Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Capstone Poster Reiman-2 Final Group12
Uploaded by
api-244837193Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Capstone Poster Reiman-2 Final Group12
Uploaded by
api-244837193Copyright:
Available Formats
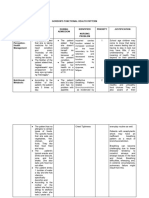
The Effectiveness of Manual Therapy and Exercise in Isolation or in Combination
for the Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review
Bryan Pyrc, SPT; Susan Rhea, SPT; Lauren Ryan, SPT; Chelsea Wolfe, SPT; Justin Zych, SPT;
Dr. Michael Reiman, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC, FAAOMPT, CSCS
Introduc0on
Conclusion
Results
Article
Osteoarthritis (OA) currently affects over
27 million Americans and is projected to
rise with an increasing aging population.
Symptoms of OA include joint stiffness,
pain, and decreased range of motion.
Manual Therapy (MT) and Exercise
Therapy (EX) have both been suggested
as effective conservative treatments for
hip and knee OA in lower level studies.
Outcome
Most Effective
Intervention
Hip OA
Pain
Hoeksma
MT+stretching vs. EX
VAS: significantly improved in MT+stretching vs. EX
MT+stretching
Abbott
MT vs. EX vs.
MT+EX vs. usual care
Pain intensity: significantly improved in MT vs. EX
MT
MT vs. EX vs.
MT+EX vs. usual care
WOMAC: significant difference at 1 year for MT vs.
no MT
MT
3/3 measures: all groups improved, greatest in EX
EX
Harris Hip Score & Walking Speed: Significantly
improved in MT+stretching vs. EX
MT+stretching
Function
Abbott
Purpose
Hoeksma
Determine the effectiveness of MT, EX, or
the two in combination with respect to the
conservative treatment of hip and knee
OA.
Intervention
MT+stretching vs. EX
Patient Satisfaction
French
Hoeksma
MT+EX vs. EX
MT+stretching vs. EX
Methods
Patient Satisfaction & Patient Perceived Change:
greater in MT+EX vs. EX
MT+EX
Likert Scale: 81% improvement reported with MT +
stretching and only 50% for EX
MT+stretching
Pain
Azlin
Passive knee movement
+PT vs. PT alone
VAS: Significant decrease in Passive knee
movement+PT vs. PT only
MT+EX
Nam
PT+trunk stabilization
+MWM vs. PT+trunk
stabilization
VAS: significant difference with increased pain
control in PT+MWM group
MT+EX
Abbott
MT vs. EX vs.
MT+EX vs. usual care
Pain intensity: significantly improved in MT vs. EX
MT
Deyle
Supervised MT+EX+HEP
vs. HEP alone
WOMAC: Treatment group showed twice as much
improvement at 4 weeks compared to HEP
MT+EX
Ko
Resisted MT+EX vs.
Resisted EX alone
3/3 Functional Performance tests: increased
significantly in the MT+EX
MT+EX
Total # of
Articles 1361
Nam
Korean WOMAC: significant difference with
increased pain control in PT+MWM group
MT+EX
Title/Abstract
Screen
36
PT+trunk stabilization
+MWM vs. PT+trunk
stabilization
Abbott
MT vs. EX vs.
MT+EX vs. usual care
WOMAC: significant difference at 1 year for MT vs.
no MT
MT
3/3 measures: all groups improved, greatest in EX
EX
5-point Likert-type question on overall satisfaction:
Greater patient satisfaction in clinical treatment
group at 4 weeks
MT+EX
Function
Full Text Review
7
Patient Satisfaction
Hip OA
2
Hip & Knee OA
1
Knee OA
4
Deyle
Supervised MT+EX+HEP
vs. HEP alone
Recommenda0ons
Knee OA
A computerized literature database
search in PubMed, Web of Science,
CINAHL, Embase, and Scopus ending
February 24, 2014.
Inclusion criteria: adults greater than 18
years old, hip and/or knee OA, MT and/or
EX, human subjects, & RCT study design.
Exclusion criteria: no prior hip or knee
arthroplasty, no congenital or adolescent
hip or knee disease, no RA, and no hip or
knee surgeries in the past 6 months.
Quality was assessed using PEDro.
Isolated or combined MT and EX are
effective in treating patients with hip and
knee OA.
Pain, self-reported measures, function
and patient satisfaction all improved with
the combined treatment approach.
Isolated use of MT had a greater
positive effect on both patient satisfaction
and pain, while isolated use of EX had
greater increases in physical function.
One study found the combined
treatment to be less effective than either
isolated MT or EX.
Treatment time is a potential limiting
factor in applying the combined
treatments in a single treatment session.
Patient presentation and goals should
be considered when selecting the proper
treatment approach.
The benefits of both therapeutic
interventions should be understood by the
clinician and the patient in order to form a
cohesive program that aligns with patient
and clinician goals.
Further well-conducted studies are
needed to clarify the proper dosage and
precise combination of interventions for
the treatment of patients with hip and
knee OA.
More
Informa0on/References
For more information and references,
please visit our website by scanning this
QR code or at our website
http://oatherapy.wix.com/poster.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chapter7 B and T Cell Activation (1) ImmunologyDocument21 pagesChapter7 B and T Cell Activation (1) ImmunologyIka BakarNo ratings yet
- A Proposed Biomechanical Explanation of Low Back Pain PDFDocument25 pagesA Proposed Biomechanical Explanation of Low Back Pain PDFapi-244837193No ratings yet
- Interventions For Cervical Musculoskeletal Dysfunction Unf PDFDocument42 pagesInterventions For Cervical Musculoskeletal Dysfunction Unf PDFapi-244837193No ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitale JZDocument6 pagesCurriculum Vitale JZapi-244837193No ratings yet
- Resume JZDocument3 pagesResume JZapi-244837193No ratings yet
- Gordon's Functional Health PatternDocument8 pagesGordon's Functional Health PatternDanica NuevaexcijaNo ratings yet
- Principles & Practice of First AidDocument298 pagesPrinciples & Practice of First AidJoshua100% (2)
- Mock SurgeryDocument7 pagesMock SurgeryElegant Dental clinicNo ratings yet
- Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument42 pagesScience: Modified Strategic Intervention Materialsmichelle sumatNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Root Canal TreatmentDocument157 pagesStep by Step Root Canal TreatmentKaaroma Tamoaieta100% (1)
- GROW VP NB Combined Zs Boys enDocument2 pagesGROW VP NB Combined Zs Boys enHazel GaringoNo ratings yet
- Katharina Hiria Daundy - Premature Contraction in PregnancyDocument11 pagesKatharina Hiria Daundy - Premature Contraction in PregnancyObgyn AgustusNo ratings yet
- Rajkumar PDFDocument5 pagesRajkumar PDFAmaradeepika JagannathanNo ratings yet
- Natural History of Chronic Subdural Haematoma: K.-S.LEEDocument8 pagesNatural History of Chronic Subdural Haematoma: K.-S.LEEAngelSosaNo ratings yet
- Chap-2 Notes For Clinical Nutrition and DieteticsDocument5 pagesChap-2 Notes For Clinical Nutrition and Dieteticsstar “Hjaljimmer” platinumNo ratings yet
- HIRA ToolDocument26 pagesHIRA Toolsreekala2007No ratings yet
- Perspective: New England Journal MedicineDocument4 pagesPerspective: New England Journal MedicineGary MaoNo ratings yet
- Common Poison in ChildrenDocument31 pagesCommon Poison in ChildrenNimi BatuboNo ratings yet
- MiscarriageDocument1 pageMiscarriageJen BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Sampling Procedure PDFDocument4 pagesArterial Blood Gas Sampling Procedure PDFAna Carolina NegreteNo ratings yet
- ID Consult TemplateDocument5 pagesID Consult TemplateRohitKumar100% (1)
- Renal, Urinary Systems - ElectrolytesDocument692 pagesRenal, Urinary Systems - ElectrolytesRoshan MevadaNo ratings yet
- Trelegy and Device InformationDocument40 pagesTrelegy and Device Informationtechang1No ratings yet
- Reflections On Physical Activity and HealthDocument10 pagesReflections On Physical Activity and HealthShabila RahmadantiNo ratings yet
- Surgical Complication of Typhoid FeverDocument10 pagesSurgical Complication of Typhoid FeverHelsa Eldatarina JNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 17 - Overview of Human Infectious DiseasesDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 17 - Overview of Human Infectious DiseasesJacob PallorinaNo ratings yet
- Full Report-Disinfectant and SanitizerDocument19 pagesFull Report-Disinfectant and Sanitizermohd addinNo ratings yet
- Tablet PCR Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesTablet PCR Cheat Sheetapi-253658656No ratings yet
- TyphoidDocument10 pagesTyphoidpeterjongNo ratings yet
- 2714 - Peripheral Venous Catheter Care Policy For AdultsDocument10 pages2714 - Peripheral Venous Catheter Care Policy For AdultssofiinhaptNo ratings yet
- Anti-Inflammatory Nutraceuticals and Chronic Diseases: Subash Chandra Gupta Sahdeo Prasad Bharat B. Aggarwal EditorsDocument479 pagesAnti-Inflammatory Nutraceuticals and Chronic Diseases: Subash Chandra Gupta Sahdeo Prasad Bharat B. Aggarwal EditorsRora11100% (1)
- Neonatology Thesis TopicsDocument7 pagesNeonatology Thesis Topicspwqlnolkd100% (1)
- Mulit Ligand Control ML 300 - 01A07 - MB Rev 4 - Protocol PDFDocument1 pageMulit Ligand Control ML 300 - 01A07 - MB Rev 4 - Protocol PDFvivicon2004No ratings yet