNo ratings yet
- SABIC HDPE M200056 TOYD Global en 2021 08 02Document2 pagesSABIC HDPE M200056 TOYD Global en 2021 08 02Rishi100% (1)
- Edited MSDS TDM 02.05.2022Document1 pageEdited MSDS TDM 02.05.2022Sajjad MaqboolNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report Experiment 5 - Group 7Document26 pagesLaboratory Report Experiment 5 - Group 7Jeremy Kyle Edson AustriaNo ratings yet
- Content Vocabulary: Longman Dictionary of American EnglishDocument14 pagesContent Vocabulary: Longman Dictionary of American EnglishSeyed Mahdi MousaviNo ratings yet