Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transport in Plants2
Uploaded by
Zul Abror Bin Ya'akop0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views9 pagesplants
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentplants
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views9 pagesTransport in Plants2
Uploaded by
Zul Abror Bin Ya'akopplants
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Fig. 5.1 shows a graph drawn by a student of the rate of photosynthesis in a plant exposed to
the same concentration of carbon dioxide at two different temperatures.
rate of
photosynthesis
Fig. 5.1
{a) (i) Name one limiting factor, other than carbon dioxide and temperature, that affects
the rate of photosynthesis
(1)
(ii) Suggest a likely temperature for curve A. Give an explanation for your answer.
likely temperature
explanation...
[3]
{b) The student failed to label the horizontal (x) axis of the graph. Suggest a suitable label
for this axis and explain your suggestion.
label for x axis.
explanation
ld]
[Total: 8]
(a) Describe the functions of xylem in a plant.
(3)
(b) Explain how starch and protein stored in the roots of a plant during the day can be used
in the growth of a shoot during the night.
7
[Total: 10]
Fig. 4.1 shows the effect of increasing light intensity on photosynthesis in two different
species of plants, species C and species D.
uptake
uptake or
loss of CO,
from plant
loss
light intensity / arbitrary units
Fig. 4.4
(a) (i) Use Fig. 4.1 to find the light intensity at which the rate of respiration is equal to the
rate of photosynthesis in plant C.
.. arbitrary units [1]
(ii) Explain why carbon dioxide is lost from plant € at a light intensity below the value
you have stated in (a)(i).
13)
(b) Using Fig. 4.1, suggest why plant species D is more likely than species C to grow on the
ground in a wooded area such as a tropical rain forest.
{c) When leaves fall from plants, they are decomposed to return nutrients to the soil.
Suggest why the rate of decomposition will be particularly high in a tropical rain forest.
eeseeeeeeesee eoseeseeeneeetneeeeneneeeneeteetenneeentneeeceerssecseeseeeee [SD
[Total: 10]
(a) Complete the equation to summarise the process of photosynthesis.
ca]
A young, green, leafy stem was placed in a clear glass beaker of water in bright light.
Fig. 4.1 shows the stem 12 hours later.
bubbles formed —__
‘on stem
Fig. 4.4
(b) (i) Suggest two places where the bubbles could have come from.
1
2. ca]
(ii) Tests proved that the bubbles contained oxygen. Explain how they appeared on the
side of this green stem.
(c) Explain the benefits to other organisms of having submerged water plants in a pond
‘ecosystem.
BI
[Total: 10]
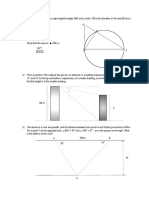
Fig. 3.1 shows a small, deep-rooted bush growing in a warm, dry climate.
Branches B and C have a similar number of leaves, but the leaves of branch B are enclosed
ina transparent polythene bag that empties into a container.
leaves of leaves of
branch B 7 braneh ©
4m
transparent __
bag
Fig. 3.4
Fig. 3.2 is a graph showing the total volume of water lost by the leaves of each of the two
branches during the same day.
total
volume
of water
lost
0600 1200 1800
time of day/h
Fig. 3.2
(a)
(b)
(c)
State two environmental factors responsible for the water loss during the day by
branch C. For each factor, explain how it affects water loss.
factor 1...
explanation
factor 2.
explanation
(5)
Explain how the volume of water lost from branch B is at first greater, then less than that
lost from branch C.
2]
Suggest why, even for certain plants that are poisonous to humans, the container in
Fig. 3.1 can supply travellers with safe drinking water.
Bl
[Total: 10]
‘Black sigatoka’ is a fungal disease of banana leaves. The hyphae of the fungus spread
through the intercellular spaces as shown in Fig. 2.1.
Fig. 2.1
(c) Suggest ways by which the fungus would eventually cause the leaf to die.
[4]
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Periodic Table and AtomsDocument1 pagePeriodic Table and AtomsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium and Turning ForcesDocument3 pagesEquilibrium and Turning ForcesZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument5 pagesMathsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument4 pagesMathsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Secondary 1Document6 pagesMathematics: Secondary 1Zul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry RevisionDocument2 pagesTrigonometry RevisionZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Oxidation ReductionDocument7 pagesOxidation ReductionZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- PSLE Foundation ScienceDocument7 pagesPSLE Foundation ScienceZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- 13 Stoic ProbDocument3 pages13 Stoic ProbZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Vectors Summary PDFDocument6 pagesVectors Summary PDFZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- 1.intro To Organic Chem-PracticeDocument2 pages1.intro To Organic Chem-PracticeZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Force QuestionsDocument12 pagesForce QuestionsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Electricity StructuredDocument10 pagesElectricity StructuredZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Inference For Two Population Means: Case StudyDocument33 pagesInference For Two Population Means: Case StudyZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Draw Best Fit LineDocument11 pagesDraw Best Fit LineZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- 2011 Answers To AS1.3Document1 page2011 Answers To AS1.3Zul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- GCE O Level Chemistry (5070) - Topical Experimental TechniquesDocument15 pagesGCE O Level Chemistry (5070) - Topical Experimental TechniquesZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Wwwautomaticpaperscom - CheDocument15 pagesWwwautomaticpaperscom - CheZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- O' Level Physics Revision MechanicsDocument8 pagesO' Level Physics Revision MechanicsNeural Spark Physics CieNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)