Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12 Plant Study
Uploaded by
api-302664410Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12 Plant Study
Uploaded by
api-302664410Copyright:
Available Formats
EXPERIMENT NO.
AIM:
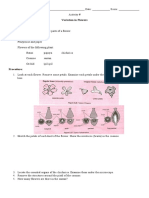
To compare the external features of monocot and dicot plants.
THEORY:
Angiosperms or flowering plants are the most dominant plants on
the earth. They are divided into two major groups, namely
monocots and dicots. Seeds of monocots, as the name suggests,
have one cotyledon and those of dicots have two. Besides this
major difference, there are many other distinct differences in
their morphological and anatomical features. Such features
enable us to differentiate between monocots and dicots even
when their seeds are not available to check the number of
cotyledons. In this experiment, we intend to make a comparison
of external features of monocot and dicot plants.
MATERIALS REQUIRED:
Plants of Hibiscus/rose/Petunia/pea and grass/maize/bamboo/lily/
Chlorophytum/any other ornamental herb with flowers and fruits,
simple or dissecting microscope, a hand lens, slide, cover slip,
and a razor blade.
PROCEDURE:
1. From the list given above, select a dicot and a monocot plant
with roots, leaves, flowers, and fruits.
2. Observe the differences in the external features of stem, leaf,
roots, flowers, and seeds. To study the root system, wash the
roots carefully and spread them on a sheet of paper and study
their nature.
3. Study the leaves for their shape and venation.
4. Carefully observe the flower and identify the different floral
parts. Count the number of sepals, petals and stamens in the
flower. Take a transverse section of ovary and count the
number of carpels.
5. Remove the seed coat and count the number of cotyledons.
6. Note down your observations; draw diagrams of all the parts
you have studied.
OBSERVATIONS:
Some important features that distinguish a monocot and a dicot
plant are listed in the table given below. You may observe some
more features of difference between them. Record your
observations.
Sl.No.
Feature
Monocot
Dicot
1.
Roots: fibrous/tap root
2.
Leaf shape: broad/narrow
3.
Leaf venation: parallel/reticulate
4.
Floral parts: multiple of 3 or 5
5.
Sepals: number and colour
6.
Petals: number and colour
7.
Stamen: number
8.
Pistil: number of carpels
9.
Cotyledon: one or two
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION:
The study reveals many differences between dicot and
monocot plants. The distinctive features are consistently seen
in most other plants belonging to these groups.
QUESTIONS:
How do we differentiate betwen fibrous root system and taproot system?
A plant has leaves with reticulate venation and floral parts
consisting of 5 sepals, 5 petals, 5 stamens, and 5 carpels. In
which group of angiosperms would you place this plant? Give
reasons.
In a plant, name two features which you would examine to
categorise it into a monocot or a dicot plant.
Do all flowers have all the floral parts? Explore.
You might also like
- BIOLO001plants Parts and Function EditedDocument18 pagesBIOLO001plants Parts and Function EditedChristine angel mae BalsomoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - The Body of PlantsDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 - The Body of PlantsEuge Acbang PeñarubiaNo ratings yet
- Biology M7 Plant Parts & FunctionsDocument22 pagesBiology M7 Plant Parts & FunctionsSheila Pardines100% (4)
- Comparing Monocots and Dicots LabDocument2 pagesComparing Monocots and Dicots Labapi-269733681No ratings yet
- Activity 7 Angiosperm Plant BodyDocument13 pagesActivity 7 Angiosperm Plant BodyHerlyn SabulaanNo ratings yet
- Biology - Lab Report 7 and 8Document6 pagesBiology - Lab Report 7 and 8Unnati NihalaniNo ratings yet
- Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and SeedsDocument5 pagesAngiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and SeedsAurora ÇizmjaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and MorphologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and MorphologyminichelNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 MONOCOT AND DICOTDocument3 pagesExperiment 2 MONOCOT AND DICOTmary antonette pagal100% (1)
- VERANO - The Body of PlantsDocument5 pagesVERANO - The Body of PlantsColleen VeranoNo ratings yet
- Task Biology Monocotile and Dicotile: Sma Negeri 1 Bojonegoro School YearDocument17 pagesTask Biology Monocotile and Dicotile: Sma Negeri 1 Bojonegoro School YearSaifulHadiNo ratings yet
- Monocot Dicot ColoringDocument3 pagesMonocot Dicot ColoringdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Monocot and Dicot IdentificationDocument3 pagesMonocot and Dicot IdentificationMaria Gizelle DecenaNo ratings yet
- LEAVES Lab ActDocument12 pagesLEAVES Lab ActJoses CalindasNo ratings yet
- Monocot Dicot ColoringDocument3 pagesMonocot Dicot ColoringMashgol KarimNo ratings yet
- Daryl GuinayenDocument9 pagesDaryl GuinayenEmmanuel GallidoNo ratings yet
- Monocots Vs Dicots LabDocument2 pagesMonocots Vs Dicots LabCaselyn ButayNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationDocument7 pagesI. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationBethymay EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Siti Aishah Binti Abdul LatiffDocument1 pageSiti Aishah Binti Abdul Latiffaesha89No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument12 pagesLesson Plan Morphology of Flowering PlantsSHILPA AGARWAL100% (1)
- Morphology of Flowering Plants - Structure of Flowering PlantDocument5 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants - Structure of Flowering Plantmohammed amaan paNo ratings yet
- SBA #6 - Surface Area of A LeafDocument5 pagesSBA #6 - Surface Area of A LeaflucyNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1645490440596 6901687136957622992Document6 pagesOrca Share Media1645490440596 6901687136957622992Kelly CasterNo ratings yet
- Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My!: TeksDocument10 pagesRoots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My!: TeksagapolusNo ratings yet
- Flower VariationDocument2 pagesFlower VariationRuchi Briam James LagitnayNo ratings yet
- FLPMCTN 12686Document2 pagesFLPMCTN 12686LalaNo ratings yet
- Intro To PlantsDocument33 pagesIntro To PlantsBALQIS NURAZIZAHNo ratings yet
- 3rd UNIT EXAMDocument3 pages3rd UNIT EXAMisabel lopezNo ratings yet
- Agr 516 - Laboratory ManualDocument20 pagesAgr 516 - Laboratory ManualAiman WafiyNo ratings yet
- Agr122 Lab Report 2Document11 pagesAgr122 Lab Report 2Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- 2nd Practical Study GuideDocument2 pages2nd Practical Study GuidejaypdemarcoNo ratings yet
- Growing Plants Without SeedsDocument9 pagesGrowing Plants Without Seedschristian capunongNo ratings yet
- Activity Guide - 4Document3 pagesActivity Guide - 4giocarlo.tiblaniNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study CheckDocument2 pagesExam 1 Study Checkpam481475107No ratings yet
- Lesson 12.1Document13 pagesLesson 12.1Chrise RajNo ratings yet
- Act. 1 Agri-FisheryDocument6 pagesAct. 1 Agri-FisheryBenissa PepitoNo ratings yet
- B L R D P: F, F, S: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesB L R D P: F, F, S: ObjectivesJorelyn Giron NaniongNo ratings yet
- FBS 101.forest Botany: Undag, Vens Ric V. BSF-1Document8 pagesFBS 101.forest Botany: Undag, Vens Ric V. BSF-1VENS RIC VIOS UNDAGNo ratings yet
- Monocot vs. DicotDocument2 pagesMonocot vs. DicotRonalynNo ratings yet
- Plant Dissection LabDocument9 pagesPlant Dissection Labmischa.noelleNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - StomataDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - StomataSumit BissuNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 12 Botany LabDocument3 pagesEXERCISE 12 Botany Labzara ryleNo ratings yet
- 5e Flower Dissection Investigation - Spring 2016Document3 pages5e Flower Dissection Investigation - Spring 2016api-309653899No ratings yet
- Monocots and Dicots: Chart Showing Differences Monocot DicotDocument3 pagesMonocots and Dicots: Chart Showing Differences Monocot DicotCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Flowers and Fruits WorksheetDocument8 pagesFlowers and Fruits WorksheetfatimaNo ratings yet
- Flower LabDocument2 pagesFlower LabDeanna-Danny ThomasonNo ratings yet
- Plant Organ - Lab - Rayan AliDocument16 pagesPlant Organ - Lab - Rayan AliRayan AliNo ratings yet
- Group 2-Excercise 2Document9 pagesGroup 2-Excercise 2James Carbonell Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Act.2-Leaves and StemDocument2 pagesAct.2-Leaves and StemMa Josella SalesNo ratings yet
- Group 2-Excercise 2Document10 pagesGroup 2-Excercise 2James Carbonell Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Day 4Document23 pagesDay 4api-3759646No ratings yet
- Getting To Know PlantsDocument8 pagesGetting To Know PlantsHappy HomeNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Flower! Flower Dissection L. IntroductionDocument3 pagesParts of A Flower! Flower Dissection L. IntroductionDaryl Boldios LoterteNo ratings yet
- World of Plants WebquestDocument4 pagesWorld of Plants Webquestapi-169639475100% (1)
- Systematic ACTIVITY2Document2 pagesSystematic ACTIVITY2Rosie RoseNo ratings yet
- Flower Dissection Lab: Peduncle, Head, Ray Flower and Bracts (Modified Leaves at The Base of The Composite Flower)Document4 pagesFlower Dissection Lab: Peduncle, Head, Ray Flower and Bracts (Modified Leaves at The Base of The Composite Flower)Joanica Mae G. VeraNo ratings yet
- 1 - Plant Characteristics WorksheetDocument6 pages1 - Plant Characteristics WorksheetArminda Annabelle BangksNo ratings yet
- Suggestions On How To Prepare The PortfolioDocument2 pagesSuggestions On How To Prepare The PortfolioPeter Pitas DalocdocNo ratings yet
- LNWH Alcohol GUIDELINE SUMMARY 2018Document1 pageLNWH Alcohol GUIDELINE SUMMARY 2018Ai Hwa LimNo ratings yet
- C7.5 Lecture 18: The Schwarzschild Solution 5: Black Holes, White Holes, WormholesDocument13 pagesC7.5 Lecture 18: The Schwarzschild Solution 5: Black Holes, White Holes, WormholesBhat SaqibNo ratings yet
- Qualification of Class Y Flip Chip Cga Package Technology For SpaceDocument8 pagesQualification of Class Y Flip Chip Cga Package Technology For SpacePepe ChorizoNo ratings yet
- N164.UCPE12B LANmark - OF - UC - 12x - Singlemode - 9 - 125 - OS2 - PE - BlackDocument2 pagesN164.UCPE12B LANmark - OF - UC - 12x - Singlemode - 9 - 125 - OS2 - PE - BlackRaniaTortueNo ratings yet
- Technology in Society: SciencedirectDocument10 pagesTechnology in Society: SciencedirectVARGAS MEDINA ALEJANDRANo ratings yet
- Evolution of Management AccountingDocument35 pagesEvolution of Management AccountingNuqiah Fathiah Seri100% (1)
- TSR 9440 - Ruined KingdomsDocument128 pagesTSR 9440 - Ruined KingdomsJulien Noblet100% (15)
- Installation, Operation & Maintenance Manual - Original VersionDocument11 pagesInstallation, Operation & Maintenance Manual - Original VersionAli AafaaqNo ratings yet
- Venere Jeanne Kaufman: July 6 1947 November 5 2011Document7 pagesVenere Jeanne Kaufman: July 6 1947 November 5 2011eastendedgeNo ratings yet
- Using Ms-Dos 6.22Document1,053 pagesUsing Ms-Dos 6.22lorimer78100% (3)
- SchedulingDocument47 pagesSchedulingKonark PatelNo ratings yet
- Aits 2122 PT I Jeea 2022 TD Paper 2 SolDocument14 pagesAits 2122 PT I Jeea 2022 TD Paper 2 SolSoumodeep NayakNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human MovementDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Human MovementNiema Tejano FloroNo ratings yet
- Theory of Construction of The Giza Plateau Pyramids (Original Title Hypothesis of Construction of The Pyramids of The Valley of Gizeh (Giza)Document15 pagesTheory of Construction of The Giza Plateau Pyramids (Original Title Hypothesis of Construction of The Pyramids of The Valley of Gizeh (Giza)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Unix SapDocument4 pagesUnix SapsatyavaninaiduNo ratings yet
- Aryan Civilization and Invasion TheoryDocument60 pagesAryan Civilization and Invasion TheorySaleh Mohammad Tarif 1912343630No ratings yet
- Old Man and The SeaDocument10 pagesOld Man and The SeaXain RanaNo ratings yet
- Sip Poblacion 2019 2021 Revised Latest UpdatedDocument17 pagesSip Poblacion 2019 2021 Revised Latest UpdatedANNALLENE MARIELLE FARISCALNo ratings yet
- 20 Ijrerd-C153Document9 pages20 Ijrerd-C153Akmaruddin Bin JofriNo ratings yet
- Study of Subsonic Wind Tunnel and Its Calibration: Pratik V. DedhiaDocument8 pagesStudy of Subsonic Wind Tunnel and Its Calibration: Pratik V. DedhiaPratikDedhia99No ratings yet
- Reviewer CSCDocument22 pagesReviewer CSCChristopher CocalNo ratings yet
- How Do I Predict Event Timing Saturn Nakshatra PDFDocument5 pagesHow Do I Predict Event Timing Saturn Nakshatra PDFpiyushNo ratings yet
- Ryff's Six-Factor Model of Psychological Well-BeingDocument7 pagesRyff's Six-Factor Model of Psychological Well-BeingYogi Sastrawan100% (1)
- Annotated Bibliography 2Document3 pagesAnnotated Bibliography 2api-458997989No ratings yet
- A List of 142 Adjectives To Learn For Success in The TOEFLDocument4 pagesA List of 142 Adjectives To Learn For Success in The TOEFLchintyaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Policy in IndonesiaDocument23 pagesCurriculum Policy in IndonesiaEma MardiahNo ratings yet
- AJ IntroductionDocument31 pagesAJ IntroductiontrollergamehuydkNo ratings yet
- Award Presentation Speech PDFDocument3 pagesAward Presentation Speech PDFNehal RaiNo ratings yet
- Basics of Petroleum GeologyDocument23 pagesBasics of Petroleum GeologyShahnawaz MustafaNo ratings yet