Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GRSRG
Uploaded by
Pranjal SinghOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GRSRG
Uploaded by
Pranjal SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
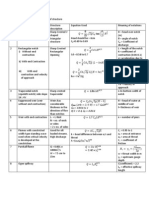
Particles in Water: Settling
CD
24
NR
NR
v S .d
(For NR < 1)
4 ( ) d
4 ( ) d
vS2 .g. p
.
.g. p
.
.vs d
3
CD 3
24.
g ( p ) d 2
vS
.
18
For circular particles:
vS
4 ( p ) d
.g.
.
3
CD
CD
18.5
( N R ) 0 .6
For NR values of 1 - 1000
Particles in Water: Scouring: Re-suspension of settled particles in flowing water
s
.d
vsc 4. g.
Intake
b
Inlet Channel
Inlet Channel:
h
b
No particle <2.5 mm in diameter must settle in the
inlet channel
s
.d
Vsc of 2.5 mm particle = 4. g.
Q = Design flow
b = Channel width
h = depth of flow
S = channel slope
A = flow cross section
VH = flow velocity
4. 9.81.
(2650 1000)
.(0.0025) 0.805 m/s
1000
VH > Vsc
Silt Excluder: To remove particles up to 0.25 mm in diameter
Vsc (0.25 mm particles) = 0.254 ms-1; Thus, VH < Vsc
1.5L
L
Inlet Channel
Sludge
b
B
Plan
0.25 m
H
h
h1
0.25 m
Hw
Elevation
0.25 m
Sludge
Primary Sedimentation Tank
(To remove particles up to 20 m size completely)
Inlet Channel
Baffle
Scum Remover
Settling Zone
Sludge
Effluent
Launder
Primary Sedimentation Tank (PST): Design Theory
Objective: To remove particles up to 20 m size completely.
Vsc = 0.072 m s-1;
Vs = 3.56 x 10-4 m s-1
Detention Time (T) = average time for which water stays in the tank = V/Q
V = Volume of the tank;
Q = Flowrate
Surface overflow rate (SOR) = Q/As; As = surface area of the tank
For a rectangular tank, L = length, B = width; D = depth
SOR = Q/(L.B);
Detention time (T) = V/Q = D/Vs = (L.B.D)/Q
Vs = Q/(L.B) = Q/As;
In a rectangular sedimentation tank, the critical settling velocity is always numerically equal to the SOR
For a 20 m particle, Vs = 3.56 x 10-4 m s-1, i.e., SOR = 30.77 m3/m2/d
A PST is generally designed with SOR of 30-50 m3/m2/d
VH = Q/(B.D); VH < Vsc
You might also like
- M303, Fluid MEchanics FM - M III P.P. Binu & Sunand CDocument21 pagesM303, Fluid MEchanics FM - M III P.P. Binu & Sunand CPremjith SugunanNo ratings yet
- Primary Sedimentation Tank DesignDocument42 pagesPrimary Sedimentation Tank DesignRohab100% (1)
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Design of Siphon Hydraulic, Irrigation SystemDocument8 pagesDesign of Siphon Hydraulic, Irrigation SystemRommel Carlo Largado100% (1)
- Sedimentation Sanitary Engineering-Lecture4-2003Document41 pagesSedimentation Sanitary Engineering-Lecture4-2003motuz adamNo ratings yet
- Annex 30 Tool - Design - Waste Stabilization PondsDocument8 pagesAnnex 30 Tool - Design - Waste Stabilization Pondsmurkeking100% (1)
- Civil Works ExampleDocument52 pagesCivil Works ExampleSushmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- WTP Design 3.12 MLDDocument21 pagesWTP Design 3.12 MLDSandeep VaishnavNo ratings yet
- SedimentationDocument26 pagesSedimentationDavid Charles Meissner100% (1)
- Jack WellDocument2 pagesJack Welldpk60% (5)
- Complete Water Supply Treatment PlantDocument27 pagesComplete Water Supply Treatment PlantMario Sajulga Dela Cuadra100% (8)
- FlocculationDocument54 pagesFlocculationSudhir JadhavNo ratings yet
- Pipe Line DesignDocument6 pagesPipe Line DesignanbukgiNo ratings yet
- Hydr-Design of Settling Basin NewDocument36 pagesHydr-Design of Settling Basin NewHendarmin Lubis100% (1)
- 14Document4 pages14dpkNo ratings yet
- Design of Micro Hydro PowerDocument119 pagesDesign of Micro Hydro PowerSufi Shah Hamid Jalali100% (1)
- SedimentationDocument8 pagesSedimentationAnkush AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning and Design of Nitrogen - Stefan RettigDocument33 pagesDimensioning and Design of Nitrogen - Stefan RettigNguyen Phuc PhamNo ratings yet
- Particles in Water: Settling: (For N 1)Document5 pagesParticles in Water: Settling: (For N 1)Pranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- Particles in Water: Settling: d) (4 ⎤ ⎡ ρ − ρ C d .) (. g - 3 4 v ⎥ ⎦ ⎤ ⎢ ⎣ ⎡ ρ ρ − ρ =Document5 pagesParticles in Water: Settling: d) (4 ⎤ ⎡ ρ − ρ C d .) (. g - 3 4 v ⎥ ⎦ ⎤ ⎢ ⎣ ⎡ ρ ρ − ρ =Pranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 8 Grit ChamberDocument31 pagesLECTURE 8 Grit ChamberG. Prasanna50% (2)
- Module - 8 Primary-TreatmentDocument26 pagesModule - 8 Primary-TreatmentARSLAN MASOODNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8aDocument9 pagesLecture 8aPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engg - Water TreatmentDocument14 pagesEnvironmental Engg - Water TreatmenthitkcivilNo ratings yet
- Ecw567-Wastewater SedimentationDocument34 pagesEcw567-Wastewater Sedimentationhanif aiyadNo ratings yet
- Module - 8 Primary-TreatmentDocument26 pagesModule - 8 Primary-TreatmentFaran MasoodNo ratings yet
- Lec 10Document26 pagesLec 10shahid aliNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Management 5Document18 pagesWastewater Management 5Narendra GandhiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 SedimentationDocument6 pagesLecture 4 Sedimentationth3-encyclopediaNo ratings yet
- Bab 3 Desain Grit ChamberDocument8 pagesBab 3 Desain Grit ChamberCat VelNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Lecture 4 EENVDocument35 pagesWater Treatment Lecture 4 EENVEllina TehNo ratings yet
- Topic 6.1 Sewage TreatmentDocument21 pagesTopic 6.1 Sewage TreatmentOmar IsaackNo ratings yet
- Module - 10 Primary-TreatmentDocument26 pagesModule - 10 Primary-TreatmentAdeel AbbasNo ratings yet
- BAB IV PBPAM Lusi RevisiDocument31 pagesBAB IV PBPAM Lusi RevisiNaufal D WidjayaNo ratings yet
- 3 KSU SedimentationDocument26 pages3 KSU SedimentationDeivys Ramirez SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Coefficient of Discharge Test.Document9 pagesCoefficient of Discharge Test.AhmadGhanemNo ratings yet
- P1175-Discharge Flow-R2Document6 pagesP1175-Discharge Flow-R2Zack ZakariaNo ratings yet
- 5.6 SedimentationDocument26 pages5.6 SedimentationMd. Habibur Rahman Bejoy Khan ,155408No ratings yet
- Ws Design CourseDocument70 pagesWs Design Coursesayed samiullahNo ratings yet
- P P PP P PP P PDocument23 pagesP P PP P PP P PAvinash GoyalNo ratings yet
- W4 - Water Purification-2Document33 pagesW4 - Water Purification-2Ibrahim AdelNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment: Monroe L. Weber-Shirk S Civil Environmental EngineeringDocument80 pagesWater Treatment: Monroe L. Weber-Shirk S Civil Environmental EngineeringamoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Labarotary Workbook Record CUSAT PSRTDocument16 pagesFluid Mechanics Labarotary Workbook Record CUSAT PSRTArjun Satheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit IvDocument20 pagesUnit IvArwaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Flow Through Orifices and MouthpiecesDocument44 pagesChapter One: Flow Through Orifices and MouthpiecesGetahun TukaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Water & WastewaterDocument40 pagesTreatment of Water & WastewaterAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Dip - Orifices and Mouth PiecesDocument19 pagesDip - Orifices and Mouth PiecesDan KiswiliNo ratings yet
- Tray ColumnDocument24 pagesTray ColumnGokulraj MNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 SedimentationDocument6 pagesLecture 4 Sedimentationdania alnajiNo ratings yet
- Flow Over Weir ExperimentDocument3 pagesFlow Over Weir ExperimentcsyahirnNo ratings yet
- Discharge of WeirsDocument8 pagesDischarge of WeirsUnknownNo ratings yet
- Flow of Water by Notch and WeirsDocument15 pagesFlow of Water by Notch and WeirsAngelica Joyce BenitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3D (Sedimentation)Document18 pagesChapter 3D (Sedimentation)Syamim BakriNo ratings yet
- Discharge Over Various Types of StructureDocument2 pagesDischarge Over Various Types of StructureSunil DuwalNo ratings yet
- Orifice and MouthpieceDocument8 pagesOrifice and MouthpieceAdithya MathivananNo ratings yet
- Time To Empty Out Vessel No Dished EndsDocument2 pagesTime To Empty Out Vessel No Dished Endsbb.tiwari100% (1)
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Sewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionFrom EverandSewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in Fluid Mechanics with Sensitivities to Governing VariablesFrom EverandCase Studies in Fluid Mechanics with Sensitivities to Governing VariablesNo ratings yet
- Upto Silit ExcluderDocument4 pagesUpto Silit ExcluderPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8aDocument9 pagesLecture 8aPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- Branding & Brand Equity in B2B Market - Case Of: TatasteelDocument26 pagesBranding & Brand Equity in B2B Market - Case Of: TatasteelPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing by Design: Group-1 Mude Veera Bramhendra Naik Shweta Srivastava Manju Yadav Kuldeep Merottha Vijay DevraDocument25 pagesManufacturing by Design: Group-1 Mude Veera Bramhendra Naik Shweta Srivastava Manju Yadav Kuldeep Merottha Vijay DevraPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- Sand, Silt and Clay: Humic SubstancesDocument4 pagesSand, Silt and Clay: Humic SubstancesPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- Capacity Strategies For The 1980sDocument22 pagesCapacity Strategies For The 1980sPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- FGNGDocument45 pagesFGNGPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- Group 8: Harsh Faujdar Lakshay Idiwal Rittik Mondal Sachit Aggrawal Ujjwal PorwalDocument30 pagesGroup 8: Harsh Faujdar Lakshay Idiwal Rittik Mondal Sachit Aggrawal Ujjwal PorwalPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- CVFDDVDocument2 pagesCVFDDVPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- JR) PT-02 Date: 12-10-2014: Test SyllabusDocument64 pagesJR) PT-02 Date: 12-10-2014: Test SyllabusPranjal SinghNo ratings yet
- MBA 623 A - Points Distribution - 1. 2 X Quizzes (2 X 10) 20 PointsDocument1 pageMBA 623 A - Points Distribution - 1. 2 X Quizzes (2 X 10) 20 PointsPranjal SinghNo ratings yet