Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Knock Sensor
Uploaded by
Tommy Tribbiani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
184 views1 pagedensknock
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdensknock
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
184 views1 pageKnock Sensor
Uploaded by
Tommy Tribbianidensknock
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Basic Technology Series
"Sensor Fundamentals"
2nd Session: Knock Sensor
In this session, the knock sensor will be explained.
1 OUTLINE
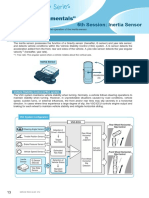
The knock sensor is mounted on the engine block and detects engine knocking.
The engine ECU of the vehicle uses the signal from this sensor to correct the ignition timing.
2 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION
There are two knock sensor types: a resonance knock sensor and a flat (non-resonance) knock sensor.
2-1
Resonance Knock Sensor
When vibration is received from the cylinder block, pressure is added to the piezoceramic plate as the
diaphram of the piezoceramic plate bends around the fulcrum of the cylinder installation point, generating
voltage. When the diaphragm resonates at the frequency specific to knocking, a voltage is output by the
knock sensor, the engine ECU determines that there is knocking.
Construction
External View
Bends due to the vibration
of the cylinder block.
Cylinder
Block Side
Piezoceramic
Plate
Cylinder
Block
Diaphragm
2-2
Piezoceramic
Plate
Diaphragm
Flat (Non-Resonance) Knock Sensor
When vibration is received from the cylinder block, pressure is added to the piezoceramic plate installed
between the base and the weight, generating voltage from the delay in weight movement due to intertial
force. Since this output voltage is almost constant across all frequency bands, the engine ECU detects a more
accurate knocking by detecting the specific frequency at which knocking may occur.
In recent years, this flat (non-resonance) knock sensor has been the most commonly used.
Construction
Weight
Weight
Piezoceramic
Plate
Piezoceramic Plate
Pressurized
by Cylinder
Block Vibration.
Base
Cylinder Block Side
13
External View
SERVICE TECH Vol.486 06-10
Base
Cylinder
Block
You might also like
- XR700 and XR3000: Ignition InspectionDocument20 pagesXR700 and XR3000: Ignition InspectionDevine LightNo ratings yet
- 208 - 1 - 1 Production Line 2009 208 - 1 - 3: Spare Parts For Preventive Maintenance J 208 GSDocument13 pages208 - 1 - 1 Production Line 2009 208 - 1 - 3: Spare Parts For Preventive Maintenance J 208 GSPopa MihaiNo ratings yet
- J320 Maintenance Spare Parts ListDocument1 pageJ320 Maintenance Spare Parts ListKeith ChengNo ratings yet
- Reference Cable Schedule - JGS 320 - Non-Grid SynchronizationDocument2 pagesReference Cable Schedule - JGS 320 - Non-Grid SynchronizationfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Engine Mecanical System PDFDocument99 pagesEngine Mecanical System PDFErkki IsokangasNo ratings yet
- 02 GBDocument9 pages02 GBjahzooneNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Fuel Pumps Air Flow 17122009135336Document88 pagesCatalogo Fuel Pumps Air Flow 17122009135336evailson2No ratings yet
- Cumbusiton Test WurthDocument1 pageCumbusiton Test WurthDiogov32No ratings yet
- MAN marine medium duty enginesDocument4 pagesMAN marine medium duty enginesKost KurniaNo ratings yet
- 95 Egge KatlogDocument196 pages95 Egge KatlogMartin J.No ratings yet
- Formula R1 Racing - Explosionszeichnungen Und Adapter PDFDocument9 pagesFormula R1 Racing - Explosionszeichnungen Und Adapter PDFIBC_TobiNo ratings yet
- Echlin Part No RefDocument85 pagesEchlin Part No Refpilveni100% (1)
- SS-7157028-18397893-012 SS Page 1 of 6: Page: M-1 of M-4 © 2017 Caterpillar All Rights Reserved MSS-IND-18397893-006 PDFDocument6 pagesSS-7157028-18397893-012 SS Page 1 of 6: Page: M-1 of M-4 © 2017 Caterpillar All Rights Reserved MSS-IND-18397893-006 PDFПавелNo ratings yet
- Price List 2006 Spare Parts / Accessories: Artikel-Nr Part-No. Designation ME Unit OVH Alv22%Document52 pagesPrice List 2006 Spare Parts / Accessories: Artikel-Nr Part-No. Designation ME Unit OVH Alv22%Vesa KemppainenNo ratings yet
- 450t BelAZ 75710 Dump TruckDocument2 pages450t BelAZ 75710 Dump TruckArturo AllendeNo ratings yet
- 350 Ab PartsDocument54 pages350 Ab PartsAbin AndrewsNo ratings yet
- Manual Yamaha E48 y 55hpDocument80 pagesManual Yamaha E48 y 55hpLeonardo Ocando100% (1)
- 0606 - TD - E2842 LE312 - Nat - EngDocument8 pages0606 - TD - E2842 LE312 - Nat - EngfaridNo ratings yet
- CX Rebuild Engine Sheet 4.6 BDocument19 pagesCX Rebuild Engine Sheet 4.6 BRijal Furqaan MardhatillahNo ratings yet
- Installation Instructions: WarningDocument35 pagesInstallation Instructions: WarningwcuevasmNo ratings yet
- Engine Rebuild Inspection Sheet C Series: Job No: Eng. Model: Customer: ESN: CPL: Pump CodeDocument10 pagesEngine Rebuild Inspection Sheet C Series: Job No: Eng. Model: Customer: ESN: CPL: Pump CodeRijal Furqaan Mardhatillah100% (1)
- Workshop Manual: 125 Cc/150 CC 4-Stroke EngineDocument48 pagesWorkshop Manual: 125 Cc/150 CC 4-Stroke EngineMaris ErbssNo ratings yet
- KPC Master Catalog Parts v1!08!27 12Document77 pagesKPC Master Catalog Parts v1!08!27 12nachoNo ratings yet
- Design of IC EngineDocument30 pagesDesign of IC EngineAshitosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Alum EngineDocument20 pagesAlum EnginePedro PedrazaNo ratings yet
- Toyota Nico PDFDocument33 pagesToyota Nico PDFDaniel GarciaNo ratings yet
- LH2.2 & EZ-F User Manual Issue 2bDocument73 pagesLH2.2 & EZ-F User Manual Issue 2bphilro52No ratings yet
- TATA Minibus 407 MaintainanceDocument13 pagesTATA Minibus 407 MaintainancePraveen Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Tedom Handbook For Designers 2008Document57 pagesTedom Handbook For Designers 2008ManretyNo ratings yet
- Ks Si 0014 en WebDocument0 pagesKs Si 0014 en WebMoaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- O-Ring Standar Sizes PDFDocument14 pagesO-Ring Standar Sizes PDFJoseJSanchezNo ratings yet
- Manual Trans., Actuation, Housing PDFDocument163 pagesManual Trans., Actuation, Housing PDFAlpaslan AksoyNo ratings yet
- Subaru WRX (STi) 07 Lubrication FSMDocument22 pagesSubaru WRX (STi) 07 Lubrication FSMGustavo RivasNo ratings yet
- PVM 74 EtonDocument48 pagesPVM 74 Etoncaprit_her_771605No ratings yet
- 2015 Marine CatalogDocument21 pages2015 Marine CatalogFaraz HaiderNo ratings yet
- DeLorean Engine Parts ManualDocument39 pagesDeLorean Engine Parts ManualSpammyNo ratings yet
- SSP 374 Traction Control PDFDocument88 pagesSSP 374 Traction Control PDFRomeo BelkoNo ratings yet
- G3306Document4 pagesG3306carlucido247970100% (1)
- TMP - 6810-Delco History IC1488159342 PDFDocument123 pagesTMP - 6810-Delco History IC1488159342 PDFAnonymous NwinYA8x2100% (1)
- Lista Base Instalada LATAM FLESANDocument19 pagesLista Base Instalada LATAM FLESANWiliam SeguraNo ratings yet
- Ignition Coils TypesDocument27 pagesIgnition Coils TypesMohamed EssamNo ratings yet
- Schedle Maintenance JenbacherDocument3 pagesSchedle Maintenance JenbacherEnrique Garcia0% (1)
- Basic I.S.O. Programming GuideDocument202 pagesBasic I.S.O. Programming GuideAmit JholaparaNo ratings yet
- InjectorsDocument339 pagesInjectorsKapil AppyNo ratings yet
- Screws With External Hexalobular Driving Feature: Mercedes-Benz MBN 10 142Document6 pagesScrews With External Hexalobular Driving Feature: Mercedes-Benz MBN 10 142achin123No ratings yet
- Belt Tension Deflection TableDocument2 pagesBelt Tension Deflection TabletaherNo ratings yet
- Catalogues$lpt 809 Ex2 Ex Bs-Ii PDFDocument282 pagesCatalogues$lpt 809 Ex2 Ex Bs-Ii PDFveereshNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Adjustment: 1. Checking The Ring Gear Backface RunoutDocument7 pagesGroup 4 Adjustment: 1. Checking The Ring Gear Backface RunoutAndré TarginoNo ratings yet
- NPR 2013noacatalogforprintoutDocument596 pagesNPR 2013noacatalogforprintoutSelvaraji MuthuNo ratings yet
- 750 Ss Parts 2002Document108 pages750 Ss Parts 2002LouisNo ratings yet
- Servicing Instructions and Illustrated Parts List For Hewland FTR GearboxesDocument28 pagesServicing Instructions and Illustrated Parts List For Hewland FTR GearboxesIgnacio ManriquezNo ratings yet
- Beta43-60 Spares List Rev 002Document56 pagesBeta43-60 Spares List Rev 002Sean LynchNo ratings yet
- Building a WWII Jeep: Finding, Restoring, & Rebuilding a Wartime LegendFrom EverandBuilding a WWII Jeep: Finding, Restoring, & Rebuilding a Wartime LegendNo ratings yet
- Inertia SensorDocument2 pagesInertia SensorTommy TribbianiNo ratings yet
- Current SensorDocument1 pageCurrent SensorTommy TribbianiNo ratings yet
- Communication ProtocolDocument4 pagesCommunication ProtocolTommy TribbianiNo ratings yet
- Injector Install HowtoDocument19 pagesInjector Install HowtoMadara DusaNo ratings yet
- Common Rail PDFDocument60 pagesCommon Rail PDFGarry BlakeNo ratings yet