Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Understandings
Uploaded by
api-2274536710 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
94 views1 pageATP from cell respiration is immediately available as a source of energy in the cell. Details of the metabolic pathways of cell respiration are not needed but the substrates and final waste products should be known. Students are expected to know that an alkali is used to absorb CO2, so reductions in volume are due to oxygen use.
Original Description:
Original Title
understandings
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentATP from cell respiration is immediately available as a source of energy in the cell. Details of the metabolic pathways of cell respiration are not needed but the substrates and final waste products should be known. Students are expected to know that an alkali is used to absorb CO2, so reductions in volume are due to oxygen use.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
94 views1 pageUnderstandings
Uploaded by
api-227453671ATP from cell respiration is immediately available as a source of energy in the cell. Details of the metabolic pathways of cell respiration are not needed but the substrates and final waste products should be known. Students are expected to know that an alkali is used to absorb CO2, so reductions in volume are due to oxygen use.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
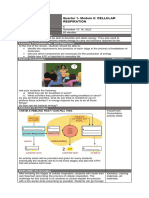
Understandings, Applications and Skills (This is what you maybe assessed on)
Statement
Guidance
2.8.U1
Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from
organic compounds to produce ATP.
Details of the metabolic pathways of cell
respiration are not needed but the
substrates and final waste products should
be known.
2.8.U2
ATP from cell respiration is immediately available as a
source of energy in the cell.
2.8.U3
Anaerobic cell respiration gives a small yield of ATP from
glucose.
2.8.U4
Aerobic cell respiration requires oxygen and gives a large
yield of ATP from glucose.
2.8.A1
Use of anaerobic cell respiration in yeasts to produce
ethanol and carbon dioxide in baking.
2.8.A2
Lactate production in humans when anaerobic respiration
is used to maximize the power of muscle contractions.
2.8.S1
Analysis of results from experiments involving
measurement of respiration rates in germinating seeds or
invertebrates using a respirometer.
There are many simple respirometers which
could be used. Students are expected to
know that an alkali is used to absorb CO2,
so reductions in volume are due to oxygen
use. Temperature should be kept constant
to avoid volume changes due to
temperature fluctuations.
You might also like
- Respiration WorksheetDocument7 pagesRespiration Worksheet한서현No ratings yet
- Topic 2.8 Cell RespirationDocument5 pagesTopic 2.8 Cell RespirationFlori de CâmpNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration IB BIoDocument27 pages2.8 Cell Respiration IB BIoPerson Anonymous100% (1)
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cellular RespirationDocument2 pages2.8 Cellular Respirationbkhazma17No ratings yet
- 2.8 - Cell RespirationDocument27 pages2.8 - Cell Respirationmarisa colegateNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument29 pagesCellular RespirationDominic MaderaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration RevisionDocument10 pagesAerobic Respiration RevisionJenny JanssonNo ratings yet
- Inbound 9168743087088869744Document9 pagesInbound 9168743087088869744MarkNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology PracDocument6 pagesBiotechnology PracNathan ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 5Document14 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 5Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration 2020Document10 pagesCellular Respiration 2020Stephanie BoatengNo ratings yet
- RespirationreviewDocument2 pagesRespirationreviewbiologija.rv2gNo ratings yet
- GB1 Q2 Week-5Document6 pagesGB1 Q2 Week-5Leah Jean PonlaonNo ratings yet
- Jinky Oraiz@deped Gov PHDocument11 pagesJinky Oraiz@deped Gov PHAnnejhel Mae Poralan100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Group 1Document7 pagesLesson 2 Group 1Zyreine MenoriasNo ratings yet
- 5Document2 pages5Mohamad YasinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.4 Cell Respiration PDFDocument48 pagesChapter 2.4 Cell Respiration PDFFloraaGUNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch14 Respiration in PlantsDocument8 pages11 Biology Notes ch14 Respiration in Plantssanjay kannaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionsumeshp664No ratings yet
- S.6 Physics Revision Questions - 2020Document12 pagesS.6 Physics Revision Questions - 2020Kizito JohnNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectrometry and Stable Isotopes in Nutritional and Pediatric ResearchFrom EverandMass Spectrometry and Stable Isotopes in Nutritional and Pediatric ResearchHenk SchierbeekNo ratings yet
- Topic 8-Cellular Respiration PART 1,2,3 - StudentDocument35 pagesTopic 8-Cellular Respiration PART 1,2,3 - StudenthadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- CRH Cellular Respiration (Principles) - Measure Energy Consumption During Exercise Lab ManualDocument6 pagesCRH Cellular Respiration (Principles) - Measure Energy Consumption During Exercise Lab ManualVanesha AnesNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- Primary Productivity and Energy Dynamics Manuel TzulDocument7 pagesPrimary Productivity and Energy Dynamics Manuel Tzulapi-323831182No ratings yet
- BioDocument18 pagesBiomarcneil773No ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Second QTR Module RevisedDocument37 pagesGen Bio 1 Second QTR Module RevisedMichaela CasabaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3: When Cells BreatheDocument26 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3: When Cells BreathePLS help me get 1k subsNo ratings yet
- 2.8-Cell Respiration:: Cell Respiration Is The Controlled Release of Energy From Organic Compounds To Produce ATPDocument4 pages2.8-Cell Respiration:: Cell Respiration Is The Controlled Release of Energy From Organic Compounds To Produce ATPTanvir KauraNo ratings yet
- 2.25 Respiration H 2.28, 2.2.10Document22 pages2.25 Respiration H 2.28, 2.2.10George Oswald Junior CarringtonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Cellular Respiration 1Document6 pagesChapter 15 Cellular Respiration 1zeemboyzNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Essay QuestionsDocument4 pagesCellular Respiration Essay QuestionsLaila Abdul100% (1)
- Aerobic Respiration in Animals.Document4 pagesAerobic Respiration in Animals.studyklieNo ratings yet
- 3 RespirationDocument12 pages3 Respirationbiologija.rv2gNo ratings yet
- Biodas 8 (Aeman Hakim)Document19 pagesBiodas 8 (Aeman Hakim)aekimNo ratings yet
- Week 7 ScienceDocument4 pagesWeek 7 ScienceKaru GreyNo ratings yet
- Jinnah University For Women: Group Members: Javeria Shahzad Kanza Naseer Muqaddas Raees Zainab GhufranDocument13 pagesJinnah University For Women: Group Members: Javeria Shahzad Kanza Naseer Muqaddas Raees Zainab GhufranDEVIL GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Respiration Worksheet CsecDocument2 pagesRespiration Worksheet CsecjhoyvanNo ratings yet
- EARTH & LIFE SCIENCE Reviewer Note #2.5Document3 pagesEARTH & LIFE SCIENCE Reviewer Note #2.5Ristan RectoNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 3Document19 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 3Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document15 pagesPresentation 5Rahanie Gadungan PajijiNo ratings yet
- Biology The Essentials 1st Edition Hoefnagels Solutions Manual DownloadDocument15 pagesBiology The Essentials 1st Edition Hoefnagels Solutions Manual DownloadGraham Hissem100% (26)
- 7e's - Cellular RespirationDocument5 pages7e's - Cellular RespirationVea Patricia AngeloNo ratings yet
- MYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerDocument4 pagesMYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerRishar bokNo ratings yet
- UNIT - : Aerobic Respiration: NameDocument9 pagesUNIT - : Aerobic Respiration: NameTanishq SimonNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- (Aerobic VS Fermentation)Document20 pages(Aerobic VS Fermentation)Eucille SilvaNo ratings yet
- GB 1 NotesDocument10 pagesGB 1 Notesrenlie jane pedronanNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- Primary Productivity and Energy Dynamics-RennelDocument6 pagesPrimary Productivity and Energy Dynamics-Rennelapi-323831182No ratings yet
- Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration 1Document21 pagesAerobic and Anaerobic Respiration 1LP May JaymeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesLesson 14 Cellular RespirationGinalyn QuimsonNo ratings yet
- Q2 ELS L4 Cellular RespirationDocument30 pagesQ2 ELS L4 Cellular RespirationJoshNo ratings yet
- Biology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaDocument3 pagesBiology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaAmirul HakimNo ratings yet
- Substitute Natural Gas from Waste: Technical Assessment and Industrial Applications of Biochemical and Thermochemical ProcessesFrom EverandSubstitute Natural Gas from Waste: Technical Assessment and Industrial Applications of Biochemical and Thermochemical ProcessesMassimiliano MaterazziNo ratings yet
- 3 7 Cell RespirationDocument3 pages3 7 Cell Respirationapi-296446683No ratings yet
- Ruangrat Natthanicha - Cell Respiration ReviewDocument2 pagesRuangrat Natthanicha - Cell Respiration Reviewapi-452284231No ratings yet
- 8 3Document22 pages8 3lianneNo ratings yet
- 6 3 UnderstandingsDocument1 page6 3 Understandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- 6 4 UnderstandingsDocument1 page6 4 Understandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- 6 6 UnderstandingsDocument1 page6 6 Understandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- SM Website SlideDocument1 pageSM Website Slideapi-227453671No ratings yet
- 4 1 UnderstandingsDocument1 page4 1 Understandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- 5 3 UnderstandingsDocument1 page5 3 Understandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- Postcards Around The World Honors Biology Biome ProjectDocument12 pagesPostcards Around The World Honors Biology Biome Projectapi-227453671No ratings yet
- UnderstandingsDocument1 pageUnderstandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- UnderstandingsDocument1 pageUnderstandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- UnderstandingsDocument1 pageUnderstandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- UnderstandingsDocument1 pageUnderstandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- JrinviteDocument1 pageJrinviteapi-227453671No ratings yet
- SrinviteDocument1 pageSrinviteapi-227453671No ratings yet
- UnderstandingsDocument1 pageUnderstandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- UnderstandingsDocument1 pageUnderstandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- UnderstandingsDocument1 pageUnderstandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- UnderstandingsDocument1 pageUnderstandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- UnderstandingsDocument1 pageUnderstandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- UnderstandingsDocument1 pageUnderstandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- Understandings, Applications and Skills: Statement GuidanceDocument1 pageUnderstandings, Applications and Skills: Statement Guidanceapi-227453671No ratings yet
- UnderstandingsDocument1 pageUnderstandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet
- UnderstandingsDocument1 pageUnderstandingsapi-227453671No ratings yet