Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inorganic Chemistry Review
Uploaded by
Pj DeclaradorCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inorganic Chemistry Review
Uploaded by
Pj DeclaradorCopyright:
Available Formats
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY
REVIEWER
Prepared by Cherry Caroline S. Chua, 11-2012
Revised by Joanna J. Orejola, 09-2013
GROUP IA (1): ALKALI METALS
Possess only one valence electron
Very reactive chemically
Seldom found free in nature
Lithium, Sodium, and potassium metals are stored under
keroseneViolent (exothermic, explosive) reaction with water
Hydrogen, H (Gk. hydro, water; genes, forming produces water
when burned with oxygen)
Lithium, Li (Gk. lithos, rock because it occurs in rocks)
Sodium, Na (L. sodanum, headache remedy; symbol, L. natrium,
soda)
Potassium, K (L. kalium, potash)
Rubidium, Rb (L. rubidius, dark red discovered with the
spectroscope, its spectrum shows red lines)
Cesium, Cs (L. caesium, blue spectral lines are blue)
Francium, Fr (France)
HYDROGEN, H
Inflammable Air
Lightest element
o
Among the alkali metals, only Hydrogen can exist as a monovalent
ion (H+) or a monovalent anion (H-)
Isotopes:
o Protium Most abundant isotope
o Deuterium Heavy hydrogen
D2O, heavy water
o Tritium Radioactive isotope
Hydrogen, under normal conditions, exist as a diatomic molecule
(H2), though this form is not very useful pharmaceutically
Industrial uses:
o Haber process (production of ammonia)
o Hydrogenation of oils
o Inflating balloons
WATER, H2O
Natural Water/Mineral Water
contain dissolved minerals (Ca+2, Mg+2, Fe+3, Na+, K+, HCO3-, SO4-2,
Cl-), varying amounts of suspended matter (clay, sand,
microorganisms, fragments of plants and animals), and traces of
dissolved atmospheric gases, ammonia, and metabolic
decomposition products
Not fit for drinking
Example
ALKALINE
WATER
CARBONATED
WATER
CHARACTERISTICS
o contain appreciable quantities of Na2SO4,
MgSO4 and NaHCO3
o contains CO2 under pressure and usually
effervesce on coming to the surface
o contain calcium and magnesium carbonates in
solution as bicarbonate
o can be natural or artificial
CHALYBEATE
o Contains iron in solution or in suspension
WATER
o Characterized by its ferruginous taste
o Forms ferric hydroxide or ferric oxide upon
exposure to air
LITHIA WATER o Do not contain appreciable quantities of lithium,
either as carbonate or chloride
SALINE WATER o Contain relatively high amounts of MgSO4,
(PURGATIVE
Na2SO4 and NaCl
WATER)
SULFUR WATER o Contains dissolved H2S and deposit S upon
exposure to the atmosphere
SILICEOUS
o Water that contain soluble alkali silicates
WATER
Water Hardness due to presence of dissolved minerals in water
Soft waterWater that does not contain appreciable amounts of
Ca+2 and Mg+2 ions
Hard waterWater that contains appreciable quantities of minerals
Temporary hardness
o Contains mainly dissolved calcium and magnesium
bicarbonate
o Can be removed by boiling (promotes formation of insoluble
calcium carbonate) or by addition of lime, Ca(OH)2
Permanent hardness
o Contains mainly dissolved calcium and magnesium sulfate
and chloride in water
o Cannot be removed by boiling
o Water softening is achieved by the use of ion-exchange resins
Potable Water
water that is fit to drink
USP Definition: Water that is obtained by distillation, ion exchange,
or reverse osmosis
meets standards for freedom from coliform organisms
water treated to remove insoluble matter through appropriate
coagulating, settling, and filtering processes; destruction of
pathogenic microorganisms by aeration, chlorination, or other
methods, and improvement of palatability through aeration and
filtration through charcoal
water fluoridation
o Achieved via addition of sodium fluorosilicate
o For prevention of dental caries
o Drawback: could cause dental fluorosis (mottling of teeth)
Purified Water
Intended for use as an ingredient of official preparations and in tests
and assays unless otherwise specified
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
Not for parenteral preparations
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE, H2O2
Agua oxigenada, agua oxenada
Oxygenated acid, oxygenated water
Use: treatment for Vincents stomatitis (severe form of gingivitis), as
mouthwash
Commercial availability:
o 10-volume solution (3% w/v) and 20-volume solution (6% w/v)
o Hydrogen Peroxide Topical Solution, USP
o 3% w/v stabilized aqueous solution
o 10-volume solution
o Stabilizer: acetanilide 0.03%
LITHIUM, Li
Lithos - Earth
Lightest metal
Pharmacologic action of lithium compounds:
o Mood stabilizer (depressant)
o Diuretic
LITHIUM BROMIDE, LiBr
Combined sedative effects of lithium ion and bromide ion
LITHIUM CARBONATE, Li2CO3
Brand names: Eskalith, Lithase, Quilonium-R
Widely used in the prophylaxis and treatment of bipolar disorders and
mania and in the maintenance treatment of recurrent depression
Also used for treatment of mania:
o Lithium Citrate
o Lithium Hydroxide
o Lithium Oral Solution
SODIUM, Na
From Latin word natrium
Principal extracellular ion
Accumulation of too much sodium in the body causes fluid retention
Cation of choice for organic medicinals
CALCIUM DISODIUM EDETATE, C10H12N2Na2 CaO8
Used in antidotal therapy for certain heavy metal poisoning
(particularly for lead)
Does not precipitate hypocalcemia
EDETATE DISODIUM, C10H14N2Na2O8.2H2O
EDTA Disodium salt
Pharmacologic Use: Chelating agent administered IV in the
emergency treatment of hypercalcemia
Hypocalcemia may occur if the drug is administered too rapidly or to
patients who are not initially hypercalcemicLife threatening
Not used in treatment of heavy metal poisoning since
hypocalcemia rapidly develops
MONOBASIC SODIUM PHOSPHATE, NaH2PO4
Component of Fleet enema
Fleet Enema is composed of Sodium Phosphate and Sodium
Biphosphate
Saline laxative
o Not absorbed from the intestines
Systemic and urinary acidifier
With Methenamine, treatment of cystitis (release of formaldehyde)
o Hairs of corn, as decoction used for cystitis
Source of phosphorus in hypophosphatemia and TPN
Indirectly lowers plasma calcium levelsExcess plasma phosphate
interacts with plasma calcium and is transferred to the bone
Used in the treatment of hypercalcemia
DIBASIC SODIUM PHOSPHATE, Na2HPO4
Sodium Phosphate, Phosphate of Soda
Dibasic phosphate ion is the primary anion in the intracellular fluid
Saline laxative
Antihypercalcemic, as oral solution
TRIBASIC SODIUM PHOSPHATE, Na3PO4
No pharmacologic use
Used for cleaning glass apparatus
Very alkaline reaction with water (corrosive)
SODIUM ACETATE, NaCH3COO
Diuretic
Systemic and urinary alkalizer
Pharmaceutical necessity used in solutions for hemodialysis and
peritoneal dialysis
Alkalinizing agent for Benedicts Solution
SODIUM ASCORBATE, NaC6H7O6
Vitamin C supplement
Antioxidant
SODIUM BICARBONATE, NaHCO3
Baking Soda
Solvay process
Bicarbonate ion is the 2nd major anion in the extracellular fluid
Systemic alkalizer
Systemic antacid
o Readily absorbed by the body
o Could cause systemic alkalosis
o Rebound hyperacidity
Pharmaceutically used as source of carbonation for effervescent
preparations
o Organic acid component: tartaric, citric, ascorbic acid
o CO2 enhances palatability of preparation
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
Antidote for zinc poisoning (ingestion)
Enhance elimination of acidic drugs
4 commonly used antacids
o Sodium Bicarbonate
o Calcium Carbonate
o Magnesium Hydroxide
o Aluminum Hydroxide
SODIUM BORATE, Na2B4O7
Borax
Pharmaceutic necessity: alkalinizing agent
Externally: as eyewash, bufferWater-softener
SODIUM CARBONATE, Na2CO3
Anhydrous soda ash
Dihydrate trona
Decahydrate soda crystals, washing soda, sal soda
Carbonating agent
SODIUM CHLORIDE, NaCl
Table salt, rock salt, sea salt, solar salt, dendritic salt
Chloride is the major extracellular anion
Electrolyte replenisher
o NSS 0.9% w/v NaCl in water
o Ringers Solution NaCl, KCl and CaCl2 in waterIsotonic
Solution of Three Chlorides
o Lactated Ringers NaCl, KCl, CaCl2, sodium lactate
Hartmanns Solution
o Oral rehydration saltsNaCl, glucose, KCl, sodium citrate
Tonicity-adjusting agent
Condiment
Preservative
SODIUM CITRATE, Na3C6H5O7
In vitro: anticoagulant, forming complex with Ca++ necessary for
blood clotting
In vivo:
o Systemic and urinary alkalizer
o Expectorant
o In vivo (parenteral): blood coagulant
o Excessive oral administration of citrate salts can have a
laxative effect
Best expectorant: water vapor
SODIUM FLUORIDE, NaF
Anticariogenic agent (1.1%) in dentifrices
Excess of fluoride ion causes dental fluorosis (mottling of teeth)
NaMFP (Sodium Monofluoride Phosphate) also used in
dentifrices
Fluoride ion is toxic and should not be ingested in large amounts
o Precautions for use in children
Nonpharmaceutical use:
Rodenticide and insecticide
Hydrofluoric Acid is used in glass etching and causes slow-healing
burns (antidote: calcium gluconate)
SODIUM FORMALDEHYDE SULFOXYLATE
Best antidote for mercuric chloride poisoning
SODIUM GLUCONATE, NaC6H11O7
Electrolyte replenisher
Gluconate salts:
o less irritating
o water soluble
o Acceptors of hydrogen ions produced by metabolic processes
and act as indirect source of bicarbonate ions
SODIUM HYDROXIDE, NaOH
Caustic soda, lye, sosa, soda lye
Very deliquescent readily absorb water from the environment and
readily dissolve in the water that was absorbed
Saponifying agent Manufacture of soaps
o Soft Soap vs. Hard Soap
Corrosive
Readily attack glass
Too alkaline to be of medicinal valuerapidly destroys tissue
(caustic)
Pharmaceutical use:
o alkalinizing agent to form soluble sodium salts of various drugs
o Pharmaceutical necessity in preparation of Glycerin
Suppositories
Ingestion of solutions of sodium hydroxide causes liquefaction
necrosis/ saponification necrosis
(vs. strong acids coagulative necrosis)
SODA LIME, NaOH. Ca(OH)2
Calx sodica
Mixture of calcium hydroxide and sodium or potassium hydroxide or
both
Good carbon dioxide absorber for anesthesia machines, oxygen
therapy, and metabolic tests
SODIUM HYPOPHOSPHITE, NaHPO2
Reducing agent
SODIUM HYPOCHLORITE, NaOCl
Household bleach, Chlorox 4-6% w/w NaOCl in water
Bleaching agent
Disinfectant (oxidizing property)
Dakins Solution disinfectant
Labarraques Solution (~2.5%) disinfectant
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
Modified Dakins Solution(450-500 mg NaOCl per 100 mL
solution) antiseptic
SODIUM IODIDE, NaI
Iodide is an essential ion necessary for synthesis of triiodothyronine
and thyroxine
Source of iodine
o Lack of iodine simple or colloid goiter Iodides: expectorant
action (oral administration)
expectorant
Pharmaceutical use Solubilizer of iodine in iodine-containing
preparations such as Iodine Tincture and Iodine Solution
Protect from moisture and light
SODIUM METABISULFITE, Na2S2O5
Water-soluble antioxidantGood reducing agent
A combination of sodium bisulfite and sodium metabisulfite in
varying proportions
It is the bisulfite of commerce and for all practical purposes
possesses the same properties as the true bisulfite
Antioxidant for drugs which contain phenol or catechol nucleus (e.g:
phenylephrine HCl, epinephrine HCl solutions) to prevent oxidation
to quinones; also in Vitamin C solutions (usually 0.1%)Solutions
must be acid in pH
Antimicrobial property:
o Fermentation industries
o Preservative and bleach in food
To prepare water-soluble analogs of water-insoluble drugs (e.g.:
menadione sodium bisulfite)
Drawback of sulfites and SO2 Hypersensitivity reactions in
susceptible individuals (angioedema, bronchospasm, anaphylaxis)
SODIUM NITRATE, NaNO3
Chile saltpeter, salitre
Preservative
SODIUM NITRITE, NaNO2
Internally acts as a vasodilator due to relaxation of smooth muscle
(can cause lowering of blood pressure)
Antidote for cyanide poisoning
Used for curing meats and fish
o Color development
o Flavor production (with sodium chloride)
o Preservation against bacteria
However: carcinogenic
SODIUM NITROPRUSSIDE, Na2[Fe(CN)5NO] . 2H2O
Hypotensive agent
SODIUM PERBORATE, NaBO3
Mild disinfectant and deodorant
Readily releases oxygen in contact with oxidizable matter
SODIUM POLYMETAPHOSPHATE
Calgon, Grahams salt
Water-softener
detergent
SODIUM POLYSTYRENE SULFONATE
Brand name: Kayexalate
Cation-exchange resin for treatment of hyperkalemia resulting from
kidney failure
SODIUM POTASSIUM TARTRATE, NaKC4H4O6 . H2O
Rochelle Salt, Sal Seginette
Saline laxative poorly absorbed in the intestine
Sequestering Agent in Fehlings Solution
Acidity Regulator in food
SODIUM SACCHARIN
Artificial sweetener
SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE
Brand name: Explotab
Tablet disintegrant
SODIUM SULFATE, Na2SO4 . 10H2O
Glaubers salt
Saline laxative Sulfate ion poorly absorbed in GIT
SODIUM TARTRATE, Na2C4H4O6
Primary standard for Karl Fischer Reagent used for Water Content
Determination
Laxative
Diuretic
NOT converted to bicarbonate inside the body
SODIUM THIOCYANATE, NaSCN
Hypotensive agent
Also used in cleaners for contact lenses and as antioxidant
synergist in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations
SODIUM THIOSULFATE, NaS3O3
Hypochlor, Photographers hypo, hypo
Sodium hyposulfite (misnomer)
Antidote for cyanide poisoning, in conjunction with sodium nitrite
Used as volumetric solution in titration
Acids decompose thiosulfate to sulfur
Bases decompose thiosulfate to sulfate
Prone to bacterial decomposition
Removal of chlorine from aqueous solutions
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
MONOSODIUM GLUTAMATE (MSG)
Brand: Ajinomoto
Flavor enhancer
o Imparts a meat flavor to foods (flavor enhancer)
o Sharpens weaker flavors already present in food without
adding any significant taste of their own
Causes Chinese Restaurant Syndrome some individuals
sensitive to glutamate: light-headedness, headache, uncomfortable
sense of warmth, difficulty in breathing
POTASSIUM, K
Kalium
Principal intracellular cation
Deficiency state Hypokalemia
o Due to severe burns, diarrhea, or other causes
o Signs and symptoms: muscle weakness and muscle paralysis
Pharmacologic action:
o Diuretic
o Involved in muscle contraction
DIBASIC POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE, K2HPO4
Potassium Phosphate
Treatment of hypercalcemia
o Favors deposition of calcium and phosphate in the bone
o A portion is converted to pyrophosphate, a chelator of calcium,
the complex excreted in the urine
o High plasma phosphate levels decrease calcitriol levels and
decrease absorption of calcium
Used in conjunction with monobasic salt for potassium or phosphate
deficiency
Reagent for various buffers and parenteral fluids
No longer used as laxative
MONOBASIC POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE, KH2PO4
Sorensens Potassium Phosphate
For treatment of hypercalcemia Used in conjunction with the
dibasic salt
Urinary acidifier
o For treatment of calcific kidney stones (nephrolithiasis)
decrease in free calcium excretion in the urine decreases
stone formation and acidification of urine and free
pyrophosphate ion favor dissolution of stones
o Can cause diarrhea
POTASSIUM ACETATE, KCH3COO
Urinary and systemic alkalizer
Diuretic
Antacid
POTASSIUM ALUM, AlK(SO4)2 .12H2O
Tawas
Astringent
Styptic
Antiperspirant
Deodorant
POTASSIUM BICARBONATE, KHCO3
Systemic antacid
Diuretic
Electrolyte replenisher
May cause hyperkalemia on prolonged use
Carbonating agent for Magnesium Citrate Oral Solution, USP
POTASSIUM BITARTRATE, KHC4H4O6
Cream of tartar, argol, acid potassium tartrate
Occurs in acidulous fruits = grapes
Saline laxative
Ingredient on baking powder to raise dough
POTASSIUM BROMIDE, KBr
Depressant
Sedative
Used for preparation of samples for IR analysis (pellets)
POTASSIUM CARBONATE, K2CO3
Potash, Pearl ash, Salt of tartar, Salt of wormwood
Pharmaceutical necessity (basic property)
Carbonating agent
POTASSIUM CHLORATE, KClO3
Deodorant action due to oxidizing capability
POTASSIUM CHLORIDE, KCl
Potassium salt of choice for potassium replenishment
Electrolyte replenisher
Component of Ringers Injection
As IV injection, administered as drip, not push Muscles and heart
contracts
Used in lethal injection
Component of Ringers and Darrows Solution (composition: KCl,
NaCl and sodium lactate)
High local concentrations in the GIT can lead to ulceration
POTASSIUM CITRATE, K3C6H5O7
Systemic alkalizer
Osmotic diuretic
POTASSIUM GLUCONATE, KC6H11O7
Electrolyte replenisher for hypokalemic states
Less irritating compared to potassium chloride
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE, KOH
Caustic potash, lye potash
Strong base; very corrosive
Saponifying agent
Used for manufacture of soft soap
POTASSIUM IODIDE, KI
Iodide salt of choice
Expectorant
Solubilizer for iodine
Prolonged use could lead to hypothyroidism
Excessive amounts could lead to Iodism
o a condition produced by excessive amounts of iodine in the
body
o characterized by increased lacrimation and salivation, rhinitis,
weakness, and skin eruption
Used for prevention of goiter
o Iodine, in the form of iodide, is a necessary nutrient for the
synthesis of thyroid hormones
For treatment of hyperthyroidism
To prepare for thyroid surgery (with anti-thyroid medications)
o As saturated solution
To protect the thyroid in cases of radiation emergency
o Tablets, oral solution
Drug of choice for cutaneous lymphatic sporotrichosis (SSKI 1g/mL)
Used for prevention of goiter
Iodine, in the form of iodide, is a necessary nutrient for the
synthesis of thyroid hormones
For treatment of hyperthyroidism
To prepare for thyroid surgery (with antithyroid medications)
As saturated solution
To protect the thyroid in cases of radiation emergency
Tablets, oral solution
Drug of choice for cutaneous lymphatic sporotrichosis (SSKI 1g/mL)
POTASSIUM METABISULFITE, K2S2O5
Antioxidant
Can trigger allergic reactions in hypersensitive individuals
POTASSIUM NITRATE, KNO3
Saltpeter, salitre, salt prunelle
Used as a meat preservative
Tooth-desensitizing agent
POTASSIUM PERCHLORATE,KClO4
Strong oxidizing agent
Anti-thyroid agent (for the treatment of hyperthyroidism)
As blocking agent for I-131
POTASSIUM PERMANGANATE, KMnO4
Mineral chameleon
Dark purple or almost black crystals or granular powder, almost
opaque by transmitted light and with a blue metallic luster by
reflected light
Strong oxidizing agent
Local anti-infective, antiseptic, deodorant
Used as volumetric solution in titrimetry
POTASSIUM SORBATE, KC6H7O2
Pharmaceutical aid preservative (0.2%)
Antimicrobial control growth of yeasts and mold in enteral
formula, foods, and cosmetic preparations
Relatively ineffective above pH 6.5
POTASSIUM THIOCYANATE, KSCN
Hypotensive agent
SULFURATED POTASH, K2Sx. . K2S2O3
Liver of sulfur, hepar sulfuris, potassa sulfurata
o Irregular, liver brown pieces rapidly changing to greenishyellow on exposure to air
o Possess odor of hydrogen sulfide
Used in preparation of White Lotion
Reacts with zinc sulfate to precipitate zinc sulfide
o Source of sulfide ion in preparation of White Lotion, USP used
in dermatological practice as:
Astringent, protective, mild antimicrobial and antifungal
Treatment of parasitic diseases of the skin
AMMONIA AND AMMONIUM COMPOUNDS
Ammonium ion is a hypothetical alkali metal
Pseudo-alkali metal ion
Generally, ammonium compounds are very water soluble
BUT: ammonium hydroxide is a weak base as compared to alkali
hydroxides which are strong bases
Pharmacologic action:
o Osmotic diuretic
o Buffer component
o Expectorant
AMMONIA, NH3
Synthesized via Haber Process
Involves combination of hydrogen and nitrogen gas at high
pressures to produce ammonia
Used in pharmacy in dilute form as respiratory stimulant
Household ammonia: 10% NH3 and is known as 16o ammonia
(degrees Baum)
STRONG AMMONIA SOLUTION
Stronger ammonia water, stronger ammonium hydroxide solution,
spirit of Hartshorn
Prepared by Haber process: N2 + 3H2 2NH3 + heat
o Contains 27% to 31% w/w of NH3
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
o
o
o
o
o
Very pungent and characteristic odor
Strongly alkaline to litmus even when diluted
On exposure to air it loses ammonia rapidly
Solution is caustic and vapors irritating (avoid inhalation)
Cool container well before opening, cover the closure with
cloth while opening
AMMONIA WATER
Dilute Ammonia Solution
o Contains 9.5-10.5% w/w of NH3
o Used as reflex respiratory stimulant
o To neutralize insect stings and jellyfish stings of Portuguese
man-of-war
AROMATIC AMMONIA SPIRIT
Respiratory stimulant
Components: Ammonium Carbonate, NF and Strong Ammonia
Solution, NF
Components: Ammonium Carbonate, NF and Strong Ammonia
Solution, NF, volatile oils (nutmeg and lemon) and ethanol
AMMONIATED MERCURY, HgNH2Cl
White precipitate
Topical anti-infective
AMMONIUM ACETATE, Al(CH3COO3)3
Spirit of Mindererus
Buffer Component
AMMONIUM ALUM, Al(NH4)(SO4)212H2O
Depressant
Tawas
Astringent
Styptic
Antiperspirant
Deodorant
AMMONIUM BROMIDE, NH4Br
Depressant
Sedative
AMMONIUM CARBONATE, (NH4)2 CO3
Ammonia crystal, sal volatile, ammonium sesquicarbonate,
Prestons salt, Hartshorn, bakers ammonia
Composed of ammonium bicarbonate and ammonium carbamate
(NH2COONH4)
Readily converted to ammonium carbonate in the presence of
ammonia
Expectorant
Respiratory stimulant decomposes to NH3 and CO2
Source of ammonia for smelling salts
Used in the preparation of Aromatic Ammonia Spirit
o
o
Spirit of sal volatile, Spirit of Hartshorn
Used as a respiratory stimulant in cases of hysterical syncope
AMMONIUM CHLORIDE, NH4Cl
Muriate of Hartshorn, sal ammoniac
Diuretic
Expectorant
Systemic acidifier
Urinary acidifier
AMMONIUM FERRIC CITRATE
hematinic
AMMONIUM IODIDE, NH4I
expectorant
AMMONIUM PHOSPHATE, (NH4)2HPO4
Formerly used as diuretic
Used as buffering agent in pharmaceutical preparations
GROUP IB (11): COINAGE METALS
Copper
Silver
Gold
COPPER AND COPPER COMPOUNDS
COPPER, Cu
Cuprum
Only reddish colored metal
Third most malleable metal
Excellent conductor of heat (surpassed only by silver and gold) and
electricity (surpassed by silver)
Forms two series of salts
o Cuprous ion (Cu+1)
Readily undergo disproportionation
Water insoluble
All are white except Cu2S and Cu2O
o Cupric ion (Cu+2)
Generally blue in solution
Important alloys
o Bronze Cu and Sn
o Brass Cu and Zn
Present on hemocyanin and cytochrome oxidase
Respiratory proteins chromoproteins
Color is due to copper
Pharmacologic action:
o Protein precipitant (heavy metal)
o Enhances utilization of iron
Toxicity: Wilsons Disease
o Accumulation of too much copper in the body
o Antidote: Penicillamine (Cuprimine)
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
COPPER ACETO-ARSENATE
Paris green
Insecticide
CUPRIC SULFATE, CuSO4 . 5H2O
Blue vitriol, blue stone, Roman vitriol, Salzburg vitriol
Component of Benedicts solution, Fehlings solution and Barfoeds
solutionTest for reducing substances
Bordeaux MixtureCupric sulfate and lime (CaO)
o Algaecide and fungicide in swimming pools
Enhance utilization of iron
Antidote for phosphorus poisoning
SILVER AND SILVER COMPOUNDS
SILVER, Ag
Argentum
Very soft, ductile and malleable metal
Fine silver 99.9% pure too soft
Usually alloyed to give strength while preserving ductility and
beauty of the metal
o Sterling Silver (92.5% Ag, 7.5% Cu, usually)
Pharmacologic action:
o Protein precipitant (heavy metal)
o Oligodynamic action
Toxicity : Argyria
o Darkening of skin due to chronic use of silver preparations
o Antidote: NSS
SILVER IODIDE, AgI
germicide
SILVER NITRATE, AgNO3
Lunar caustic
Water soluble salt of silver
Lapiz infernularis (caustic pencil)
Component of indelible ink
Used for treatment of warts
1% ophthalmic solution: prophylaxis for gonorrhea ophthalmia
neonatorum (can cause blindness to the newborn)
Tollens Reagent (ammoniacal silver nitrate)
o Silver mirror test (presence of reducing substances, such as
aldehydes)
SILVER PROTEINATES
Silver Proteinate
Mild Silver Protein (Argyrol)
Strong Silver Protein (Protargol)
Colloidal Silver Protein(Collargol)
Medicinal Use
Antiseptic for eyes
Antiseptic for ears and
throat
% Ag
19-23
7.5-8.5
General germicide
18-22
GOLD AND GOLD COMPOUNDS
GOLD, Au
Aurum
King of all metals
Most malleable metal
Best conductor of electricity
Precious metal expensive
Very soft and ductile
Can only be dissolved by:
o Aqua Regia (3 parts HCl: 1 part HNO3)
o Selenic Acid
Purple of CassiusColloidal gold with stannic hydroxide
Toxicity: Gold dermatitis
o Antidote: BAL/ Dimercaprol
GOLD COMPOUNDS
Used for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Aurothioglucose
Gold Sodium Thiomalate
Auranofin p.o.
GROUP IIA (2): ALKALINE EARTH METALS
2 valence electrons
Form divalent ions
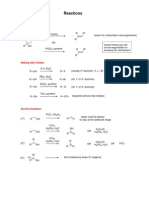
Selected General Reactions of Group 2A Elements:
Equations
Reaction
M + 2H2O M(OH)2 + H2
Be probably reacts with
steam
Mg reacts with hot water
Ca, Sr and Ba reacts rapidly
with cold water
M + 2HCl MCl2 + H2
All metals react with acids,
liberating H2
Be + 4NaOH
Na2[Be(OH)4] + 2Na+
Be is amphoteric
Only Be reacts with NaOH
2M + O2 2MO
Ba + O2 (excess) BaO2
M + H2 MH2
3M + N2 M3N2
Normal oxide formed by all
group members
Tendency and stability in
forming peroxides increases
with increasing atomic
number
Ba forms peroxides
All metals from hydrides
All form nitrides at high
temperatures
BERYLLIUM, Be
Not used pharmaceutically
Most toxic metal
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
MAGNESIUM AND MAGNESIUM COMPOUNDS
MAGNESIUM, Mg
Lightest of all structurally important metals
Natural sources:
o Silicate talc, asbestos
o Carbonate magnesite, dolomite
o Sulfate kieserite
Mg2+:
o 2nd most abundant intracellular cation
o Found in chlorophyll
o Grignard Reagent (RMgX) used for synthesis of alcohols
o Pharmacologic action:
Cathartic
Depressant action
Natural calcium-channel blocker
MAGNESIUM CARBONATE, MgCO3
Magnesia
2 forms: light and heavy
Antacid
Laxative
MAGNESIUM TRISILICATE, 2MgO . 3SiO2 . H2O
Antacid
Advantages:
o Can protect ulcers by forming a protective coating on the
stomach
o Gelatinous consistency provides prolonged antacid effect
CALCIUM AND CALCIUM COMPOUNDS
CALCIUM, Ca
Calcium ion is the second most abundant extracellular cation
Sources:
o Dolomite MgCO3CaCO3
o Fluorite CaF
o Gypsum CaSO4
o Phosphate Rock Ca3(PO4)2
o Apatite CaF and Ca3(PO4)2
MAGNESIUM CITRATE, Mg3(C6H5O7)2
Lemonada purgante, purgative lemon
Saline cathartic
MAGNESIUM HYDROXIDE, Mg(OH)2
Milk of Magnesia, Magnesia Magma
Antacid
Side effect: can cause diarrhea
MAGNESIUM OXIDE, MgO
Calcined Magnesia
Antacid
Laxative
Component of Universal Antidote MgO, activated charcoal, tannic
acid
Not effective for cyanide and kerosene poisoning
MAGNESIUM SULFATE, MgSO4
Epsom salt
Oral administration: cathartic
Intramuscular administration: anticonvulsant
HYDRATED MAGNESIUM TRISILICATE (TALC), 3MgO.4SiO2.H2O
Soapstone, French chalk
Softest mineral
Dusting powder
Clarifying agent
Filtering aid
Adsorbent
Pharmacologic action:
o Blood coagulation factor
o needed for the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin
o Release of neurotransmitters (norepinephrine)
o Muscle contraction
o Structural material of bones and teeth
Vitamin D is required for maximum absorption of Calcium
Vitamin C = Fe absorption
Vitamin E = Se absorption
Calcium deficiency:
o Osteomalacia (adults)
o Rickets (children)
o Osteoporosis
CALCIUM BROMIDE, CaBr2
Sedative/depressant
CALCIUM CARBIDE, CaC2
Kalburo
CALCIUM CARBONATE, CaCO3
Two important forms:
o Precipitated Calcium Carbonate
Commercially produced by chemical means
o Prepared Calcium Carbonate
Native, calcium carbonate purified by elutriation
2 crystal forms:
o Aragonite
o Calcite natural birefringent crystal
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
Iceland Sparvery pure form of calcite
Polarimeters
Optical birefringence
Antacid
Can cause rebound hyperacidity
CALCIUM CHLORIDE, CaCl2
Muriate of lime
Electrolyte replenisher in hypocalcemic states
Component of Ringers solution
CALCIUM GLUCONATE, C12H22CaO14
Most commonly used calcium salt as electrolyte replenisher
Less irritating than Calcium Chloride
CALCIUM HYDROXIDE, Ca(OH)2
Slaked lime, milk of lime, calcium hydrate
Saponifying agent
CALCIUM HYPOCHLORITE, Ca(OCl)2
Bleaching agent
Disinfectant
CALCIUM OXIDE, CaO
Lime, Quicklime, Calx, Apog, Burnt Lime, Calx Usta
Component of Bordeaux mixture insecticide
CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, Ca3(PO4)2
Bone ash
Antacid
Major component of bone
Product of cremation
(CaSO4)2.H2O
CALCIUM SULFATE,
Plaster of Paris
Used in surgical cast
CaSO4 2H2O
Gypsum, terra alba
Dentifrice
or
CaSO4 .1/2H2O
STRONTIUM AND STRONTIUM COMPOUNDS
STRONTIUM, Sr
Imparts crimson red to a nonluminous flame
STRONTIUM CHLORIDE, SrCl2
Tooth desensitizing agent
Active ingredient in Sensodyne toothpaste
BARIUM AND BARIUM COMPOUNDS
BARIUM, Ba
heavy
Toxicity: Baritosis
o
o
o
o
10
inhalation
ingestion of water-soluble barium compounds:
Muscle stimulating action
Antidote: Magnesium Sulfate
BARIUM HYDROXIDE, Ba(OH)2.8H2O
Component of Barium Hydroxide Lime
Similar to soda lime
CO2 absorber
A saturated solution of barium hydroxide in water is known as
baryta water
BARIUM SULFATE, BaSO4
Radiopaque for imaging of GIT
Can cause constipation
RADIUM
RADIUM,Ra
Discovered by Marie Curie
Radioactive
Old unit for radioactivity: Curie
SI unit: Becquerel
Diagnostic purposes
Treatment of certain types of cancers
GROUP IIB (12):VOLATILE METALS/VOLATILE ELEMENTS
Zinc Family
Metals have relatively low melting points
Zinc
Cadmium
Mercury
ZINC AND ZINC COMPOUNDS
ZINC, Zn
Present in insulin
Container for batteries and dry cells
Protective coating in galvanized iron
Pharmacologic properties:
o Astringent
o Antiseptic
o Antiperspirant
o Deodorant
o similar to Aluminum
Deficiency state: Parakeratosis
o Skin appears to be scaly, thickened and inflamed
Important in immune system
Deficiency state leads to impaired immunity
Antidote for Zn2+ poisoning: Sodium Bicarbonate
ZINC CHLORIDE, ZnCl2
Butter of Zinc
Burnetts Disinfecting Fluid
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
Antiseptic found in mouthwashes
Dentin desensitizer
ZINC OXIDE, ZnO
Zinc White
Component of Lassars Paste
mild antiseptic
Astringent
Topical protectant
Toxicity: Metal Fume Fever
o occupational disease from inhalation of ZnO fumes
ZnO heated with CoO Rinmans Green (CoZnO2)
Thenards Blue Cobalt metaaluminate
ZINC PEROXIDE, ZnO2
Antiseptic
Properties similar to that of hydrogen peroxide
Release of nascent oxygen provides powerful oxidizing action
HYDRATED ZINC SILICATE
Natural calamine
prepared calamine ZnO with traces of ferric oxide as impurity
ZINC SULFATE, ZnSO4
White vitriol
Used as ophthalmic astringent
o 0.25% aqueous solution is the only FDA-approved OTC
ophthalmic astringent
Used in preparation of White Lotion
o Sulfurated potash and zinc sulfate
o Active ingredient in White Lotion: ZnS
o Scabicide, topical anti-infective
ZINC-EUGENOL CEMENT
Dental protective
Source of eugenol: clove oil
CADMIUM AND CADMIUM COMPOUNDS
CADMIUM, Cd
Pharmacologic action of water-soluble compounds Astringent
Heavy metal
Very poisonous
Toxicity: Itai-itai disease (Japan)
Source of cadmium: cigarette smoking
Antidote: BAL/ Dimercaprol
Cadmium has high affinity for metallothioneins (stress proteins)
CADMIUM CHLORIDE, CdCl2
Emetic
Used for tinea infections
11
CADMIUM SULFIDE, CdS
Only yellow sulfide
Antiseborrheic agent (for dandruff)
Capsebon
CADMIUM SULFATE, CdSO4
Ophthalmic antiseptic
MERCURY AND MERCURY COIMPOUNDS
MERCURY, Hg
Hydrargyrum, quicksilver, asoge
Forms two series of salts:
o Mercurous, Hg22+ More difficult to absorb
o Relatively less toxic compared to Hg+2
o Mercuric (Hg2+)
SourceCinnabar (Aethrops mineral), - HgS
Encountered in thermometers, amalgams
Toxicity : Minamata Disease
Signs and symptoms
o Metallic taste, thirst, soreness of throat, salivation, sore gums,
bloody diarrhea, severe gastric pain, vomiting (ingestion of
inorganic Hg salts)
o Acute poisoningHg+2: severe vomiting, damage to
intestinal mucosa, diuresis, additional renal damage
o Chronic poisoningBehavioral and personality changes,
decreased visual acuity, tremors, insomnia, ataxia
o Mad hatters disease
Hg compounds were used to convert fur to felt
Tremors, behavioral changes in makers of felt hats
(1900s)
Toxic Forms
o Hg+2 > Hg2+2 > Hgo
o Organic mercury more toxic than inorganic mercury
(methylmercury)
o Organic mercury toxicity:
Brain damage
Numbness
Loss of vision
Deafness
Madness
Death
o Elemental and methylmercury CNS
o Mercury vapor pulmonary irritant
o Methylmercury teratogenic
o Inorganic mercury salts corrosive to skin, eyes, GIT,
nephrotoxic
o Chronic inhalation of Hg vapor
Tremor, neuropsychiatric disturbances
Gingivostomatitis
Erethism
Mood changes
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
Acrodynia (children)Pain in extremities, pinkish
discoloration and desquamation (pink disease),
hypertension, profuse sweating, anorexia, insomnia,
irritability or apathy, rash
Mechanism of Toxicity
o Cumulative poisons
o Once absorbed, Hg+2 concentrates in kidneys
o Combine with SH groups of protein leading to inactivation
(generally for heavy metals)
Antidotes
o Sodium Formaldehyde Sulfoxylate, NF
Best antidote for Hg poisoning, especially Hg2+
Reduces Hg+2 to Hg2+2, less soluble
o Penicillamine (Cuprimine)
For elemental Hg
o Dimercaprol (BAL)
not used for poisoning with metallic and organic mercury
for inorganic Hg salts only
o DMSA (Succimer) water-soluble analog of BAL
Chelating agents
For all types of mercury posioning
May redistribute Hg to brain from other tissue
Pharmacologic action
o Diuretic, useful for cardiac edema
o Antiseptic protein precipitant action
o Antisyphilitic
o Cathartic
o Parasiticide and fungicide
MERCUROUS CHLORIDE, Hg2Cl2
Calomel
Cathartic
Active ingredient in Ly-Na
MERCURIC CHLORIDE, HgCl2
Corrosive sublimate
disinfectant
MERCURIC IODIDE, HgI2
Treatment of syphilis
KI and HgI2 Mayers reagent
o most sensitive alkaloidal reagent
o White precipitate (+ result)
MERCURIC OXIDE, HgO
Yellow precipitate
Ophthalmic anti-infective
GROUP IIIA (13) BORON/ALUMINUM FAMILY
Mg has a diagonal relationship with aluminium
12
BORON AND BORON COMPOUNDS
BORIC ACID, H3BO3
Sal sedativum Hombergi, Boracic acid, orthoboric acid
Toxic by ingestion or dermal absorption
o Boiled lobster appearance of skin
o Reddish-orange color of skin
Eyewash (2%) antiseptic property
Tonicity adjusting agent
Buffer component
o Standard pH buffer pH 8-10: Alkaline Borate Buffer
o Pharmaceutical buffer systems:
Feldmans (pH 7-8.2)
Atkins and Pantin (pH 7.6-11) Borate buffer system
Giffords (pH 6-7.8)
Sorensens (pH 5.9-8) Phosphate buffer system
o Borate buffers are used in ophthalmic and nasal solutions and
external preparations (NOT for parenteral preparations)
o Limitation of phosphate buffers: formation of precipitate with
certain metal ions (Ag, Zn, Al)
SODIUM BORATE, Na2B4O7 .10H2O
Sodium tetraborate decahydrate
Borax
Dobells Solution
o aqueous solution of sodium borate, sodium bicarbonate,
phenol, and glycerol
o used as an astringent or antiseptic wash for the throat and
nose
ALUMINUM AND ALUMINUM COMPOUNDS
ALUMINUM, Al
Most abundant metal
3rd most abundant element
Abrasive
Toxicity (inhalation) Shavers Disease
o Neurotoxin (brain)
o Cause Alzheimers disease in elderly
SourceCryolite 3NaFAlF3
ALUMINUM CHLORIDE, AlCl3 . 6H2O
Astringent
Antiseptic
Antiperspirant
Deodorant
ALUMINUM HYDROXIDE, Al(OH)3
Gastric antacid
Brand names: Amphojel, Cremalin
Side effects:
o Constipation
o Can interfere with absorption of phosphates
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
Maalox
o Combination of Mg(OH)2 and Al(OH)3
o Counteract side effects of one another
ALUMINUM PHOSPHATE, AlPO4
Gastric antacid
Brand name: Phosphagel
Advantage over Al(OH)3Does not interfere with phosphate
absorption
ALUMINUM CARBONATE, Al2(PO4)3
Treatment of phosphatic calculi Promotes elimination of
phosphate via fecal route
ALUM
Tawas
Ammonium Alum and Potassium Alum
Antiperspirant
Astringent
Deodorant
ALUMINUM OXIDE, Al2O3
Alumina
Treatment of silicosis
ALUMINUM SILICATES
Bentonite
o Soapclay, mineral soap
o Native colloidal hydrated aluminum silicate
o Bentonite Magma
5% suspension in water
Suspending agent
Kaolin
o China clay
o Native hydrated aluminum silicate
o Adsorbent Treatment of mild diarrhea
o Demulcent
Pumice
o Complex silicate of aluminum, sodium and potassium
o Volcanic origin
o Dental abrasive
Disadvantage: too abrasive for daily use
GALLIUM
Melts at near body temperature
Substitute for mercury in the manufacture of arc lamps
Treatment of cancer-related hypercalcemia by binding with
transferrin
GROUP IVA (14) CARBON FAMILY
Nonmetallic in character
CARBON AND CARBON COMPOUNDS
CARBON, C
Exclusively nonmetallic
Only element which can form multiple bonds with itself
CATENATION Chain-formation
2 allotropic modifications of Carbon:
o Crystalline
Diamond (tetrahedral)
Graphite (planar
o Amorphous
Coal and anthracite
Activated Charcoal
o Residue from destructive distillation of various organic
materials treated to increase its adsorptive power
o Official in the USP: fine form
o Used as adsorbent (poisoning by ingestion)
Effective for alkaloidal poisons
Ineffective against cyanide and kerosene
o Treatment of diarrhea
CARBON DIOXIDE, CO2
Carbonic acid gas
Most potent respiratory stimulant
Stored in GRAY containers
Used for treatment of persistent hiccups
Toxicity through suffocation
Dry ice solid form
o Used as refrigerant
o For treatment of acne, warts, corns and eczema
CARBON MONOXIDE, CO
Colorless, odorless, tasteless gas
Systemic poison
Mechanism of Action: binds to hemoglobin of blood leading to
hypoxia
CO has higher affinity for hemoglobin compared to oxygen gas
Treatment:
o 100% Oxygeninhalation
o Artificial Air80% He and 20% O2
o CO2-O2 mixture
o Hyperbaric Oxygen
SILICON AND SILICON COMPOUNDS
SILICON, Si
Second most abundant element
13
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
SILICON DIOXIDE, SiO2
Silica
Inert
Very abundant in nature
Glass is made up of silica and other additives
Causative agent of silicosis
o Signs and symptoms similar to TB
o Haemoptysis blood in sputum
o Silica becomes deposited in the lungs --- irritation
o Alumina forms a coat with silica particles (antidote
Glass
Pure silica fused with
Effect
sodium carbonate
With MnO2
With Boron (as borate)
With Potassium
Mask blue green color of iron usually present
in glass
Decrease coefficient of expansion of glass
Render glass brown with light-resistant
property amber-colored glass
With Lead
Increase refractive index of glass
Rare Earths
Selectively absorb light of certain
wavelengths
Purified Siliceous Earth
o Adsorbent
o Filtering aid
o Clarifying agent
Silicates
o Magnesium trisilicate
o Aluminum silicates Bentonite, Pumice, Kaolin
o Attapulgite Diatabs, Polymagma, Quintess
o Mg5(Si8O20)(OH)28H2O
o Adsorbent used for diarrhea
Simethicone
o Polymer of dimethylsiloxane
o Antiflatulent
o Antifoaming agent
TIN AND TIN COMPOUNDS
TIN, Sn
Stannum
Used in production of cans
two series of salts:
o Stannous (Sn+2)
o Stannic (Sn+4)
STANNOUS FLUORIDE, SnF2
Anticariogenic agent\
14
Vs. Sodium Fluoride at least 4 applications\Stannous Fluoride
only one application
BUT: solutions should be freshly prepared
STANNOUS PEROXIDE, SnO
Germicide against Staphylococcal organisms
LEAD AND LEAD COMPOUNDS
LEAD, Pb
Plumbum
Protein precipitant (heavy metal)
Forms two series of salts:
o
Plumbous (Pb+2)
o
Plumbic (Pb+4)
Poisoning: Plumbism/ Saturnism
o Automobile exhaust
o Canned foods
o Old lead pipes
o Paints containing lead
o Diagnosis: foot drop/wrist drop
o Most serious effect Lead encephalopathy
Memory loss
Irritability
Clumsiness
Projectile vomiting
LEAD ACETATE, Pb(CH3COO3)2
Sugar of Lead
Astringent
Used for the preparation of Lead Subacetate Solution
LEADSUBACETATE, Pb(CH3COO3)2
Pb(CH3COO3)2 + PbO
Goulards Extract
Antiseptic
Astringent
GROUP IVB (4) TITANIUM FAMILY
TITANIUM AND TITANIUM COMPOUNDS
TITANIUM, Ti
Titans
o Sons of the Earth
o Chemically: powerful reducing agent
TITANIUM DIOXIDE, TiO2
Solar ray protectant w/ high refractive indexSunblock
White pigment
o High coverage area
o Opacifying agent
o White capsules
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
o
o
Pilocarpine Ocusert System (for glaucoma)
Provides white background for easy visibility
ZIRCONCIUM AND ZIRCONIUM COMPOUNDS
ZIRCONIUM, Zr
Similar to Aluminum
Antiperspirant
Deodorant
Forms:
o Aluminum Zirconium Trichlorohydrate
o Aluminum Zirconium Tetrachlorohydrex Gly
o Aluminum Zirconium Tetrachlorohydrex PG
o Aluminum Zirconium Tetrachlorohydrex PEG
Zirconium salts are are known to cause skin granuloma
Use of antiperspirants/deodorants have been linked to breast
cancer no clear scientific evidence
Use in aerosols prohibited pulmonary granuloma
ZIRCONIUM OXIDE, ZrO
Former official compound
Antiperspirant
Treatment of athletes foot
ZIRCONIUM CARBONATE, ZrCO3
Former official compound
Antiperspirant
Treatment of athletes foot
GROUP VA (15) NITROGEN FAMILY
NITROGEN AND NITROGEN COMPOUNDS
NITROGEN, N2
Exists as a diatomic molecule in ordinary conditions
without life
Synonyms: Azote, Mephitic Air
Provides an inert atmosphere for readily oxidizable pharmaceuticals
Used as a carrier gas in GC
Stored in BLACK containers
Liquid nitrogen:
o Used as a refrigerant
o Cryogenic preservation
NITRATES, NO3-; NITRITES, NO2 Used as preservatives
NO3- NO2- N-nitrosoamines (carcinogenic)
NITROUS OXIDE, N2O
Laughing gas, sweet air
Inhalatory anesthetic
Stored in BLUE containers
15
PHOSPHORUS
PHOSPHORUS, P
Light- carrier
St. Elmos Fire
Essential constituent of protoplasm, nervous tissue and bones
Three main allotropic forms:
o White Phosphorus
Colorless or white solid with waxy appearance
Darkens on exposure to light
Sometimes called Yellow Phosphorus, color due to
impurities
Stored under water handled using forceps
When exposed to air in the dark, it emits a greenish light
and gives off white fumes with garlicky odor
Uses: rat poison
VERY POISONOUS!
o Acute Ingestion: Garlic odor of breath, luminous
vomitus, severe GI irritation, bloody diarrhea, liver
damage general protoplasmic poison
o Chronic Poisoning: bony necrosis, esp. the mandible
(phossy jaw)
o Black Phosphorus
Resembles graphite in texture
Produced from white P under high pressures
Stable in air
Does not catch fire spontaneously
o Red Phosphorus
Appears as red to violet powder
Properties of red P are intermediate between those of
black and white P
Insoluble in organic solvents (vs. White P which is soluble
in certain org. solvents)
Less chemically active compared to White P
Relatively nontoxic unless it contains White P as impurity
Uses: safety matches, pyrotechnics
Phosphates Of physiologic and medicinal importance
ARSENIC AND ARSENIC COMPOUNDS
ARSENIC, As
Lewisite metal
Salvarsan/ Compound 606/ Arsphenamine First anti-syphilis
drug by Paul Ehrlich
Paris Green cupric aceto-arsenite
o Rodenticide, insecticide, pigment, blue colorant for fireworks
o Made by combining cupric sulfate and arsenic trioxide
o Cu(C2H3O2)23Cu(AsO2)2
Scheeles Green cupric hydrogen arsenite
Fowlers Solution 1% potassium arsenite solution (KAsO2)
o Antileukemic (before)
Donovans Solution arsenic (III) iodide solution
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
For trypanosome infections, rheumatism, arthritis, malaria, TB,
diabetes (before)
Acute poisoning:
o Digestive problems vomiting, abdominal pains, diarrhea
accompanied by bleeding
o Mees lines characteristic white lines on nails
o Hair loss
Chronic poisoning: Arsenicosis
o Smelters, patients treated with arsenicals, drinking water with
high levels of arsenic
o cancer
Antidote: BAL (Dimercaprol)
General protoplasmic poison
o Arsenious ion (As+3):
High affinity for SH compounds
Trivalent arsenic more toxic than pentavalent arsenic
o Toxic to all types of cells
Napoleon BonaparteArsenic detected on hair strand
o
ARSENIC TRIOXIDE, As2O3
Synonyms: arsenious oxide, white arsenic, arsenic (III) oxide,
arsenicum album
Amphoteric oxide
Used as a wood preservative
Primary standard in titrimetric analysis
Trisenox used as treatment for leukemia that is not responsive to
first line agents Induces cancer cells to undergo apoptosis
ANTIMONY AND ANTIMONY COMPOUNDS
ANTIMONY, Sb
Stibium
Antimony glance
o Most important source of antimony
o Sb2S3
o Red-orange in color
Pharmacologic action of water-soluble compounds:
o Astringent
o Emetic
o Expectorant
o Anthelmintic
Kills and expels intestinal worms
Vs. vermifuge only expels worms
ANTIMONY POTASSIUM TARTRATE, C8H4K2O12Sb2.3H2O
Tartar emetic
Brown mixture
o Emetic
o Expectorant
o For treatment of schistosomiasis (liver fluke)
Schistosoma japonicum requires 2 hosts: snails and humans
16
BISMUTH AND BISMUTH COMPOUNDS
BISMUTH, Bi
beautiful meadow
Astringent
Antiseptic
Protectant
Bismuth compounds are poisonous
Cause black stools --- combination with sulfide ion
Antidote: Dimercaprol
BISMUTH SUBNITRATE, Bi(OH)2NO3
Used as antacid, with astringent and antiseptic properties
BISMUTH HYDROXIDE, Bi(OH)3
Milk of Bismuth bismuth hydroxide and bismuth subcarbonate in
suspension in water
o Prepared from Bismuth subnitrate, nitric acid, ammonium
carbonate, strong ammonia solution, and purified water
o Internal protective for gastric ulcers
o Bismuth salts inhibit growth of H. pylori
BISMUTH CITRATE
Colloidal bismuth subcitrate used in tx of PUD
BISMUTH SUBCARBONATE
BISMUTH SUBGALLATE
BISMUTH SUBSALICYLATE (PINK BISMUTH)
Active ingredient in Pepto-Bismol and Kaopectate
Anti-inflammatory, bactericidal, antacid
Bismuth Subsalicylate Magma
VANADIUM
Insulin-mimetic effect (vanadate, vanadyl ion, coordination
compounds)
Drawback: toxicity of the metal
GROUP VB (5)
TANTALUM
Unaffected by body fluids inert
Sheet form surgical repair of bones
GROUP VIA (16): CHALCOGENS (OXYGEN FAMILY)
OXYGEN AND OXYGEN COMPOUNDS
OXYGEN, O2
Dephlogisticated air, Empyreal air, Yne
Exists as a diatomic molecule under ordinary conditions
Consists of 1/5 of air, by weight (in free form)
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
Consists of 7/8, by weight, of water and in minerals (in combined
state)
Obtained industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air
Three allotropes:
o Nascent[O]
o Atmospheric/ molecularO2
o OzoneO3
Employed as a therapeutic gas in the treatment of conditions
involving hypoxia
Stored in GREEN containers
Very active chemically
o Combines directly with elements except Hg, Ag, Au and
members of the Pt family
o Second most electronegative element (vs. fluorine)
o Oxides (-2 oxidation state)
Metallic
Nonmetallic
Amphoteric
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE, H2O2
Oxidation state of oxygen is -1
Good oxidizing and reducing agent
Pure solutions are stable
Commercial solutions are stabilized by acetanilide and addition of
acid (e.g., H3PO4)
Commonly available in 3% and 6% solution
Reagent: 30% solution
30% Solution
o Hydrogen Peroxide Concentrate, USP
o Disinfectant, powerful oxidant
3% Solution (10-volume solution)
o Hydrogen Peroxide Topical Solution, USP
o Antiseptic (oxidizing germicide)
6% Solution (20-volume solution)
o Hair bleach
Hydrogen Peroxide in anhydrous glycerin (1.5%)
Urea Peroxide in anhydrous glycerin (4-10%)
Carbamide Peroxide Topical Solution
o More preferred for treatment of oral and ear infections
ZINC PEROXIDE AND SODIUM PERBORATE
Former official compounds
OZONE, O3
Powerful oxidizing agent Disinfectant, bleach (industrial)
SULFUR AND SULFUR COMPOUNDS
SULFUR, S
Brimstone, Shulbari (Sanskrit: enemy of copper), Asupre
Several allotropes
o At room temp.: -Sulfur (rhombic sulfur) is stable
17
At equilibrium point (96oC): -Sulfur (monoclinic sulfur)
becomes the stable form
Occurs in free state and in combination, mainly as sulfides and
sulfates
Constitutes 0.05% of the crust of the Earth
Pharmaceutical Sulfur
PRECIPITATED
SUBLIMED SULFUR WASHED SULFUR
SULFUR
o
Milk of Sulfur; Lac
sulfur
Flowers of Sulfur
Made by boiling Sulfur
with Lime and
precipitating the
filtered solution with
HCl
Very fine, pale
yellow, amorphous or
microcrystalline
powder, odorless and
tasteless
Readily dissolves in
carbon disulfide
Used in ointments
and lotions
Fine, yellow,
crystalline powder,
with faint odor and
taste
Slowly and usually
incompletely
soluble in carbon
disulfide
Used as cathartic
Made by treating
Sublimed Sulfur with
Ammonia to dissolve
impurities, particularly
arsenic and to remove
traces of acid
Fine, yellow crystalline
powder, with faint odor
and taste
Slowly and usually
incompletely soluble
in carbon disulfide
Used as scabicide --- fungicidal action
Keratolytic effect
Stimulant cathartic
Stimulates hair growth
Depilatory as thioglycollate
Fumigant SO2
Antiseborrheic agent as SeS2
Pharmaceutically relevant chemical forms:
o Sulfide (-2 oxidation state) Hydrogen sulfide and soluble
sulfides react readily with finely divided sulfur to produce
polysulfides, Sx-2
o Sulfite (+4 oxidation state)
o Sulfate (+6 oxidation state
SULFUR OINTMENT
Prepared from precipitated sulfur, mineral oil and White Ointment
10% Sulfur
SULFURATED LIME
Vleminckxs Solution
SULFURATED POTASH
Liver of Sulfur
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
Consist mainly of polysulfide, thuisulfate and sulfate
Prepared by careful heating of a solution of potassium carbonate
and sublimed sulfur
Used in the form of lotions, ointments, and aqueous solutions for
treatment of psoriasis
Also has antiparasitic activity
WHITE LOTION
Prepared from Sulfurated Potash and Zinc sulfate
o Astringent and protective
SELENIUM SULFIDE, SeS2
SeS2 and SeS2 Lotion (Selsun Blue)
2.5% suspension used for the topical treatment of seborrheic
dermatitis
o Hands should be washed off --- Se is toxic
o Should not come in contact in eyes and mouth
o Cadmium Sulfide, in the past, was also used for this purpose
SULFUR DIOXIDE, SO2
Acid anhydride of sulfurous acid
Oxyacid: sulfurous acid
Used pharmaceutically as antioxidant and preservative
SODIUM METABISULFITE, Na2S2O5
Obtained when sodium bisulfite is crystallized on an atmosphere of
sulfur dioxide
Forms bisulfite upon dissolving in water
Should be used when sodium bisulfite is specified
Antioxidant
SODIUM THIOSULFATE, Na2S2O3
Prepared from sulfur reacing with sulfite ions
Antidote for cyanide poisoning
Analytical reagent for determination of iodine
SODIUM SULFATE, Na2SO4
Saline cathartic
SELENIUM
SELENIUM, Se
Selena moon
Toxic Prolonged contact with skin causes contact dermatitis
Important trace element
Absorbed very slowly on the skin
Promotes absorption of Vitamin E
GROUP VIB (6)
Chromium and Molybdenum Important trace elements
CHROMIUM AND CHROMIUM COMPOUNDS
CHROMIUM, Cr
Glucose Tolerance Factor
Essential trace element
Deficiency symptoms are similar to that of DM
Forms
o Hexavalent Chromium, Cr6+
Toxic
Dichromate strong oxidizing agent
Primary standard Sodium Thiosulfate VS
Chromate precipitant
o Trivalent Chromium , Cr3+
CHROMIC CHLORIDE AND CHROMIC CHLORIDE INJECTION
CHROMIUM PICOLINATE
MOLYBDENUM AND MOLYBDENUM COMPOUNDS
MOLYBDENUM, Mo
Essential trace element
Cofactor for enzymes associated with flavin-dependent enzymes
Cofactor for Xanthine Oxidase
Important for bacterial fixation of atmospheric oxygen
MOLYBDENUM OXIDE, MoO
with ferrous sulfate hematinic
URANIUM, U
Radioactive element
Discovered by Becquerel
Never employed in medicine as such
Used in atomic reactors and atomic bombs
GROUP VIIA (17): HALOGENS
Halogen = Sea-salt producer
FLUORINE AND FLUORINE COMPOUNDS
FLUORINE, F2
Most electronegative element
Strongest oxidizing agent
SODIUM FLUORIDE, NaF
Sodium Fluoride Tablets; Oral Solution
Sodium Fluoride and Phosphoric Acid Gel
Sodium Fluoride and Phosphoric Acid Topical Solution
Also used in the treatment of osteoporosis
Excess fluoride in adults:
o Weakening of bones
o Adverse effects on the kidney
o Low IQ
18
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
Suppressive effect on thyroid, particularly when iodine is
deficient
Excess fluoride in children dental fluorosis
o
19
Bromine TS
Bromine Water1% Bromine in water
STANNOUS FLUORIDE, SnF2
easily air-oxidized
Stannous Fluoride Gel
Bromine VS
Koppeschaars Solution
0.1 N Bromine VS
Components
SODIUM MONOFLUOROPHOSPHATE
Anticariogenic agent added in dentifrices
CHLORINE AND CHLORINE COMPOUNDS
CHLORINE, Cl2
Dephlogisticated muriatic acid
Chlorine is used as a water disinfectant
Cl- principal extracellular cation
IODINE AND IODINE COMPOUNDS
IODINE, I2
Heaviest nonmetallic element
Easily undergoes sublimation, giving off violet vapor
Solid with metallic sheen
Poisonous Antidote: Starch solution
Io Expectorant
o Antiseptic
o Essential trace element necessary for synthesis of T3 and T4
hormones
o T3 triiodothyronine more active
o T4 thyroxine more numerous
o Toxicity: Iodism
o Deficiency state: Simple Goiter
Dangerous for pregnant women cretinism
Prevention: iodized salt
Iodine Preparations
CHLOROFLUOROCARBONS
Dichlorodifluoromethane, CCl2F2
o Freon
o Refrigerant; aerosol propellant
o Implicated in ozone layer depletion
HYDROCHLORIC ACID, HCl
In diluted form treatment for gastric achlorrhydria
present in gastric juice
Pepsinogen is secreted by chief cells, which is activated by HCl
secreted by parietal cells, to pepsin
Diluted Hydrochloric Acid is official --- 10% w/v solution
SODIUM HYPOCHLORITE, NaOCl
Bleaching agent
Disinfectant
Sodium Hypochlorite Solution (Dakins Solution)
o Effective germicide, viricide, and deodorant
o Strong oxidizing agent
Sodium Hypochlorite Topical Solution
o 0.025% NaClO, pH 8 (close to 7.4), buffered with phosphate
o allows tissues to regenerate healing of burns
o Antiviral and antimicrobial
BROMINE AND BROMINE COMPOUNDS
BROMINE, Br2
Dark, reddish brown fuming liquid with suffocating odor
Powerful caustic and germicide
Mainly used as a chemical reagent
Poisoning: Bromism
o Skin eruption
o Headache
o Weakness
o Psychosis
o NaCl and Ammonium Chloride
Br - internally acts as a sedative (depressant)
Three Bromides Elixir
Iodophors
Iodine complexed with an organic complexing agent as solubilizer
Povidone Iodine (Betadine)
Advantages:
o Reduced irritation
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
o
o
o
o
o
Reduced oral tox
Lack of staining potential
Low incidence of idiosyncratic reactions
Slow release of iodine
Stability, virtually 0 vapor pressure of I2
Phenolated iodine solution Boultons solution
ASTATINE, At
The only metallic and radioactive halogen
GROUP VIIB (7)
MANGANESE AND MANGANESE COMPOUNDS
MANGANESE, Mn
Essential trace element
Cofactor involved in protein synthesis, phosphorylation, fatty acid,
and cholesterol synthesis
Toxicity: similar to Parkinsonism
o Muscle tremors
POTASSIUM PERMANGANATE, KMnO4
Mineral chameleon
Strong oxidizing agent
Antiseptic
Drawback: staining of skin
TECHNETIUM, Tc
technetos artificial
First element produced artificially
GROUP VIIIA (18)
HELIUM, He
Second lightest gas
Inhalation of pure helium produces Donald Duck -like sound
Component of Artificial Air
BROWN container
80% He and 20% O2
NEON, Ne
Advertising purposes as Neon lights
ARGON, Ar
Most abundant noble gas
Substitute for nitrogen as inert atmosphere for pharmaceuticals
KRYPTON, Kr
Least abundant noble gas
Inhalational anesthesia, also Xenon
RADON, Rn
Niton
Used for the treatment of certain types of cancers
GROUP VIIIB (8): IRON TRIAD
First Triad: Fe, Co, Ni
Second Triad: Rh, Ru, Pd
Third Triad: Os, Ir, Pt
IRON AND IRON COMPOUNDS
IRON, Fe
Ferrum
Common ores
o Hematite (Fe2O3)
o Pyrite/ Fools Gold (FeS2)
o Iron stone FeCO3
Exists in two oxidation states
o Fe2+ aqueous solutions are green in color
o Fe3+ aqueous solutions are yellow to orange to brown in
color
In the body:
o Hemoglobiniron in blood
o TransferrinTransport form of iron in the body
o Ferritin Storage form of iron in the body
Physiologic role
o Hematinic In +2 oxidation state
For correction of microcytic hypochromic anemia (iron
deficiency anemia)
Toxicity
o Cardiac collapse
o GI distress
o Black stools
FERROUS SULFATE, FeSO4.7H2O
Green vitriol
FERROUS GLUCONATE
Fergon
Produces less gastric irritation compared to Ferrous Sulfate
FERROUS FUMARATE
Toleron
More stable compared to Ferrous Sulfate
FERROUS CARBONATE, FeCO3
Chalybeate Pills
Blauds Pills
Ferruginous Pills
IRON + AMMONIUM ACETATE
Bashams Mixture
o Astringent
o Styptic
20
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
FERRIC CHLORIDE, FeCl3
Astringent
Styptic
Test for presence of tannins
FERRIC SUBSULFATE SOLUTION
Monsels Solution
Basic ferric sulfate solution
Prepared from ferrous sulfate and nitric and sulfuric acids
Used as styptic (hemostatic agent)
FERROUS FERRICYANIDE
Turnbulls Blue
FERRIC FERROCYANIDE
Prussian Blue
COBALT AND COBALT COMPOUNDS
COBALT, Co
Development of erythrocytes and hemoglobin
As Co+2: central metal ion in Vit. B12 (Cyanocobalamin)
Permanent magnets
Used on the manufacture of beers
o Enhances foam quality
COBALTOUS, CoCl2
Lovers Ink
Sympathetic Ink Used as indicator in silica gel beads
pink wet
blue blue
PALLADIUM, Pd
catalyst in organic reactions
OSMIUM, Os
Heaviest and most dense metal
Osmium Tetroxide, Osmic Acid
Staining of specimens for electron microscopy
PLATINUM, Pt
Catalyst in organic reactions
Production of crucibles and wires
Cisplatin prostate cancer
Cis-diamminedichloroplatinum
CHEMICAL ANALYSIS
FLAME TEST
ANION GROUP
NICKEL AND NICKEL COMPOUNDS
NICKEL, Ni
Old Nicks Copper
Found in fossil fuel combustion
Fancy jewelries
Nickel itch --- contact dermatitis
Exists in +2 oxidation state evelopment of erythrocytes and
hemoglobin
NICKEL CARBONATE, NiCO3
Tonic
NICKEL SULFATE, NiSO4
Tonic
Parasiticide
RUTHENIUM, Ru
Ru complexes are investigated for its anticancer properties
CATION GROUP
21
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
SILVER HALIDES
Silver halides are light sensitive >> they easily darken upon
exposure to light
Silver halides have a characteristic curdy appearance
All silver halides are insoluble in dil. Nitric acid solution
AgCl white curdy ppt soluble in diluted ammonia solution
AgBr light yelow curdy ppt partially soluble in diluted ammonia
solution
AgI yellow curdy ppt insoluble in diluted ammonia solution
ACTIVITY SERIES
Useful for predicting displacement reactions
For non-metals: F2>Cl2>Br2>I2
For metals
o Metals located above hydrogen can displace hydrogen gas
from acids
o Metals located above the series are more active and can
displace salts of metals from solutions
o Metals located below the series are easily reduced into their
metallic states
2.
22
With sodium hydroxide TS or sodium sulphide TS aluminum
hydroxide (white gelatinous precipitate soluble in excess of the
reagent)
AMMONIUM
1. Add excess 1N sodium hydroxide and warm ammonia
(pungent odor, vapour turns red litmus to blue)
ANTIMONY
1. Acidify with hydrochloric acid, add hydrogen sulphide
antimony sulphide (orange precipitate, insoluble in 6N
ammonium hydroxide, soluble in ammonium sulphide TS)
2. Neutral pH then add ferric chloride ferric acetate (blood red
solution, destroyed by addition of mineral acids)
BARIUM
1. With 2N sulphuric acid barium sulfate (white precipitate,
insoluble in hydrochloric or nitric acid)
2. Yellowish green color to a nonluminous flame, blue through
green glass
BENZOATE
1. Neutral pH, add ferric chloride TS ferric benzoate (salmoncolored precipitate)
2. In concentrated solutions, add 2N sulphuric acid benzoic
acid (white precipitate, soluble in ethyl ether)
BICARBONATE
1. Add acidsCO2 (effervescence, gives white precipitate upon
addition of calcium hydroxide TS)
2. Add drops of phenolphthalein TS (no color formation)
source: www.sjesci.wikispaces.com
USP OFFICIAL IDENTIFICATION TESTS
BISMUTH
1. Dissolve in light excess nitric or hydrochloric acid then dilute
with water bismuth hydroxide (white precipitate colored
brown by hydrogen sulphide, the resulting compound dissolves
in warm mixture of equal parts of nitric acid and water)
ACETATE
1. Warm with conc sulphuric acid and 95% ethanol ethyl
acetate (plastic balloon, fruity odor)
2. Neutralize solution then add ferric chloride TS ferric acetate
(blood red solution, destroyed by addition of mineral acids)
BORATE
1. Acidify solution with hydrochloric acid, drops of iodine TS,
drops of polyvinyl alcohol solution(1 in 50) (intense blue
color)
2. Add sulphuric acid, add methanol, ignite (green-bordered
flame)
ALUMINUM
1. With 6N ammonium hydroxide aluminum hydroxide (white
gelatinous precipitate insoluble in excess of the reagent)
BROMIDE
1. Add chloroform, then chlorine TS dropwise, shake bromine
(red to reddish brown lower organic layer)
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
2.
With silver nitrate TS silver bromide (yellowish white
precipitate, insoluble in nitric acid, slightly soluble in 6N
ammonium hydroxide)
CALCIUM
1. 2 drops methyl red TS, neutralize with 6N ammonium
hydroxide, add 3N hydrochloric acid until solution is pink, add
ammonium oxalate TS calcium oxalate (white precipitate,
insoluble in 6N acetic acid, soluble in hydrochloric acid)
2. Acidified solution transient yellowish red color to
nonluminous flame
CARBONATE
3. Add acidsCO2 (effervescence, gives white precipitate upon
addition of calcium hydroxide TS)
4. Add drops of phenolphthalein TS (fuschia pink solution)
CHLORATE
1. Add silver nitrateno precipitate
2. Add sulphurous acid white precipitate insoluble in nitric
acid, soluble in 6N ammonium hydroxide
3. ignitionchlorides (forms white precipitate with silver nitrate
TS, insoluble in nitric acid, soluble in ammonium hydroxide)
4. Add sulphuric acid to dry sample decrepitation, greenish
yellowish gas
CHLORIDE
1. To sample solution Add silver nitrate TS silver chloride
(white curdy precipitate, insoluble in nitric acid, soluble in slight
excess of 6N ammonium hydroxide)
2. To dry salts, add equal weight manganese dioxide moisten
with sulphuric acid, gently heat chlorine gas (turns starch
iodide paper to blue)
CITRATE
1. Add a few mg of dry salt to 15 ml pyridine, dissolve or suspend
in 1 ml water, shake then add 5ml acetic anhydride then
shake light red color
COBALT
1. Add 3N hydrochloric acid, heat on steam bath with equal
volume nitroso-2-naphthol in 9N acetic acid red precipitate
2. Sample solution, saturate with potassium chloride, add
potassium nitrite and acetic acid potassium cobaltinitrite
(yellow precipitate)
3.
COPPER
1. Acidify with hydrochloric acid, metallic iron copper metal (red
film on surface of iron)
2. Excess 6N ammonium hydroxide deep blue solution
3.
23
With potassium ferrocyanide TS cupric ferrocyanide (reddish
brown precipitate, insoluble in dilute acids)
HYPOPHOSPHITE
1. strong heating phosphine (flammable gas)
2. with mercuric chloride TS mercurous chloride become
metallic mercury with excess hypophosphite (white precipitate
turns gray)
3. with sulphuric acid and cupric sulphate TS cuprous oxide
(reddish brown precipitate, insoluble in diluted acids)
IRON
1.
Ferrous or ferric solution with ammonium sulphide TS
ferrous or ferric sulphide (black precipitate, soluble in 3N
hydrochloric acid with evolution of hydrogen sulphide)
Ferric Salts
1. Acid solutions with potassium ferrocyanide TS ferric
ferrocyanide (dark blue gelatinous precipitate)
2. With 1N sodium hydroxide ferric hydroxide (reddish brown
gelatinous precipitate)
3. With ammonium thiocyante TS ferric thiocyanate (deep red
colored solution, cannot be destroyed with dilute mineral acids)
Ferrous Salts
1. with potassium ferricyanide TS ferrous ferricyanide (dark
blue gelatinous precipitate, insoluble in 3N hydrochloric acid,
soluble in 1 N sodium hydroxide)
2. With 1N sodium hydroxide ferrous hydroxide (green-white
gelatinous precipitate, turns brown upon shaking)
LACTATE
1. Acidified with sulphuric acid, add potassium permanganate,
heat acetaldehyde (filter paper moistened with 20%
morpholine and sodium nitroferricyanide TS turns blue)
LEAD
1.
2.
With 2 N sulphuric acidlead sulphate (white precipitate,
insoluble in 3N hydrochloric or 2N nitric acid, soluble in 1N
warm sodium hydroxide or ammonium acetate TS)
With potassium chromate TS lead chromate (yellow
precipitate, insoluble in 6N acetic acid but is soluble in 1N
sodium hydroxide)
LITHIUM
1. With sodium carbonate TS and made alkaline with sodium
hydroxide lithium carbonate (white precipitate on boiling,
soluble in ammonium chloride TS)
2. Rendered acidic then nonluminous flame red colored flame
3. 2 N sulphuric acid no precipitation
MAGNESIUM
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
1.
With ammonium chloride, ammonium carbonate, dibasic
sodium phosphate TSmagnesium ammonium phosphate
(white crystalline precipitate, insoluble in 6N ammonium
hydroxide.
MANGANESE
1. With ammonium sulphide TSmanganese sulphide (salmoncolored precipitate, soluble in acetic acid)
MERCURY
1. Salt solutions, metallic copper is added metallic mercury
(deposits with silvery appearance)
2. With hydrogen sulphide mercuric/mercurous sulphide (black
precipitate, insoluble in ammonium sulphide TS and in boiling
with 2N nitric acid.
Mercuric Salts
1. With 1N sodium hydroxide mercuric oxide (yellow
precipitate)
2. With potassium iodide TS potassium mercuric iodide (scarlet
precipitate, soluble in excess reagent)
Mercurous Salts
1. With 1N sodium hydroxide black precipitate
2. With hydrochloric acidmercurous chloride (white precipitate,
blackened by 6N ammonium hydroxide)
3. With potassium iodide TS potassium mercurous iodide
(yellow precipitate, turns green upon standing)
NITRATE
1. With equal volume sulfuric acid, cooled, add ferrous
sulfatebrown color is produced at the junction of 2 liquids
2. When heated with sulphuric acid and metallic copper
brownish-red fumes
3. Cannot decolorize potassium permanganate
NITRITE
1. With dilute mineral acid or with 6N acetic acid brownish-red
fumes
2. With starch-iodide paper turns paper blue
OXALATE
1. Neutral or alkaline solutions with calcium chloride TScalcium
oxalate (white precipitate, insoluble in 6N acetic acid but
dissolved by hydrochloric acid)
2. Hot acidified solution, add permanganate decolorization
PERMANGANATE
1. When acidified with sulphuric acid is decolorized by hydrogen
peroxide TS, sodium bisulfite TS, in the cold, and by oxalic
acid, in hot solution
24
PEROXIDE
1. Slightly acidified with sulphuric acid, add ether, add potassium
dichromate TS deep blue solution that is more soluble in the
ether layer
PHOSPHATE
1. With silver nitratesilver phosphate (yellow precipitate,
soluble in 2N nitric acid and in 6N ammonium hydroxide)
2. Acidified solutions with ammonium molybdateammonium
phosphomolybdate (yellow precipitate soluble in 2N nitric acid
and in 6 N ammonium hydroxide
POTASSIUM
1. Impart violet color in nonluminous flame
2. Neutral or moderately concentrated solutions, with sodium
bitartrate TSwhite crystalline precipitate soluble in 6N
ammonium hydroxide and solutions of alkali hydroxides and
carbonates, hastened by addition of glacial acetic acid or
ethanol)
SALICYLATE
1. With ferric chloride TSferric salicylate (violet solution)
2. Moderately concentrated solutions with addition of
acidssalicylic acid (white crystalline precipitate)
SILVER
1. With hydrochloric acidsilver chloride (white curdy precipitate,
insoluble in nitric acid but soluble in 6 N ammonium hydroxide)
2. With 6N ammonium hydroxide and formaldeyhde silver
mirror upon warming
SODIUM
1. To a 2mL solution, add 2ml 19% potassium carbonate and
heat to boiling, then add potassium pyroantimonate TS then
boil white precipitate
2. Impart persistent yellow color to nonluminous flame
SULFATE
1. With barium chloride TS barium sulphate (white precipitate,
insoluble in hydrochloric and nitric acid)
2. With lead acetate TSlead sulphate(white precipitate soluble
in ammonium acetate TS)
3. With hydrochloric acidno precipitation (distinction from
thiosulfates)
SULFITE
1. With 3N hydrochloric acidsulfur dioxide(blackens filter paper
moistened with mercurous nitrate TS
TARTRATE
INORGANIC PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
1.
Few mg of the sample salt to 2 drops of sodium metaperiodate
solution (1 in 20), 1 drop 1N sulphuric acid, then sulphurous
acid, then few drops fuchsin-sulfurous acid TS reddish pink
color
THIOCYANATE
1. With ferric chloride TS ferric thiocyanate(red colored
solution, not decolorized by concentrated mineral acids)
THIOSULFATE
1. With hydrochloric acid white precipitate that turns yellow and
sulphur dioxide blackens filter paper moistened with mercurous
nitrate TS
ZINC
1.
2.
3.
With sodium acetate and hydrogen sulfidezinc sulphide
(white precipitate, insoluble in acetic acid, but dissolved by 3N
hydrochloric acid)
With ammonium sulfidezinc sulphide (white precipitate,
neutral medium)
With potassium ferrocyanide TS zinc ferrocyanide (white
precipitate, insoluble in 3 N Hydrochloric acid)
25
You might also like
- Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument29 pagesInorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistryRaymond Godfrey Dagwasi40% (5)
- 1 - General Chemistry (MANOR 2017)Document13 pages1 - General Chemistry (MANOR 2017)Michaela Berndt100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Synthesis IedxcelDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Synthesis IedxcelAliya Rahman100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Past Exam KeyDocument102 pagesOrganic Chemistry Past Exam KeyParker McColl86% (7)
- Analytical Chemistry Reviewer (Finals)Document3 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Reviewer (Finals)Jannina Luciano88% (8)
- Inorganic Chemistry (MIT Lecture Notes)Document266 pagesInorganic Chemistry (MIT Lecture Notes)jkmathur100% (9)
- Organic I Reactions (COMPLETE) PDFDocument10 pagesOrganic I Reactions (COMPLETE) PDFcztinu88% (50)
- Analytical ChemistryDocument33 pagesAnalytical ChemistryKuo Sarong100% (1)
- Problems in Organic ChemistryDocument408 pagesProblems in Organic ChemistryGowri Shankar100% (11)
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry of Inorganic MedicalsDocument21 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry of Inorganic MedicalsJuliane Caniele Indiongco0% (2)
- Introduction To Medicinal ChemistryDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Medicinal ChemistryRakesh Kumar100% (3)
- Organic Chemistry All ReactionsDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry All ReactionsWaseem Alkakoz100% (4)
- Organic Chemistry Review: Structural and Functional GroupsDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Review: Structural and Functional GroupsRanie MagpocNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFAzadnikov94% (16)
- Pharmacy Board Exam: Module 3Document1 pagePharmacy Board Exam: Module 3Pia PalaciosNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument15 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compoundsapi-1986055092% (24)
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument8 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notesaovogt75% (4)
- Summary of All Reactions For Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesSummary of All Reactions For Organic Chemistryfoodytang91% (23)
- Biochemistry Answer Key BLUE PACOPDocument26 pagesBiochemistry Answer Key BLUE PACOPRizzel Angeles100% (1)
- Classification Tests For Carboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesDocument9 pagesClassification Tests For Carboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesAngelyka Cabalo100% (1)
- Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesOrganic ChemistryBrian Smith86% (51)
- Phle Reviewer Module 5 PharmaceuticsDocument97 pagesPhle Reviewer Module 5 PharmaceuticsCarlstine Ileto100% (3)
- HKDSE Chemistry Exam Questions on Analytical MethodsDocument27 pagesHKDSE Chemistry Exam Questions on Analytical MethodsFrank Massiah100% (1)
- Manufacturing Pharmacy Lecture HandoutsDocument23 pagesManufacturing Pharmacy Lecture HandoutsKate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Summary ReactionsDocument49 pagesOrganic Chemistry Summary Reactionsjordi1710100% (1)
- Chemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic Chemistryhelixate100% (5)
- CHEM 3369 EXAM #2 PREPDocument5 pagesCHEM 3369 EXAM #2 PREPchrisie007100% (2)
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives ExplainedDocument26 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives ExplainedAyush Gangwani50% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Laboratory Techniques PDFDocument108 pagesOrganic Chemistry Laboratory Techniques PDFNeil AdonaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Organic ReactionsDocument6 pagesSummary of Organic ReactionsAbudi Alsagoff100% (5)
- Analytical ChemistryDocument55 pagesAnalytical ChemistryMarnel Roy Mayor100% (1)
- Cheat Sheet For Organic Chemistry Midterm 1 2015 - 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet For Organic Chemistry Midterm 1 2015 - 1Norma Leticia Ramos33% (3)
- Flow Charts in Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesFlow Charts in Organic ChemistryJessie McCartney85% (27)
- PCI Board Review HandoutsDocument8 pagesPCI Board Review HandoutsChrissy LayugNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument19 pagesModule 1 - Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistryMichaela100% (10)
- Reviewer Organic Chemistry LectureDocument9 pagesReviewer Organic Chemistry LectureAlyanna Elisse Vergara100% (1)
- CM2192 CheAnalytical Chemistry Cheat Analytical Chemistry Cheat Sheet 2Document1 pageCM2192 CheAnalytical Chemistry Cheat Analytical Chemistry Cheat Sheet 2dorothyhuangNo ratings yet
- 400 Important Chemistry Questions and AnswerDocument28 pages400 Important Chemistry Questions and Answerhnin pwint100% (2)
- Physical Pharmacy NotesDocument10 pagesPhysical Pharmacy NotesLorenzo Dominick Cid100% (8)
- Inorganic ChemistryDocument15 pagesInorganic ChemistryBench Gueco100% (1)
- Alkene and Alcohol Reactions OverviewDocument11 pagesAlkene and Alcohol Reactions OverviewPhirun Cheng97% (29)
- BS Pharm 1 Course SyllabusDocument2 pagesBS Pharm 1 Course SyllabusMarecar100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Practical Manual - Compound IdentificationDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Practical Manual - Compound Identificationsp_douglas83% (35)
- Reagent and The Reactions They CauseDocument3 pagesReagent and The Reactions They CauseChip Timmons100% (8)
- Pharmacognosy Answer Key-RED PACOP PDFDocument14 pagesPharmacognosy Answer Key-RED PACOP PDFArk Olfato ParojinogNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Thermochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry Chemistry AP Chapter 23: Nuclear Chemistry 23.1: The Nature of Nuclear ReactionsDocument16 pagesUnit 4: Thermochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry Chemistry AP Chapter 23: Nuclear Chemistry 23.1: The Nature of Nuclear ReactionsPankaj Kumar50% (4)
- General Chemistry Reference Sheet GuideDocument5 pagesGeneral Chemistry Reference Sheet Guidedadadabababa100% (8)
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument142 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryHafiz Hamidi100% (1)
- Alcohols and PhenolsDocument8 pagesAlcohols and PhenolsMomer83% (6)
- Chemistry: Inorganic Qualitative Analysis in the LaboratoryFrom EverandChemistry: Inorganic Qualitative Analysis in the LaboratoryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Group Properties of ElementsDocument7 pagesGroup Properties of Elementsjeniccax17100% (1)
- Boiler Journal - Sodium ChemicalsDocument9 pagesBoiler Journal - Sodium ChemicalsabdoelandhakimNo ratings yet
- Project On ChemistryDocument13 pagesProject On ChemistryBadhal PaudelNo ratings yet
- Chapter-17 Antimicrobials: Hydrogen PeroxideDocument9 pagesChapter-17 Antimicrobials: Hydrogen PeroxideZafar WasiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Acids, Bases & SaltsDocument3 pagesChemistry: Acids, Bases & SaltsSarvesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- HYP E R ACI D I T Y Cause FOR Intake OF AntacidsDocument14 pagesHYP E R ACI D I T Y Cause FOR Intake OF AntacidsamuNo ratings yet
- COPD Case StudyDocument4 pagesCOPD Case StudyPj Declarador100% (4)
- DentistryDocument1 pageDentistryPj DeclaradorNo ratings yet
- Love Is A FallacyDocument6 pagesLove Is A FallacyPj DeclaradorNo ratings yet
- Classifying FingerprintsDocument5 pagesClassifying FingerprintsPj DeclaradorNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction2Document6 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction2Pj DeclaradorNo ratings yet
- An Abundance of LithiumDocument17 pagesAn Abundance of LithiumWill TohallinoNo ratings yet
- Plating ChromeDocument18 pagesPlating ChromemtrisaktiagusnNo ratings yet
- Water Analysis Volume IIDocument16 pagesWater Analysis Volume IIRaphael Belano BrionesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter 7th Edition Jespersen Test BankDocument32 pagesChemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter 7th Edition Jespersen Test Bankmichellebrownodzabfqtkn100% (17)
- Mole Concept Solution Practice Set Objective by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument1 pageMole Concept Solution Practice Set Objective by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry50% (2)
- AtofanDocument141 pagesAtofanEduardo Jara CornejoNo ratings yet
- Methods of Separating & Purifying Substances 1 QPDocument11 pagesMethods of Separating & Purifying Substances 1 QPShahzaib AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ncert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 4 Structure of The AtomDocument18 pagesNcert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 4 Structure of The AtomShah RukhNo ratings yet
- ChemT5HLQ - With AnswersDocument16 pagesChemT5HLQ - With AnswersNeha Mathew100% (1)
- Phase Diagram Exercises - Worked Answers - CorrectedDocument14 pagesPhase Diagram Exercises - Worked Answers - CorrectedHayden Reeves75% (4)
- ASM Specialty Handbook@: Stainless SteelsDocument589 pagesASM Specialty Handbook@: Stainless SteelsWilliam CoupeNo ratings yet
- Chem 115 PLTL Activity Sheet 4Document8 pagesChem 115 PLTL Activity Sheet 4Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Qualitative Analysis of Different CoinsDocument26 pagesChemistry Project Qualitative Analysis of Different CoinsParth SinhaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Alloy SteelDocument2 pagesCarbon Alloy SteelDeepak HoleNo ratings yet
- 2-5 Redox Reactions Practice Worksheet With AnswersDocument9 pages2-5 Redox Reactions Practice Worksheet With AnswersIlincaVasilescu50% (2)
- FDC FlexDuctConn SubmittalDocument2 pagesFDC FlexDuctConn SubmittalRaj SekharNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry January 2012 P032Document7 pagesCSEC Chemistry January 2012 P032AshleyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations-Question BankDocument23 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations-Question Bankharrissraghavv18No ratings yet
- Earth Materials and ProcessesDocument1 pageEarth Materials and ProcessesJemarjo SalandananNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Chemistry Week 16 Live Lesson 1 Alkali Metals and Halogens PDFDocument13 pagesYear 10 Chemistry Week 16 Live Lesson 1 Alkali Metals and Halogens PDFsweet.miyuxNo ratings yet
- Welding Variables Guide: Effects of Current, Voltage, Speed & MoreDocument34 pagesWelding Variables Guide: Effects of Current, Voltage, Speed & MoremilindNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document12 pagesChem 1Ellaine NacisNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Ferrous Material-BmcDocument18 pagesCorrosion Ferrous Material-Bmcsakshi soniNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Review SheetDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table Review SheetWendell Kim LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Self-absorption in 4% beta counting sourcesDocument6 pagesSelf-absorption in 4% beta counting sourcesphanthanhhungNo ratings yet
- Fluorides IN Dentistry: Meghna VermaDocument20 pagesFluorides IN Dentistry: Meghna Vermanew bieeNo ratings yet
- Darkle Slideshow by SlidesgoDocument8 pagesDarkle Slideshow by SlidesgoShahjahan IqbalNo ratings yet
- MSrinivas - STEELS FOR CRITICAL APPLICATIONSDocument46 pagesMSrinivas - STEELS FOR CRITICAL APPLICATIONSamit gajbhiye100% (1)
- Engineering Materials NotesDocument25 pagesEngineering Materials NotesRoobanesh ManoharanNo ratings yet
- Set 7 Paper 2Document19 pagesSet 7 Paper 2Miesya87No ratings yet