Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elasticity and Marginal Effects - Linear - Regression - Continuous Vars
Uploaded by
Subhrodip SenguptaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elasticity and Marginal Effects - Linear - Regression - Continuous Vars
Uploaded by
Subhrodip SenguptaCopyright:
Available Formats
Elasticity and Marginal Effects _Linear_Regression_Continuous vars case.
For Problem Set, visit here:
https://www.chegg.com/homework-help/questions-and-answers/econometricsmultiple-regrssion-analysis-issues-use-data-greene78-following-exercise-consiq8756039
Based on Guided Computations made by Student (Khan Larn, Econ 318)
https://s3.amazonaws.com/iedu-attachmentsmessage/761a87c6931581757e70eeda61fc52f2_57481e0556710994297c56d1dbe2202c.jpg
https://s3.amazonaws.com/iedu-attachmentsmessage/d25f541e5f8d340761ced0812b48802f_8e169f021fe909fee3f63fca18b46dd8.jpg
(Question and Ans 1-4 see above)
5- For both models calculate marginal effect and elasticity of price (Pg) and income (Y)
when Pg=3, Y=10,000, and Pnc=2
Answer:
One assumption we make throughout the analysis (prerequisite of the regressand G to
be partially differentiable (ceteris Paribus) in Pg and Y), is that all underying variables
are continuous and can take all possible values in R, or at least throughout our open
interval of consideration. This gives us partial differentiability of log function, and thus
of our underlying Equation which is linear/ Log Linear.
Model 1
G = B0 + B1Pg + B2 ln(Y) + B3Pnc + u
Marginal effect of Pg on G:
= 1 = 14.8629
Marginal effect of Y on G:
1
1
=
=
=
= 2 = 294.64
1
Hence,
| =
294.64
10000
= .029464
Page 1 of 3
Elasticity and Marginal Effects _Linear_Regression_Continuous vars case.
This is the required marginal effect.
Next, we shall plug value of marginal effect into the formula of elasticities.
Price Elasticity of G=
Price Elasticity of G (when Pg=3, Y=10,000, and Pnc=2 )
3
=
=
14.8629 { is obtained from Ans2 } = 0.179536
248.3547
Income Elasticity of G=
10000
248.3547
.029464 = 1.186368
Model 2
ln(G) = B0 + B1Pg + B2 ln(Y) +B3Pnc + u
Marginal effect of Pg on G:
1
=
= 1 = 0.0491644
|{, , } =
| = 0.0491644
244.29 { is obtained from Ans4 which uses sae values of regressors to compute this E(G)} =
12.0104
Which is the required marginal effect.
1
1
1
1
=
=
=
=
= 1.63414
ln
Hence
|{, , } =
|{, } =
10000
244.29
1.63414
{ is obtained from Ans4 which uses sae values of regressors to compute this E(G)}
= 66.8934
Which is the required marginal effect.
Next, we can use marginal effects to compute the respective Elasticities.
Page 2 of 3
Elasticity and Marginal Effects _Linear_Regression_Continuous vars case.
Price Elasticity of G =
. =
Income Elasticity of G =
3
244.29
10000
244.29
12.0104 =-0.1475
66.8934 = 2738.2783
Let me know if you need additional help, especially with notation.
Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"From EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Geometry AlgorithmsDocument142 pagesGeometry AlgorithmsThahir ShahNo ratings yet
- Gaussian QuadratureDocument24 pagesGaussian QuadratureAbera DeressaNo ratings yet
- The Thomas Algorithm For Tridiagonal Matrix Equations PDFDocument3 pagesThe Thomas Algorithm For Tridiagonal Matrix Equations PDFAndra Walileuw100% (3)
- Solutions Stochastic Modeling. Analysis and Simulation PDFDocument130 pagesSolutions Stochastic Modeling. Analysis and Simulation PDFtrikay98No ratings yet
- Integer Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementFrom EverandInteger Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementNo ratings yet
- C6.Earthquake Analysis Compatibility ModeDocument27 pagesC6.Earthquake Analysis Compatibility ModeAgus Budiman SikumbangNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression ExampleDocument2 pagesLinear Regression ExampleridzimNo ratings yet
- Homework 6 SolutionDocument9 pagesHomework 6 SolutionKai SamaNo ratings yet
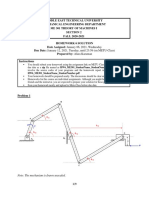
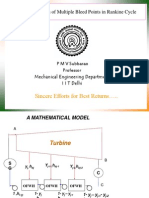
- Optimal Location of Multiple Bleed Points in Rankine Cycle: Sincere Efforts For Best Returns .Document28 pagesOptimal Location of Multiple Bleed Points in Rankine Cycle: Sincere Efforts For Best Returns .pvenky_kkdNo ratings yet
- Yjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsDocument8 pagesYjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- On the Ramanujan formulas: mathematical connections with some sectors of Particle physics, in particular on the masses of the dilaton, of the candidate glueball and of the two Pion mesons. - Michele Nardelli, Antonio NardelliDocument174 pagesOn the Ramanujan formulas: mathematical connections with some sectors of Particle physics, in particular on the masses of the dilaton, of the candidate glueball and of the two Pion mesons. - Michele Nardelli, Antonio NardelliMichele NardelliNo ratings yet
- Traveling Salesman ProblemDocument14 pagesTraveling Salesman ProblemPooja KapoorNo ratings yet
- EE644 - Discrete Time Systems Spring 2009 Midterm Exam #2 With Solutions Problem 1. Polyphase RepresentationsDocument5 pagesEE644 - Discrete Time Systems Spring 2009 Midterm Exam #2 With Solutions Problem 1. Polyphase RepresentationsDecker JamesNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.1 A)Document11 pagesProblem 4.1 A)Renxiang LuNo ratings yet
- Principles of Econometrics 4e Chapter 2 SolutionDocument33 pagesPrinciples of Econometrics 4e Chapter 2 SolutionHoyin Kwok84% (19)
- Michele Nardelli: Sezione Filosofia - Scholar of Theoretical PhilosophyDocument126 pagesMichele Nardelli: Sezione Filosofia - Scholar of Theoretical PhilosophyMichele NardelliNo ratings yet
- R R A S: Quantitative MethodsDocument9 pagesR R A S: Quantitative MethodsMehmoodulHassanAfzalNo ratings yet
- CH 5 SolDocument20 pagesCH 5 SolAdam NortonNo ratings yet
- Unsymmetric BendingDocument10 pagesUnsymmetric BendingBLLL100% (1)
- 6062b08a804f2b4fbd2985b5 - AP Calculus UNIT 2Document6 pages6062b08a804f2b4fbd2985b5 - AP Calculus UNIT 2cdsNo ratings yet
- HW 02 Solutions Spring 2012Document6 pagesHW 02 Solutions Spring 2012shlaeaNo ratings yet
- CE206 - System of Linear EquationsDocument17 pagesCE206 - System of Linear EquationsImdadul HaqueNo ratings yet
- P0748Document3 pagesP0748Alex FernandoNo ratings yet
- PDMADocument7 pagesPDMAali_naghedifarNo ratings yet
- Analisa Output Flowchart/Program Eleminasi Gauss (Standart) : X X X X X XDocument5 pagesAnalisa Output Flowchart/Program Eleminasi Gauss (Standart) : X X X X X XweniNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 Lab With PythonDocument3 pagesCalculus 1 Lab With PythonWaleed RiazNo ratings yet
- 6 - Probability Generating FunctionsDocument10 pages6 - Probability Generating FunctionsAdonia AretinaNo ratings yet
- Orthogonality of The Natural ModesDocument39 pagesOrthogonality of The Natural ModesEduardo OrozNo ratings yet
- Gauss ElimDocument8 pagesGauss ElimRachmawati BadrudinNo ratings yet
- Project (1) Modified4Document26 pagesProject (1) Modified4dks697bvhcNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2012 13 CP0854 06 Mar 2013 RM01 7 Numerical MethodsDocument23 pagesWINSEM2012 13 CP0854 06 Mar 2013 RM01 7 Numerical MethodsAtul ShindeNo ratings yet
- Analyzing various equations concerning some topics of Field Theory, String Theory and Gravity. Mathematical connections and applications of κ formula regarding the Zeros of Riemann Zeta Function and Ramanujan Mathematics. IIIDocument129 pagesAnalyzing various equations concerning some topics of Field Theory, String Theory and Gravity. Mathematical connections and applications of κ formula regarding the Zeros of Riemann Zeta Function and Ramanujan Mathematics. IIIAntonio NardelliNo ratings yet
- Sol - Taller Transformador Trifásico - DeltaDocument7 pagesSol - Taller Transformador Trifásico - DeltaSebastian PuertaNo ratings yet
- Vibration and Control: Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Y.T.UDocument82 pagesVibration and Control: Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Y.T.Udora901No ratings yet
- DerivativeDocument2 pagesDerivativechrosun lacht100% (1)
- W10 Chapter 4MatricesExerciseW10Document5 pagesW10 Chapter 4MatricesExerciseW10mohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
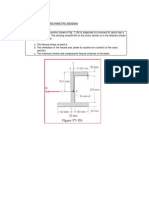
- Punching Shear Worked ExamplesDocument14 pagesPunching Shear Worked ExamplesKragon LordNo ratings yet
- MOOC Course - Introduction To R Software July 2017 Solution To Assignment 1Document5 pagesMOOC Course - Introduction To R Software July 2017 Solution To Assignment 1xlntyogeshNo ratings yet
- Subiectul I: Varianta 038Document2 pagesSubiectul I: Varianta 038sfateugenNo ratings yet
- Michele Nardelli: Sezione Filosofia - Scholar of Theoretical PhilosophyDocument200 pagesMichele Nardelli: Sezione Filosofia - Scholar of Theoretical PhilosophyMichele NardelliNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 SolutionDocument10 pagesHomework 4 SolutionKai SamaNo ratings yet
- Basics of FEM: Prof. S. V. KulkarniDocument28 pagesBasics of FEM: Prof. S. V. KulkarniKiran Kumar KandregulaNo ratings yet
- San Agustin Institue of Technology Valencia City, Bukidnon Senior Highschool Department Summative Test in PrecalculusDocument6 pagesSan Agustin Institue of Technology Valencia City, Bukidnon Senior Highschool Department Summative Test in PrecalculusDindo HiocoNo ratings yet
- Least Cost System Operation: Economic Dispatch 2: Smith College, EGR 325 March 10, 2006Document37 pagesLeast Cost System Operation: Economic Dispatch 2: Smith College, EGR 325 March 10, 2006engidawabelNo ratings yet
- Assignemnt 1 Muhammad Awais (NUML-S20-11149)Document40 pagesAssignemnt 1 Muhammad Awais (NUML-S20-11149)Muhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- Year 11 T2 Maths AssignmentDocument10 pagesYear 11 T2 Maths AssignmentAlesha TNo ratings yet
- 2 Evaluating Functions-1Document21 pages2 Evaluating Functions-1Ahlyssa AnsagayNo ratings yet
- Application of Carson Formula To Overhead Line by Prof - KerstingDocument15 pagesApplication of Carson Formula To Overhead Line by Prof - KerstingAlex MunandarNo ratings yet
- QR Decomposition: Numerical Analysis Massoud MalekDocument4 pagesQR Decomposition: Numerical Analysis Massoud MalekAshwini Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- Particle Physics, in Particular The Masses of The Two Pion MesonsDocument123 pagesParticle Physics, in Particular The Masses of The Two Pion MesonsMichele NardelliNo ratings yet
- Mws Gen Sle PPT GaussianDocument94 pagesMws Gen Sle PPT GaussianBoo CoriNo ratings yet
- System of Linear Equations: Direct & Iterative MethodsDocument36 pagesSystem of Linear Equations: Direct & Iterative MethodsLam WongNo ratings yet
- Operaciones Con Radicales: 1. - Extrae Las Siguientes RaícesDocument10 pagesOperaciones Con Radicales: 1. - Extrae Las Siguientes RaícesJavier AlexNo ratings yet
- Reliability Engineering CEO852: Date: March 10, 2022Document5 pagesReliability Engineering CEO852: Date: March 10, 2022jagadish mahataNo ratings yet
- Bivariate Regression AnalysisDocument15 pagesBivariate Regression AnalysisCarmichael MarlinNo ratings yet
- Predicting Economic Costs of Cyclones1Document3 pagesPredicting Economic Costs of Cyclones1Subhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- List of Sanctioning Authority and Its Corresponding Disbursing Agency (As On 10th Oct' 2019)Document1 pageList of Sanctioning Authority and Its Corresponding Disbursing Agency (As On 10th Oct' 2019)Subhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Cost ConceptDocument5 pagesCost ConceptSubhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- EssentialExcelTraining Ammatuer ShortCourseDocument1 pageEssentialExcelTraining Ammatuer ShortCourseSubhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Apa Ananya Guha PDFDocument1 pageApa Ananya Guha PDFSubhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- ExecutiveSummary - ElectricCarGearDesignOptimisation (Code Accompaniment)Document2 pagesExecutiveSummary - ElectricCarGearDesignOptimisation (Code Accompaniment)Subhrodip Sengupta100% (1)
- Exploring Determinant and Cramers Rule For Economics Students (Questions Only)Document3 pagesExploring Determinant and Cramers Rule For Economics Students (Questions Only)Subhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Implementation and Solution of Graph Theoretic Solutions in MATLABDocument2 pagesImplementation and Solution of Graph Theoretic Solutions in MATLABSubhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Cool FInancial Metrics ExcelTricks ProblemsDocument13 pagesCool FInancial Metrics ExcelTricks ProblemsSubhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Diagonal Entry VBA SolvedDocument3 pagesDiagonal Entry VBA SolvedSubhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Sample Excel Template To Sample Answers To Questions Relating To Use of Standard Normal Distribution, Studentised T DistributionsDocument1 pageSample Excel Template To Sample Answers To Questions Relating To Use of Standard Normal Distribution, Studentised T DistributionsSubhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Ans 3Document6 pagesAns 3Subhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Garage ListDocument674 pagesGarage ListtejasNo ratings yet
- Few Basic Financial Econometrics Q&ADocument9 pagesFew Basic Financial Econometrics Q&ASubhrodip Sengupta100% (1)
- Else Cable India Final Exam Aggregate PlanningDocument5 pagesElse Cable India Final Exam Aggregate PlanningSubhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Binomial Option Pricing 2 Period Excercise.Document4 pagesBinomial Option Pricing 2 Period Excercise.Subhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Sales Team Selection Report: Industrial Organisation, Educator, Commercial Educator, Psychology, SAS, Validation, Measures, HR, EXPLAINING CAPABILITY THROUGH PERSONALITY and Other RecommendationsDocument13 pagesSales Team Selection Report: Industrial Organisation, Educator, Commercial Educator, Psychology, SAS, Validation, Measures, HR, EXPLAINING CAPABILITY THROUGH PERSONALITY and Other RecommendationsSubhrodip Sengupta100% (1)
- Aggregate Planning Transportation (Production) Problem in MS ExcelDocument53 pagesAggregate Planning Transportation (Production) Problem in MS ExcelSubhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Matrices and Vectors 3 ProblemsDocument4 pagesMatrices and Vectors 3 ProblemsSubhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Sengupta Mixing of AnswersDocument16 pagesSengupta Mixing of AnswersSubhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Answers - Small Projects-Assignment1-150bDocument4 pagesAnswers - Small Projects-Assignment1-150bSubhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Statisticss Work I N Decision Sciences.Document5 pagesStatisticss Work I N Decision Sciences.Subhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Stata Log of Cross Section Macro Econometrics .M2 (Money) and Inflation As Instruments On GDP.Document7 pagesStata Log of Cross Section Macro Econometrics .M2 (Money) and Inflation As Instruments On GDP.Subhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Basic - MSExcel - VBA For Stat101Document895 pagesBasic - MSExcel - VBA For Stat101Subhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Basic - MSExcel - VBA For Stat101Document895 pagesBasic - MSExcel - VBA For Stat101Subhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Questions Small Projects Assignment 150bDocument2 pagesQuestions Small Projects Assignment 150bSubhrodip SenguptaNo ratings yet