Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Middle Adulthood Ppts - 11-23-2015
Uploaded by
api-302104260Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Middle Adulthood Ppts - 11-23-2015
Uploaded by
api-302104260Copyright:
Available Formats
What to expect during
middle adulthood
What is middle adulthood?
Middle
adulthood is the age period in which
you gain and lose, as well as the biological
and sociocultural factors that balance each
other.
Usually
starts around forty to forty-five
years and last until about sixty to sixty-five
years.
Why study middle adulthood?
Developmentalist
study middle age
because of the dramatic increase in the
number of individuals entering this
period of life span.
Changes in middle adulthood include:
Physical
Cognitive
Careers,
Work, and Leisure
Religion,
Spirituality, and Meaning in
Life
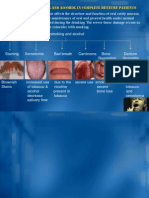
Physical development in middle adulthood:
The
changes you face during middle
adulthood are usually gradual.
Changes
include wrinkles, age spots, decrease
in height, increase in weight, strength, joints,
bones, vision, hearing, lungs, and sleep.
Your
physical appearance inside and out can
change.
Physical development in middle adulthood:
You
can face many problems including your
health, disease, stress, and control.
You
are less susceptible to colds and
allergies, and frequency of accidents
decline.
Arthritis
is the leading chronic disorder in
middle age, followed my hypertension.
Physical development in middle adulthood:
Your
immune system functioning declines with aging
Chronic
diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and
cancer are the main causes of death.
For
women, menopause is an important marker
because it is the end of childbearing capability (Male
menopause does not occur)
Once entering middle adulthood, sexual behavior
occurs less frequently.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jTarGavG4cM
Cognitive development in middle adulthood:
Your intelligence and information process can be effected when
entering middle adulthood.
Developmentalist Horn stated that there are two different types of
intelligence; crystallized intelligence and fluid intelligence. Crystallized
intelligence is accumulated information and verbal skills which
continues to increase in middle adulthood whereas fluid intelligence is
ability to reason abstractly which begins to decline.
Your speed of information processing and reaction time continues to
decline in middle adulthood.
Cognitive development in middle adulthood:
Developmentalist Schaie found that verbal memory increases in middle
age, but others found that memory declines in middle age.
Researchers found that not only does your working memory decline,
but also that your memory can decline when individuals do not use
effective strategies.
Expertise can also be a factor. Expertise is having an extensive and
highly organized knowledge and an understanding of a particular
domain. Expertise is known to increase during middle adulthood, but
then declines in late adulthood.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xs1kzLLXTgA
Careers, Work, and Leisure in Middle Adulthood:
For
many people, midlife is a time of
reflection, assessment, and evaluation
of their current work.
During
midlife, many people ask
themselves what are their plans for the
future.
Careers, Work, and Leisure in Middle Adulthood:
One issue that many individuals have is whether they want to continue
doing the type of work they do currently, or change their job or career.
Problems in working include globalization of work, development in
information technology, downsizing in organizations, retirement,
pensions, and health care.
Though midlife job or career changes are usually by choice, they can
also sometimes be forced on a given individual.
Careers, Work, and Leisure in Middle Adulthood:
During
midlife, you need to learn how to
enjoy leisure.
Many
say midlife could be one of the most
important times for leisure because of all the
physical changes you have to encounter.
Leisure
can be important during midlife as
you prepare for an active retirement.
Religion, Spirituality, and Meaning in Life in Middle
Adulthood:
Though
women show a stronger interest in religion and
spirituality, it is important to many Americans lives.
Some
researchers found that spirituality and religion
can be negatively linked to physical health, while in
mainstream religions, researchers say religion is
positively related to health.
Meaning
ways.
in life can affect an individual in different
Religion, Spirituality, and Meaning in Life in Middle Adulthood:
Facing
the death of older relatives can show the
less time to live for themselves.
Many
midlife-aged individuals examines their life
meaning.
Baumeister
and Vohs argue that a quest for
meaningful life involves fulfilling four main needs.
Those four main needs include purpose, values,
efficacy, and self-worth.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XUKyJVgGG2Q
Citations:
Feldman, Robert. "Middle Adulthood: Physical & Cognitive
Development." Middle Adulthood: Physical & Cognitive Development.
N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Oct. 2015.
Santrock, John W. A Topical Approach to Life-span Development.
Fifteenth ed. N.p.: McGraw-Hill Education LLC, 2015. Print.
"Chapter 15 Physical and Cognitive Development in Middle Adulthood."
Chapter 15 Physical and Cognitive Development in Middle Adulthood.
N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Oct. 2015.
"Physical Development in Adulthood - Boundless Open Textbook."
Boundless. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Oct. 2015.
You might also like
- The Longevity Code: Unlocking the Secrets to a Long, Healthier, Vibrant, Happier Life Beyond 100From EverandThe Longevity Code: Unlocking the Secrets to a Long, Healthier, Vibrant, Happier Life Beyond 100No ratings yet
- Case Study On LeukemiaDocument33 pagesCase Study On LeukemiaBhupesh PatidarNo ratings yet
- PSYC FP3210 AntonioRachel Assessment7 Attempt1Document6 pagesPSYC FP3210 AntonioRachel Assessment7 Attempt1danielBookerNo ratings yet
- PsychologyDocument12 pagesPsychologybronz3 tigr3No ratings yet
- Late Adulthood: Characteristics, Developmental Tasks, Ageing and AgeismDocument12 pagesLate Adulthood: Characteristics, Developmental Tasks, Ageing and AgeismkikiNo ratings yet
- Week 17 - AdulthoodDocument19 pagesWeek 17 - AdulthoodPaul DeliyosNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Personality DevelopmentDocument6 pagesUnit 1. Personality DevelopmentKarthi Keyan VeeraNo ratings yet
- UNIT THREE Final Area Adult AgeDocument46 pagesUNIT THREE Final Area Adult Agemoy topoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Physical Cognitive and Socioemotional Development in Middle AdulthoodDocument36 pagesChapter 10 Physical Cognitive and Socioemotional Development in Middle Adulthoodranieestrella12No ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument7 pagesDevelopmental PsychologyAengewycaNo ratings yet
- Adulthood and Ageing (221 KB)Document9 pagesAdulthood and Ageing (221 KB)Praveen Kumar ThotaNo ratings yet
- Physical and Cognitive Development in Middle AdulthoodDocument2 pagesPhysical and Cognitive Development in Middle Adulthoodzahasher100% (1)
- Dev Psych - Module 1Document7 pagesDev Psych - Module 1The Lyric ListsNo ratings yet
- Adulthood and AgingDocument16 pagesAdulthood and AgingRafieq YazidNo ratings yet
- Holistic Health and Health DimensionsDocument19 pagesHolistic Health and Health DimensionsRoniell YapNo ratings yet
- Real ThesisDocument40 pagesReal ThesisEtherious Natsu DragneelNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Middle AdulthoodDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Middle Adulthoodafeazleae100% (1)
- Early AdulthoodDocument5 pagesEarly AdulthoodMarienuelle AquinoNo ratings yet
- HEALTHDocument4 pagesHEALTHGarcia, Danna EliseNo ratings yet
- Old AgeDocument7 pagesOld AgeM TAQQINo ratings yet
- Cognitive Development in Middle AdulthoodDocument16 pagesCognitive Development in Middle Adulthoodabhinav yadavNo ratings yet
- Module 22: Developing Into Adulthood: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pagesModule 22: Developing Into Adulthood: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 6 On Middle AdulthoodDocument8 pagesModule 6 On Middle AdulthoodRaquel CantosNo ratings yet
- MIDDLE-ADULTHOODDocument6 pagesMIDDLE-ADULTHOODNoelen Matienzo PosadaNo ratings yet
- Practical Report LSD - Aryan Malik - 20-3017Document11 pagesPractical Report LSD - Aryan Malik - 20-3017swati meherNo ratings yet
- Middle Adulthood HE BrochureDocument4 pagesMiddle Adulthood HE Brochuretony montanNo ratings yet
- Middle AgeDocument23 pagesMiddle AgeosamaNo ratings yet
- Personal HealthDocument42 pagesPersonal Healthninideli51No ratings yet
- Mental Health and Well-Being in Middle and Late AdolescenceDocument3 pagesMental Health and Well-Being in Middle and Late AdolescenceAndrei NicoleNo ratings yet
- CHCCCS023 Support Independence and WellbeingDocument22 pagesCHCCCS023 Support Independence and WellbeingSushma karkiNo ratings yet
- Purpose and Meaning in Old Age: WisdomDocument2 pagesPurpose and Meaning in Old Age: WisdomTalluri Keerthana RajNo ratings yet
- What Is The Definition of Successful Aging?: Staying Healthy As You AgeDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Definition of Successful Aging?: Staying Healthy As You Agemarianistor1410No ratings yet
- Health Education for Young Adults: A Community Outreach ProgramFrom EverandHealth Education for Young Adults: A Community Outreach ProgramNo ratings yet
- The Human Program in The Midst of Time: by Khodor Khalil Saad " "Document29 pagesThe Human Program in The Midst of Time: by Khodor Khalil Saad " "khodorsaadNo ratings yet
- Middle and Late Adulthood StageDocument2 pagesMiddle and Late Adulthood StageSATOR DOMINICNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument20 pagesDevelopmental PsychologyMobin AlamNo ratings yet
- What Is Late AdulthoodDocument2 pagesWhat Is Late AdulthoodbeanieNo ratings yet
- Advance Developmental Psychology REFLECTIONDocument2 pagesAdvance Developmental Psychology REFLECTIONTopaz Stone GimedaNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Personal Developement 12Document14 pagesWeek 4 Personal Developement 12Charles PabalateNo ratings yet
- Why Am I Here?Document4 pagesWhy Am I Here?amilcarsoaresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Dev PsychDocument14 pagesLesson 1 Dev PsychJemely ButronNo ratings yet
- Envejecimiento Saludable A Través de Las Etapas Del EnvejecimientoDocument10 pagesEnvejecimiento Saludable A Través de Las Etapas Del EnvejecimientoAlejandro GuzmanNo ratings yet
- CH.9 Psychology and SportsDocument6 pagesCH.9 Psychology and SportsDhruv GuptaNo ratings yet
- Early Adulthood - Written ReportDocument16 pagesEarly Adulthood - Written ReportCHRISTINE KYLE CIPRIANONo ratings yet
- Older AdultsDocument10 pagesOlder AdultsMia Grace GarciaNo ratings yet
- Qol, QWL, HealthDocument3 pagesQol, QWL, Healthgussugyono 17No ratings yet
- Lifespan Development 09 Middle AdulthoodDocument41 pagesLifespan Development 09 Middle AdulthoodJordan CarinuganNo ratings yet
- Development Middle Adulthood ADocument11 pagesDevelopment Middle Adulthood AJorge BulitNo ratings yet
- Cop Module1 PDFDocument33 pagesCop Module1 PDFAmber Mae L. DeocampoNo ratings yet
- L.4 Health Needs and Problems of AdultsDocument43 pagesL.4 Health Needs and Problems of AdultsMunira SulimanNo ratings yet
- Health First GradingDocument9 pagesHealth First GradingRoen RamonalNo ratings yet
- Stages of Human Development: Infancy and ChildhoodDocument2 pagesStages of Human Development: Infancy and ChildhoodchubbychubzNo ratings yet
- Psychology ArticleDocument3 pagesPsychology ArticleNadeem KianiNo ratings yet
- Adolescence: Physical and Cognitive Development: Villanueva BarbosaDocument33 pagesAdolescence: Physical and Cognitive Development: Villanueva BarbosaRia り あ Hitsugaya100% (1)
- Cognitive Changes in Adulthood and Old AgeDocument8 pagesCognitive Changes in Adulthood and Old AgeNam JesusNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument11 pagesDevelopmental Psychologyadiba KhanNo ratings yet
- 5.0 Family Functions Over The Lifespan: Birth To Death, Hereafter-Rituals Surrounding DeathDocument9 pages5.0 Family Functions Over The Lifespan: Birth To Death, Hereafter-Rituals Surrounding DeathMchere AnkkhemNo ratings yet
- Middle AdulthoodDocument6 pagesMiddle AdulthoodKiel AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Running Head: HEALTH EDUCATION 1Document10 pagesRunning Head: HEALTH EDUCATION 1Sammy GitauNo ratings yet
- The PartographDocument45 pagesThe PartographKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Summary of AB236 AmendmentsDocument9 pagesSummary of AB236 AmendmentsMichelle Rindels100% (1)
- Physiology Practical 2: Toad HeartDocument10 pagesPhysiology Practical 2: Toad HeartAdams OdanjiNo ratings yet
- Tugas 2Document17 pagesTugas 2NuretikaSalmiaNo ratings yet
- Connections Issue 11Document21 pagesConnections Issue 11Victoria University, Melbourne, AustraliaNo ratings yet
- L 65 - Prevention of Fire and Explosion, and Emergency Response On Offshore Installations - Approved Code of Practice and Guidance - HSE - 2010Document56 pagesL 65 - Prevention of Fire and Explosion, and Emergency Response On Offshore Installations - Approved Code of Practice and Guidance - HSE - 2010Barkat UllahNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mohamed Ali Hamedh - DKA - 2023Document25 pagesDr. Mohamed Ali Hamedh - DKA - 2023ÁýáFáŕőúgNo ratings yet
- Medical Equipment Quality Assurance (Tobey Clark, U Vermont)Document151 pagesMedical Equipment Quality Assurance (Tobey Clark, U Vermont)MelissaBarriosUrcia100% (2)
- Gastro-Intestinal Tract: Entamoeba HistolyticaDocument25 pagesGastro-Intestinal Tract: Entamoeba Histolyticanh2411No ratings yet
- CPT CODING Power PointDocument24 pagesCPT CODING Power PointJack100% (1)
- Peplu Theory ApplicationDocument7 pagesPeplu Theory ApplicationVarsha Gurung100% (1)
- Book Review Contemporary Public Administration (2021) PDFDocument119 pagesBook Review Contemporary Public Administration (2021) PDFTiyas Vika WidyastutiNo ratings yet
- Pts 1 Klas XI 2022 (Print)Document11 pagesPts 1 Klas XI 2022 (Print)WoldiaNo ratings yet
- Course 1.2: What You Should KnowDocument27 pagesCourse 1.2: What You Should KnowGeorgios MilitsisNo ratings yet
- The Superheroes of PharmaDocument13 pagesThe Superheroes of PharmaMPANo ratings yet
- Malaysia School ImmunizationDocument41 pagesMalaysia School ImmunizationKalai ArikaranNo ratings yet
- Caz 4Document17 pagesCaz 4Marinela MeliszekNo ratings yet
- Punjab General Industries Private Limited: Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment (HIRA)Document9 pagesPunjab General Industries Private Limited: Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment (HIRA)Rohit VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Patient Teaching Checklist: TB Skin Test (Mantoux) Fact Sheet TB Blood Test (IGRA) Fact SheetDocument2 pagesTuberculosis Patient Teaching Checklist: TB Skin Test (Mantoux) Fact Sheet TB Blood Test (IGRA) Fact SheetDaniel GarratonNo ratings yet
- Applying 5S ProceduresDocument70 pagesApplying 5S ProceduresSanta Best100% (3)
- Literature Review On DVTDocument4 pagesLiterature Review On DVTaflsdefaq100% (1)
- ToothpasteDocument6 pagesToothpasteNelly SuriamahNo ratings yet
- Bereavement SupportDocument26 pagesBereavement SupportAdiAri RosiuNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument62 pagesPreviewpdfImtiazAhmedNo ratings yet
- Effects of Smoking and Alcohol On Complete Denture PatientsDocument2 pagesEffects of Smoking and Alcohol On Complete Denture PatientsAshwin ThejaswiNo ratings yet
- CelecoxibDocument2 pagesCelecoxibXtinegoNo ratings yet
- RabiesDocument190 pagesRabiesIr Ardy YusriawanNo ratings yet
- Employees' State Insurance Corporation E-Pehchan Card: Insured Person: Insurance No.: Date of RegistrationDocument3 pagesEmployees' State Insurance Corporation E-Pehchan Card: Insured Person: Insurance No.: Date of RegistrationSaikatNo ratings yet
- Skema Modul Skor A+ Bab 5Document8 pagesSkema Modul Skor A+ Bab 5Siti MuslihahNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord Blood BankingDocument290 pagesUmbilical Cord Blood BankingcmNo ratings yet