Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 14 Modified
Uploaded by
api-248642018Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 14 Modified
Uploaded by
api-248642018Copyright:
Available Formats
1
by: Mr. Naveed
Expected short questions from theory and exercise
Atif
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
Chapter # 14: Current Electricity
SHORT QUESTIONS (EXERCISE)
Question#1: Define Electric Current and its mechanism of flow?
The rate of flow of electric charges through any cross sectional area is called
electric current. Electric Current is denoted by I. Mathematically:
I = Q/t
In SI System, the unit of current is Ampere.
Mechanism of flow of current in conductor: Let a copper wire is a conductor.
It has a large number of free electrons in random motion.
In absence of any electric field no current passes through wire.
But when we connect it terminals with a battery.
Now current flows from positive terminal to negative terminal of battery.
Current always flows from higher potential to lower potential.
Question#2: What is meant by conventional current?
Let a stream of positively charged particles is being injected in a metal cup.
We will say that electric current is flowing through upper area of cup.
Due to this positive charges are increasing on the cup.
So, this current is due to motion of positive charges.
If we stop injecting positive charges into the cup. Instead start injecting a
beam of electrons into the cup, then positive charges start neutralizing.
Thus the effect of flow of current due to negative charges is same as that of
positive charges, but in opposite direction.
This equivalent current of positive charge is known as conventional current.
Question#3: What is meant by electronic current?
Ans: The current due to the motion of negative charges or electrons that flows
from the negative terminal of the battery to the positive terminal in the electric
circuit is called electronic current.
Question#4: What is electromotive force? Is it really a force? Explain.
Electromotive Force (EMF):The electromotive force of a battery or cell is the total energy supplied in driving
one coulomb of charge round a complete circuit in which the cell is connected.
The complete circuit includes the cell and external circuit connected to its
terminals.
Suppose the amount of this energy is 2 joule, and then the e.m.f. of the battery
will be 2 volt.
EMF is a scalar quantity because it is not actually a force and it is measured in
volts.
Question#5: What is difference between electromotive force and
potential difference?
Electromotive Force (EMF):Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
by: Mr. Naveed Atif
www.naveedatif.weebly.com
by: Mr. Naveed
Expected short questions from theory and exercise
Atif
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
The electromotive force of a battery or cell is the total energy supplied in driving
one coulomb of charge round a complete circuit in which the cell is connected.
The complete circuit includes the cell and external circuit connected to its
terminals.
Potential Difference: The potential difference determines the energy between any two points of the
circuit, which is required in moving a charge from one point to another.
EMF is always greater than the potential difference.
The concept of EMF is only applicable to an electrical field while the
potential difference is applicable to magnetic, gravitational and electric
field.
Question#6: What was the first source of current?
First battery was made in 1800. It consisted of copper and zinc plates which
were soaked in salt water.
Question#7: Explain ohms law? What are its limitations?
Ohms Law: The value of current I passing through a conductor is directly proportional to
the potential difference V applied across its ends, provided the temperature
and the physical state of the conductor does not change. Mathematically it is
defined as: VI
V = IR
Where R is constant of proportionality. The value or R is different for each
conductor.
Limitations: Ohms law is applicable only in conductors even when its temperature and
physical state does not change.
Materials that obeys Ohms law are said to be Ohmic.
Question#8: Define resistance and its units.
The property of a substance, which opposes the flow of current through it, is
called its resistance.
Its unit is ohm defined as When a potential difference of one volt is applied
across the ends of a conductor and one ampere of current passes through it,
the resistance will be one ohm.
Question#9: What is the difference between conductors and insulators?
Conductors
Insulators
A material that conducts heat,
A material that does not conduct
electricity or sound called conductors. electricity are called insulators.
They have free electrons.
They have no free electrons.
They have very small value of
They have very large value of
resistance.
resistance.
e-g: gold, silver and other metals etc. e-g: wood, glass, plastic etc.
Question#10: What is meant by specific resistance?
At a certain temperature the resistance of a conducting wire depends upon: Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
by: Mr. Naveed Atif
www.naveedatif.weebly.com
by: Mr. Naveed
Expected short questions from theory and exercise
Atif
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
i) Its length
ii) Area of cross-section
iii) Nature of material of wire
It is found that
i) Resistance is directly proportional to length of conductor.
RL
ii) Resistance is inversely proportional to cross-sectional area of conductor
R 1/A
OR
R L/A
OR
R = p L/A
Where p is the constant of proportionality, known as specific resistance.
Question#11: What is the effect of temperature upon Resistance?
When temperature of conductor rises, average speed of free electrons
increases, which increases the rate of collision of electrons and the atoms. This
causes an increase in the resistance of the conductor. So, temperature is
directly proportional to resistance
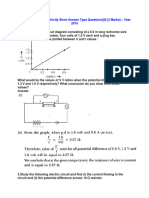
Question#12: How are resistances connected in series? What are
characteristics of this combination?
i) In this method only one path is present for flow of current because
resistances are connected end to end.
ii) The magnitude of current through each resistor is same.
iii) The sum of voltages across each resistor is equal to the voltage of battery.
V = V1 + V2 + V3
If current is passing through resistors R1, R2,
R3 then
V = IR1 +IR2 +IR3
V = I (R1 +R2 +R3)
iv) The equivalent resistance Re of a series
combination is that resistance which when
substituted in place of the combination the
same current would flow through the circuit.
R = R1 + R2 + R3 +.Rn
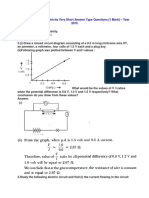
Question#13: How are resistances are connected in parallel. What are
the characteristics of this combination?
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
by: Mr. Naveed Atif
www.naveedatif.weebly.com
by: Mr. Naveed
Expected short questions from theory and exercise
Atif
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
i) In this combination potential drop across all the
resistances is the same.
ii) The sum of current flowing through the various
resistances is equal to the total current.
I = I1 +I2 +I3
iii) The equivalent resistance Re of the parallel
combination is that resistance which when substituted
in place of the parallel combination does not alter the
total current of the circuit.
1/Re = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3
1/Re = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 .1/Rn (For n
resistances)
Question#14: Write note on?
Galvanometer and Ammeter: i) Galvanometer is very sensitive instrument.
ii) Only few milli-ampere current can cause full deflection in it.
iii) Therefore it is used directly to measure current during experiments.
iv) A modification is obtained by connecting a resistance parallel with
galvanometer.
v) This resistance is called shunt.
vi) Shunt provides an alternate path for flow of current.
vii) In this way range of galvanometer is increased.
viii) This modified galvanometer is called ammeter.
Voltmeter: i) Galvanometer is converted into voltmeter by connecting a suitable resistance
in series.
ii) Voltmeter can directly measure the potential difference.
iii) Value of series resistance depends upon the range of the voltmeter.
iv) Voltmeter is always connected in parallel with the resistance across which
the potential difference is to be measured.
Question#15: Explain the energy dissipation in a resistance. What is
Joules law?
Ans: Energy dissipation:
The power dissipated in a resistor is the energy dissipated per unit time. If an
amount of charge dq moves through the resistor in time dt then the power loss
is
P = dq / dt = IV
The amount of heat generated in a resistor due to flow of charges is equal to
the product of square of current, resistance and time duration.
W = QV = I x t x V
Question#16: Define the Direct Current and Alternating Current?
Ans:
Direct Current
Alternating Current
The current which always flows in one The current whose directions changes
direction is called direct current or
again and again is called Alternate
D.C.
Current or A.C.
The +ive & -ive terminals of dc have
AC is a current which changes its
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
by: Mr. Naveed Atif
www.naveedatif.weebly.com
by: Mr. Naveed
Expected short questions from theory and exercise
Atif
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
fixed polarity, therefore level of DC
remains constant with time.
It is derived from a cell or a battery.
polarity again and again.
It is produced by AC generators.
Question#17: What is frequency of A.C?
The number of cycles which the current completes in one second is known as
frequency of A.C.
Question#18: What is Neutral Wire? What type of risk involved in using
electricity in homes? What are safety measures?
Electric energy is distributed in houses from a power station by means of two
wires.
One wire is earthed at the power station so it is at zero potential. This is called
neutral wire. Tester shows no glow at this wire. The electric potential of the
other wire changes. This is called live wire. Tester show glow at this wire.
Human body is conducting, so electric current can pass through it. When a
person touches the live wire, then potential difference is created between
touching point and feet (on earth). Due to which electric current can flow in the
body of a person, which could be fatal.
To avoid this, supply lines are covered with insulating material. Insulation
covered wire is called cable.
Question#19: What is fuse?
If a small wire is connected in series with the live wire. It is known as fuse wire
or fuse.
Question#20: What is circuit breaker?
It is a safety device, which is used in place of fuse. Due to any fault when the
current exceeds the safety limit, then the button of the circuit breaker moves
upward. Due to which, the circuit breaks and the flow of current stops in it. The
button of the circuit breaker is pressed after the correction of the circuit. The
circuit again gets completed and the current flows in it.
Q#21: What is electricity Hazards?
A. Hazards
The electricity comes to our houses by means of cable. These cables consist of two wire
live wire and neutral wire. The live wire and any terminal connected to it are very
dangerous. Anyone who touches a live wire would suffer a fatal shock, because human
body conducts electricity. The electric shock also occurs due to damage insulation,
overheating of cables and damped condition. We should not walk upon wires bare foot.
Q#22: Describe four safety measures that should be taken in connection with the
household circuit. OR
How electricity is used safely in homes?
A. The electricity supplied to our homes is alternating current (A-C). It changes its direction
50 times in a second. So its frequency is 50Hz and voltage is 220V. For the safe use of
electricity the following devices should be used in the house circuit.
Fuse
It consists of a thin piece of metal wire having low melting point. When too much current
flows through the fuse wire. It melts before the copper wire in the circuit get hot. As a result
the circuit breaks and no damage occur.
Circuit breaker
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
by: Mr. Naveed Atif
www.naveedatif.weebly.com
by: Mr. Naveed
Expected short questions from theory and exercise
Atif
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
It consists of an electromagnet, when current exceeds the rated value of the circuit breaker.
It automatically separates the contact of the circuit wires and breaks the circuit. Now a day it
is used instead of fuse, because it works quickly than fuse.
Earth wire
A wire which goes to the top connection on all power sockets and is connected with the
earth. This wire is a safety precaution to prevent electric shock when an appliance develops
a fault.
Q#22: The voltage chosen for the transmission of electrical power over large
distances is many times greater than the voltage of the domestic supply. State two
reasons why electrical power is transmitted at high voltage.
Ans: 1) Electricity is transmitted at high voltages to reduce the energy lost in long distance
transmission.
2) As we know
Electric power = current * voltage
So, for transmission of high power either we provide high voltage or high current.
Q#22: Why is the voltage used for the domestic supply much lower than the voltage
at which the power is transmitted?
Ans: The voltage used for the domestic supply is much lower because
Electrical appliances used in homes require low voltage.
To avoid any type of danger which can cause death.
To get rid of damaging of electrical appliances.
Q#23: Describe briefly the hazards of household electricity.
Ans: see from text book.
Q#24: Design a circuit diagram for a study room that needs the following equipment
in parallel:
A. One 100 W lamp operated by one switch;
B. One reading lamp fitted with a 40 W bulb which can be switched ON and OFF
from two points.
Lamp
AC supply
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
by: Mr. Naveed Atif
www.naveedatif.weebly.com
by: Mr. Naveed
Expected short questions from theory and exercise
Atif
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
C. What is the advantage of connecting the equipments in parallel instead of
series combination?
Ans: The advantage is to get the full main voltage and one can turn ON any
appliance without having to turn ON another.
Conceptual Questions
Q#1: Why in conductors charge is transferred by free electrons rather than by
positive charges?
Ans: Positive charges are present in the nucleus of the atom and are not responsible
for the transfer of charge. So, the free electrons which are randomly present in the
conductors and when electric field is applied these free electrons carry charge or
causes flow of current.
Q#2: What is the difference between cell and battery?
Ans: A cell is a single unit that supplies small current and have small voltage but in
battery there are many cells that are connected together in series or parallel.
Q#3: Can current flow in a circuit without potential difference?
Ans: No, current does not flow in the circuit without potential difference.
Q#4: Two points on an object are at different electric potentials. Does charge
necessarily flow between them?
Ans: Yes, charge will flow between them because in the circuit the flow of charges
continuous as long as there is a potential difference.
Q#5: In order to measure current in a circuit why ammeter is always connected in
series?
Ans: The ammeter is connected in series so, that the whole current passes through the
ammeter because the resistance of the ammeter is very small.
Q#6: In order to measure voltage in a circuit voltmeter is always connected in
parallel. Discuss.
Ans: Voltmeter is always connected in parallel with the resistance across which the
potential difference is to be measured. Higher the resistance of the voltmeter, more
reliable would be its readings. If the resistance of the voltmeter is low it will draw more
current from the circuit. Due to this the potential difference across the resistance for
measurement which voltmeter connected, would drop.
Q#7: How many watt-hours are there in 1000 joules?
Ans:
As we know
1 KWh = 3.6 106 J
1 Wh = 3.6 106 J / 1000
1 Wh = 3.6 103 J
1 J = (1 / 3.6 103 ) Wh
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
by: Mr. Naveed Atif
www.naveedatif.weebly.com
by: Mr. Naveed
Expected short questions from theory and exercise
Atif
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
1 J = (0.000278 ) Wh
1000 J = 0.27778 watt-hour
Q#8: From your experience in watching cars on the roads at night, are automobile
head lamps connected in series or in parallel?
Ans: Head lamps are generally connected in parallel.
Q#9: A certain flash light can use a 10 Ohm bulb or a 5 Ohm bulb. Which bulb
should be used to get brighter light? Which bulb will discharge the battery first?
Ans: Both 10 ohm & 5 ohm bulb gives equal brightness because it depends upon
voltage of battery. The bulb having high resistance will discharge the battery first.
Q#10: It is impracticable to connect an electric bulb and an electric heater in
series. Why?
Ans: In series connection current remains same and voltage divided according to the
resistance of the appliance. When we put electric bulb and electric heater in series then
it will divide the voltage which ultimately divided the power.
Q#11: Does a fuse in a circuit control, the potential difference or the current?
Ans: A fuse in a circuit controls the excess amount of current.
Chapter wise Notes (Physics)
by: Mr. Naveed Atif
www.naveedatif.weebly.com
You might also like
- ELECTRICITYDocument4 pagesELECTRICITYAkash DuttaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project: Class Xii SESSION 2021-2022Document16 pagesPhysics Project: Class Xii SESSION 2021-2022Coc6 GuptaNo ratings yet
- Law of Resistance (Parallel) PDFDocument12 pagesLaw of Resistance (Parallel) PDFAmogha kantakNo ratings yet
- 2m Current ElectricityDocument20 pages2m Current ElectricityRohitt MathurNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity. MiaDocument42 pagesCurrent Electricity. MiaVerla MfeerNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Physics Current Electricity ChapterDocument15 pages2nd Year Physics Current Electricity ChapterphooolNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit1 (BEEE)Document48 pagesNotes Unit1 (BEEE)Vedashree ShetyeNo ratings yet
- Electric Currents & DC CircuitsDocument49 pagesElectric Currents & DC CircuitsHergene FanerNo ratings yet
- DC Current Physics Project GuideDocument34 pagesDC Current Physics Project GuideAmrita SinghNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class X NotesDocument15 pagesElectricity Class X NotesGrgg Hkhkk100% (5)
- Current and ResistanceDocument42 pagesCurrent and ResistancehelsaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Maintenance FAQsDocument416 pagesElectrical Maintenance FAQsVivek PainkraNo ratings yet
- Most Expected Viva Questions - Physics PracticalsDocument14 pagesMost Expected Viva Questions - Physics Practicalsitzspam121fNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits: Key Concepts of Electrical Conduction, Ohm's Law, and MoreDocument69 pagesElectric Circuits: Key Concepts of Electrical Conduction, Ohm's Law, and MoreSherena Peter GovindNo ratings yet
- ' ElectricityDocument98 pages' Electricitya9758127118No ratings yet
- Educ376 Electrical Circuits Instructional MaterialsDocument30 pagesEduc376 Electrical Circuits Instructional Materialsapi-583788842No ratings yet
- Phy Pract Viva QNDocument19 pagesPhy Pract Viva QNkunala523No ratings yet
- 10 Chapter-12-: Electricity CBSE Study NotesDocument11 pages10 Chapter-12-: Electricity CBSE Study Notesrucha BNo ratings yet
- CBSE Study Notes on ElectricityDocument11 pagesCBSE Study Notes on ElectricityNaseeb YadavNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Electricity (Notes)Document10 pagesClass 10th Electricity (Notes)Kamya SyalNo ratings yet
- Class10 Science Notes Chapter12Document6 pagesClass10 Science Notes Chapter12ng_nirmalNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Current Electricity Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesClass 10 Current Electricity Lesson PlanObul Reddy PolimeraNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity PDFDocument52 pagesCurrent Electricity PDFMaahiNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument7 pagesCurrent ElectricityMakrand ShirsatNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design PackageDocument6 pagesElectrical Design Packageapi-272622659No ratings yet
- Chapter ELECTRICITYDocument21 pagesChapter ELECTRICITYunknown072006No ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Join @cbse10bystudentshelper On TelegramDocument26 pagesOhm's Law: Join @cbse10bystudentshelper On TelegramValerie CoxNo ratings yet
- Electrical QuestionsDocument416 pagesElectrical QuestionsSoutrik Chowdhury100% (1)
- CH - 3 Class XII Physics (E-Notes)Document9 pagesCH - 3 Class XII Physics (E-Notes)tejasNo ratings yet
- N10. Electrical QuantitiesDocument11 pagesN10. Electrical QuantitiesAwais FarooqiNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Electric CurrentDocument10 pagesElectricity: Electric CurrentTajiriMollelNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity PDFDocument18 pagesCurrent Electricity PDFSri DNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Electricity Short Answer Type QuestionsDocument39 pagesClass 10 Science Electricity Short Answer Type QuestionsLawrence GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Important Viva QuestionsDocument19 pagesImportant Viva QuestionsAtul TripathiNo ratings yet
- El 2Document27 pagesEl 2ashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- SSS 1 3RD TermDocument21 pagesSSS 1 3RD TermabiodunokoyaNo ratings yet
- Voltage Sources Produce Electric Current in ConductorsDocument4 pagesVoltage Sources Produce Electric Current in ConductorsKazi Mahbubur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Electricity Physics NotesDocument17 pagesElectricity Physics NotesbhagyavathinrhoneyNo ratings yet
- GR Bee PPTS Unit - I To IvDocument205 pagesGR Bee PPTS Unit - I To IvSri HarshaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science Learn CBSEDocument39 pagesElectricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science Learn CBSELushila MinjNo ratings yet
- Electricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science - Learn CBSEDocument39 pagesElectricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science - Learn CBSEAmitChopraNo ratings yet
- Physics2 10Document29 pagesPhysics2 10BayuNo ratings yet
- Essential Current Electricity Notes for JEE Main & AdvancedDocument16 pagesEssential Current Electricity Notes for JEE Main & Advancedvikranth bakkashettyNo ratings yet
- Important Questions With Answers Part IDocument5 pagesImportant Questions With Answers Part Iashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Electricity Numerical StudyPhobia ExclusiveDocument39 pagesElectricity Numerical StudyPhobia ExclusiveYtnew SubNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Ohm's Law-BBDocument48 pagesElectricity - Ohm's Law-BBfarahNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Lab ReportDocument9 pagesElectrical Circuit Lab Reportapi-297082885100% (1)
- Rocket Revision and Full Syllabus in Less Than 5 Hour - 1709443751566648Document109 pagesRocket Revision and Full Syllabus in Less Than 5 Hour - 1709443751566648gracegrace7380No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Basic Atomic Theory: Key PointsDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Basic Atomic Theory: Key PointsDaahirshiiq MadoobeNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectricityDocument18 pagesBasics of Electricitygsantosh06No ratings yet
- Current Electricity: Written WorkDocument35 pagesCurrent Electricity: Written WorkShaari KashaniNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument44 pagesCurrent Electricityvarshasaindane8640No ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Phy 18 NotesDocument10 pagesPhy 18 Notesapi-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 17 NotesDocument12 pagesPhy 17 Notesapi-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 16 NotesDocument16 pagesPhy 16 Notesapi-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 9 30Document1 pagePhy 9 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 6 30Document1 pagePhy 6 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 15 NotesDocument8 pagesPhy 15 Notesapi-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 14 NotesDocument8 pagesPhy 14 Notesapi-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 10 NotesDocument9 pagesPhy 10 Notesapi-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 13 NotesDocument5 pagesPhy 13 Notesapi-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 12 NotesDocument19 pagesPhy 12 Notesapi-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 7 30Document1 pagePhy 7 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 8 30Document1 pagePhy 8 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 15 35Document1 pagePhy 15 35api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 2 30Document1 pagePhy 2 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 5 30Document1 pagePhy 5 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- U15 QuestionsDocument2 pagesU15 Questionsapi-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 4 30Document1 pagePhy 4 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 2 30Document1 pagePhy 2 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 2 30Document1 pagePhy 2 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 16 35Document1 pagePhy 16 35api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 14 35Document1 pagePhy 14 35api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 2 30Document1 pagePhy 2 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 2 30Document1 pagePhy 2 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 1 30Document1 pagePhy 1 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- Phy 2 30Document1 pagePhy 2 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 ModifiedDocument5 pagesChapter 13 Modifiedapi-248642018100% (1)
- Phy 2 30Document1 pagePhy 2 30api-248642018No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 ModifiedDocument6 pagesChapter 12 Modifiedapi-248642018No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 ModifiedDocument5 pagesChapter 11 Modifiedapi-248642018100% (2)
- Alarm Valve Combo Unit Alert-1: Installation and Maintenance Manual V1.1Document31 pagesAlarm Valve Combo Unit Alert-1: Installation and Maintenance Manual V1.1MSSNo ratings yet
- HVDC StationDocument26 pagesHVDC StationmeraatNo ratings yet
- Solis Manual S5-GR3P (15-20) K DW EUR V1.1 (20221024)Document28 pagesSolis Manual S5-GR3P (15-20) K DW EUR V1.1 (20221024)om_zahidNo ratings yet
- Single Phase RectificationDocument13 pagesSingle Phase RectificationMariusNo ratings yet
- Operations and Maintenance Manual: Tebevert III 25kVA 120VDC Inverter System 028-0009-006 Rev. CDocument70 pagesOperations and Maintenance Manual: Tebevert III 25kVA 120VDC Inverter System 028-0009-006 Rev. CpatopickNo ratings yet
- DIY 150W Inverter: Build a Portable Power Inverter to Run Small Appliances from a Car BatteryDocument14 pagesDIY 150W Inverter: Build a Portable Power Inverter to Run Small Appliances from a Car BatteryvipinNo ratings yet
- Praharsh PPT (Modelling of Unified Power Flow Controller) GGDocument16 pagesPraharsh PPT (Modelling of Unified Power Flow Controller) GGPraharsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Modeling of DC Link Capacitor Current Ripple For Electric VehicleDocument26 pagesModeling of DC Link Capacitor Current Ripple For Electric VehicleBojan BankovicNo ratings yet
- Manual Partes DGCD Con DetectorDocument64 pagesManual Partes DGCD Con Detectorluis alvarezNo ratings yet
- Catalogue FREECOLD EN 2020Document12 pagesCatalogue FREECOLD EN 2020Belly Yan DewantaraNo ratings yet
- Luminous ReportDocument85 pagesLuminous ReportBella Stewart88% (8)
- NorsokDocument26 pagesNorsokOchie RomeroNo ratings yet
- REVO-VP 5000 User ManualDocument38 pagesREVO-VP 5000 User ManualMiro SekulaNo ratings yet
- Im582136800-Netsure-502-Full-System - (Dragged) 3Document1 pageIm582136800-Netsure-502-Full-System - (Dragged) 3fghjk hjkNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Brief - Unit 13 - LA 062016 No ComDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 - Brief - Unit 13 - LA 062016 No ComIsaiahNo ratings yet
- Kyoritsu 2009 Full Line Test Equipment CatalogueDocument84 pagesKyoritsu 2009 Full Line Test Equipment CatalogueRadio Parts100% (1)
- 1-Bill Cantor Steve McCluer - DC Arc FlashDocument10 pages1-Bill Cantor Steve McCluer - DC Arc FlashMarco Miranda RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Powerflex AB Trouble Shooting-Chapter 4-137Document137 pagesPowerflex AB Trouble Shooting-Chapter 4-137Milky SandNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument16 pagesSodapdfJaat JiNo ratings yet
- Isolation in Electric Vehicle Systems: Quick Reference GuideDocument12 pagesIsolation in Electric Vehicle Systems: Quick Reference GuideThien Dinh100% (1)
- 21-pin engine connector responsibilitiesDocument6 pages21-pin engine connector responsibilitiesClaudio Rene Silva Hernandez100% (1)
- I Ma 3010.71 1320 622 Huy 067 - A - ComDocument140 pagesI Ma 3010.71 1320 622 Huy 067 - A - ComValério de Oliveira Santos100% (1)
- ELL 100 - Introduction to Single Phase AC CircuitsDocument74 pagesELL 100 - Introduction to Single Phase AC CircuitsZulqarnain KhanNo ratings yet
- MJR MSE LLL DSL BookDocument147 pagesMJR MSE LLL DSL Bookbalaji817150No ratings yet
- Dual Ingecon Sun U B Series Family at 1500vdcDocument4 pagesDual Ingecon Sun U B Series Family at 1500vdcRoberto SNo ratings yet
- MP53Document3 pagesMP53Rehan KhanNo ratings yet
- Trio 50.0 TL Outd Us 480 Rev.gDocument1 pageTrio 50.0 TL Outd Us 480 Rev.gChRa JhonNo ratings yet
- SP 1103 Electrical Engineering GuidelinesDocument22 pagesSP 1103 Electrical Engineering Guidelinesabdou0% (2)
- SCADAPack 32 ControllerDocument66 pagesSCADAPack 32 Controllersergio_costa_28No ratings yet
- Mobile Wind Charger for Automobile BatteriesDocument7 pagesMobile Wind Charger for Automobile Batteriessuraj dhulannavarNo ratings yet