Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ept Concept Map 9
Uploaded by
api-263357086Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ept Concept Map 9
Uploaded by
api-263357086Copyright:
Available Formats
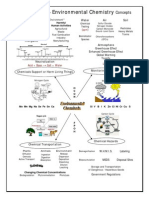
Grade 9 - Unit 4 Electrical Principles & Technologies Concepts
STATIC Electricity
CURRENT Electricity
Charge Separation
Electrical Discharge
Continuous flow of electrons through
conductors.
Laws of
Electric
Charges
Electrical Circuit
conductor - energy source - load
Electrical SAFETY
Short Circuits
Insulators
Plugs (Ground)
Fuses
Breakers
Safety Regulations
Power Grid
VanDeGraff
Generator
VOLTS
Potential Difference
Voltage Drop
Safety Rules
AMPERES
Current flow rate
Galvanometers
OHMS
Resisting the flow
Multimeter
Ohms Law R = V / I
Voltmeter
Source Load Conductor - Switch
CELLS
Electrical Circuit Symbols
CIRCUITS
2 different Electrodes
in an Electrolyte
Series
(Only 1 Path)
WET Cell
Electrolyte is
a liquid
Parallel
(Multiple Paths)
Conductors Insulators
Superconductors
Types of Resistors
Wire-bound
Carbon composite
Variable Resistors
Rheostat (varies resistance)
Varistor (temperature change)
Thermistor (surge protector)
DRY Cell
Electrolyte
chemicals in
a paste
Microcircuits
Transistors act as switches
2 cells make a BATTERY
Battery Types
Primary Secondary
Electrochemistry
Electrolysis Electroplating
Galvanizing Electro-refining
Energy E = P x t
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy
TRANSFORMATIONS
Energy
TRANSFORMATIONS
Chemical
Electrical
Mechanical
Thermal
Light
Sound
Generators
Motors ( DC AC )
Energy can neither be created nor
destroyed, it can only be transformed from
one form to another
EFFICIENCY
St. Louis Motor
Transformers
Energy SOURCES
Fossil Fuels Light (Solar)
Geothermal Gravity Tides Wind Biomass Fuel Cells
Energy (output) x 100
Energy (input)
IMPACTS
Renewable vs Non-Renewable Energy
Air Pollution
Conservation of Energy
Sustainability
You might also like
- GCSE Electronics Summary: 1. Basic ElectricityDocument4 pagesGCSE Electronics Summary: 1. Basic ElectricitytheedisoncureNo ratings yet
- ELE 1111 (First Class)Document4 pagesELE 1111 (First Class)Senarine PersaudNo ratings yet
- Electricity 1Document86 pagesElectricity 1Jm MagnoNo ratings yet
- Electricity Int SciDocument20 pagesElectricity Int SciTushti RamloganNo ratings yet
- UTILITIES1 Lecture1Document14 pagesUTILITIES1 Lecture1Carjez LoveNo ratings yet
- UTILITIES1 Lecture1Document14 pagesUTILITIES1 Lecture1Potter XxNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument22 pagesElectricityanu.pavansuresh30No ratings yet
- Basic Principal of Electrical CircuitryDocument19 pagesBasic Principal of Electrical CircuitryAreeba ParvezNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electricity WorkDocument16 pagesBasics of Electricity WorkMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Electrical - BeeeDocument27 pagesUnit - I Electrical - BeeeBubblee BennuNo ratings yet
- Syllabus and Study Guide ELE Category 2Document4 pagesSyllabus and Study Guide ELE Category 2Shavoy RichardsonNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Mesh, NodalDocument98 pagesIntroduction and Mesh, Nodalkv5928No ratings yet
- Series CircuitsDocument3 pagesSeries CircuitsEnglish TeacherNo ratings yet
- Notebook 4 Electrical CircuitDocument4 pagesNotebook 4 Electrical Circuitapi-335583967No ratings yet
- Bee Practical 1 PDFDocument5 pagesBee Practical 1 PDFA NI LNo ratings yet
- Passive Two-Terminal Electrical Component Electrical Resistance Bias Transmission Lines Watts GeneratorsDocument9 pagesPassive Two-Terminal Electrical Component Electrical Resistance Bias Transmission Lines Watts GeneratorsShubham PatidarNo ratings yet
- FEEEDocument56 pagesFEEEnetra msajjan100% (1)
- The Basic Principles of ElectricityDocument10 pagesThe Basic Principles of ElectricityGowri ShankariNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument10 pagesBasic ElectronicsFrancess Mae AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Name of Electrical Symbols PDFDocument6 pagesName of Electrical Symbols PDFHarsh MittalNo ratings yet
- Rajkiya Engineering College, Ambedkar Nagar: Presentation ON Summer Training From Uppcl 33/11 KV Sub-Station Basti (U.P.)Document20 pagesRajkiya Engineering College, Ambedkar Nagar: Presentation ON Summer Training From Uppcl 33/11 KV Sub-Station Basti (U.P.)Ratnesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Powerpoints Electric CircuitsDocument9 pagesPowerpoints Electric CircuitsmvmbappleNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Terms and Definitions - E-Green ElectricalDocument5 pagesBasic Electrical Terms and Definitions - E-Green ElectricalJohn Florenz VasquezNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year ElectronicsDocument131 pages2nd Year ElectronicsManav MiddhaNo ratings yet
- Docs EEEPELNotes2013Document99 pagesDocs EEEPELNotes2013Mr. Amit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Components in AutomotiveDocument11 pagesBasic Electronic Components in Automotivedray09No ratings yet
- Handout Basic Electrical and Electronics AllisonDocument6 pagesHandout Basic Electrical and Electronics AllisonSRIREKHANo ratings yet
- Electronics For Mechanical EngineersDocument35 pagesElectronics For Mechanical EngineersLungisaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Electricity - Part 6Document11 pagesUnit 2 Electricity - Part 6Maurya AdeshraNo ratings yet
- Simple CircuitsDocument3 pagesSimple CircuitsOnur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- Short Term Training For AutomotiveDocument60 pagesShort Term Training For AutomotiveBiruk TilahunNo ratings yet
- Actividad 5 InglesDocument10 pagesActividad 5 InglesVictoria FlorezNo ratings yet
- RCA - Power Transistor Applications Manual (OCR)Document288 pagesRCA - Power Transistor Applications Manual (OCR)miguellm507180% (5)
- Semester 2 Final Concept ReviewDocument2 pagesSemester 2 Final Concept ReviewRasha RahmanNo ratings yet
- TehgjdDocument23 pagesTehgjdAditya YewleyNo ratings yet
- I RobotricksDocument22 pagesI RobotricksShivanshscribdNo ratings yet
- Electricity Lesson 1: Electron TheoryDocument11 pagesElectricity Lesson 1: Electron TheoryMarie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of ECEDocument136 pagesFundamental of ECEPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Wiring ReviewerDocument4 pagesBasic Electrical Wiring ReviewerRoselyn CantosNo ratings yet
- Workshop 13Document67 pagesWorkshop 13TahirNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary - Power ProductionDocument6 pagesVocabulary - Power ProductionFola AdedejiNo ratings yet
- Introductory Concepts of Circuit Topology and DC ExcitationsDocument34 pagesIntroductory Concepts of Circuit Topology and DC ExcitationsFrance Mae CamogaoNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesInterview QuestionsJeevaNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE NC II MODULE New Edited MASTER LEODocument26 pagesELECTRICAL INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE NC II MODULE New Edited MASTER LEOOLINSTERG COLLEGENo ratings yet
- LOG ElectricalPowerGeneration 130722 1811 32410Document46 pagesLOG ElectricalPowerGeneration 130722 1811 32410zola1976No ratings yet
- Electronics by Sir JoelDocument47 pagesElectronics by Sir JoelDann SarteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Automotive Electrical and Electronic SystemDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Automotive Electrical and Electronic SystemThao HuynhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Automotive Electrical and Electronic SystemDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Automotive Electrical and Electronic SystemThao HuynhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 A PDFDocument79 pagesUnit 1 A PDFJayasri ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- The Basic Principles of ElectricityDocument37 pagesThe Basic Principles of ElectricityCris Yirah DaclanNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument10 pagesREVIEWERgen zNo ratings yet
- Text 1Document6 pagesText 1Rohan SiegfriedNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of ElectricityDocument53 pagesBasic Principles of ElectricityRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- SSS 1 3RD TermDocument21 pagesSSS 1 3RD TermabiodunokoyaNo ratings yet
- 0005unit V NotesDocument33 pages0005unit V Noteskishan kumarNo ratings yet
- 3rd Chapter Medical Physics Notes by Abdul Ghafoor Sajjad Physiotherapist AFIRMDocument9 pages3rd Chapter Medical Physics Notes by Abdul Ghafoor Sajjad Physiotherapist AFIRMAbdul Ghafoor Sajjad64% (11)
- Electricity & ElectronicsDocument82 pagesElectricity & ElectronicsCassandra Noreen Pacayra SantosNo ratings yet
- Electrical Terms PDFDocument7 pagesElectrical Terms PDFglai Ramos0% (1)
- Bio 20 Section 6 1 Chemistry of Life AliceaDocument85 pagesBio 20 Section 6 1 Chemistry of Life Aliceaapi-263357086No ratings yet
- Kidneys and ExcretionDocument68 pagesKidneys and Excretionapi-263357086No ratings yet
- Muscles and MovementDocument61 pagesMuscles and Movementapi-263357086No ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument67 pagesThe Circulatory Systemapi-263357086No ratings yet
- Breathing and Gas Exchange PowerpointDocument53 pagesBreathing and Gas Exchange Powerpointapi-263357086100% (1)
- Blood and Immunity PowerpointDocument94 pagesBlood and Immunity Powerpointapi-263357086100% (1)
- Unit D Chapter 2Document28 pagesUnit D Chapter 2api-263357086No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument51 pagesPhotosynthesisapi-263357086No ratings yet
- Digestive System PowerpointDocument65 pagesDigestive System Powerpointapi-263357086No ratings yet
- CHP 2 Biogeochemical Cycles PowerpointDocument44 pagesCHP 2 Biogeochemical Cycles Powerpointapi-263357086No ratings yet
- Adaptation and Evolution PowerpointDocument64 pagesAdaptation and Evolution Powerpointapi-263357086No ratings yet
- Fresh and Saltwater Systems: Grade 8 - Unit 5 - ConceptsDocument1 pageFresh and Saltwater Systems: Grade 8 - Unit 5 - Conceptsapi-263357086No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument39 pagesCellular Respirationapi-263357086No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Ecological PyramidsDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Ecological Pyramidsapi-263357086No ratings yet
- MFM Concept Map 8Document1 pageMFM Concept Map 8api-263357086No ratings yet
- Unit B Chapter 2Document35 pagesUnit B Chapter 2api-263357086No ratings yet
- Unit D Chapter 1Document41 pagesUnit D Chapter 1api-263357086No ratings yet
- 10c Course Outline AliceaDocument13 pages10c Course Outline Aliceaapi-263357086No ratings yet
- Unit C Chapter 1Document70 pagesUnit C Chapter 1api-263357086No ratings yet
- Unit C Chapter 2Document37 pagesUnit C Chapter 2api-263357086No ratings yet
- Ms Concept Map 8Document1 pageMs Concept Map 8api-263357086No ratings yet
- Laos Concept Map 8Document1 pageLaos Concept Map 8api-263357086No ratings yet
- Science 30 Course Outline AliceaDocument3 pagesScience 30 Course Outline Aliceaapi-2633570860% (1)
- Unit B Chapter 1Document70 pagesUnit B Chapter 1api-263357086No ratings yet
- Ccs Concept Map 8Document1 pageCcs Concept Map 8api-263357086No ratings yet
- Se Concept Map 9Document1 pageSe Concept Map 9api-263357086No ratings yet
- Ec Concept Map 9Document1 pageEc Concept Map 9api-263357086No ratings yet
- BD Concept Map 9Document1 pageBD Concept Map 9api-263357086No ratings yet
- MCC Concept Map 9Document1 pageMCC Concept Map 9api-263357086No ratings yet