Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Automatic Battery Charger
Uploaded by
Juli SetiawanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Automatic Battery Charger
Uploaded by
Juli SetiawanCopyright:
Available Formats
Automatic Battery Charger
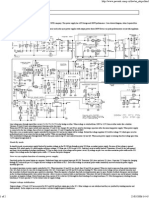
Charging current as well as the power to the circuit is obtained from a 0-18 volt 2
Ampere step-down transformer. The low voltage AC is rectified by the bridge rectifier
comprising D1 through D4 and made ripple free by the smoothing capacitor C1. For
charging purpose, 18 volt DC is used while to power the circuit, 9 volt regulated DC from
IC1 is used.
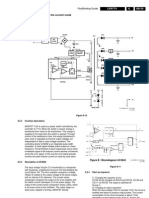
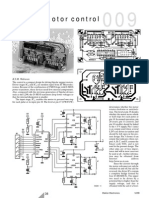
Schematic of the Automatic Battery Charger Circuit
IC2 (CA3140) is used as a simple voltage comparator to drive the relay. Its inverting
input gets 4.7 volt reference voltage from the Zener ZD, while the non inverting input
gets an adjustable voltage through the POT VR1.So normally, the inverting input pin 2
gets higher voltage from the Zener (as adjusted by VR1) and output of IC2 remains low.
T1 then remains off keeping the relay off. The charging current passes to the battery
through the NC (Normally Connected) contacts of the relay.
When the terminal voltage of the battery increases to 13.5 volts, pin 3 of IC2 gets higher
voltage than pin2 and the output of IC2 becomes high. This activates the relay and the
contacts break. Charging current to the battery cut off and the relay remains as such
since the battery voltage(13.5V or more) keeps the voltage at pin3 of IC2 is higher than
that of pin 2.
Charger Settings
Before connecting the battery, set the input voltage to IC2 using a fully charged battery
or variable power supply. Turn the switch S1 to the off position and switch on the power.
Then connect a fully charged battery/ variable power supply to test points TP observing
polarity. Measure the input voltage to pin 3 of IC2.
Slowly adjust VR1 till the input voltage to pin 3 of IC2 raises to 5 volts. At this point,
relay should energize and Red LED turns on. Then connect the battery for charging and
switch on S1. If the battery takes charge, current to pin 3 of IC2 will be low since most
of the current drain occurs into the battery. This keeps the relay off. When the battery
voltage increases above 13.5 volts, no more current passes into the battery, so that the
voltage at pin3 of IC2 rises and relay turns on.
You might also like
- PHILIPS CDR775 - AlimentaciónDocument10 pagesPHILIPS CDR775 - Alimentaciónvideoson100% (1)
- Automatic Battery Charger CircuitDocument2 pagesAutomatic Battery Charger Circuitajith_b88100% (1)
- Mobile Cellphone Battery ChargerDocument2 pagesMobile Cellphone Battery ChargerWahyu NovendiNo ratings yet
- Qa 00187 Mobile Charger CircuitDocument3 pagesQa 00187 Mobile Charger CircuitShivam JainNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram of Mobile Phone Battery Charger TestedDocument3 pagesCircuit Diagram of Mobile Phone Battery Charger TestedMashood NasirNo ratings yet
- 12V Battery Charger-cum-Variable Power SupplyDocument11 pages12V Battery Charger-cum-Variable Power SupplyLOLO ISMUNASIBNo ratings yet
- Qa 00187 Mobile - Charger - CircuitDocument3 pagesQa 00187 Mobile - Charger - CircuitShayan FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Over and Under-Voltage Protection Circuit: The Parts ListDocument4 pagesOver and Under-Voltage Protection Circuit: The Parts Listbelacheweshetu222No ratings yet
- 12v 7ah Smart Battery Charger With PCB DiagramDocument3 pages12v 7ah Smart Battery Charger With PCB DiagramRajeeb DasNo ratings yet
- Battery-Low Indicator: Raj K. GorkhaliDocument1 pageBattery-Low Indicator: Raj K. GorkhaliÁsgeirr Ánsgar Ósgar CanuroNo ratings yet
- 200w Atx PC Power SupplyDocument7 pages200w Atx PC Power SupplyGustavo OchoaNo ratings yet
- Best 12 Volt Auto Battery Charger Circuit Using LM311Document3 pagesBest 12 Volt Auto Battery Charger Circuit Using LM311Anjali Sharma100% (1)
- Solar Battery Charging Indicator: T.K. HareendranDocument2 pagesSolar Battery Charging Indicator: T.K. HareendranRakeshNo ratings yet
- Auto Reset Over-UnderDocument1 pageAuto Reset Over-UnderSai Krishna KodaliNo ratings yet
- K193 - Smart SLA Battery Charger: Heatsink Will Be Too Hot To TouchDocument3 pagesK193 - Smart SLA Battery Charger: Heatsink Will Be Too Hot To TouchuimNo ratings yet
- ChargerDocument2 pagesChargerRuslan ChengNo ratings yet
- Auto Reset Over-UnderDocument1 pageAuto Reset Over-UnderVishnu K NairNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics ProjectsDocument5 pagesPower Electronics ProjectsEngr FN ANo ratings yet
- Fast Charger With Auto Cut OffDocument3 pagesFast Charger With Auto Cut OffAlberto BrulNo ratings yet
- Low Cost LED Emergency LightDocument2 pagesLow Cost LED Emergency LightAmir AshrafiNo ratings yet
- 12 Volt Car Battery Charger Circuit SchematicDocument2 pages12 Volt Car Battery Charger Circuit SchematicJaved hashimNo ratings yet
- Mini Offline UPSDocument13 pagesMini Offline UPSGadhiya KhimjiNo ratings yet
- Automatic 40 Watt LED Solar Street Light Circuit ProjectDocument4 pagesAutomatic 40 Watt LED Solar Street Light Circuit Projectsamsai888No ratings yet
- Mobile Battery Charging Circuit: Deepak GuptaDocument2 pagesMobile Battery Charging Circuit: Deepak Guptaujjwalgupta4No ratings yet
- Constant-Current Batter Char Er: IdeasDocument54 pagesConstant-Current Batter Char Er: IdeasKliffy Fernandes100% (1)
- Experiment - 10: Prepare Circuit of Automatic Emergency Light Using IC-LM317Document3 pagesExperiment - 10: Prepare Circuit of Automatic Emergency Light Using IC-LM317ArjunAgharaNo ratings yet
- 200w Power SupplyDocument4 pages200w Power SupplySungyong SohnNo ratings yet
- Automatic Battery ChargerDocument2 pagesAutomatic Battery ChargervipincktyNo ratings yet
- Project DescriptionDocument8 pagesProject DescriptionChester Kyle SantosNo ratings yet
- Best 12V Battery Charger Circuit Using LM311Document3 pagesBest 12V Battery Charger Circuit Using LM311Aïn' FidyNo ratings yet
- 94 96 DIY 12V Battery Charger EFY Nov 16Document3 pages94 96 DIY 12V Battery Charger EFY Nov 16Vaz PatrickNo ratings yet
- How To Build An Automatic 6 Volt, 12 Volt, 24 Volt Lead Acid Battery Charger CircuitDocument3 pagesHow To Build An Automatic 6 Volt, 12 Volt, 24 Volt Lead Acid Battery Charger Circuitmaster chibukingNo ratings yet
- Best Auto Bat Charger LM311Document2 pagesBest Auto Bat Charger LM311bbela77No ratings yet
- Li-Ion Accu ChargerDocument3 pagesLi-Ion Accu ChargervdwuNo ratings yet
- 12V 4A Solar ChargerDocument2 pages12V 4A Solar Chargerdoraemon007No ratings yet
- Driver L297 + L6203Document2 pagesDriver L297 + L6203TatiiieleeeNo ratings yet
- Pyroelectric Fire AlarmDocument2 pagesPyroelectric Fire AlarmUma ShankarNo ratings yet
- Battery ChargersDocument8 pagesBattery ChargersRez HabloNo ratings yet
- Mobile ChargerDocument1 pageMobile ChargerVaz Patrick100% (1)
- Title of The Miniproject: "Mini UPS System"Document4 pagesTitle of The Miniproject: "Mini UPS System"vinay_lamkhadeNo ratings yet
- K241 AwebnotesDocument3 pagesK241 Awebnotespetre_blackNo ratings yet
- Charger For Mobile PhonesDocument2 pagesCharger For Mobile PhonessivaganeshanNo ratings yet
- 200w 20atx 20pc 20powerDocument2 pages200w 20atx 20pc 20powerdanielradu27No ratings yet
- Variable Switch Mode Power Supply 0Document4 pagesVariable Switch Mode Power Supply 0Raj KanungoeNo ratings yet
- Digital ThermometerDocument4 pagesDigital ThermometerPran KumarNo ratings yet
- Circuit ExplanationDocument3 pagesCircuit ExplanationRizan ShahNo ratings yet
- 6V 12V 24V Battery Charger CircuitDocument3 pages6V 12V 24V Battery Charger Circuitsuvarna247750% (2)
- Rain AlarmDocument3 pagesRain AlarmSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Project of Electronics SubjectDocument14 pagesProject of Electronics SubjectDarren Troy Lingao MayorNo ratings yet
- 555 DC Voltage Doubler CircuitDocument1 page555 DC Voltage Doubler CircuitWaskita IITNo ratings yet
- TL494Document4 pagesTL494Siddiq Al FajarNo ratings yet
- Lab Power Supply 0-20V and 0.002-4A: InstructablesDocument9 pagesLab Power Supply 0-20V and 0.002-4A: InstructablesOliveira OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Thyristor Application & Photosensitive Control Circuits: Chapter No.5Document28 pagesThyristor Application & Photosensitive Control Circuits: Chapter No.5Kim ManaloNo ratings yet
- Variable Switch Mode Power Supply 0Document5 pagesVariable Switch Mode Power Supply 0silviaNo ratings yet
- 12V Car Battery Charger: Part ListDocument3 pages12V Car Battery Charger: Part ListronnelnacpilNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)