Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of Nephrolithiasis
Uploaded by
anreilegarde80%(5)80% found this document useful (5 votes)
7K views2 pagesOriginal Title
pathoPhysiology of Nephrolithiasis
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
80%(5)80% found this document useful (5 votes)
7K views2 pagesPathophysiology of Nephrolithiasis
Uploaded by
anreilegardeCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
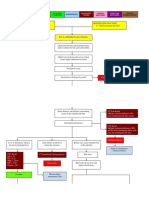
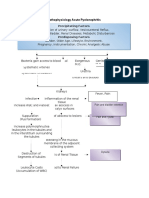
NEPHROLITHIASIS : PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
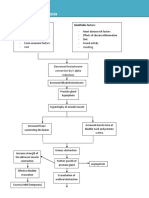
Modifiable factors:
-Diet (unusually high in soy & fish
Non modifiable factors: sauce, bagoong, softdrinks, legumes,
protein & salt)
-Age (64 years old) -Certain meds (Analgesics)
-Sex (male) -Low fluid intake
-Urinary stasis
-Smoking & alcoholic drinking
-Gouty arthritis
Uric acid (523.83mmoL/L), ammonia
phosphate (BUN=16.50mmoL/L), and calcium
oxalate stone material deposition on proximal
renal tubule
Super saturation of urine Nephrocalcinosis on proximal
by stone forming tubule
constituents (↓OFI,
pH(5)
Episodes of
Randall’s plaque pain in side
radiating in
the back
Hyperkalemia
(5.62 mmoL/L) Urinary Tract Infection caused by urea
splitting organism
Nidation of crystals or foreign Increase production of Pyuria
bodies from the WBC
supersaturated urine
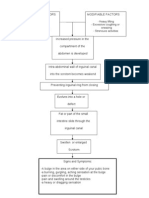
Nidation of crystals or foreign Increase production of Pyuria
bodies from the WBC
supersaturated urine
Progression of stones in
Loop of Henle
Dysuria
Accumulation of stones & increasing in size
Blood vessels wall surface
attraction and erosion Hematuria
Stones formation <5mm in kidneys Proteinuria
Renal colic radiating (+1)
to the back & leg
Stones >5mm to 10mm obstructing
the kidneys
(15.5mm on left kidney)
(12.2mm on right kidney)
Bilateral swelling of Staghorn
the knees and calculus
adjacent parts Stone matrix & progression
(Edema)
MULTIPLE URINARY CALCULUS
You might also like
- PRC forms for midwifery recordsDocument4 pagesPRC forms for midwifery recordsjhimeady92% (12)
- Pathophysiology of Liver Cancer 2Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Liver Cancer 2Charis Paroginog92% (12)
- Pathophysiology of Colon CancerDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Colon CancerClaring Cipriano54% (13)
- Lesson 16 Nutrition HESI RN FLMIR 1904COHORT PDFDocument16 pagesLesson 16 Nutrition HESI RN FLMIR 1904COHORT PDFLuis Hernandez100% (5)
- Pathophysiology - Obstructive JaundiceDocument3 pagesPathophysiology - Obstructive JaundiceAbigail Lonogan0% (1)
- SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM Obstructive JaundiceDocument1 pageSCHEMATIC DIAGRAM Obstructive JaundiceJan Niño EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology OsteosarcomaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology OsteosarcomaGladys Barcelona0% (1)
- Hernia PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHernia PathophysiologyIvan Louise Fajardo Maniquiz83% (6)
- Pathophysiology of Gallstones: Risk Factors and ComplicationsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Gallstones: Risk Factors and ComplicationsBernalene Sy100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of UTIDocument1 pagePathophysiology of UTIKeannepotz80% (5)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeAqeel Al-Mahdaly0% (1)
- NCP For Pain - NephrolithiasisDocument3 pagesNCP For Pain - NephrolithiasisDepia Leah NgislawanNo ratings yet
- B R Robbins and Cotran: Pathologic Basis of Disease, 8th EditionDocument1 pageB R Robbins and Cotran: Pathologic Basis of Disease, 8th EditionabdallhNo ratings yet
- NEPHROLITHIASIS - PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesNEPHROLITHIASIS - PathophysiologyJon Corpuz Aggasid100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of NephrolithiasisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Nephrolithiasismissmakai100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Nephrolithiasis, Struvites Stone (Staghorn Calculi)Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Nephrolithiasis, Struvites Stone (Staghorn Calculi)Floyd100% (2)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia PathophysiologyDarla SaulerNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsYuyu Tulawie100% (1)
- Coronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFMohd Amir Bin Bashir0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Katherine Clarisse Carvajal Lavarias100% (1)
- Causes and Symptoms of Untreated Congenital HerniaDocument2 pagesCauses and Symptoms of Untreated Congenital HerniaArt Christian Ramos67% (15)
- Addison's Disease Patho-PhysiologyDocument1 pageAddison's Disease Patho-PhysiologyAca Ramirez100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of CholecystitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of CholecystitisAnonymous gDp7y3Cl86% (21)
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of FractureVenus Tagaan UcatNo ratings yet
- Ovarian New GrowthDocument1 pageOvarian New GrowthLouie Cedrick Camposano Tria50% (2)
- Pathophysiology - PyelonephritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology - PyelonephritisFrancis Kevin Sagudo92% (13)
- Community Diagnosis Tramo Uno, San Dionisio, Paranaque CityDocument85 pagesCommunity Diagnosis Tramo Uno, San Dionisio, Paranaque CityanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Controlling - Nursing ManagementDocument43 pagesControlling - Nursing Managementanreilegarde94% (18)
- Planning - Nursing Management FunctionDocument27 pagesPlanning - Nursing Management Functionanreilegarde100% (17)
- Physical Assessment of School Age Children - SCHOOL NURSINGDocument3 pagesPhysical Assessment of School Age Children - SCHOOL NURSINGanreilegarde100% (8)
- Planning - Nursing Management FunctionDocument27 pagesPlanning - Nursing Management Functionanreilegarde100% (17)
- CPR SeminarDocument76 pagesCPR SeminarAmy Lalringhluani Chhakchhuak100% (3)
- Why I Desire to Study Medical MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesWhy I Desire to Study Medical MicrobiologyRobert McCaul100% (1)
- NCP NSDDocument3 pagesNCP NSDshigemasamayumi60% (5)
- Nursing Fundamentals Exam ReviewDocument10 pagesNursing Fundamentals Exam ReviewAlain CheryNo ratings yet
- IV. The PATIENTS ILLNESS (Nephrolithiasis) Pathophysiology (Book-Based)Document3 pagesIV. The PATIENTS ILLNESS (Nephrolithiasis) Pathophysiology (Book-Based)wapakalypseNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of UrolithiasisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of UrolithiasisNavjot Brar100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisAnonymous 75TDy2y100% (1)
- Risk Factors and Pathogenesis of Peritonitis in Peritoneal Dialysis PatientsDocument2 pagesRisk Factors and Pathogenesis of Peritonitis in Peritoneal Dialysis PatientsLeslie PaguioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Uric Acid NephrolithiasisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Uric Acid NephrolithiasisAia JavierNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis Case StudyDocument31 pagesNephrolithiasis Case StudyL.a.Zumárraga67% (3)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYrye100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Prostate CancerDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Prostate CancerArnzz Agbulos100% (2)
- Case Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisDocument84 pagesCase Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisSteph BulanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology OsteosarcomaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology OsteosarcomaVernadeth Dumagat50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of BPH: Risk Factors, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument1 pagePathophysiology of BPH: Risk Factors, Symptoms & TreatmentKevin Jade Herrera0% (2)
- Chronic Cholecystitis With Cholelithiasis PathoDocument2 pagesChronic Cholecystitis With Cholelithiasis PathoBill Clinton Lamira BabanNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisDocument85 pagesCase Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisShoixi ⎝⓿⏝⓿⎠100% (1)
- Urolithiasis Case ReportDocument14 pagesUrolithiasis Case ReportCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of AGEDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AGEtinatin9890% (1)
- Calvit Tablet/Suspension for Calcium and Vitamin D SupplementationDocument2 pagesCalvit Tablet/Suspension for Calcium and Vitamin D SupplementationdentsavvyNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis - NCPDocument9 pagesNephrolithiasis - NCPAia Javier83% (6)
- Pathophysiology of CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of CholelithiasisSherilNo ratings yet
- Kidney Stones: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment /TITLEDocument41 pagesKidney Stones: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment /TITLERachel Semilla50% (2)
- Concept Map on Risk Factors and Nursing Care for End Stage Renal DiseaseDocument4 pagesConcept Map on Risk Factors and Nursing Care for End Stage Renal DiseaseAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pyelonephritis PathoDocument1 pageAcute Pyelonephritis PathoGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramMeine MheineNo ratings yet
- CystolithiasisDocument7 pagesCystolithiasisRaul Nocete100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Gouty ArthritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Gouty ArthritiskyawNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsReina SamsonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- Patho 1 2Document5 pagesPatho 1 2KATHLEEN JOSOLNo ratings yet
- IV PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesIV PathophysiologyJanedear Pasal100% (1)
- NEPHROLITHIASIS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY CAUSESDocument2 pagesNEPHROLITHIASIS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY CAUSESHeyy KuwiNo ratings yet
- Patho FinalnajodDocument5 pagesPatho FinalnajodKATHLEEN JOSOLNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis / Renal Calculi: Clinical Manifestation: Stones in The Renal PelvisDocument3 pagesUrolithiasis / Renal Calculi: Clinical Manifestation: Stones in The Renal PelvisErika ArceoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease and Chronic Kidney DiseaseRryje SallevaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument3 pagesPa Tho PhysiologyMike GarciaNo ratings yet
- Struvite (Consists of Uric Acid Cystine Xanthine Frequenc y Clinical RFDocument3 pagesStruvite (Consists of Uric Acid Cystine Xanthine Frequenc y Clinical RFAdnin ShereenNo ratings yet
- Marinov - Urinary System 2016 (Eng)Document25 pagesMarinov - Urinary System 2016 (Eng)Самат Джусупбекович ДжусупбековNo ratings yet
- Bilateral: Etiology Manifestations Diagnosis Management, Prognosis, Prevention ComplicationsDocument8 pagesBilateral: Etiology Manifestations Diagnosis Management, Prognosis, Prevention ComplicationsJayesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- UrolithiasisDocument99 pagesUrolithiasisgeorgejobinputhenpurackalNo ratings yet
- Resume' of AnreiDocument3 pagesResume' of AnreianreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Directing Nursing ManagementDocument26 pagesDirecting Nursing Managementanreilegarde83% (6)
- Laws and Ordinances Affecting Nursing PracticeDocument3 pagesLaws and Ordinances Affecting Nursing PracticeanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Forms of Organizational ChartDocument2 pagesForms of Organizational ChartanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Steps in The Criminal Justice ProcessDocument3 pagesSteps in The Criminal Justice ProcessanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Micu MedsDocument3 pagesMicu MedsanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Nepal Bhutan Maldives ComparisonsDocument2 pagesNepal Bhutan Maldives ComparisonsanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Staffing Nursing ManagementDocument55 pagesStaffing Nursing Managementanreilegarde90% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan FormatDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan FormatanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment FormatDocument4 pagesPhysical Assessment Formatanreilegarde67% (3)
- Nursing Leadership and Its TheoriesDocument71 pagesNursing Leadership and Its Theoriesanreilegarde100% (1)
- Nursing Management IntroductionDocument42 pagesNursing Management Introductionanreilegarde100% (5)
- Organizing - Nursing ManagementDocument104 pagesOrganizing - Nursing Managementanreilegarde100% (19)
- SuicideDocument10 pagesSuicideanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Maria Estrella T. Caoili, RN, MANDocument62 pagesPrepared By: Maria Estrella T. Caoili, RN, MANanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Sjdefi PRC Forms SignatoriesDocument1 pageSjdefi PRC Forms SignatoriesanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- All About Resume and Curriculum VitaeDocument8 pagesAll About Resume and Curriculum VitaeanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Osteogenesis ImperfectaDocument8 pagesOsteogenesis ImperfectaDokter ZukieNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory DiseasesDocument3 pagesUpper Respiratory DiseasesanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Pyrazinamide Drug StudyDocument1 pagePyrazinamide Drug Studyanreilegarde100% (2)
- General Management For Potts DiseaseDocument2 pagesGeneral Management For Potts Diseaseanreilegarde100% (1)
- Immuno JournalDocument3 pagesImmuno JournalanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Malaria: Causative OrganismsDocument5 pagesMalaria: Causative OrganismsanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- MR - Molina's P.A and Nursing HistoryDocument4 pagesMR - Molina's P.A and Nursing HistoryanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Cover LetterDocument2 pagesCover Letteralaa KassabNo ratings yet
- Smoking and Hypertension - UpToDateDocument25 pagesSmoking and Hypertension - UpToDatemehdi.chlif4374No ratings yet
- Organizing Nursing Services for Quality Patient CareDocument28 pagesOrganizing Nursing Services for Quality Patient CareSimran JosanNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Examination - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument9 pagesMental Status Examination - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfGRUPO DE INTERES EN PSIQUIATRIANo ratings yet
- Skenario C Blok 22Document40 pagesSkenario C Blok 22Ambhi GanaNo ratings yet
- Fansidar Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFansidar Drug StudyjangzieNo ratings yet
- PE 3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesPE 3 ReviewerZac GarciaNo ratings yet
- Prevention & Early Outpatient Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Document4 pagesPrevention & Early Outpatient Treatment Protocol For Covid-19jack mehiffNo ratings yet
- Digital Healthcare Market Research 3Document33 pagesDigital Healthcare Market Research 3Nero AngeloNo ratings yet
- Marco-Equinox-Patient Hand OutDocument2 pagesMarco-Equinox-Patient Hand OutDr. Richard JohnsonNo ratings yet
- WVSU Adult Nursing ProcessDocument9 pagesWVSU Adult Nursing ProcessMark ArconadaNo ratings yet
- Health Checklist Form For Visitors: Nakaranas Ka Ba NG Mga Sumusunod: Oo HindiDocument2 pagesHealth Checklist Form For Visitors: Nakaranas Ka Ba NG Mga Sumusunod: Oo HindiCoin CharNo ratings yet
- Dizziness - Vertigo and HomoeopathyDocument38 pagesDizziness - Vertigo and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD HomNo ratings yet
- Sutter Health may cancel up to 90k vaccine appointments due to low supplyDocument2 pagesSutter Health may cancel up to 90k vaccine appointments due to low supplyAryan PgzNo ratings yet
- Running Head: DRUG PROBLEMDocument38 pagesRunning Head: DRUG PROBLEMHassan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Medical Leave CertificatesDocument4 pagesMedical Leave CertificatesDhana LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Indipendent Short TermDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Indipendent Short TermKenneth PoncialNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris KeperawatanDocument6 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris KeperawatanIndah PermatasariNo ratings yet
- Institutional Biosafety Committee: Role of TheDocument14 pagesInstitutional Biosafety Committee: Role of TheSyeda Wardah NoorNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Stress PDFDocument30 pagesMetabolic Stress PDFNurul Latifa MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Persuasive SpeechDocument4 pagesPersuasive Speechapi-437996036No ratings yet
- Shalini Tummala ResumeDocument2 pagesShalini Tummala Resumeapi-385467850No ratings yet
- Acute Purulent Diseases of Fingers and HandDocument9 pagesAcute Purulent Diseases of Fingers and Handvem_nikhil4uNo ratings yet
- Veinuino RiceDocument10 pagesVeinuino RiceAshley NacarNo ratings yet