Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ISU Billing Master Data
Uploaded by
soumyajit1986Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ISU Billing Master Data
Uploaded by
soumyajit1986Copyright:
Available Formats
ISU Billing Master Data:
Billing Class - usually it represents the customer class: residential, industrial, commercial, wholesale
Rate Category - represents the product that is sold to the customer
Rate - represents a unit of variant programs associated with a charge. For example if you calculate the energy charge
for 4 products is better to create only one rate and use it for all 4 products
Schema: it contains the collection of the rates. Best practice is to have one schema for one rate category. This is
better for readability of the schema.
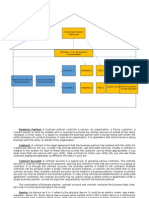
The rate is the most important element of billing. The appropriate
rate is derived from the rate category and the rate type during rate
determination. A rate category is allocated to each utility
installation. It contains data that controls the cross-rate processing
of meter reading data and billing. The data can be overridden by
individual specifications in the installation. The rate
type establishes the rate allocation of the registers and is usually
stored in the installation structure. It can also be stored in the rate
category or in the installation, for example, in the case of flat-rate
installations. The graphic below illustrates the interaction between
the different elements of contract billing.
Operands are descriptive variables defined by the utility company.
The rate allocates values such as price or demand to the
operands. The operand values serve as input and output parameters
for the variant programs. The contractual billing rules are stored in
the variant programs (for example, quantity x price). You define
how billing values such as measured consumption or demand are to
be processed and calculated. The billing schema groups together
one or more rates and determines the sequence in which the variant
programs for the rates to be billed are executed.
What is the process to create ISU Master Data?
The process to create master data in the standard SAP IS-U sistem is:
1) Create Technical Objects:
1.1 Create Connection Object - transaction ES55
1.2. Create Premise - transaction ES60
1.3 Create Installation - transaction ES30
1.4. Create Device - transaction IQ01 or EG44 for device info record
1.5 Install Device in the Installation - transaction EG31 (full installation) or EG33 tehnical installation
and EG34 billing related installation
2) Create Business master data
2.1 Create Business Partner - transaction FPP1
2.2 Create contract account - transaction CAA1
2.3 Create Move In (Move the business partner into the premise) - transaction EC50E
What is the process to create ISU Billing Master Data?
These are the stepts to create a billing master data construct.
1) Configure billing classes (SPRO -> SAP Utilities -> Contract Billing -> Billing Master Data ->
Define Billing Class)
2) Configure Rate types - transaction EA56
3) Define Rate - transaction EA30
4) Create regster operands - from within EA30
5) Define fact groups - (SPRO -> SAP Utilities -> Contract Billing -> Billing Master Data -> Rate
Structrures -> Rates->Define Rate Fact Groups)
6) Create Schema - transaction EA35
7) Create Rate category - transaction EA53
8) Create Rate Determination. - transaction EA87
What is the process to create an invoice?
1. Create Schedule master records:- transaction EA43
2.Create meter reading orders: transaction EL01
3.Enter Meter Reading Results: transaction EL28
4.Check if Billing order is billable: transaction EL28
5.Perform Billing Similation: transaction EA00
6. Perform Billing : transaction EASIBI
7.Check for Outsorting: transaction EA05
8.Perform Invoicing: transaction EA19/EASIBI
Others:
Reversals: EA13
Meter Reading Correction: El27
What is ISU EDM?
These are the three pillars of EDM:
1) Profile Management - This area manages data values in profile.
2) RTP Billing - This area manages interval meter read billing through RTP interface.
3) Settlement & Scheduling - This area manages energy settlements.
Areas in Profile Management:
Key Types of Profile
i) Historic Profile - Stores historic data such as consumption.
ii) Forecast profile - Stores prognostic values such as forecast.
iii) Synthetic profile - Profile containing values generated on the basis of predefined periods (day and
season groups) and corresponding day and annual profiles.
iv) Formula profile - Profile containing values calculated from historic/ forecast profiles using a user
defined formula such as addition, subtraction.
Areas in RTP Billing:
Consumption recorded in profile are billed through Real Time Pricing (RTP) Interface through which
interval readings can be billed on RTP or Time of use (TOU).
i) Integrates ISU-EDM with ISU-Contract billing
ii) Is easy to enhance (customer-specific formulas and results functions)
iii) Period-based billing
iv) Time-of-day blocks (e.g. on-peak rate / off-peak rate)
v) Day blocks (e.g. weekday / weekend day)
vi) Season blocks (e.g. summer / winter)
vii) Application of a spot price or index price
viii) Determination of demand values (e.g. maximum demand)
Areas in Settlement & Scheduling:
In a de-regulated market scenario energy settlement is a key process, which can be used to
calculate the actual/forecast for a area (Settlement unit)
Based on the role in the utility market ISU -EDM settlement can be used for:
i) Sending schedules (Supplier)
ii) Sending consumption (distributor)
iii) Energy settlement (Settlement co-ordinator)
Key Functionalites of EDM:
a) Acts as a Energy repository for storing interval data such as meter reads, prices with interval as
small as 5 mins.
b) Handles complex billing such as real time pricing and time of use pricing through RTP billing.
c) Handles energy settlement process via settlement workbench.
d) Forecasting by using synthetic profiles.
e) Reporting Energy values at various levels e.g.customer, with the help of formula profile.
f) Consistency check for while importing the data.
g) Automatic replacement of missing data values.
h) Publishing interval data on the internet via SAP transaction server and internet application
components.
i) Graphical analysis of interval data such as Consumption v/s Forecast.
j) Integration with Excel for import and exporting the profile values
Key Benifits of EDM:
a) Complete solution for Energy Data Management especially for customers in de-regulated industry.
b) Pre-configured interfaces for automated meter reading (AMR) systems.
c) Complete solution for interval meters.
d) Seamless integration with other my-SAP solutions such as CRM, BW.
e) SAP is continuously enhancing system to meet the challenges of de-regulated industry.
The IS-U process for billing and invocing is:
1. Create Meter Reading Orders
2. Download / Print Meter Reading Orders
3. Read the meter (outside SAP IS-U)
4. Upload / Manual Entry of Meter Reading Results
5. Billing the installations (mass billing)
6. Invocing the created billing documents
7. Print the invoices
The prerequisite for this process is that master data must exist in the system
The process to create master data in the standard SAP ISU sistem is:
1) Create Technical Objects:
1.1 Create Connection Object
1.2. Create Premise
1.3 Create Installation
1.4. Create Device
1.5 Install Device in the Installation
2) Create Business master data
2.1 Create Business Partner
2.2 Create contract account
2.3 Create Move In (Move the business partner into the premise).
Another prerequisite would be to have billing master data in the system:
These are the stepts to create a billing master data construct.
1) Configure billing classes
2) Configure Rate types
3) Define Rate
4) Create regster operands
5) Define fact groups
6) Create Schema
7) Create Rate category
8) Create Rate Determination.
Hi Ramesh,
Try these links:
http://help.sap.com/saphelp_utilities472/helpdata/EN/45/556a3591541f67e10000009b38f889/frameset
.htm
http://help.sap.com/saphelp_utilities472/helpdata/EN/c4/02693582f4db60e10000009b38f889/frameset
.htm
http://help.sap.com/saphelp_utilities472/helpdata/EN/9f/03693582f4db60e10000009b38f889/frameset.
htm
Billing Master data:
1.Billing class-The billing class classifies installations for billing
2.Rate type-Used to classify a)Registersb) Devicesc) Flat rates d)Reference values
Tcode:EA56.
3.price-The price key is the name of a price
Tcode:EA89.
4.Operand-An operand is always allocated to only one division,it is used as input and output parameters in variant
programs
Tcode:EA50.
5. Variant Program- Are small,independent ABAP/4 programs (EA99)
6. Rate-A variant program is processed for each rate step.
Tcode:EA30
7. Fact Group-Fact groups enable different operand values to be used within one rate.
8. Schema-Rates and their variant programs and operands are included in a billing schema
Tcode:EA35
9. Rate category- Controls billing - used to determine the rate in conjunction with the rate type
Tcode:EA53.
10.Rate determination-Rate type + rate category = Rate
Tcode:EA87.
You might also like
- ISU InterviewQsAsDocument7 pagesISU InterviewQsAssryalla0% (1)
- My IS-UDocument205 pagesMy IS-Uapi-19771573100% (2)
- SAP ISU Sample Questions:: Please Choose The Correct Answer. November 16Document7 pagesSAP ISU Sample Questions:: Please Choose The Correct Answer. November 16affanNo ratings yet
- ISU BillingDocument3 pagesISU Billingrafay123100% (1)
- Meter reading organization and ordersDocument22 pagesMeter reading organization and ordersNuman Değirmenci100% (2)
- SAP Help - IsU Device ManagementDocument96 pagesSAP Help - IsU Device ManagementBinh Tran100% (1)
- Fica IsuDocument99 pagesFica IsuCaro Romero100% (1)
- SAP ISU Master DATACreationDocument33 pagesSAP ISU Master DATACreationKalyan Abap100% (5)
- ISU Billing Interview Ques & AnsDocument1 pageISU Billing Interview Ques & Anstrip2ashish0% (1)
- Manage Utilities Customers with SAP UtilitiesDocument466 pagesManage Utilities Customers with SAP UtilitiesAndrea Pellati100% (1)
- SAP Is-U Overall ProcessDocument47 pagesSAP Is-U Overall ProcessMinh Khoa89% (9)
- Business Model Canvas TemplateDocument23 pagesBusiness Model Canvas Templatesoumyajit198667% (6)
- How To Implement SAP AMIDocument20 pagesHow To Implement SAP AMISachin Sawant50% (2)
- SAP BDEx Config GuideDocument101 pagesSAP BDEx Config Guidech_sidhartha100% (1)
- IS-U TcodesDocument14 pagesIS-U Tcodesapi-19771573100% (1)
- CookBook - CollectiveBillDocument32 pagesCookBook - CollectiveBillRahul Jain75% (4)
- Sap FicaDocument34 pagesSap Ficahoney_213289% (9)
- SAP ISU FICA Online TrainingDocument4 pagesSAP ISU FICA Online TrainingGloryittechnologies0% (1)
- ISU Master Data ObjectsDocument4 pagesISU Master Data ObjectsTudor LivadaruNo ratings yet
- ISU SPRO - Meter ReadingDocument9 pagesISU SPRO - Meter ReadinggkraoatlNo ratings yet
- ISU Tables01Document21 pagesISU Tables01sureva65No ratings yet
- SAP Is-U Best PracticesDocument3 pagesSAP Is-U Best PracticesSaravanan SakthivelNo ratings yet
- FicaDocument41 pagesFicaSai ParekhNo ratings yet
- SAP ISU FICA ConfigurationsDocument35 pagesSAP ISU FICA ConfigurationsAnonymous ct0sfqJy491% (11)
- SAP ISU TOU Rate Options Project RecommendationDocument14 pagesSAP ISU TOU Rate Options Project Recommendationvicky_89inNo ratings yet
- Billing Rate Configuration ProcedureDocument70 pagesBilling Rate Configuration ProcedureAnit Gautam100% (1)
- ISU Process OverviewDocument12 pagesISU Process OverviewShammi ManchandaniNo ratings yet
- Sap Is Utilities Certification MaterialsDocument1 pageSap Is Utilities Certification Materialseswar85No ratings yet
- SAP Isu Billing TopicsDocument5 pagesSAP Isu Billing TopicsAlan Sam Baby50% (2)
- SAP ISU Meter-to-Cash-Cycle-New PDFDocument64 pagesSAP ISU Meter-to-Cash-Cycle-New PDFKiran Sugandhi100% (1)
- Sap - IsuDocument10 pagesSap - IsuRohit BebartaNo ratings yet
- Schedule Master Device Master: Create A PortionDocument12 pagesSchedule Master Device Master: Create A PortionSaqibNo ratings yet
- Manage Advanced Meters and Meter Data ExchangeDocument70 pagesManage Advanced Meters and Meter Data ExchangeAmiz IzmmNo ratings yet
- SAP Comparison of FI-AR Vs FI-CADocument29 pagesSAP Comparison of FI-AR Vs FI-CAsid_das7193% (15)
- SAP Meter TO Cash NDocument64 pagesSAP Meter TO Cash NJohn100% (1)
- SAP FICA configuration stepsDocument28 pagesSAP FICA configuration stepsshammi_manchandani71% (7)
- Overview of SAP IS-U CCS ModulesDocument14 pagesOverview of SAP IS-U CCS Modulesapi-19771573100% (1)
- Sap Isu UtilitiesDocument30 pagesSap Isu UtilitiesMohanta Das67% (9)
- Utilities C - FSUTIL - 60 Certification Sample Questions With KeyDocument6 pagesUtilities C - FSUTIL - 60 Certification Sample Questions With KeyMadhukar Reddy SuramNo ratings yet
- Configuration Steps in SAP FICADocument33 pagesConfiguration Steps in SAP FICAMinh Khoa100% (1)
- Sap Fica Overview With Configuration Details 39 PagesDocument39 pagesSap Fica Overview With Configuration Details 39 Pagesmayura80% (5)
- FI-CA Basics and Master Data ObjectsDocument12 pagesFI-CA Basics and Master Data ObjectsIvica999No ratings yet
- FICA OverviewDocument81 pagesFICA OverviewHFNo ratings yet
- Edm Cookbook Basic Customizing Settings)Document62 pagesEdm Cookbook Basic Customizing Settings)Chong Wang100% (1)
- SAP ISU overview for utility billing and customer managementDocument11 pagesSAP ISU overview for utility billing and customer managementabhimittal007No ratings yet
- IS-Utilities: Manish KumarDocument23 pagesIS-Utilities: Manish Kumarsuman_yarlagaddaNo ratings yet
- SAP FICA - Business Functions - Sachin H PatilDocument25 pagesSAP FICA - Business Functions - Sachin H PatilLynguyenNo ratings yet
- SAP ISU TheoryDocument5 pagesSAP ISU TheoryNilesh NagarNo ratings yet
- FICA Configuration Step by Step - SAP Expertise Consulting PDFDocument35 pagesFICA Configuration Step by Step - SAP Expertise Consulting PDFsrinivaspanchakarla50% (6)
- Dynamic Periodic Control CookbookDocument10 pagesDynamic Periodic Control CookbookRehan Khan100% (2)
- Collective Bill: Creation of Posting DocumentsDocument1 pageCollective Bill: Creation of Posting DocumentsErika AraujoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Process To Create ISU Master Data?Document4 pagesWhat Is The Process To Create ISU Master Data?Suhas MisalNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument13 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentsoumyajit1986No ratings yet
- Substationsfinal2013 PDFDocument137 pagesSubstationsfinal2013 PDFManoj RanaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installations On Construction SitesDocument36 pagesElectrical Installations On Construction SitesvozoscribdNo ratings yet
- Varient Details1Document119 pagesVarient Details1soumyajit1986100% (1)
- Billing and InvoicingDocument6 pagesBilling and Invoicingsoumyajit1986100% (1)
- Process for Move-In, Date Change, and Display using EC50E, EC51E, EC52E Transaction CodesDocument5 pagesProcess for Move-In, Date Change, and Display using EC50E, EC51E, EC52E Transaction Codessoumyajit1986No ratings yet
- Business Model Canvas TemplateDocument23 pagesBusiness Model Canvas Templatesoumyajit198667% (6)
- Billing and InvoicingDocument6 pagesBilling and Invoicingsoumyajit1986100% (1)
- EDM - Screen Shot For Profile CreationDocument20 pagesEDM - Screen Shot For Profile Creationsoumyajit1986No ratings yet
- QuizDocument14 pagesQuizsoumyajit1986No ratings yet
- QuizDocument14 pagesQuizsoumyajit1986No ratings yet
- Map relationships between utility registersDocument18 pagesMap relationships between utility registerssoumyajit1986No ratings yet
- Sap PM End User Manual Calibration ProcessDocument41 pagesSap PM End User Manual Calibration ProcessMike Tan100% (2)
- Plant Maintenance OverviewDocument47 pagesPlant Maintenance OverviewSatyaprasad ChilkaNo ratings yet
- EDM - Screen Shot For Profile CreationDocument20 pagesEDM - Screen Shot For Profile Creationsoumyajit1986No ratings yet
- 02 ACSR ZEBRA ConductorDocument37 pages02 ACSR ZEBRA Conductorsanjeevchhabra100% (2)
- Aud Sap Integration White Paper FinalDocument7 pagesAud Sap Integration White Paper Finalsoumyajit19860% (1)
- Structure For Flat Rate BillingDocument1 pageStructure For Flat Rate Billingsoumyajit1986No ratings yet
- Isu TablesDocument1 pageIsu Tablessoumyajit1986No ratings yet
- Season Group Calculation in Noninterval Scenario PDFDocument34 pagesSeason Group Calculation in Noninterval Scenario PDFsoumyajit1986No ratings yet
- Plumbing Arithmetic RefresherDocument80 pagesPlumbing Arithmetic RefresherGigi AguasNo ratings yet
- CGL Flame - Proof - MotorsDocument15 pagesCGL Flame - Proof - MotorspriteshNo ratings yet
- Capex Vs RescoDocument1 pageCapex Vs Rescosingla.nishant1245No ratings yet
- Country Profile - NigerDocument1 pageCountry Profile - Nigernana kayNo ratings yet
- Raptor SQ2804 Users Manual English v2.12Document68 pagesRaptor SQ2804 Users Manual English v2.12JaimeNo ratings yet
- MP & MC Module-4Document72 pagesMP & MC Module-4jeezNo ratings yet
- Abend CodesDocument8 pagesAbend Codesapi-27095622100% (1)
- Clinical Indications, Treatment and Current PracticeDocument14 pagesClinical Indications, Treatment and Current PracticefadmayulianiNo ratings yet
- O-L English - Model Paper - Colombo ZoneDocument6 pagesO-L English - Model Paper - Colombo ZoneJAYANI JAYAWARDHANA100% (4)
- SWOT AnalysisDocument6 pagesSWOT Analysishananshahid96No ratings yet
- Classification of Methods of MeasurementsDocument60 pagesClassification of Methods of MeasurementsVenkat Krishna100% (2)
- Self-Learning Module in General Chemistry 1 LessonDocument9 pagesSelf-Learning Module in General Chemistry 1 LessonGhaniella B. JulianNo ratings yet
- Developmen of Chick EmbryoDocument20 pagesDevelopmen of Chick Embryoabd6486733No ratings yet
- Unitary Small Air-Conditioners and Air-Source Heat Pumps (Includes Mixed-Match Coils) (RATED BELOW 65,000 BTU/H) Certification ProgramDocument65 pagesUnitary Small Air-Conditioners and Air-Source Heat Pumps (Includes Mixed-Match Coils) (RATED BELOW 65,000 BTU/H) Certification ProgramAmer GaladNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing Eighth Edition Philip Kotler and Gary ArmstrongDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Marketing Eighth Edition Philip Kotler and Gary ArmstrongJunaid KhalidNo ratings yet
- Lte Numbering and AddressingDocument3 pagesLte Numbering and AddressingRoderick OchiNo ratings yet
- Popular Tools CatalogDocument24 pagesPopular Tools CatalogCarbide Processors IncNo ratings yet
- IS 2848 - Specition For PRT SensorDocument25 pagesIS 2848 - Specition For PRT SensorDiptee PatingeNo ratings yet
- Performance of a Pelton WheelDocument17 pagesPerformance of a Pelton Wheellimakupang_matNo ratings yet
- Marketing of Agriculture InputsDocument18 pagesMarketing of Agriculture InputsChanakyaNo ratings yet
- Talon Star Trek Mod v0.2Document4 pagesTalon Star Trek Mod v0.2EdmundBlackadderIVNo ratings yet
- Government of The Punjab Primary & Secondary Healthcare DepartmentDocument3 pagesGovernment of The Punjab Primary & Secondary Healthcare DepartmentYasir GhafoorNo ratings yet
- Pic Attack1Document13 pagesPic Attack1celiaescaNo ratings yet
- FIDIC delay and disruption standardsDocument7 pagesFIDIC delay and disruption standardsMohammad FayazNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Mental Health Nursing Exam ReviewDocument28 pagesAIIMS Mental Health Nursing Exam ReviewImraan KhanNo ratings yet
- Pharma Pathway SopDocument350 pagesPharma Pathway SopDinesh Senathipathi100% (1)
- Gavrila Eduard 2Document6 pagesGavrila Eduard 2Eduard Gabriel GavrilăNo ratings yet
- Verification of First Law V-SonometerDocument3 pagesVerification of First Law V-SonometerRick astley's microphoneNo ratings yet
- EasyLogic PM2000 Series - METSEPM2130Document4 pagesEasyLogic PM2000 Series - METSEPM2130ٍJordan SportNo ratings yet
- Siemens MS 42.0 Engine Control System GuideDocument56 pagesSiemens MS 42.0 Engine Control System GuideIbnu NugroNo ratings yet