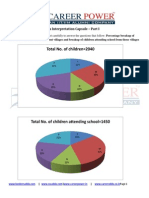
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Class 11 Syllabus - 2015-2016 CBSEsyllabus
Uploaded by
Tushar SaxenaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Class 11 Syllabus - 2015-2016 CBSEsyllabus
Uploaded by
Tushar SaxenaCopyright:
Available Formats
5/6/2015
ChemistryClass11Syllabus20152016CBSEsyllabus.in
CBSEsyllabus.in
ALL ABOUT CBSE AND SCHOOL EDUCATION...
Home
CBSE Syllabus
Resources
Download
Contact
Book Store
CBSEsyllabus.in
Student Guide
Explore
All Free Stuff
EMail us
Buy Books!
MINISPORTSBIKEINMUMBAI
Rs.3,50,000
Andheri_West,
Mumbai
Rs.28,000
Rs. 16,999
Rs.2,95,000
ChatNow
Rs.16,999
USER LOGIN
Chemistry Class 11 Syllabus
User Name
Like 76peoplelikethis.Bethefirstofyourfriends.
Course Structure
Unit Title
Password
Marks
Remember Me
LOGIN
Basic Concepts of Chemistry
II
Structure of Atom
III
Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties 4
IV
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
username?
States of Matter: Gases and Liquids
Create an account
VI
Thermodynamics
VII
Equilibrium
VIII
Redox Reactions
IX
Hydrogen
sBlock Elements
XI
Some pBlock Elements
XII
Organic Chemistry: Basic Principles & Techniques
XIII
Hydrocarbons
XIV
Environmental Chemistry
Total
11
Rs.1,50,000
Forgot your password?
Forgot your
21
Rs.2,95,000
RECENTLY
UPDATED
NTSE National Talent
16
Search Examination
Rs.65,000
NTSE Class 10 Syllabus
and Exam Pattern
Philosophy Class 11
18
Syllabus
Sociology Class 12
70
Unit I: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Rs.5,25,000
Syllabus
Psychology Class 12
Syllabus
General Introduction: Importance and scope of chemistry.
Nature of matter, laws of chemical combination, Dalton's atomic theory: concept of
elements,atoms and molecules.
Atomic and molecular masses, mole concept and molar mass, percentage composition,
empirical and molecular formula, chemical reactions, stoichiometry and calculations based on
stoichiometry.
Unit II: Structure of Atom
Discovery of Electron, Proton and Neutron, atomic number, isotopes and isobars. Thomson's
modeland its limitations. Rutherford's model and its limitations, Bohr's model and its limitations,
concept of shells and subshells, dual nature of matter and light, de Broglie's relationship,
Heisenberg uncertainty principle, concept of orbitals, quantum numbers, shapes of s, p and d
orbitals, rules for filling electrons in orbitals Aufbau principle, Pauli's exclusion principle and
Hund's rule, electronicconfiguration of atoms, stability of half filled and completely filled orbitals.
Unit III: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
Significance of classification, brief history of the development of periodic table, modern
periodic law and the present form of periodic table, periodic trends in properties of elements
atomic radii, ionic radii, inert gas radii Ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy,
electronegativity, valency.Nomenclature of elements with atomic number greater than 100.
Unit IV: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Valence electrons, ionic bond, covalent bond; bond parameters, Lewis structure, polar character
of covalent bond, covalent character of ionic bond, valence bond theory, resonance, geometry
of covalent molecules, VSEPR theory, concept of hybridization, involving s,p and d orbitals and
shapes of some simple molecules, molecular orbital theory of homonuclear diatomic molecules
qualitativeidea only, hydrogen bond.
Unit V: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids
http://www.cbsesyllabus.in/class11/chemistryclass11syllabus
1/4
5/6/2015
ChemistryClass11Syllabus20152016CBSEsyllabus.in
Three states of matter, intermolecular interactions, types of bonding, melting and boiling
points,role of gas laws in elucidating the concept of the molecule, Boyle's law, Charles law, Gay
Lussac's law, Avogadro's law, ideal behaviour, empirical derivation of gas equation, Avogadro's
number, ideal gas equation. Deviation from ideal behaviour, liquefaction of gases, critical
temperature,kinetic energy and molecular speeds elementary ideaLiquid State vapour pressure,
viscosity andsurface tension qualitative idea only, no mathematical derivations
Unit VI: Chemical Thermodynamics
Concepts of System and types of systems, surroundings, work, heat, energy, extensive and
intensiveproperties, state functions.
First law of thermodynamics internal energy and enthalpy, heat capacity and specific heat,
measurement of U and H, Hess's law of constant heat summation, enthalpy of bond
dissociation, combustion, formation, atomization, sublimation, phase transition, ionization,
solution and dilution.Second law of Thermodynamics brief introduction
Introduction of entropy as a state function, Gibb's energy change for spontaneous and non
spontaneousprocesses, criteria for equilibrium.
Third law of thermodynamics brief introduction.
Unit VII: Equilibrium
Equilibrium in physical and chemical processes, dynamic nature of equilibrium, law of mass
action, equilibrium constant, factors affecting equilibrium Le Chatelier's principle, ionic
equilibriumionization of acids and bases, strong and weak electrolytes, degree of ionization,
ionization of poly basic acids, acid strength, concept of pH, Henderson Equation, hydrolysis of
salts elementary idea, buffer solution, solubility product, common ion effect with illustrative
examples.
Unit VIII: Redox Reaction
Concept of oxidation and reduction, redox reactions, oxidation number, balancing redox
reactions,in terms of loss and gain of electrons and change in oxidation number, applications of
redox reactions.
Unit IX: Hydrogen
Position of hydrogen in periodic table, occurrence, isotopes, preparation, properties and uses
of hydrogen, hydridesionic covalent and interstitial; physical and chemical properties of water,
heavywater, hydrogen peroxide preparation, reactions and structure and use; hydrogen as a fuel.
Unit X: s Block Elements Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals
Group 1 and Group 2 Elements
General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, anomalous properties of the first
element of each group, diagonal relationship, trends in the variation of properties such as
ionization enthalpy, atomic and ionic radii, trends in chemical reactivity with oxygen, water,
hydrogen and halogens,uses.
Preparation and Properties of Some Important Compounds:
Sodium
Carbonate,
Sodium
Chloride,
Sodium
Hydroxide
and
Sodium
Hydrogencarbonate,Biological importance of Sodium and Potassium.Calcium Oxide and Calcium
Carbonate and their industrial uses, biological importance ofMagnesium and Calcium.
Unit XI: Some p Block Elements
General Introduction to p Block Elements
Group 13 Elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, variation
ofproperties, oxidation states, trends in chemical reactivity, anomalous properties of first element
ofthe group, Boron physical and chemical properties, some important compounds, Borax, Boric
acid,Boron Hydrides, Aluminium: Reactions with acids and alkalies, uses.
Group 14 Elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, variation
of properties, oxidation states, trends in chemical reactivity, anomalous behaviour of first
elements. Carboncatenation, allotropic forms, physical and chemical properties; uses of some
important compounds: oxides. Important compounds of Silicon and a few uses: Silicon
Tetrachloride, Silicones,Silicates and Zeolites, their uses.
Unit XII: Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Technique
General introduction, methods of purification, qualitative and quantitative analysis,
classification and IUPAC nomenclature of organic compounds. Electronic displacements in a
covalent bond:inductive effect, electromeric effect, resonance and hyper conjugation. Homolytic
and heterolytic fission of a covalent bond: free radicals, carbocations, carbanions, electrophiles
and nucleophiles,types of organic reactions.
Unit XIII: Hydrocarbons
Classification of Hydrocarbons
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons:
http://www.cbsesyllabus.in/class11/chemistryclass11syllabus
2/4
5/6/2015
ChemistryClass11Syllabus20152016CBSEsyllabus.in
Alkanes Nomenclature, isomerism, conformation ethane only, physical properties,
chemicalreactions including free radical mechanism of halogenation, combustion and pyrolysis.
Alkenes Nomenclature, structure of double bond ethene, geometrical isomerism,
physical properties, methods of preparation, chemical reactions: addition of hydrogen, halogen,
water, hydrogen halides Markownikov's addition and peroxide effect, ozonolysis, oxidation,
mechanismof electrophilic addition.
Alkynes Nomenclature, structure of triple bond ethyne, physical properties, methods
of preparation, chemical reactions: acidic character of alkynes, addition reaction of hydrogen,
halogens,hydrogen halides and water.
Aromatic
Hydrocarbons:
Introduction,
IUPAC
nomenclature,
benzene:
resonance,
aromaticity,chemical properties: mechanism of electrophilic substitution. nitration, sulphonation,
halogenation, Friedel Craft's alkylation and acylation, directive influence of functional group in
monosubstitutedbenzene. Carcinogenicity and toxicity.
Unit XIV: Environmental Chemistry
Environmental pollution air, water and soil pollution, chemical reactions in atmosphere,
smog, major atmospheric pollutants, acid rain, ozone and its reactions, effects of depletion of
ozone layer, greenhouse effect and global warming pollution due to industrial wastes, green
chemistry as an alternative tool for reducing pollution, strategies for control of environmental
pollution.
Download Files:
URL
Chemistry Class 11 Syllabus 201516
Class 1 to Class 12
meritnation.com/CBSE
Lessons, Animations, Videos & more Math,
EVS, Science, English, SST
SBI GK PDF Free Download
Free IIT-JEE Coaching DVD
Completed 12th?
COMMENTS
#56 yograjprakash 20150506 14:05
without hardwork chemistry cant b scored........hardwork n our concentration is very
important
Quote
#55 sankarrocks#q%$#
20150424 15:32
I think by paying attention and by hard work we can access that chemistry is quite easy
Quote
#54 Suzzane 20150424 11:54
Class 11 chemistry is quite easy. Through hardwork and determination we can pass out with
flying colours. No dream is too extreme
Quote
#53 ManirujjamanAkash
XDD, love chemistry too :3
20150415 08:51
Quote
#52 AbhishekChatterjee 20150414 08:43
It's mentioned that is 201516 syllabus but actually is the 201415 syllabus plz give the
latest one.....
Quote
#51 ADITIKUSH 20150406 11:41
ENJOY 11TH 12TH 2015 2017 LIFE INSURANCE !!!
Quote
#50 sakshigaur 20150405 12:55
i love chemistry and maths and i opt pcm next year i praying that next week my interviewgo
super and i also worried for it
Quote
http://www.cbsesyllabus.in/class11/chemistryclass11syllabus
3/4
5/6/2015
ChemistryClass11Syllabus20152016CBSEsyllabus.in
#49 Nishuman
20150401 19:35
thanks for the syllabus
Quote
#48 adrija
20150401 11:41
love chem
Quote
#47 kanugoyal 20150331 21:58
wow ths chemistry is v.v.v.v.esy
Quote
Refresh comments list
ADD COMMENT
Name(required)
Email(required,butwillnotdisplay)
1000 symbols
Refresh
Send
YOU ARE HERE: HOME
CBSE SYLLABUS
CLASS 11 SYLLABUS
http://www.cbsesyllabus.in/class11/chemistryclass11syllabus
CHEMISTRY CLASS 11 SYLLABUS
TOP
4/4
You might also like
- Chemistry: Curriculum and Syllabus For Classes Xi & XiiDocument11 pagesChemistry: Curriculum and Syllabus For Classes Xi & Xiianon_203482044No ratings yet
- Chemistry Syllabus For First PUCDocument13 pagesChemistry Syllabus For First PUCsmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Course Structure Class XI (Theory)Document16 pagesCourse Structure Class XI (Theory)Akash MeenaNo ratings yet
- Oswaal NEET UG Syllabus ChemistryDocument8 pagesOswaal NEET UG Syllabus Chemistrysachinsahu0537No ratings yet
- Aipmt 2016 Syll ChemDocument4 pagesAipmt 2016 Syll ChemIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Syllabus (Chapter Wise Weightage)Document8 pagesChemistry Syllabus (Chapter Wise Weightage)Nandhan AnemNo ratings yet
- NSEC SyllabusDocument6 pagesNSEC SyllabusAnant M NNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class XII SyllabusDocument5 pagesCBSE Class XII Syllabusilias1973No ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 12 Syllabus - 2017-2018 CBSEsyllabus PDFDocument9 pagesChemistry Class 12 Syllabus - 2017-2018 CBSEsyllabus PDFzeeshan khanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Chemistry 11 & 12thDocument12 pagesSyllabus Chemistry 11 & 12thVijyendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2019 20Document11 pagesCbse Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2019 20Crylia StiaNo ratings yet
- HBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2020 21Document4 pagesHBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2020 21Mrsatyam KohliNo ratings yet
- NEET Chemistry SyllabusDocument10 pagesNEET Chemistry SyllabusGaurav MittalNo ratings yet
- Class XI CHEMISTRY (Theory) One Paper Time: 3 Hours 70 Marks Unit No. Title MarksDocument4 pagesClass XI CHEMISTRY (Theory) One Paper Time: 3 Hours 70 Marks Unit No. Title MarksBhagath KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of ChemDocument6 pagesSyllabus of ChemJaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Eng 2018Document216 pages11 Chemistry Eng 2018Deepanjali PalNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument5 pagesChemistryNIDANo ratings yet
- Chemistry-I1 0Document8 pagesChemistry-I1 0GOLF GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Aipmt 2016 Syll ChemDocument4 pagesAipmt 2016 Syll ChemIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Course Structure: Unit Title MarksDocument3 pagesCourse Structure: Unit Title MarksAjay00388No ratings yet
- NEET 2024 Chemistry Syllabus For Medical Entrance Examination - Free PDF DownloadDocument15 pagesNEET 2024 Chemistry Syllabus For Medical Entrance Examination - Free PDF Downloadoggybilla218No ratings yet
- 2013 Syllabus 11 ChemistryDocument6 pages2013 Syllabus 11 ChemistryvinbhatNo ratings yet
- 2012 Syllabus 11 ChemistryDocument6 pages2012 Syllabus 11 ChemistryRishiraj TripathiNo ratings yet
- Highschool ChemistryDocument9 pagesHighschool Chemistrystarskyhutch0000No ratings yet
- NEET Chemistry SyllabusDocument13 pagesNEET Chemistry SyllabusNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Syllabus For Class 11 Chemistry 2023 24Document7 pagesCBSE Syllabus For Class 11 Chemistry 2023 24artikumarikvs88No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemistrySwatee PuhanNo ratings yet
- Annexure 'I': Syllabus CHEMISTRY (043) CLASS-XII - (2013-14)Document7 pagesAnnexure 'I': Syllabus CHEMISTRY (043) CLASS-XII - (2013-14)Ravi DharawadkarNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan: CHEMISTRY (043) Split Up Syllabus (Session-2014-15)Document12 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan: CHEMISTRY (043) Split Up Syllabus (Session-2014-15)KrishnaVamsiNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2024 Chemistry SyllabusDocument6 pagesJEE Main 2024 Chemistry SyllabusVikram SinghNo ratings yet
- BSC Chemistry I 2016Document9 pagesBSC Chemistry I 2016Narpat JeengarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ChemistryDocument6 pagesSyllabus Chemistrysingharpan5180No ratings yet
- Chemisssstry NotesDocument4 pagesChemisssstry Notespratikayadav263No ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 12 SyllabusDocument13 pagesChemistry Class 12 SyllabusHunter AakashNo ratings yet
- Class 11 ChemistryDocument21 pagesClass 11 ChemistrypravinmoharilNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry SyllabusDocument2 pages11th Chemistry SyllabusFreQuency Career InsTituteNo ratings yet
- PGTChemistryDocument4 pagesPGTChemistryMukesh BhardoreNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Eng SM 2024Document296 pages11 Chemistry Eng SM 2024Sumit YadavNo ratings yet
- CMG 100 New SyllabusDocument3 pagesCMG 100 New SyllabusSakib NehalNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School (Joka) South Kolkata SYLLABUS - 2020-2021 Class Xi ChemistryDocument8 pagesDelhi Public School (Joka) South Kolkata SYLLABUS - 2020-2021 Class Xi ChemistryMalNo ratings yet
- Oswaal CBSE Class 11th Syllabus Chemistry For 2022-23 ExamDocument6 pagesOswaal CBSE Class 11th Syllabus Chemistry For 2022-23 Examlparesh267No ratings yet
- UNIT VII: Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation: Chemistry: Contents of Class Xi SyllabusDocument7 pagesUNIT VII: Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation: Chemistry: Contents of Class Xi SyllabusAbid waniNo ratings yet
- SM 11 Chemistry Eng 201617Document185 pagesSM 11 Chemistry Eng 201617Anonymous 9uu04el100% (1)
- Chemistry WorksheetDocument4 pagesChemistry WorksheetLIYA ASKARNo ratings yet
- BSC PDFDocument69 pagesBSC PDFNeha SharmaNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. (Hons.) Science / Life Sciences / Home Science: (A) EnglishDocument15 pagesB.Sc. (Hons.) Science / Life Sciences / Home Science: (A) Englishshadab ansariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry BSC 1 Samester PDFDocument4 pagesChemistry BSC 1 Samester PDFMax TNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced Syllabus 2023 ChemistryDocument5 pagesJEE Advanced Syllabus 2023 ChemistryArpanaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chem Eqns Tables ChartsDocument9 pagesClass 11 Chem Eqns Tables ChartstisaNo ratings yet
- PG Organic Chemistry SHCDocument4 pagesPG Organic Chemistry SHCjayakumarNo ratings yet
- StorageDocument12 pagesStorage6623abhishekNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Syllabus 2024Document4 pagesChemistry Syllabus 2024C1B-33-AdityaNo ratings yet
- BSC Chemistry - IIIDocument24 pagesBSC Chemistry - IIIDurgesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2022 23Document6 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2022 23Krish AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 130 Chemistry Xi, Xii 2023 24Document11 pages130 Chemistry Xi, Xii 2023 24s6580150No ratings yet
- Temario Quimica Internacional EngDocument2 pagesTemario Quimica Internacional EngjbecerramorNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Chemistry (UG Courses) Admitted Batch 2008 - 2009Document33 pagesSyllabus Chemistry (UG Courses) Admitted Batch 2008 - 2009ArunNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY (Code No. 043) 2019-20: RationaleDocument26 pagesCHEMISTRY (Code No. 043) 2019-20: RationaleShivamNo ratings yet
- Student's Solutions Manual to Accompany Organic Chemistry: Organic Chemistry by Weininger and StermitzFrom EverandStudent's Solutions Manual to Accompany Organic Chemistry: Organic Chemistry by Weininger and StermitzRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (12)
- Signal Processing:: ACF PDF CDF Communication:: Block Diagram Analog and Digital Modulation Schemes NoiseDocument1 pageSignal Processing:: ACF PDF CDF Communication:: Block Diagram Analog and Digital Modulation Schemes NoiseTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- ClassifiationDocument26 pagesClassifiationTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Andhra Bank - Recruitment of Probationary Officers (PGDBF 2016 - 17)Document1 pageAndhra Bank - Recruitment of Probationary Officers (PGDBF 2016 - 17)Tushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- L-26 (TB) Three Phase TransformerDocument16 pagesL-26 (TB) Three Phase Transformervelisbar100% (1)
- Basic Electrical NotesDocument58 pagesBasic Electrical NotesKamal Joshi100% (2)
- Signals and CommunicationDocument3 pagesSignals and CommunicationTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Di Capsule BA Part 1Document5 pagesDi Capsule BA Part 1Tushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor Lab ManualDocument43 pages8085 Microprocessor Lab ManualMukulSinghNo ratings yet
- BCADocument23 pagesBCATushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Uptu B.tech 2nd Year SyllabusDocument16 pagesUptu B.tech 2nd Year SyllabusPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- CWE-SPL-IV-Recruitment of Specialist Officers PDFDocument2 pagesCWE-SPL-IV-Recruitment of Specialist Officers PDFTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Cse 2ndyear SyllabusDocument11 pagesCse 2ndyear Syllabusashish jainNo ratings yet
- Elitmus Probability Questions For Elitmus - Elitmus Questions For PH Test Page 1 PDFDocument3 pagesElitmus Probability Questions For Elitmus - Elitmus Questions For PH Test Page 1 PDFTushar Saxena0% (1)
- Syll ELitmusDocument2 pagesSyll ELitmusTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- BtechDocument27 pagesBtechakash nairNo ratings yet
- Syll ELitmusDocument2 pagesSyll ELitmusTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Some Basic ConceptsDocument10 pagesSome Basic ConceptsTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Features of IndiaDocument2 pagesFeatures of IndiaTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- CL 11Document8 pagesCL 11Tushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- EMI BasicsDocument11 pagesEMI BasicsTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Days of National and International Importance JanurayDocument7 pagesDays of National and International Importance JanurayTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Banking Pathway 2015: English (Mix Quiz) : Bankers Adda Old Logo SeminarDocument7 pagesBanking Pathway 2015: English (Mix Quiz) : Bankers Adda Old Logo SeminarTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- AdvertisementDocument2 pagesAdvertisementTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Verification Value Rupee Savings Bank Account Modi: Crucible Theatre (UK)Document7 pagesVerification Value Rupee Savings Bank Account Modi: Crucible Theatre (UK)Tushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Why BPSKDocument1 pageWhy BPSKTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction DiodeDocument7 pagesP-N Junction DiodeTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- BJTDocument14 pagesBJTTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Progrmming LanguageDocument2 pagesProgrmming LanguageTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- InjusticeDocument1 pageInjusticeTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Tourism Signs & Symbols Published by World Tourism OrganizationDocument244 pagesTourism Signs & Symbols Published by World Tourism OrganizationJemima Pontino0% (1)
- English Grammar Book-Final - 2-5-21Document42 pagesEnglish Grammar Book-Final - 2-5-21Manav GaurNo ratings yet
- Jaw Crusher Kinematics Simulation and AnalysisDocument5 pagesJaw Crusher Kinematics Simulation and AnalysisInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and ScienceNo ratings yet
- RizalDocument6 pagesRizalKin BarklyNo ratings yet
- People Vs AbellaDocument32 pagesPeople Vs AbellaKanraMendozaNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics For Contemporary Decision Making 9th Edition Black Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesBusiness Statistics For Contemporary Decision Making 9th Edition Black Solutions ManualKevinSandovalitreNo ratings yet
- 2006 Consensus Agreement On The Design and Conduct of Clinical Studies With Low-Level Laser Therapy and Light Therapy For Musculoskeletal Pain and DisordersDocument2 pages2006 Consensus Agreement On The Design and Conduct of Clinical Studies With Low-Level Laser Therapy and Light Therapy For Musculoskeletal Pain and DisordersDetian WangNo ratings yet
- Ed 2 Module 8 1Document5 pagesEd 2 Module 8 1Jimeniah Ignacio RoyoNo ratings yet
- The Council of Nicaea and The History of The Invention of ChristianityDocument10 pagesThe Council of Nicaea and The History of The Invention of Christianitybearhunter001No ratings yet
- Civil Law - Persons FamilyDocument59 pagesCivil Law - Persons FamilyCharmaine MejiaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Teori Pertukaran SosialDocument11 pagesJurnal Teori Pertukaran SosialRhama PutraNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Assignment Retail SupermarketDocument20 pagesSupply Chain Assignment Retail SupermarketBNthangeniNo ratings yet
- J.C Tongue & Malocclusion - Copy (Recovered)Document81 pagesJ.C Tongue & Malocclusion - Copy (Recovered)meghaNo ratings yet
- Saham LQ 20Document21 pagesSaham LQ 20ALDI.S. TUBENo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysistDocument3 pagesSwot AnalysistanzelaquinNo ratings yet
- Ansari Ibnarabdoctrine 1999Document45 pagesAnsari Ibnarabdoctrine 1999JYOTI PALNo ratings yet
- Culture Shock Refers To The Feelings of Confusion and Uncertainty That You Experience When You Come Into Contact With A New CultureDocument13 pagesCulture Shock Refers To The Feelings of Confusion and Uncertainty That You Experience When You Come Into Contact With A New CultureRetno WulanNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter-Alexis ReedDocument1 pageCover Letter-Alexis Reedapi-252291947No ratings yet
- Executive ReportDocument51 pagesExecutive ReportPrecelle Joy YangaNo ratings yet
- 8035-Article Text-59635-1-10-20190329Document4 pages8035-Article Text-59635-1-10-20190329Hesti RahmadatiNo ratings yet
- 30 Feet: High Elf MediumDocument10 pages30 Feet: High Elf MediumAli Kaan (Uyau)No ratings yet
- President Uhuru Kenyatta's Speech During The Kenya@50 Celebrations at Uhuru Gardens, Nairobi On The Mid-Night of 12th December, 2013Document3 pagesPresident Uhuru Kenyatta's Speech During The Kenya@50 Celebrations at Uhuru Gardens, Nairobi On The Mid-Night of 12th December, 2013State House KenyaNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension TextsDocument15 pagesReading Comprehension TextsCMRotaruNo ratings yet
- Report Why EvolveDocument11 pagesReport Why EvolveMirela OlarescuNo ratings yet
- Brand Management Bacardi SamveditaDocument32 pagesBrand Management Bacardi SamveditaSamvedita IndrajeetNo ratings yet
- Cacao - Description, Cultivation, Pests, & Diseases - BritannicaDocument8 pagesCacao - Description, Cultivation, Pests, & Diseases - Britannicapincer-pincerNo ratings yet
- The Law of Attraction Work For YouDocument7 pagesThe Law of Attraction Work For YouBambang PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Socscipi PPT2Document9 pagesSocscipi PPT2DKY SYSNo ratings yet
- Career Indecision and Career Anxiety in High SchooolDocument19 pagesCareer Indecision and Career Anxiety in High SchooolP.CNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Modes of ExtinguishmentDocument19 pagesChapter 4 - Modes of ExtinguishmentcartyeolNo ratings yet