Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flowering Plants
Uploaded by
api-2853538830 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views4 pagesPlants reproduce both sexually and asexually. Use your notes and text to draw a diagram of a cutting and explain how the process occurs.
Original Description:
Original Title
flowering+plants
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPlants reproduce both sexually and asexually. Use your notes and text to draw a diagram of a cutting and explain how the process occurs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views4 pagesFlowering Plants
Uploaded by
api-285353883Plants reproduce both sexually and asexually. Use your notes and text to draw a diagram of a cutting and explain how the process occurs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Flowering Plants:
Plants reproduce both sexually and asexually.
Types of asexual reproduction in plants:
1. Cuttings- a part of a plant is removed and the meristem tissue can grow new
roots, stems and leaves. The cutting and the parent are identical.
2. Runners: the parent plant sends out long shoots that develop into new plants that
are the same as the parent. Ex. strawberries
3. Suckers: outgrowths of roots the develop into new plants that are the same as the
parent. Ex. Lilac bushes
4. Bulbs/Tubers: underground stems that produce new shoots that are the same as
the parent. Ex. potatoes
5. Self-fertilization/ self pollination: occurs when the male sex cells of a single
plant fertilize the female sex cell of the same plant.
Types of sexual reproduction in plants:
Cross-fertilization/ cross pollination: involves two plants. The pollen from one
plant fertilizes the ovule of a different plant.
Sexual spores: ferns and mosses can produce spores that combine to produce new
individuals. Organisms produced by sexual spores are NOT identical to either
parent.
1.) Use your notes and your text to draw a diagram of a cutting and explain how the
process occurs: (p. 28)
Diagram
Description
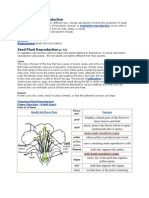
2.) Label the parts of a flower and describe what each part does:
Structure:
Stigma
Style
Ovary
Pistil
Anther
Filament
Ovule
Receptacle
Sepal
Stamen
Pollen
tube
Petal
Pollen
(not on
diagram)
Description/ Function
3.) Explain the process of self-fertilization, using a diagram and a description:
Diagram
Description
Things you need to include in your description:
Process of fertilization (p.2 of notes)
Asexual or sexual
Is the DNA the same or different than the
parents?
Does it involve one or two parents?
4.)
Explain the process of cross-fertilization, using a diagram and a description.
Diagram
Description
You might also like
- AsexualDocument39 pagesAsexualKathleen Joy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Notes - Reproduction-1Document19 pagesNotes - Reproduction-1Nathan mwapeNo ratings yet
- Class X Reproduction Notes 1Document13 pagesClass X Reproduction Notes 1vratNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants - The Processes of Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument9 pagesReproduction in Plants - The Processes of Asexual and Sexual Reproductionmr. unknownNo ratings yet
- Asexual Vs Sexual ReproductionDocument53 pagesAsexual Vs Sexual ReproductioncriselNo ratings yet
- Y10 Reproduction TeacherDocument143 pagesY10 Reproduction Teachervijayp22No ratings yet
- Essential Reproduction Process in All Living OrganismsDocument15 pagesEssential Reproduction Process in All Living Organismseugene_970418755No ratings yet
- Notes Chappter REPRODUCTIONDocument8 pagesNotes Chappter REPRODUCTIONKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Plants & Seeds: Prior KnowledgeDocument60 pagesPlants & Seeds: Prior KnowledgeGurpreet Bedi0% (1)
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants 2020Document22 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants 2020Kestina MillerNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument5 pagesPlantsjleodennisNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument6 pagesReproductionzainahNo ratings yet
- Allaboutplants 151024155216 Lva1 App6891Document14 pagesAllaboutplants 151024155216 Lva1 App6891Nerea MongeNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterDocument7 pagesScience 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterHoneylet Alberto Castro ArilloNo ratings yet
- Classification of PlantsDocument2 pagesClassification of PlantsNhecel PascuaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument20 pagesReproduction in PlantsAndrea AgustinNo ratings yet
- Ppt.x.reproduction 10 23Document83 pagesPpt.x.reproduction 10 23ammara hyderNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Asexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Asexual ReproductionpixelhoboNo ratings yet
- A. Abstraction: Sexual ReproductionDocument5 pagesA. Abstraction: Sexual ReproductionJoy MagbutongNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesReproduction in PlantsRenuNo ratings yet
- How Non-Flowering Plants ReproduceDocument37 pagesHow Non-Flowering Plants ReproduceMariel Anne AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument7 pagesUntitled Documentmax.gabuteroocampoNo ratings yet
- 16 REPRODUCTIONDocument20 pages16 REPRODUCTIONEmanuel SafiNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - PERPETUATION OF LIFEDocument15 pagesModule 6 - PERPETUATION OF LIFEMharcjhefferson RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Asexual and Sexual Reproduction (ARA)Document6 pagesAsexual and Sexual Reproduction (ARA)Leonora Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Plant Breeding As A HobbyDocument20 pagesPlant Breeding As A HobbyJirobuchon100% (1)
- Perpetuation of Life: Elsc Lesson 6Document60 pagesPerpetuation of Life: Elsc Lesson 6Kai ClavelNo ratings yet
- Living Non-Living Things Plants AnimalsDocument10 pagesLiving Non-Living Things Plants AnimalsEstherJimenezNo ratings yet
- Asexual Sexual ReproductionDocument32 pagesAsexual Sexual ReproductionReymart VillapeñaNo ratings yet
- Flower Parts and Reproduction TypesDocument2 pagesFlower Parts and Reproduction TypesWalang PoreberNo ratings yet
- PLANT BIOLOGY Plant Form and FunctionDocument12 pagesPLANT BIOLOGY Plant Form and FunctionNis DancelNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy and Physiology: What Are The Parts of The Plant, and How Do They Work?Document66 pagesPlant Anatomy and Physiology: What Are The Parts of The Plant, and How Do They Work?Magy Tabisaura GuzmanNo ratings yet
- First Look Background InformationDocument6 pagesFirst Look Background Informationahuddle1No ratings yet
- Module 11: Plant Knowledge: SummaryDocument27 pagesModule 11: Plant Knowledge: SummaryEduardo Salazar RNo ratings yet
- Flowers, fruits and seeds: A morphological continuityDocument4 pagesFlowers, fruits and seeds: A morphological continuityJobadzNo ratings yet
- Reproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)Document10 pagesReproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)richelyn navalesNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction 4 1Document4 pagesPlant Reproduction 4 1Belen MartinezNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Reproduction ExplainedDocument53 pagesAnimal and Plant Reproduction ExplainedSheryl Osorio100% (1)
- Week 3 Perpetuation of Life (Autosaved)Document38 pagesWeek 3 Perpetuation of Life (Autosaved)SANTIAGO, David Joshua B.No ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument5 pagesReproduction in OrganismsRenuNo ratings yet
- Plants and Reproduction PDFDocument22 pagesPlants and Reproduction PDFJohanna UrwinNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument62 pagesPlant ReproductionAdonis BesaNo ratings yet
- Crop 1Document6 pagesCrop 1Cynel DelaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants NotesDocument5 pagesReproduction in Plants Notesalviayaan807No ratings yet
- What Plants Need to Grow and ReproduceDocument14 pagesWhat Plants Need to Grow and Reproduceveverica666No ratings yet
- Bryophytes and TracheophytesDocument4 pagesBryophytes and TracheophytesNoor NabiNo ratings yet
- Tracheophyte NotesDocument11 pagesTracheophyte NotesTracy Lou FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Vital Functions in Animals and Plants1Document24 pagesVital Functions in Animals and Plants1caruabzoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument11 pagesReproduction in Flowering PlantsdarkadainNo ratings yet
- Types of Plant ReproductionDocument6 pagesTypes of Plant ReproductionNaNa Liyana Elias INo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 4Document16 pagesSCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 4Mary Ann Gabion100% (11)
- Bio NotesDocument6 pagesBio NotesKean Debert SaladagaNo ratings yet
- Science BiologyDocument9 pagesScience BiologyMaryClaire RemorosaNo ratings yet
- Asm 3628Document19 pagesAsm 3628Shashank NandanNo ratings yet
- ,reproduction: Advantages of Asexual Reproduction IncludeDocument7 pages,reproduction: Advantages of Asexual Reproduction IncludeChoolwe CheeloNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument7 pagesEmbryologyFor spaceNo ratings yet
- Modes of Reproduction in PlantsDocument15 pagesModes of Reproduction in Plantsjudy andrade100% (1)
- Flowering vs. Non-Flowering Plants : Knowing the Difference - Biology 3rd Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandFlowering vs. Non-Flowering Plants : Knowing the Difference - Biology 3rd Grade | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- LastchildDocument2 pagesLastchildapi-285353883No ratings yet
- Martens - Productive QuestionsDocument5 pagesMartens - Productive Questionsapi-285353883No ratings yet
- Sander & Nelson - Sci Conv For Young LearnersDocument3 pagesSander & Nelson - Sci Conv For Young Learnersapi-285353883No ratings yet
- Sound Science CerDocument3 pagesSound Science Cerapi-302638649No ratings yet
- An Example of Novak Et Al Claim+evidence+reasoningDocument1 pageAn Example of Novak Et Al Claim+evidence+reasoningapi-285353883No ratings yet
- Marzano StrategiesDocument5 pagesMarzano Strategiesapi-285353883No ratings yet
- ConstructivismDocument4 pagesConstructivismapi-285353883No ratings yet
- Developing Students Questioning Skills - Prek-2Document3 pagesDeveloping Students Questioning Skills - Prek-2api-285353883No ratings yet
- JurisprudentialDocument3 pagesJurisprudentialapi-317512128No ratings yet