Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Submrg Subm Hydrostatic
Uploaded by
hernandez15Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Submrg Subm Hydrostatic
Uploaded by
hernandez15Copyright:
Available Formats
Hydrostatic Loading
Pgina 1 de 1
AutoPIPE Reference Information
Buoyancy/Hydrostatic Loading
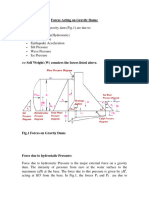
Under hydrostatic loading, submerged piping is subject to an upward buoyant force (F ) which reduces the (above water) self
b
weight of the pipe (W) as shown by Equation E-1. In the absence of fluid motion, only the vertical forces depicted in the free body
diagram shown in Figure E-2 are nonzero.
(E-1)
Figure E-1 shows an arbitrary submerged pipe element, and the buoyant forces calculated by AutoPIPE.
Figure E-1
Buoyancy
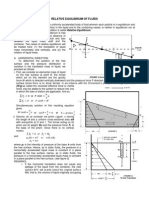
A body submerged in fluid is subjected to a vertical force which is proportional to the volume of the displaced fluid. The magnitude
of this force is given as:
(E-2)
where
specific weight of the fluid
volume of fluid displaced by the body
The Buoyancy command can be used to include the buoyant effect in the gravity load case (GR). AutoPIPE treats buoyant forces as
a uniformly distributed load acting along the submerged length of pipe. If the location of the water surface with respect to the
piping points is expected to significantly influence the buoyancy analysis results, closely spaced points in the vicinity of the water
surface, preferably with a point located at the water surface should be used to obtain an accurate discretization of the loading.
mk:@MSITStore:C:\A%20COMIMSA\Gral\Gral%2006-2015\Respaldo%20KBR\P...
11/11/2015
You might also like
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisFrom EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNo ratings yet
- Forces Acting On Gravity DamsDocument6 pagesForces Acting On Gravity DamsRama Sagar Naik100% (2)
- Documents - Null-Forces Acting On Gravity Dams - Nagendra SirDocument6 pagesDocuments - Null-Forces Acting On Gravity Dams - Nagendra SirArarsa FayisaNo ratings yet
- 1 Hydrostatic Force On A Curved SurfaceDocument6 pages1 Hydrostatic Force On A Curved SurfaceAriane EstradaNo ratings yet
- Soils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationFrom EverandSoils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 3: Soils and Water CirculationGuilhem BourrieNo ratings yet
- 02.03 Chapter 3Document41 pages02.03 Chapter 3jotiram baban ghadgeNo ratings yet
- EN200 Naval Engineering Chapter 3 PDFDocument42 pagesEN200 Naval Engineering Chapter 3 PDFanusha_wiproNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Design For Sub-Surface FlowDocument3 pagesHydraulic Design For Sub-Surface FlowSuktara-Drubatara TaritNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Buoyancy StabilityDocument18 pagesChapter 2 Buoyancy StabilitykohNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (MR 231) Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics (MR 231) Lecture NotesAhmedTahaNo ratings yet
- Nechvoglod Bridge 1991Document14 pagesNechvoglod Bridge 1991Kevin NathanielNo ratings yet
- CH 2 For PresentationDocument34 pagesCH 2 For PresentationNesru Jemal100% (1)
- Module I HMDocument23 pagesModule I HMAnilkumar GopiNo ratings yet
- Gravity DamsDocument17 pagesGravity DamsParikshith PrasadNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Force On Curve SurfaceDocument3 pagesHydrostatic Force On Curve Surfacetala starNo ratings yet
- Full TextDocument1 pageFull TextAhmad Adel El TantawyNo ratings yet
- 8-Chapter 3 Text 2011Document50 pages8-Chapter 3 Text 2011medievoloNo ratings yet
- AJC TutorialDocument4 pagesAJC TutorialYong Ming HengNo ratings yet
- Energy DissipatorDocument41 pagesEnergy DissipatorC_C_871775% (4)
- Module 4 - Hydrostatic Force IIDocument4 pagesModule 4 - Hydrostatic Force IIkrikorNo ratings yet
- S1 FM BuoyancyDocument12 pagesS1 FM Buoyancyakinduhiman2No ratings yet
- Dynamics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesDynamics Multiple Choice QuestionsPaola Rafaela FacchineiNo ratings yet
- CE 1022 Fluid Mechanics-Buoyancy Lecture NoteDocument61 pagesCE 1022 Fluid Mechanics-Buoyancy Lecture NoteNipuna Nuwan Nanayakkara0% (1)
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1sgrsthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 2Document5 pagesChapter 7 2Behar AbdurahemanNo ratings yet
- 82 To 88 CompleteDocument6 pages82 To 88 CompleteUmer KhanNo ratings yet
- Document From Prøfessør ?????Document40 pagesDocument From Prøfessør ?????Hassan Fofanah AlieuNo ratings yet
- Buoyancy, Stability and Masses Subjected To AccelerationDocument12 pagesBuoyancy, Stability and Masses Subjected To AccelerationandreinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Fluid Mechanics IDocument39 pagesChapter 2 - Fluid Mechanics IAbdelsattar Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Wanted Gravity DamDocument167 pagesWanted Gravity Damhabtamu0% (1)
- Fluid 1Document40 pagesFluid 1NateNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Structure I - CENG 3161: Design Principle of DamsDocument152 pagesHydraulic Structure I - CENG 3161: Design Principle of DamsAbduljebar HussienNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 BuoyancyDocument9 pagesChapter 4 BuoyancyRavindu Jayalath100% (1)
- Gravity DamDocument26 pagesGravity Damsamayan bhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Relative Equilibrium of FluidsDocument3 pagesRelative Equilibrium of FluidsMike Mor'z25% (4)
- Ju, Jit, Hydralic and Water Reasources Engineering: Energy Dissipation Below Spillways Energy Dissipation Below SpillwaysDocument14 pagesJu, Jit, Hydralic and Water Reasources Engineering: Energy Dissipation Below Spillways Energy Dissipation Below SpillwaysRefisa JiruNo ratings yet
- Machine Dynamics Kimathi NotesDocument28 pagesMachine Dynamics Kimathi NotesBenardMbithiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PDFDocument16 pagesUnit 2 PDFveerendraNo ratings yet
- 1957-Dynamic Pressure On Accelerated Fluid ContainersDocument21 pages1957-Dynamic Pressure On Accelerated Fluid ContainersbehzadNo ratings yet
- Ch13 SSMDocument18 pagesCh13 SSMJuanca AbadNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 03Document31 pagesLecture Notes 03kavinNo ratings yet
- Fluid StaticsDocument30 pagesFluid StaticsKalani WakehamNo ratings yet
- 2824 Ch2-HydrostaticDocument41 pages2824 Ch2-HydrostaticThiago de Santana SouzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two EDocument23 pagesChapter Two ErtyiookNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Concrete Gravity DamDocument24 pagesChapter 3-Concrete Gravity DamMohamed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2.2 - Hydrostatic Force On SurfacesDocument10 pagesMODULE 2.2 - Hydrostatic Force On SurfacesLyndon PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Energy Principle: 1. Mechanical Energy of A Fluid ParticleDocument10 pagesEnergy Principle: 1. Mechanical Energy of A Fluid ParticleSteven KuaNo ratings yet
- 2012 Lecture Revision QN (Forces) 19 July NgLT1Document11 pages2012 Lecture Revision QN (Forces) 19 July NgLT1timchanymNo ratings yet
- Energy DissipatorDocument41 pagesEnergy DissipatorweynNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - 1 Fluid DynamicsDocument60 pagesChapter 4 - 1 Fluid DynamicsChara ZerihunNo ratings yet
- Labsheet StabilityDocument5 pagesLabsheet StabilityNur HamizahNo ratings yet
- Geofisical Fluid Dinam 2d1Document9 pagesGeofisical Fluid Dinam 2d1koalagrisNo ratings yet
- Geometric Stiffness and P Delta EffectsDocument14 pagesGeometric Stiffness and P Delta EffectsWahid Omar100% (1)
- Fluid DynamicsDocument13 pagesFluid DynamicsAnik MahmudNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 8 Energy Dissipator - ModifiedDocument16 pagesChapter - 8 Energy Dissipator - Modifiedsulaiman mohammedNo ratings yet
- Consider A Random Element of A Flow NetDocument8 pagesConsider A Random Element of A Flow NetPeteris SkelsNo ratings yet
- Slope StabilityDocument12 pagesSlope StabilityRobert NyirendaNo ratings yet
- Arizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksFrom EverandArizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptFrom EverandThe Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Japanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensFrom EverandJapanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensNo ratings yet
- New York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksFrom EverandNew York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksNo ratings yet
- South Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptFrom EverandSouth Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Naples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoFrom EverandNaples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)