Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chromosome Mapping
Uploaded by
Vipin100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views22 pagesEach chromosome has many loci. Genes are arranged in a linear fashion. Genetic maps are a graphical representation of relative distances between linked genes. The linear order of linked genes is identical in both the maps.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEach chromosome has many loci. Genes are arranged in a linear fashion. Genetic maps are a graphical representation of relative distances between linked genes. The linear order of linked genes is identical in both the maps.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views22 pagesChromosome Mapping
Uploaded by
VipinEach chromosome has many loci. Genes are arranged in a linear fashion. Genetic maps are a graphical representation of relative distances between linked genes. The linear order of linked genes is identical in both the maps.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
Chromosome Mapping
In1903 Sutton and Boveri came up with
the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance.
Evidences accumulated pointing that
genes make up chromosomes.
Each chromosome has many loci.
Genes are arranged in a linear fashion on
the chromosomes.: Sturtevant.
Sturtevant’s map included 5 genes on the X
chromosome of Drosophila
Alleliccombinations would be permanent if
the loci are locked.
At meiosis, crossing over allows the
associated alleles to show a degree of
independence.
Loci carried on the same chromosome are
said to be linked.
Number of linkage groups (l) is equal to
the number of haploid set of
chromosomes plus the sex chromosomes
in an organism.
Drosophila (2n = 8) has l = 3 autosomes
+ x + y = 5 linkage groups.
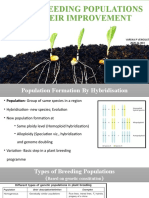
Diagrammatic graphical
representation of relative distances
between linked genes of a
chromosomes is called Linkage or
Genetic map.
Determination of linkage groups
Hybridisationexperiments between wild
and mutant strains.
Linked phenotypic traits can be
determined.
Map Distance
Calculated depending on the percentage
of crossing over.
Crossing over frequency is directly
proportional to the distance between
genes.
Map unit / morgan / centi morgan
Two point test cross
Three point cross
Gene order
After
determining the relative distances
between the genes of a linkage group, it
becomes easy to place genes in their
proper linear order.
Combining map segments
Thedifferent segments of maps of a
complete chromosome are combined to
form a complete genetic map.
Chromosome, cytological &
physical mapping
Specialcytological techniques are used to
determine the physical locations of a gene
in a chromosome.
Differences between genetic &
chromosome maps
The frequency of crossing over varies in
different segments of the chromosome.
Frequency of crossing over is predictable
between any two gene loci.
Distance between linked genes bears no
direct relation to the map distances
calculated on the basis of cross over
percentages.
Thelinear order of linked genes is
identical in both the maps.
Uses of genetic maps
Displays the exact location, arrangement
& combination of genes in a linkage group
or chromosome.
Predicts the results of di-hybrid and tri-
hybrid crosses
References
Robert Tamarin: Principles of genetics, 7th
edition.
Griffith et al: Genetics
B.D. Singh: Fundamentals of genetics
You might also like
- 7 Linkage MappingDocument86 pages7 Linkage MappingEmi JiHyeon KimNo ratings yet
- Gene MappingDocument4 pagesGene MappingOlib OlieNo ratings yet
- Crossing Over: Cc5 AssignmentDocument18 pagesCrossing Over: Cc5 AssignmentAnjishnu Mukhopadhyay BIOTECH SXCBNo ratings yet
- 12 Marker-Assisted Selection LecDocument34 pages12 Marker-Assisted Selection Lecvijjumandula0% (1)
- Fdocuments - in General Microbiology Spotters by DR Sudheer Kher MD Hod MicrobiologyDocument32 pagesFdocuments - in General Microbiology Spotters by DR Sudheer Kher MD Hod MicrobiologyOppo VivoNo ratings yet
- Population Formation by HybridisationDocument50 pagesPopulation Formation by Hybridisationvarsha pNo ratings yet
- Linkage: Harshraj Subhash Shinde KKW, Cabt, NashikDocument14 pagesLinkage: Harshraj Subhash Shinde KKW, Cabt, Nashiksivaram888No ratings yet
- Pooja Anshul Saxena Engr 692: Special Topics - Computational BiologyDocument24 pagesPooja Anshul Saxena Engr 692: Special Topics - Computational BiologyKhushman TaunkNo ratings yet
- Crop ImprovementDocument14 pagesCrop ImprovementhappydaysvsNo ratings yet
- Submitted by Aiswarya V 1St MSC Zoology Roll Number 3301Document32 pagesSubmitted by Aiswarya V 1St MSC Zoology Roll Number 3301PES PEOPLENo ratings yet
- Sequence Alignment Methods and AlgorithmsDocument37 pagesSequence Alignment Methods and AlgorithmsKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Karyotype Analysis in Zea Mays L. Var. Everta (Popcorn) Cultivated Within Owerri, Southeast NigeriaDocument6 pagesKaryotype Analysis in Zea Mays L. Var. Everta (Popcorn) Cultivated Within Owerri, Southeast NigeriaImpact JournalsNo ratings yet
- 5 Male Sterility 29-3-17Document64 pages5 Male Sterility 29-3-17Aizaz AliNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Linkage and Crossing OverDocument34 pages7.1 Linkage and Crossing OverDhungana Surya RdNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument55 pagesPolymerase Chain ReactionFareeha ZahoorNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Biology EDUNCLEDocument54 pagesInheritance Biology EDUNCLEEvita Almeida100% (1)
- Cytogenetic Slide PreparationDocument9 pagesCytogenetic Slide PreparationRicardo PalmaNo ratings yet
- Ch-Immobilization of Enzyme PDFDocument92 pagesCh-Immobilization of Enzyme PDFVNo ratings yet
- Transposons in HumansDocument22 pagesTransposons in HumansRishiNo ratings yet
- Linkage, Crossing-Over, & GeneDocument13 pagesLinkage, Crossing-Over, & GeneAbel ClaireNo ratings yet
- Crispr Cas HajarDocument21 pagesCrispr Cas HajarHajira Fatima100% (1)
- Gene PredictionDocument50 pagesGene Predictionsaeedahmad901No ratings yet
- GE IV TH SemDocument185 pagesGE IV TH Semrahul vivekNo ratings yet
- Lectures 3 and 4 - Mendelian GeneticsDocument36 pagesLectures 3 and 4 - Mendelian GeneticsnizobellNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes Using.12Document9 pagesAssessment of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes Using.12Muhammad Rifki100% (1)
- Rna EditingDocument31 pagesRna EditingAarthi VijayNo ratings yet
- Classification of Plasmid Vectors Using Replication Origin, Selection Marker and Promoter As Criteria. WWW - Picb.ac - CNDocument5 pagesClassification of Plasmid Vectors Using Replication Origin, Selection Marker and Promoter As Criteria. WWW - Picb.ac - CNAhmad SolikinNo ratings yet
- Methods To Study Soil Microbial DiversityDocument25 pagesMethods To Study Soil Microbial Diversityrd2165scribdNo ratings yet
- Dragon Genetics ProtocolDocument10 pagesDragon Genetics Protocolmu-aliNo ratings yet
- Substitution MatrixDocument10 pagesSubstitution MatrixRashmi DhimanNo ratings yet
- Signal Transduction in CellsDocument25 pagesSignal Transduction in CellsSadaf BegNo ratings yet
- ChromosomesDocument4 pagesChromosomesعامر جدونNo ratings yet
- CRISPR/Cas9 in Zebrafish: An Efficient Combination For Human Genetic Diseases ModelingDocument27 pagesCRISPR/Cas9 in Zebrafish: An Efficient Combination For Human Genetic Diseases ModelingArshia NazirNo ratings yet
- Dna Genes Chromosomes 2011Document65 pagesDna Genes Chromosomes 2011Suliman GarallehNo ratings yet
- Structure of Nuclear Genetic Material - Dna, Rna and Gene: CourseDocument65 pagesStructure of Nuclear Genetic Material - Dna, Rna and Gene: Coursebharath margamNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells and Organ CultureDocument18 pagesStem Cells and Organ CultureGEETA MOHANNo ratings yet
- Shotgun SequencingDocument29 pagesShotgun SequencingKhyati JoshiNo ratings yet
- Genetics Take Home TestDocument12 pagesGenetics Take Home TestEdgarTriff50% (2)
- Statistics: 1-Completely Randomized DesignDocument20 pagesStatistics: 1-Completely Randomized Designمصطفى الصومالNo ratings yet
- RibozymesDocument29 pagesRibozymesJesus Llorente mendozaNo ratings yet
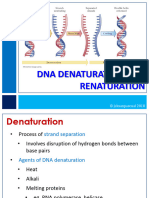
- BIO101 Lec 04-DNA Denaturation and RenaturationDocument29 pagesBIO101 Lec 04-DNA Denaturation and RenaturationMika MaravillaNo ratings yet
- PCR, RT-PCR, Nested-Pcr, Multiplex PCR, Quantitative PCRDocument116 pagesPCR, RT-PCR, Nested-Pcr, Multiplex PCR, Quantitative PCRYunizardiNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Blotting TechniquesDocument33 pages5.1 Blotting TechniquesAmir Al-AimanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3: DNA RecombinationDocument22 pagesLecture 3: DNA RecombinationBiotechnology IIUM Kuantan100% (2)
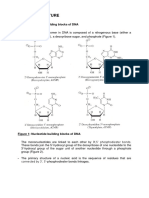
- Dna StructureDocument23 pagesDna StructureAnonymous mHS76aNo ratings yet
- Plant Taxonomy NotesDocument38 pagesPlant Taxonomy Notesopolla nianorNo ratings yet
- Application of Nanoparticles in MedicineDocument20 pagesApplication of Nanoparticles in MedicineBandita DattaNo ratings yet
- Genomics and Crop ImprovementDocument56 pagesGenomics and Crop Improvementsenguvelan100% (6)
- Primer DesignDocument37 pagesPrimer DesignRyu- MikaNo ratings yet
- Sequence Alignment Methods and AlgorithmsDocument37 pagesSequence Alignment Methods and Algorithmsapi-374725475% (4)
- NCBI - Map ViewerDocument19 pagesNCBI - Map Viewersherfudeen100% (1)
- Karyotype ActivityDocument4 pagesKaryotype ActivityRut ChristineNo ratings yet
- Genetic Mapping & Recombination Frequency PDFDocument59 pagesGenetic Mapping & Recombination Frequency PDFNandiniNo ratings yet
- Organogenesis: By, BIRAC Innovation Fellow University of Agricultural Sciences, DharwadDocument24 pagesOrganogenesis: By, BIRAC Innovation Fellow University of Agricultural Sciences, DharwadTabada NickyNo ratings yet
- Genome Sequencing: Dr. P. Balaji Vysya College, HosurDocument72 pagesGenome Sequencing: Dr. P. Balaji Vysya College, HosurBalaji PaulrajNo ratings yet
- Polytene and Lampbrush ChromosomesDocument3 pagesPolytene and Lampbrush Chromosomesneeru.bhagatNo ratings yet
- Agrobacterium Mediated Gene Transfer BA3825 SWaghmareDocument8 pagesAgrobacterium Mediated Gene Transfer BA3825 SWaghmareSubash Ragasudha100% (1)
- Isolation of Genomic DNADocument8 pagesIsolation of Genomic DNAMadhuri HarshaNo ratings yet
- Protein Microarray Naveed Up MushtaqDocument16 pagesProtein Microarray Naveed Up MushtaqAngumaniNo ratings yet
- TLC3000 Operation Manual 3Document13 pagesTLC3000 Operation Manual 3VipinNo ratings yet
- Higashiyama Temple Walk, TakayamaDocument1 pageHigashiyama Temple Walk, TakayamaVipinNo ratings yet
- The Shadow Warriors of JapanDocument49 pagesThe Shadow Warriors of JapanVipin100% (2)
- DNA ReplicationDocument83 pagesDNA ReplicationVipin100% (8)
- TranscriptionDocument56 pagesTranscriptionVipin100% (8)
- Translation 1Document71 pagesTranslation 1VipinNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiotechnologyDocument109 pagesMolecular BiotechnologyVipin100% (5)
- 3.091 - Introduction To Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 5 X-Rays and X-Ray DiffractionDocument22 pages3.091 - Introduction To Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 5 X-Rays and X-Ray DiffractionVipin83% (6)
- C.G, Vipin Shankar Iii Sem Msc. BiochemistryDocument75 pagesC.G, Vipin Shankar Iii Sem Msc. BiochemistryVipin100% (8)
- UGC - B.Sc. Life Sciences - New PDFDocument114 pagesUGC - B.Sc. Life Sciences - New PDFjerryNo ratings yet
- Botany Ug SyllabusDocument205 pagesBotany Ug SyllabusJinu MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Meiosis ppt.2014Document30 pagesMeiosis ppt.2014Ernesto Dasalla IIINo ratings yet
- Assignment Biology (II) Continuity of LifeDocument18 pagesAssignment Biology (II) Continuity of Life秋秋No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument71 pagesCell Divisionsarah575No ratings yet
- Evolución Del Genero Varanus PDFDocument20 pagesEvolución Del Genero Varanus PDFJose Ayotli AtzinNo ratings yet
- Prescotts Microbiology 10Th Edition Willey Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument25 pagesPrescotts Microbiology 10Th Edition Willey Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFbob.morris579100% (14)
- Cell CycleDocument19 pagesCell CycleLaureen BarbsNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 KaryotypesDocument2 pagesLab 5 Karyotypesapi-224251981No ratings yet
- BIO 1510 Exam III - Yellow VersionDocument8 pagesBIO 1510 Exam III - Yellow VersionPaige DarbonneNo ratings yet
- Down Syndrome Research PaperDocument4 pagesDown Syndrome Research PaperIsabeloCruzNo ratings yet
- B.SC., 2 Year, 3 Semester Paper-III: Cell Biology, Genetics and Immunology Cell DivisionDocument24 pagesB.SC., 2 Year, 3 Semester Paper-III: Cell Biology, Genetics and Immunology Cell DivisionLAZY I LEoPARDNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Biology AEODocument4 pagesSynopsis Biology AEOnoyNo ratings yet
- Biology Qns v2Document37 pagesBiology Qns v2randomvidsNo ratings yet
- Genes in A Bottle Instruction ManualDocument42 pagesGenes in A Bottle Instruction ManualdnajenNo ratings yet
- SAS For Biochemistry BIO 024 Module 6 1Document33 pagesSAS For Biochemistry BIO 024 Module 6 1vovoka449No ratings yet
- From Latin Cella, Meaning "Small Room) : All Living Things Are Made of CellsDocument18 pagesFrom Latin Cella, Meaning "Small Room) : All Living Things Are Made of CellsSyed Ali HadiNo ratings yet
- Course Contents-IISERBDocument228 pagesCourse Contents-IISERBSandeep SatapathyNo ratings yet
- KaryotypeDocument9 pagesKaryotypeAppas SahaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Medicine.Medical Biology.Document50 pagesSyllabus - Medicine.Medical Biology.MA1910o nii odoi pattersonNo ratings yet
- Ts - X - Biology Govt-Pre Final 1& 2 Chapter Wise - QuestionsDocument48 pagesTs - X - Biology Govt-Pre Final 1& 2 Chapter Wise - QuestionsqwertyuiopNo ratings yet
- Turner Syndrome: A Guide For FamiliesDocument30 pagesTurner Syndrome: A Guide For FamiliesTatiana Pogo RamosNo ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology (PDE 102)Document125 pagesDevelopmental Psychology (PDE 102)Anita Lawal100% (4)
- First Observation For Inheritance Being Related To A Metabolic PathwayDocument5 pagesFirst Observation For Inheritance Being Related To A Metabolic PathwayRakshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cbse-Ix-Bio-Mcq'S-The Cell & Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument4 pagesCbse-Ix-Bio-Mcq'S-The Cell & Fundamental Unit of LifeJonnada MrunalNo ratings yet
- Nature of Genes and ChromosomesDocument19 pagesNature of Genes and ChromosomesGenne Rose SelgueraNo ratings yet
- Gentics PDFDocument7 pagesGentics PDFHarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- BC Cellular Structure and FunctionDocument57 pagesBC Cellular Structure and FunctionPaul CriolloNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Vs Prokaryotic Cell - Difference and Comparison - DiffenDocument11 pagesEukaryotic Cell Vs Prokaryotic Cell - Difference and Comparison - DiffenAdnan Malik100% (2)
- Cells and DNA: Help Me Understand GeneticsDocument17 pagesCells and DNA: Help Me Understand Geneticsarshi_pimNo ratings yet