Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ex4 - Neurulation Reviewer
Uploaded by
rexartooz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
117 views2 pagesdsadsa
Original Title
Ex4- Neurulation Reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdsadsa
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
117 views2 pagesEx4 - Neurulation Reviewer
Uploaded by
rexartoozdsadsa
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Exercise
4: Organogenesis (Neurulation) MFDTuazon 1
Neurulation- Neurulation refers to the folding
nephrotome) excretory system
process in vertebrate embryos, which includes
the transformation of the neural plate into the
Mesomere (intermediate mesoderm =
Hypomere (lateral plate mesoderm) will
neural tube. The embryo at this stage is
differentiate into the inner splanchnic and
termed the neurula.
outer somatic
Endoderm:
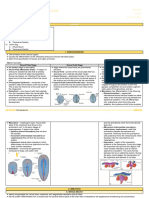
I. Neural Plate stage
surrounds the gastrocoel
II. Neural Fold Stage
Neural plate:
-
region of embryonic ectodermal cells
(neuroectoderm)
Neural folds:
folds to form the neural fold -> neural
tube
Neural groove:
syn: medullary plate
Presumptive epidermis:
-
Notochord:
directly
will give rise to the neurocoel
Hypochordal:
beneath
the
neural
plate,
originating from the mesoderm (dorsal
-
depression in the midline formed by the
folding of the neural plate
- remainder of the ectoderm
-
portion of the neural plate that is elevated
group of cells bet. The notochord and
archenteric roof
region of the archenteric roof)
fate: temporary
fate: temporary (will disappear)
syn: subnotochordal roof
Mesoderm:
-
Epimere (dorsal mesoderm) - somites
2 Exercise 4: Organogenesis (Neurulation) MFDTuazon
III. Neural Tube Stage
Pronephros
Mesomere
Metanephros
Mesenchyme
Mesonephros
outer
somatic
mesoderm
Neural tube
Hypomere
Neurocoel: cavity of the neural tube
inner
splanchnic
mesoderm
Neural crest cells:
-
group of cells above the neural tube
fate: migrate throughout the embryo to
from
ganglia,
sympathetic
nervous
system, pigment cells, parts of the gill
Note: a coelom will be formed between the outer somatic
arches, etc.
mesoderm and inner splanchnic mesoderm
Mesoderm:
-
have already differentiated
Epimere
sclerotome
axial
skeleton
myotome
muscles
dermatome
dermis
of
the
skin
You might also like
- Development of CNSDocument84 pagesDevelopment of CNSSamuel frankNo ratings yet
- Development of The Nervous System: Matt Velkey 454A Davison, Green Zone, Duke SouthDocument45 pagesDevelopment of The Nervous System: Matt Velkey 454A Davison, Green Zone, Duke SouthAbdimalik AliNo ratings yet
- Trans 5 - Frog OrganogenesisDocument32 pagesTrans 5 - Frog Organogenesisangelica sherinnNo ratings yet
- 24 HR Chick ReviewerDocument4 pages24 HR Chick ReviewerGail AmuraoNo ratings yet
- Failure of Neuropores To Close Can Cause Neural Tube DefectsDocument6 pagesFailure of Neuropores To Close Can Cause Neural Tube DefectsMargo Roth SpiegelmanNo ratings yet
- 04 - Develpment Week 3Document12 pages04 - Develpment Week 3hiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Embryology 1 Asr 3eny New 2024Document9 pagesEmbryology 1 Asr 3eny New 2024Hassan AwadNo ratings yet
- Dumaguit (2021)Document12 pagesDumaguit (2021)Dimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument38 pagesImportant Questionsas3941asNo ratings yet
- Midbrain Cerebral Aqueduct Forebrain: ThalamusDocument9 pagesMidbrain Cerebral Aqueduct Forebrain: ThalamusKrystel Mae SantistebanNo ratings yet
- 24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateDocument18 pages24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateDimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Development of Nervous System - NewkeynoteDocument49 pagesDevelopment of Nervous System - Newkeynotejesse716No ratings yet
- Acrisologobsbio2 ADocument3 pagesAcrisologobsbio2 ACrisologo AllenNo ratings yet
- 2014.08 - KIN - Spinal Cord EmbryologyDocument51 pages2014.08 - KIN - Spinal Cord Embryologyihwan Ukhrawi AlyNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument48 pagesNervous SystemSuvalari Mimi JonathanNo ratings yet
- Neuroembryology and NeurohistologyDocument5 pagesNeuroembryology and NeurohistologyCZARINA TUAZONNo ratings yet
- Histo 14 Nervous Tissue 1Document7 pagesHisto 14 Nervous Tissue 1Hashim GhazoNo ratings yet
- Module 12 Handouts Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesModule 12 Handouts Nervous Systemgianarido30No ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document4 pagesChapter 8Mia Kristhyn Calinawagan SabanalNo ratings yet
- Derivatives of EctodermDocument22 pagesDerivatives of EctodermRagdha MehdawiNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Period 4-8weekDocument25 pagesEmbryonic Period 4-8weekaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- DEVELOPMENT NERVOUS SYSTEM Brain Face PDFDocument15 pagesDEVELOPMENT NERVOUS SYSTEM Brain Face PDFChidera EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- The Differentiation of Nervous System-2018Document36 pagesThe Differentiation of Nervous System-2018NadhillaHauraWahyudianaNo ratings yet
- Tail Neural Tube Notochord Segmented Mesoderm Fin Folds: Epiphysis Olfactory Placodes Lens PlacodeDocument2 pagesTail Neural Tube Notochord Segmented Mesoderm Fin Folds: Epiphysis Olfactory Placodes Lens PlacodeMarina of The SeaNo ratings yet
- Chick NeurulationDocument14 pagesChick NeurulationSophia RubiaNo ratings yet
- Embryo Edited 2ed LectureDocument17 pagesEmbryo Edited 2ed Lectureapi-249972919No ratings yet
- Ns1 Assignment 1 Neuroembryology and NeurohistologyDocument4 pagesNs1 Assignment 1 Neuroembryology and NeurohistologyMark AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Assengment Vertebrate Embryology Ahmed M.SaladDocument4 pagesAssengment Vertebrate Embryology Ahmed M.SaladAhmed Mohammed salaadNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument296 pagesNervous SystemDr. Serin KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Brain StemDocument28 pagesChapter 12 - Brain Stemانس ابوهيبةNo ratings yet
- Development of The Nervous System and Special Senses: NeurulationDocument56 pagesDevelopment of The Nervous System and Special Senses: NeurulationTeodora GeorgescuNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve: Nikita Sebastian Mds I Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics JSSDCHDocument63 pagesTrigeminal Nerve: Nikita Sebastian Mds I Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics JSSDCHNikita SebastianNo ratings yet
- Practice QuizDocument3 pagesPractice Quizcrystal jane EnalisanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4.1Document9 pagesTutorial 4.1Rosa FinizioNo ratings yet
- Three Main Functions:: The Nervous System Is The Master Controlling System of The BodyDocument34 pagesThree Main Functions:: The Nervous System Is The Master Controlling System of The Bodyapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Anatomy No.2Document71 pagesAnatomy No.2hendalzeer02No ratings yet
- Development of The Central Nervous System: Consists of The Brain and Spinal Cord Derived From The Neural TubeDocument42 pagesDevelopment of The Central Nervous System: Consists of The Brain and Spinal Cord Derived From The Neural TubeZyra PerolNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Period: Dr. Khin Ma MADocument34 pagesEmbryonic Period: Dr. Khin Ma MAIbrahim Foondun100% (1)
- 24 HR Chick ReviewerDocument4 pages24 HR Chick ReviewerClarebelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anat 1019 NeuroDocument37 pagesAnat 1019 NeurotakakamiseriaNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The CNS 2022Document130 pagesEmbryology of The CNS 2022isicheipraise3No ratings yet
- OrganogenesisDocument6 pagesOrganogenesisnitesh.th15005No ratings yet
- Development of The NSDocument7 pagesDevelopment of The NSJean Pierre Chastre LuzaNo ratings yet
- Universal Embryology SummaryDocument6 pagesUniversal Embryology SummaryJason TonioloNo ratings yet
- Neurulation: Ormation of Neural Tube-The Best Studied Example of OrganogenesisDocument5 pagesNeurulation: Ormation of Neural Tube-The Best Studied Example of OrganogenesisKhushbuNo ratings yet
- Embryology Lecture 6: Induction of The EctodermDocument3 pagesEmbryology Lecture 6: Induction of The Ectodermferg jeanNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument76 pagesTrigeminal Nerveanhca4519No ratings yet
- Nervous SysDocument27 pagesNervous SysHakeemat AmusaNo ratings yet
- Ex4 Frog EmbryoDocument20 pagesEx4 Frog EmbryoJan Leightton Laxamana100% (2)
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabDocument3 pages24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- Embryo If Embryonic Period PDFDocument12 pagesEmbryo If Embryonic Period PDFRyna Miguel MasaNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument92 pagesTrigeminal Nervemounika33% (3)
- Embryo Lab Org 2Document14 pagesEmbryo Lab Org 2pauNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Spinal CordDocument27 pagesIntroduction and Spinal Cordapi-196413370% (1)
- Intro To NeurologyDocument10 pagesIntro To NeurologyShereen Al-ObinayNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Neural Development and Neurogenesis (Final)Document4 pages1.3 Neural Development and Neurogenesis (Final)Austin CabreraNo ratings yet
- NeurulationDocument9 pagesNeurulationaesha890% (1)
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.From EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.No ratings yet
- Gene Lecture 12 TranslationDocument4 pagesGene Lecture 12 TranslationrexartoozNo ratings yet
- Pex 10 03Document4 pagesPex 10 03rexartoozNo ratings yet
- Gene-Lecture 14-Regulation of Gene ExpressionDocument4 pagesGene-Lecture 14-Regulation of Gene ExpressionrexartoozNo ratings yet
- Genetics - Chromosome StructureDocument5 pagesGenetics - Chromosome StructurerexartoozNo ratings yet
- Gene-Lecture 13 - Gene Mutation and RepairDocument5 pagesGene-Lecture 13 - Gene Mutation and RepairLux HardinNo ratings yet
- Lec2B Skin and Exoskeleton Summer2014Document42 pagesLec2B Skin and Exoskeleton Summer2014rexartoozNo ratings yet
- Ex4 Frog EmbryoDocument20 pagesEx4 Frog EmbryoJan Leightton Laxamana100% (2)
- Gene Lecture 9 DNA StructureDocument5 pagesGene Lecture 9 DNA StructurerexartoozNo ratings yet
- Gene Lecture 11 TranscriptionDocument4 pagesGene Lecture 11 TranscriptionLux HardinNo ratings yet
- ENJOYDocument8 pagesENJOYLux HardinNo ratings yet
- Gene Lecture 8 LinkageDocument5 pagesGene Lecture 8 LinkageLux HardinNo ratings yet
- 6 Chromosome Mutations Variation in Number and ArrangementDocument12 pages6 Chromosome Mutations Variation in Number and Arrangementrexartooz100% (2)
- Gene Lecture 10 ReplicationDocument5 pagesGene Lecture 10 ReplicationLux HardinNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmDocument23 pagesExercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmrexartooz95% (19)
- Chapter 8 Cell MembraneDocument6 pagesChapter 8 Cell MembranerexartoozNo ratings yet
- Embryology ReviewerDocument6 pagesEmbryology ReviewerrexartoozNo ratings yet
- Ex 2 CmblabDocument31 pagesEx 2 CmblabrexartoozNo ratings yet
- CMB Chapter 2Document3 pagesCMB Chapter 2rexartooz100% (1)
- CMB Chapter 3Document4 pagesCMB Chapter 3rexartooz100% (1)
- CMB Chapter 4Document4 pagesCMB Chapter 4rexartoozNo ratings yet
- CatDocument5 pagesCatrexartoozNo ratings yet
- CAT Muscle Quick Study 121010.1Document4 pagesCAT Muscle Quick Study 121010.1marieleuniceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Intro To CellDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Intro To CellrexartoozNo ratings yet
- CMB Lab 1 9 1Document19 pagesCMB Lab 1 9 1rexartooz100% (1)
- 5 Sex Determination and Sex ChromosomesDocument9 pages5 Sex Determination and Sex Chromosomesrexartooz100% (1)
- Sec 18-23Document7 pagesSec 18-23rexartoozNo ratings yet
- Tundra DietDocument2 pagesTundra DietrexartoozNo ratings yet
- Artuz HwkPhysiolecDocument2 pagesArtuz HwkPhysiolecrexartoozNo ratings yet
- "Reflection in Embryology Levture": Rex Augustus D.C. Artuz 4BIO4Document1 page"Reflection in Embryology Levture": Rex Augustus D.C. Artuz 4BIO4Rex ArtuzNo ratings yet