Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio 123 Prueba
Uploaded by
GeronimoRomczykCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio 123 Prueba
Uploaded by
GeronimoRomczykCopyright:
Available Formats
1)
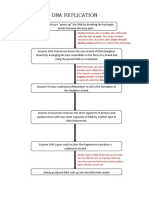
Helicase: separates the two strands of the DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds formed
between the bases.
DNA polymerase: synthesizes DNA molecules from their nucleotide building blocks
DNA ligase: facilitates the joining of DNA strands together, in order to paste the gene
that is extracted from another molecule by endonucleases. The genes are transported
by plasmids.
Endonucleases: recognizes and cuts specific parts of DNA in sets of four or six base
pairs, in order for them to be put in other DNA molecules
2)
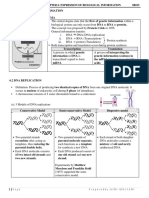
Transcription: begins with the unzipping of DNA strands by an enzyme called helicase.
Then, a RNA polymerase moves along the DNA strand acting as the template, and
joining the RNA nucleotides that float into place by complementary base pairing,
forming an mRNA strand.
You might also like
- DNA Replication: Hybridization. Synthesis. DNA Polymerases Assemble New Strands of DNA From Nucleotides, UsingDocument1 pageDNA Replication: Hybridization. Synthesis. DNA Polymerases Assemble New Strands of DNA From Nucleotides, UsingDominique LopenaNo ratings yet
- 7 - DNA Protein Synthesis Study GuideDocument2 pages7 - DNA Protein Synthesis Study Guideelursgod1No ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument28 pagesDNA ReplicationAsim Bin Arshad 58-FBAS/BSBIO/S19100% (1)
- REPLICATIONDocument9 pagesREPLICATIONdineshNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids NOTESDocument8 pagesNucleic Acids NOTESelaineNo ratings yet
- Bio Catch 33Document1 pageBio Catch 33Olivia GostkowskaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Unit IV and VDocument60 pagesMolecular Biology Unit IV and VchitraNo ratings yet
- NucleotideDocument5 pagesNucleotideReign Aiken M. LaraNo ratings yet
- DNA REPLICATION OnlineDocument25 pagesDNA REPLICATION OnlineKyle RefugioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideDocument11 pagesChapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideabdulazizalobaidiNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 1 PPH 226Document3 pagesIndividual Assignment 1 PPH 226Benjamin Aluoch OnyangoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Dna ReplicationDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Dna ReplicationAlexa ChaviraNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Study MaterialDocument58 pagesMolecular Biology Study MaterialchitraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 DNA and RNA ReviewDocument6 pagesChapter 12 DNA and RNA ReviewAndrew WatsonNo ratings yet
- Biochem Group ProjDocument21 pagesBiochem Group ProjYves Christian PineNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication, The Basis ForDocument23 pagesDNA Replication, The Basis ForDiana M. LlonaNo ratings yet
- DNA Translation: Transcription Proceeds in The Following General StepsDocument2 pagesDNA Translation: Transcription Proceeds in The Following General StepsFebz CanutabNo ratings yet
- Polynucleotide Chain of Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)Document1 pagePolynucleotide Chain of Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)Marigold D. HermonioNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids - Topic 7 HLDocument28 pagesNucleic Acids - Topic 7 HLGracieNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument18 pagesDna ReplicationOguh AugustineNo ratings yet
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFazalea freyaNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument15 pagesDNA Replicationتوتا عوضNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication NotesDocument3 pagesDna Replication NotesYash VardhanNo ratings yet
- 7.1 DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument6 pages7.1 DNA Structure and ReplicationAbdelrahman HarrathNo ratings yet
- Biochem QuinDocument4 pagesBiochem QuinKingNo ratings yet
- Pleno SintesisDocument19 pagesPleno SintesisDevinNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Molecular Biology DNA Living Organisms Biological InheritanceDocument2 pagesDNA Replication: Molecular Biology DNA Living Organisms Biological InheritancePretty UNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument2 pagesMolecular BiologyJaymark HisonaNo ratings yet
- Bnbi Oral PresentationDocument17 pagesBnbi Oral PresentationAshria Sonali PrakashNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument3 pagesDNA ReplicationGirish AdapaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument7 pagesScienceRonald Alexandrei TropelNo ratings yet
- 4 DnaDocument6 pages4 Dnadr_47839666No ratings yet
- Topic: How Cells Work - DNA Replication, Metabolic RegulationDocument3 pagesTopic: How Cells Work - DNA Replication, Metabolic RegulationDeitherNo ratings yet
- Replikasi DNA Dan Sintesis Protein (Gabungan)Document62 pagesReplikasi DNA Dan Sintesis Protein (Gabungan)adinda tyasprabandariNo ratings yet
- Biologi Individual Assessment: Name Class Matric NoDocument6 pagesBiologi Individual Assessment: Name Class Matric NoNURUL HIDAYAH BINTI SAIFUL ANUAR MoeNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument25 pagesDna ReplicationRoniec ParaisoNo ratings yet
- Bio April 14Document2 pagesBio April 14sarah sebhatuNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument26 pagesDna ReplicationJerric Cristobal100% (3)
- Dna REPLICATIONDocument5 pagesDna REPLICATIONNicki Lyn Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument21 pagesDNA ReplicationP Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication: Replication Forks. A Protein Called Single-StrandedDocument1 pageDna Replication: Replication Forks. A Protein Called Single-StrandedShivani HenryNo ratings yet
- Compressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015Document10 pagesCompressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015SYAZWAN BIN MUSTAFA MoeNo ratings yet
- Steps of DNA ReplicationDocument13 pagesSteps of DNA ReplicationShakila mumtazNo ratings yet
- What Is DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesWhat Is DNA ReplicationAmmar SaleemNo ratings yet
- Heredity:Inheritance and VariationsDocument16 pagesHeredity:Inheritance and VariationsJerome MangahasNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Summary ShuffledDocument3 pagesDNA Replication Summary ShuffledamandaNo ratings yet
- 14.4 DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDocument3 pages14.4 DNA Replication in ProkaryotesAyushi MauryaNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES 1Document5 pagesDNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES 1mngnmg8No ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument7 pagesDNA Replicationlubuto TuntepeNo ratings yet
- Replication PDFDocument12 pagesReplication PDFYi LingNo ratings yet
- BPH 2203, Bio-Molecular Pharmacy: Topic: DNA ReplicationDocument19 pagesBPH 2203, Bio-Molecular Pharmacy: Topic: DNA ReplicationNazninNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of LifeDocument17 pagesCentral Dogma of LifeSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Steps of DNA Replication ReviewerDocument2 pagesSteps of DNA Replication ReviewerAlquino Heart RubioNo ratings yet
- What You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsDocument35 pagesWhat You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsSeemaNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument3 pagesDNA ReplicationChenra Missei YoroNo ratings yet
- Semi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDocument12 pagesSemi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDibyakNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and RepairDocument7 pagesDNA Replication and RepairJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- DNA Definition: Shape, Replication, and Mutation: Nucleic Acid Double HelixDocument8 pagesDNA Definition: Shape, Replication, and Mutation: Nucleic Acid Double HelixRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- Bio001 Balag, MayreisDocument11 pagesBio001 Balag, MayreisMay Reis BalagNo ratings yet
- All About DNA: Sci 211 - GeneticsDocument13 pagesAll About DNA: Sci 211 - GeneticsPATRICK MARK FLORESNo ratings yet
- Dry Hopping Beer Achieving Consistent Flavor1Document84 pagesDry Hopping Beer Achieving Consistent Flavor1GeronimoRomczykNo ratings yet
- JASBC Extraction Efficiency Dry-Hopping PDFDocument13 pagesJASBC Extraction Efficiency Dry-Hopping PDFGeronimoRomczykNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Factors Impacting Aroma, Flavor, and Stability in Dry-Hopped Beers PDFDocument12 pagesInvestigating The Factors Impacting Aroma, Flavor, and Stability in Dry-Hopped Beers PDFGeronimoRomczykNo ratings yet
- Forzado TulipanesDocument50 pagesForzado TulipanesGeronimoRomczykNo ratings yet
- Draining Water DesignDocument2 pagesDraining Water DesignGeronimoRomczykNo ratings yet
- Code Academy HTML Css 1Document6 pagesCode Academy HTML Css 1GeronimoRomczykNo ratings yet
- Current Event 4Document1 pageCurrent Event 4GeronimoRomczykNo ratings yet
- Current Evvent 3Document2 pagesCurrent Evvent 3GeronimoRomczykNo ratings yet
- DNA and Genetics. PacketDocument42 pagesDNA and Genetics. PacketGeronimoRomczykNo ratings yet
- Articulo Current Event 1 2013Document2 pagesArticulo Current Event 1 2013GeronimoRomczykNo ratings yet
- Articulo Current Event 2 2013Document1 pageArticulo Current Event 2 2013GeronimoRomczykNo ratings yet
- PH Manifesto 2014Document31 pagesPH Manifesto 2014GeronimoRomczykNo ratings yet
- Types of FirmsDocument6 pagesTypes of FirmsGeronimoRomczykNo ratings yet