Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Course Description
Uploaded by
api-307398350Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Course Description
Uploaded by
api-307398350Copyright:
Available Formats
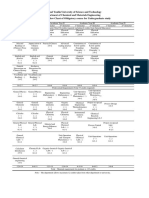
NYUST, Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering
Engineering Mathematics
(3-0-3)
Obligatory
The Engineering mathematics is to introduce the general and fundamental methods to solve the
ordinary derivative equation and partial derivative equation.
Chemical Technology Lab.
(Two semesters0-3-1 each)
Obligatory
This course is to teach analytical methods for polymers including molecular weights,
mechanical and thermal and electrical properties.
Chemical Reaction Engineering
(3-0-3)
Obligatory
The contents are: chemical reaction kinetics, reaction mechanism, isothermal reactor design,
catalytic reactor design, and studies of nonideal reactor behaviors.
(I)
Transport Phenomena(I)
(3-0-3)
Obligatory
This required core course for chemical engineering undergraduates emphasizes on an
understanding of momentum transport phenomena and operation in chemical engineering
processes.
The course is divided into five phases: fluid properties, equation of motion,
momentum transport in laminar flow, momentum transport in turbulent flow, and flow
applications in chemical engineering processes.
(II)
Transport Phenomena(II)
(3-0-3)
Obligatory
Transport phenomena are the fundamental of chemical unit operation, which introduce the
principles of hydrodynamic, heat transfer and mass transfer.
Unit Operation and Transport Phenomena (2)
(3-0-3)
Obligatory
This course deals with the transfer of energy. Gross quantities of heat added to or rejected from
a system may be evaluated by applying the control-volume expression for the first law of
thermodynamics. Certainly in designing a plant in which heat must be exchanged with the
surroundings, the size of heat-transfer equipment, the materials of which it is to be constructed,
and the auxiliary equipment required for its utilization are all important considerations for the
chemical engineer. Considerations of an engineering nature such as these require both a
familiarity with the basic mechanisms of energy transfer and an ability to evaluate quantitatively
these rates as well as the important associated quantities. Our immediate goal is to examine the
basic mechanisms of energy transfer and to consider the fundamental equations for evaluating
the rate of energy transfer. There are three modes of energy transfer: conduction, convection,
and radiation. All heat-transfer processes involve one or more of these modes. This course will
be devoted to an introductory description and discussion of these types of transfer.
249
NYUST, Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering
Unit Operation and Transport Phenomena (3)
(3-0-3)
Obligatory
The previous courses (i.e., part 1 and 2) dealing with the transport phenomena of momentum
and heat transfer have dealt with one-component phases which possessed a natural tendency to
reach equilibrium conditions. When a system contains two or more components whose
concentrations vary from point to point, there is a natural tendency for mass to be transferred,
minimizing the concentration differences within the system. The transport of one constituent
from a region of higher concentration to that of a lower concentration is called mass transfer. A
lump of sugar added to a cup of black coffee eventually dissolves and then diffuses uniformly
throughout the coffee. Water evaporates from ponds to increase the humidity of the passing air
stream. Chemical processes include the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of silane (SiH4) onto
a silicon wafer, the doping of a silicon wafer to form a semiconducting thin film and the
purification of ores and isotopes. Mass transfer underlies the various chemical separation
processes where one or more components migrate from one phase to the interface between two
phases in contact. For example, in adsorption or crystallization processes, the components
remain at the interface, whereas in gas absorption and liquid-liquid extraction processes, the
components penetrate the interface and then transfer into the bulk of the second phase. The
mechanism of mass transfer, as we have also observed in heat transfer, depends upon the
dynamics of the system in which it occurs. Mass can be transferred by random molecular
motion in quiescent fluids, or it can be transferred from a surface into a moving fluid, aided by
the dynamic characteristics of the flow. These two distinct modes of transport, molecular mass
transfer and convective mass transfer, are analogous to conduction heat transfer and convective
heat transfer. Each of these modes of mass transfer will be described and analyzed.
Unit Operations Lab.
(0-3-1)
Obligatory
It aims to train student in experimental techniques. The practical training about momentum, heat
and mass transfers can enforce the basic skills of themselves.
Process Design
(3-0-3)
Obligatory
This course is to teach how to design a chemical production process on the basis of unit
operations, thermodynamics, kinetics, etc.
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
(3-0-3)
Obligatory
In the subject of chemical engineering thermodynamics is order to derive the first to third laws
in the thermodynamics heat engine, vapor-equilibrium and their applications in the chemical
energineering region.
250
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
(3-0-3)
Obligatory
NYUST, Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering
The first law of Thermodynamics, equations of state, heat effects, the second law of
thermodynamics, Solution thermodynamics, phase equilibrium.
Process Control
(3-0-3)
Obligatory
The subject of process control aims to introduce the advantage of automatic control system for
industrial manufacture, and the basic principle of control system analysis and design.
(I)
Physical Chemistry Lab (I)
(0-3-1)
Obligatory
This lab. Course will enable students who have finished the course of physical chemistry (I)
have the opportunity to experience some measuring experiments using physical principals and
techniques to measure the difference of various chemical processes. Experimental subjects
include: thermodynamics, kinetics, gases, solid solutions, chemical equilibrium, physical
equilibrium, electrochemistry, surface chemistry, etc.
(II)
Physical Chemistry Lab (II)
(0-3-1)
Obligatory
This course will enable students who have finished the course of physical chemistry (I) and (II)
have the opportunity to experience some measuring experiments using physical principals and
techniques to explore the consequences of various chemical processes. Experimental subjects
include: thermodynamics, kinetics, gases, solid solutions, chemical equilibrium, physical
equilibrium, electro-chemistry, surface chemistry, etc.
Mass and Energy Balances
(3-0-3)
Obligatory
This required core course for chemical engineering undergraduates emphasizes on the practice
of principles and computation of mass and energy flows in chemical engineering processes.
The course is divided into four phases: unit conversion, conservation of mass, conservation of
energy, and computer-aided computation skill.
()
Physical Chemistry
(3-0-3)
Obligatory
This course introduces how to synthesize the knowledge students have learned form
mathematics, physics, and chemistry courses into a coherent pattern of knowledge. It should be
regarded as a prerequisite course to take the professional courses for chemical engineering
students. The content includes thermodynamics, gas behaviors, chemical equilibrium, phase rule,
etc.
()
Physical Chemistry
(3-0-3)
Obligatory
This course introduces students how to synthesize the knowledge they have learned from
mathematics, physics, and chemistry courses into a coherent pattern of knowledge. It should be
regarded as a prerequisite course to take the professional courses for chemical engineering
students. The content includes kinetics, electro-chemistry, photo-chemistry, surface chemistry,
colloids, macromolecules, etc.
251
NYUST, Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering
Calculator Introduction
(2-0-2)
Obligatory
To introduce the purpose of computer and its development, and also recognizes a few computer
programming in chemical engineering.
Introduction of Chemical Engineering
(1-0-1) Obligatory
This course is arranged for the fresh man of the department of chemical engineering. The
purpose of this course is to introduce the chemical engineering to the students and tell them
what courses they will learn in the future four years and how importance is it for their future
development in industry field. The contents of this course include what is the chemical
engineering? the importance and contribution of chemical engineering on advanced material,
the importance and contribution on biotechnology, the importance and contribution on
energy resource technology, the importance and contribution on environment protection and
process safety. In addition, the basic concept of material and energy balance will be introduced
to the students.
Introduction to Safety and Hygiene of Chemical Industries
(3-0-3)
Elective
The objective of this course is to enable the student to understand the concepts of industrial
hygiene and safety. The course content includes laws and regulations, boiler and pressurized
vessel, fire and explosion, chemical waste treatment, chemicals storage and transportation,
safety assessment.
Electrochemistry
(3-0-3)
Elective
Electrochemistry is a knowledge that investigates the chemical phenomena related to
electricity. It probes the relationship between the electrolyte and electric charge during chemical
reaction; it discusses the reactions occurred on various electrodes and its potential variation; it
discusses reactions occurred in various kind of cells and its electromotive force. This course will
firstly introduce the fundamental principle, then its practical applications such as electrolysis,
plating, electrowinning, electrorefining, electrolytic polishing, corrosion resistance, and its
applications in analysis such as potentiometric titration, conductometric titration, polarographic
method and other technologies such as anodic treatment, cell and battery (primary cell,
secondary cell, fuel cell, and solar cell), electrochemical synthesis method, and waste water
treatment. In addition, this course will also introduce the related electrochemical technologies
and principles applied to the electronic and semiconductor fields. It is expected that the students
can understand how to utilize the electrochemistry to produce the electronic products.
Chemical Process Industries
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is intended to guide students through chemical manufacturing processes and to
252
NYUST, Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering
introduce the carrert developments of global chemical industries.
Applied Analytical Chemistry
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is made for the introduction of todays analytical chemistry, including application of
basic theories and analytical instruments, optical methods and separation technology.
Biochemistry
(3-0-3)
Elective
The contents are: cell structure, functions of biomolecules, cell metabolism, bioenergetics, and
transfer of genetic information.
Numerical Methods
(3-0-3)
Elective
To introduce numerical analysis techniques including methods for solving simultaneous linear
equations, interpolation and the differential equations, etc. The MATLAB is a main
programming tool.
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
(3-0-3)
Elective
The Engineering mathematics is to introduce the general and fundamental methods to solve the
ordinary derivative equation and partial derivative equation
Introduction to Biotechnology
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is intended to introduce some characteristics of biotechnology, the principles and
applications of both traditional and carrent new biological processes.
Biochemical Engineering
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is concemed with applying chemical engineering principles to design and
development of biological process, including basic biological concept, selection and operation
of bio reactor, as well as application of non-traditional bio systems.
Polymer Chemistry
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is to teach polymer synthetical methods including condensation, free-radical, ionic,
emulsion, ring-opening polymerizations.
Bioseparation Technology
(3-0-3)
Elective
The purpose of this course is to introduce the downstream separation techniques of biochemical
processes. The main topics covered in the course are: removal of insolubles (filtration and
micro-filtration, centrifugation, cell disruption); isolation (extraction, adsorption); purification
(elution chromatography, precipitation); polishing (crystallization, drying).
Instrumental Analysis
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is to teach analytical methods using instruments including FTIR, UV/VIS, GC, LC
DSC, NMR, ETC, etc.
253
NYUST, Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering
Composite Materials
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course introduces the basic principal of composite materials, applications of composite
materials, manufacture and processing methods, pre-impregnated materials, reinforcements,
fracture behaviors and mechanical properties, interfaces of composite materials. The
prerequisite courses should be polymer chemistry, polymer physics, or polymer science
Polymer Physical Property
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course covers introduction of basic chemical synthesis, including oxidation reduction
reaction, alkylation, aldol condousation Environmental reaction, Dials-Alder reaction and C-C
double bond formation reaction.
Experimental Design and Analysis
(3-0-3)
Elective
The purpose of this course is to introduce the process optimization by experimental design and
analysis. The main topics covered in the course are: analysis of variance; factorial designs;
fractional factorial designs; regression analysis; response surface methodology; case studies of
process optimization.
Industrial Catalysts
(3-0-3)
Elective
This undergraduate course introduces students about catalyst materials, catalysis principles, and
applications in industry. Five phases of the course include basic concepts of catalysis,
preparation and characterization of catalyst materials, catalytic reaction kinetics, catalytic
reaction processes, and catalytic reactor design. Students are assigned to present practical
topics of applied catalysis in industry.
Semiconductor Materials
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course will mainly introduce the processes and related materials of the semiconductor
industry. They include the wafer manufacture, formation of semiconductor film, growth of oxide
layer, growth of dielectric layer, growth of metal film, synthesis and exposure of photo resistant,
growth of passivation layer and so on. In addition, it also introduce the formation mechanism
and the related tools, such as chemical vapor deposition, physical vapor deposition, plasma,
electrodeposition, spin coating, and chemical mechanical polishing. It is expected that the
students can realize the relationship between the chemical engineering and semiconductor
industry.
Enzyme Engineering
(3-0-3)
Elective
The contents are: Industrial production of enzymes, technology of enzyme technology, enzyme
reaction kinetics, enzyme reactor design, and industrial applications of enzymes.
(3-0-3)
254
Thin film Technologies
Elective
NYUST, Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering
This course addresses the major advances in the thin film technology, as related to device
fabrication, electronic packaging of microcircuits, and optical applications. The topics discussed
include the various important classes of thin film deposition techniques with an emphasis on the
principles and practices of film deposition, thin film material synthesis and characterization,
design guidelines, and applications. Chapter 1 is an introduction to thin film deposition
techniques including chemical and physical methods used in various forms to create thin films.
Chapter 2 provides an in-depth study of photolithographic techniques used to fabricate thin
films with intricate patterns. Chapter 3 presents an overview of thin film materials and their
various properties and attributes. Chapter 4 analyzes the nature of semiconductor thin films that
form the backbone of modem microelectronics. Chapter 5 outlines design considerations and
guidelines for the use of thin film materials, particularly for use in microelectronic assemblies.
Chapter 6 is a compendium of characterization techniques used to evaluate and measure the
properties of thin films, devices, and structures. The emphasis of this chapter is on
semiconductor films; however, these techniques are generally applicable to any thin film
material. The rapidly growing arena of electronic packaging is the special focus of Chapters 7
provides a detailed look at thin film multichip modules. The final chapter (Chapter 8) is a
detailed look at testing and reliability of electronic assemblies, in particular thin film modules,
which play an increasingly important role in microelectronics.
Chemical Engineering Separation Processes
(3-0-3)
Elective
This elective course for chemical engineering undergraduates emphasizes on an understanding
of mass transfer phenomena and operations in chemical engineering processes.
The course is
divided into three phases: molecular diffusion and mass transfer, phase-equilibrium separation
processes, and rate-controlled separation processes.
Industrial Catalysts
(3-0-3)
Elective
This undergraduate course introduces students about catalyst materials, catalysis principles, and
applications in industry. Five phases of the course include basic concepts of catalysis,
preparation and characterization of catalyst materials, catalytic reaction kinetics, catalytic
reaction processes, and catalytic reactor design. Students are assigned to present practical
topics of applied catalysis in industry.
Nanostructured Materials Chemistry
(3-0-3)
Elective
This graduate course emphasizes on developing an advanced understanding of the correlated
chemical nature of the atomic, molecular and bonding characteristics of the nanoscale materials
with structure, function and property. The course is composed of four phases: quantum
chemistry, solid-state chemistry, characterization techniques, and synthesis chemistry.
Students are assigned to present research-oriented topics in nanostructured materials,
nanoscience, or nanotechnology.
255
NYUST, Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering
Colloid Chemistry
(3-0-3)
Elective
The emphasis of this undergraduate course is on developing an understanding of colloidal
system based on physical chemistry principles, properties, surface phenomena and applications.
The course is divided into four phases: colloidal state, interfacial phenomena of colloidal
solution, kinetic and optical properties, and colloid stability. Students are assigned to present
topics of colloidal chemistry in chemical engineering applications.
Safety and Hygiene of Chemical Industries
(3-0-3)
Elective
The objective of this course is to enable the student to understand the concepts of industrial
hygiene and safety. The course content includes laws and regulations, boiler and pressurized
vessel, fire and explosion, chemical waste treatment, chemicals storage and transportation,
safety assessment.
Safety Design of Chemical Process
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is designed to teach and applied the fundamentals of chemical process safety. The
course content includes laws and regulations, toxicology, industrial hygiene, designs to prevent
fires and explosion, toxic release and dispersion models, relief sizing.
Multimedia Transport of Hazardous Waste
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course will provide an overview of the mechanisms and rates of movement of chemicals
across interfaces. It also will introduce how to assess the movement of substances from the site
of entry into the environment to the various geospheres by quantitative tools.
Prevention Leaks and Spills of Hazardous Waste
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course will teach students how to prevent leaks and spills of hazards from facilities that
produce hazards, store them, or transfer them to and from transportation Terminals. It also will
introduce regulations / codes and consider current local prevention practices for major hazards.
Polymer characterization
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is to teach analytical methods for polymers including molecular weights,
mechanical and thermal and electrical properties.
Computer Programming
(3-0-3)
Elective
The contents are: introduction and basic operations of VB6.0, form design, data and operators,
arrays, uses of objects, and edit of VB programs.
Material science
(3-0-3)
Elective
The material science is to introduce the material kinds, material design, material function, and
introduce advance materials, including of nanccomposites biomaterials and condutive materials,
etc.
Medical Engineering Experiment
(0-2-1)
Elective
The class is an experimental class. In the subject, the biomaterials are synthylzed in the
256
NYUST, Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering
experiment, and to research the factors, such as surface polarity, surface tension, surface
roughness, which influence the blooel compatibility and bio compatibility.
Heterogeneous Catalysts
(3-0-3)
Elective
Heterogeneous catalysts are very important for chemical industries, because it plays a very
important role in petroleum chemical industries, energy source development and environment
protection and so on. Accordingly, this course will focus mainly on the catalytic behaviors
between the solid and gas phase and on the synthesis and characterization of the related
catalysts. The contents will include basic concepts such as catalytic activity, catalyst selectivity,
active sites, and thermodynamics and energetics. It also includes the concepts of physical and
chemical adsorption; the concepts of reaction rate, reaction mechanism, and kinetics models
evaluation; the methods of catalyst preparation and manufacture; the physical characterization
and surface analysis techniques. Especially, this course will introduce the topic of supported
metal catalysts and discuss the physic-chemical interaction between the metal particles and
oxides, which its principle will also be able to apply extensively to the field of electronic
materials.
Biology
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is concerned with the essence of life, the basic concept of biology and the
relationship between organisms and their related society.
Bioremediation
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course will teach students how to evaluate contaminant transport in porous media using
numerical codes. It also will introduce environmental microbiology, bioremediation
technologies, and on-site remediation technologies. The class design project will consider
current local problems with soil and groundwater contamination.
Thermal Processing Of Hazardous Waste
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course will provide an overview of the disposal of hazardous wastes using thermal means.
It will introduce appropriate fundamentals of thermodynamics and kinetics and will introduce
hardware and permitting.
Environmental Chemistry
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is concerned with application of chemical principles to the maintenance and
enhancement of environmental quality. The chemistry of present atmosphere and natural water
as well as interactions between water and either the atmosphere or the underlying rock are
examined.
Advanced Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (3-0-3)
Elective
This course is one of the required core courses for chemical engineering graduates. The
advanced practice of thermodynamics, viewed from the standpoint of chemical engineering, is
257
NYUST, Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering
concentrated on principles, applications, and computer-aided computation methodology.
Students after taking this course are capable of solving problems of energy flow and equilibrium.
The course is divided into four phases: three laws of thermodynamics, equation of state, phase
equilibrium, and chemical reaction equilibrium.
Special Topics of Adsorptive Separations
(3-0-3)
Elective
The purpose of this course is to introduce the fundamental principles and industrial practice of
adsorptive and chromatographic separations. The main topics covered in the course are: porous
adsorbents; adsorption equilibrium; kinetics of adsorption in batch systems; dynamics of
adsorption columns; isolation by solid-phase extraction; product purification by column
chromatography; their applications.
Advanced Polymer Chemistry
(3-0-3)
Elective
The advanced polymer chemistry is to introduce the synthysis methods of polymers, synthysis
kinetics and the advanced technology of especial function polymers.
Advanced polymer property
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is to teach advanced polymer physical properties including chain conformation,
rubber elastic state, polymer sdutions, amorphous state, molten state, crystalline state, etc.
Advanced Transport Phenomena
(3-0-3)
Elective
The aim of this course is to teach student about theories on fluid flow and energy transfer. The
main topics include viscous flow, potential flow, boundary layer theory, and convective heat
flow.
Special Topics On Food Chemistry
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is concerned with chemical properties of food ingradients, products, The
composition and properties of food product are also examined.
Special Topics On Biochemical Engineering
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is concerned with application of biotechnology such as recombinant DNA
technology, protein technology, and aeration and agitation Theories to fermentation processes
Advanced numerical Analysis
(3-0-3)
Elective
To introduce numerical analysis techniques, including methods of the differential equations and
partial differential equations. The MATLAB is a main programming tool.
Advanced Process Control
(3-0-3)
Elective
To introduce the many of conventional or advanced control designs in chemical processes.
Special Topics on Safety Design of Chemical Process
(3-0-3)
Elective
This course is designed to discuss special topics on chemical process safety design. The main
258
NYUST, Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering
topics include design to prevent fires and explosions, relief system, hazards analysis and risk
assessment.
Special Topics on Composite Materials
(3-0-3)
Elective
Modern structural composites, frequently referred to as advanced composites, are blends of two
or more materials, one of which is composed of stiff, long fibers and, for polymeric composites,
a resinous binder or matrix that holds the fibers in place, Special topics of composite materials
cover general introduction, fibers and matrices, composite modeling, analysis and design, PMC
properties, repair of composite structures, Nondestructive evaluation, testing, and inspection .
Advanced Transport Phenomena
(3-0-3)
Elective
The aim of this course is to teach student about theories on fluid flow and energy transfer. The
main topics include viscous flow, potential flow, boundary layer theory, and convective heat
flow.
Hazard Evaluation For Chemical Process Industries
(3-0-3) Elective
Toxicology, Source models, Toxic Release and Dispersion Models, hazards Identification, Risk
Assessment, Discussion of Hazard Evaluation Examples.
259
You might also like
- Graduate StudyDocument1 pageGraduate Studyapi-307398350No ratings yet
- Kannur University B.SC Chemistry PDFDocument55 pagesKannur University B.SC Chemistry PDFJinu Madhavan0% (1)
- B.sc. Hons Syllabus For Delhi UniversityDocument174 pagesB.sc. Hons Syllabus For Delhi UniversityKaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Undergraduate Flow ChartDocument2 pagesUndergraduate Flow Chartapi-307398350No ratings yet
- Rr212305-Chemical and BiothermodynamicsDocument1 pageRr212305-Chemical and BiothermodynamicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- M.sc. Chemistry Compiled SyllabusDocument48 pagesM.sc. Chemistry Compiled SyllabusSadiaMaryamNo ratings yet
- EC Syllabus Kerala University (2003 Scheme)Document57 pagesEC Syllabus Kerala University (2003 Scheme)joyasams75% (4)
- Solved Problems IN Quantum Physics: Dr. Ing. Valerică D. NinulescuDocument21 pagesSolved Problems IN Quantum Physics: Dr. Ing. Valerică D. NinulescugertrudeNo ratings yet
- B.SC 2nd and 3rd Year Syllabus SVUDocument16 pagesB.SC 2nd and 3rd Year Syllabus SVUSrinivasulu Pudu100% (1)
- Vacancy For Temp DemoDocument784 pagesVacancy For Temp DemoThirunavukkarasu Pathmathas0% (1)
- Y2007 (Bard - A.J., - Stratmann - M., - Unwin - P.R.) - Encyclopedia PDFDocument642 pagesY2007 (Bard - A.J., - Stratmann - M., - Unwin - P.R.) - Encyclopedia PDFDian NursyamsiahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 2 Questions PDF August 24 2011-12-50 PM 472kDocument22 pagesChemistry Paper 2 Questions PDF August 24 2011-12-50 PM 472kJamaludin Abu KassimNo ratings yet
- Allen Kota Test Papers (Medical)Document47 pagesAllen Kota Test Papers (Medical)Dr AwesomeNo ratings yet
- STC 221 20202021 Full TimeDocument3 pagesSTC 221 20202021 Full Timewww.williamskimberly10100% (1)
- Advanced Organometallic Chemistry and Its Applications in Industry and Catalytic Reactions PDFDocument144 pagesAdvanced Organometallic Chemistry and Its Applications in Industry and Catalytic Reactions PDFdustinthewindNo ratings yet
- Understanding Advanced Chemistry Through Problem Solving The Learners Approach (Volume 1) - Revised Edition (Kim Seng Chan, Jeanne Tan) (Z-Library)Document339 pagesUnderstanding Advanced Chemistry Through Problem Solving The Learners Approach (Volume 1) - Revised Edition (Kim Seng Chan, Jeanne Tan) (Z-Library)loxadegoNo ratings yet
- A Textbook of Physical Chemistry K L Kapoor A Textbook of PhysicalDocument374 pagesA Textbook of Physical Chemistry K L Kapoor A Textbook of PhysicalEstanislao Amadeo Avogadro100% (1)
- Rr410802 Chemical Reaction Engineering IIDocument8 pagesRr410802 Chemical Reaction Engineering IISrinivasa Rao G100% (3)
- PhotoChemistry PDFDocument22 pagesPhotoChemistry PDFAnkitranjan GogoiNo ratings yet
- Anna University B.Tech Chemical Engineering SyllabusDocument4 pagesAnna University B.Tech Chemical Engineering SyllabusSanthaseelan CNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument8 pagesAtomic StructureHari GoldNo ratings yet
- NuclearFuel Olander-1 PDFDocument629 pagesNuclearFuel Olander-1 PDF강희연No ratings yet
- Mcmaster MECH ENG 3O04 - Fluid Mechanics Notes by Dr. Mohamed S. HamedDocument394 pagesMcmaster MECH ENG 3O04 - Fluid Mechanics Notes by Dr. Mohamed S. Hamedcttiger7135100% (15)
- Syllabus For Master of Science in Chemistry: The Assam Kaziranga University, JorhatDocument52 pagesSyllabus For Master of Science in Chemistry: The Assam Kaziranga University, JorhatDibyajyoti SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Pahang STPM Trial 2011 Chemistry Paper 2 (W Ans)Document21 pagesPahang STPM Trial 2011 Chemistry Paper 2 (W Ans)plouffle100% (1)
- Lecture 1Document41 pagesLecture 1Salah Farhan NoriNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Heat TransferDocument14 pagesNuclear Heat TransferDilip YadavNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Instruction Division FIRST SEMESTER 2010-2011 Course Handout Part IIDocument3 pagesBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Instruction Division FIRST SEMESTER 2010-2011 Course Handout Part IIGirish HanumaiahNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics BTech NIT CalicutDocument12 pagesEngineering Physics BTech NIT Calicutnitcalicutian100% (1)
- 18 - Kesetimbangan Fasa Dalam Kimia Fisika - Ch.4Document13 pages18 - Kesetimbangan Fasa Dalam Kimia Fisika - Ch.4SholèhNurUdinNo ratings yet
- Answer and Solutions - JEE - Main 2023 - PH 1 - 25 01 2023 - Morning - Shift 1 PDFDocument25 pagesAnswer and Solutions - JEE - Main 2023 - PH 1 - 25 01 2023 - Morning - Shift 1 PDFinduja c mNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MechanicsDocument16 pagesIntroduction To MechanicsbijoyNo ratings yet
- Hydrogenated Amorphous Silicon Cambridge Solid State Science Series PDFDocument432 pagesHydrogenated Amorphous Silicon Cambridge Solid State Science Series PDFignaciadevotoNo ratings yet
- Concept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-08) Based On AIATS-08 CF+OYM ChemistryDocument5 pagesConcept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-08) Based On AIATS-08 CF+OYM Chemistryarja keerthanaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Physical Quantities and UnitsDocument49 pages1 - Physical Quantities and UnitsNurul AtikaNo ratings yet
- CSIR Previous PapersDocument141 pagesCSIR Previous PapersSony mulgundNo ratings yet
- M.sc. Chemistry 2014 15 CBLUDocument46 pagesM.sc. Chemistry 2014 15 CBLUAnonymous780No ratings yet
- Anna Univ 3rd Sem, 5th Sem, 7th Sem Syllabus For Agriculture Irrigation Engg WWW - Annaunivedu.infoDocument72 pagesAnna Univ 3rd Sem, 5th Sem, 7th Sem Syllabus For Agriculture Irrigation Engg WWW - Annaunivedu.infosudentsideaNo ratings yet
- AITS 03 - Test Paper - Arjuna NEET 2024Document22 pagesAITS 03 - Test Paper - Arjuna NEET 2024drh.air12345678No ratings yet
- Transition Metal ComplexesDocument103 pagesTransition Metal Complexesidownloadbooksforstu100% (1)
- Energy Engineering Lab Manual (WEC)Document74 pagesEnergy Engineering Lab Manual (WEC)haseebNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Dynamic AnalysisDocument16 pagesChapter 4 - Dynamic AnalysisDimple SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii: Partial Differential Equations-I: X y Yy XX XyDocument16 pagesUnit-Ii: Partial Differential Equations-I: X y Yy XX XyKaiash M YNo ratings yet
- Structure 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 PracticeDocument6 pagesStructure 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 PracticeEthan ElliotNo ratings yet
- B.SC Physics: Sem I & Ii Recommended Text-Books & EbooksDocument18 pagesB.SC Physics: Sem I & Ii Recommended Text-Books & EbooksDebasis BehuriaNo ratings yet
- Nanoengineered Nanofibrous Materials PDFDocument534 pagesNanoengineered Nanofibrous Materials PDFRaj Narayan100% (1)
- 4 - Chemical Kinetics & RadioactivityDocument19 pages4 - Chemical Kinetics & RadioactivityNimeshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01-03Document15 pagesLecture 01-03Fayaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of ViscosityDocument8 pagesNewton's Law of ViscosityAn FakeihahNo ratings yet
- A Course in Fluid Mechanics With Vector Field TheoryDocument198 pagesA Course in Fluid Mechanics With Vector Field TheoryZeynep BurakNo ratings yet
- Advanced Inorganic ChemistryDocument12 pagesAdvanced Inorganic ChemistryDicky Tak Hin WongNo ratings yet
- PHY 309 Quantum Physics IDocument130 pagesPHY 309 Quantum Physics Ioduola ademola100% (1)
- Unit OperationDocument30 pagesUnit OperationHemanth Peddavenkatappa GariNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To The Written Test: Representative Questions of Test PaperDocument10 pagesA Brief Introduction To The Written Test: Representative Questions of Test PaperAyesha RasheedNo ratings yet
- 9701 Y14 SW v2Document116 pages9701 Y14 SW v2deaNo ratings yet
- PhotochemistryDocument24 pagesPhotochemistryVijay PradhanNo ratings yet
- Numerical Modeling of Neutron TransportDocument120 pagesNumerical Modeling of Neutron TransportAndrea SpinelliNo ratings yet
- Structure and Properties of Inorganic Solids: International Series of Monographs in Solid State PhysicsFrom EverandStructure and Properties of Inorganic Solids: International Series of Monographs in Solid State PhysicsNo ratings yet
- ME Transfer Course DescriptionDocument16 pagesME Transfer Course Descriptionsolidworksmanics2023No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Inquiry LabDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer Inquiry LabAnisNo ratings yet
- Lec2 Heat Engine and Carnot Cycle PostDocument51 pagesLec2 Heat Engine and Carnot Cycle PostAniruddha NarkhedeNo ratings yet
- Physics DefinitionsDocument2 pagesPhysics DefinitionsElaine Neo Kai WenNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power PlantDocument23 pagesDiesel Power PlantMa. Mikhaela ApuradoNo ratings yet
- GED Physics Note2 (Energy)Document5 pagesGED Physics Note2 (Energy)Shahadat Hussain Parvez100% (1)
- AE 522 IntroductionDocument68 pagesAE 522 IntroductionDerek RogersNo ratings yet
- Design 2-Pass Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument20 pagesDesign 2-Pass Shell and Tube Heat Exchangerazib100% (1)
- Gaitonde ProgAeroSci 2015 (SWBLI Review)Document20 pagesGaitonde ProgAeroSci 2015 (SWBLI Review)Taro YamadaNo ratings yet
- Amine Basis GuidelinesDocument63 pagesAmine Basis Guidelinesgion_ro401No ratings yet
- Convective Heat Transfer Coefficients of The Human Body Under Forced Convection From Ceiling 2165 7556.1000126Document6 pagesConvective Heat Transfer Coefficients of The Human Body Under Forced Convection From Ceiling 2165 7556.1000126Irfan FadhlurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Microwave Freeze-Drying of Food: A Theoretical InvestigationDocument10 pagesMicrowave Freeze-Drying of Food: A Theoretical InvestigationGabrielNo ratings yet
- Effect of Cycling Operations On An Adsorbed Natural Gas StorageDocument9 pagesEffect of Cycling Operations On An Adsorbed Natural Gas StorageMartín KunuschNo ratings yet
- HT GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-1 18082020094106AMDocument9 pagesHT GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-1 18082020094106AMJainil GajjarNo ratings yet
- Technical Notes: Dissipation in Small Scale Gaseous FlowsDocument7 pagesTechnical Notes: Dissipation in Small Scale Gaseous FlowsMauricio Fabian Duque DazaNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger DesignDocument27 pagesHeat Exchanger DesignTri Vicca WibisonoNo ratings yet
- Physics of Thermo-Acoustic Sound GenerationDocument13 pagesPhysics of Thermo-Acoustic Sound GenerationtaNo ratings yet
- Prediction of High Pressure Liquid Heat Capacities of Organic Compounds by A Group Contribution MethodDocument7 pagesPrediction of High Pressure Liquid Heat Capacities of Organic Compounds by A Group Contribution MethodCitra Adelina SitorusNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic State and State FunctionsDocument5 pagesThermodynamic State and State FunctionsnnbNo ratings yet
- Under Floor Heating BasicsDocument69 pagesUnder Floor Heating BasicsHamzeh Shihadeh100% (1)
- Enthalpy Method PDFDocument2 pagesEnthalpy Method PDFsimmaNo ratings yet
- MEM311 Manual 09192014Document77 pagesMEM311 Manual 09192014Sam Yang SunNo ratings yet
- Halac Sy 1958Document5 pagesHalac Sy 1958Anonymous sAmJfcVNo ratings yet
- CBAM Guidance - non-EU InstallationsDocument266 pagesCBAM Guidance - non-EU InstallationsNAMPNo ratings yet
- Thermal ScienceDocument1 pageThermal Scienceram dasNo ratings yet
- ENERGY CARRIERS AND CONVERSION SYSTEMS - Vol. I - Alkaline Water Electrolysis - Isao AbeDocument1 pageENERGY CARRIERS AND CONVERSION SYSTEMS - Vol. I - Alkaline Water Electrolysis - Isao AbesarasNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 5-DLP-Feb 27, 2023Document4 pagesSCIENCE 5-DLP-Feb 27, 2023rachelle.pedroNo ratings yet
- Applied Energy: SciencedirectDocument26 pagesApplied Energy: SciencedirectLéo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ic Engines /R&Ac Ic Engines /R&Ac: Course: Basic Civil and Mechanical EngineeringDocument55 pagesIc Engines /R&Ac Ic Engines /R&Ac: Course: Basic Civil and Mechanical EngineeringSrivikas MathesvaranNo ratings yet