Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 7 Solubility 1
Uploaded by
api-2723585210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
282 views1 pageSolubility is the ability of one substance to dissolve in another substance, at a given temperature and pressure. It is expressed in terms of the amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent to produce a saturated solution. Solution equilibrium is reached when the opposing process of dissolution and crystallization of a solute occurs at equal rates.
Original Description:
Original Title
4 7 solubility 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSolubility is the ability of one substance to dissolve in another substance, at a given temperature and pressure. It is expressed in terms of the amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent to produce a saturated solution. Solution equilibrium is reached when the opposing process of dissolution and crystallization of a solute occurs at equal rates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
282 views1 page4 7 Solubility 1
Uploaded by
api-272358521Solubility is the ability of one substance to dissolve in another substance, at a given temperature and pressure. It is expressed in terms of the amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent to produce a saturated solution. Solution equilibrium is reached when the opposing process of dissolution and crystallization of a solute occurs at equal rates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
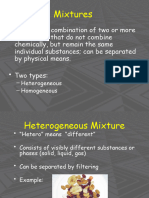
Unit 4: Solution Chemistry
Content Outline: Solubility (4.7)
I.
Solubility
A. Solubility is the ability of one substance to dissolve in another substance, at a given temperature and
pressure.
B. Solubility is expressed in terms of the amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent to
produce a saturated solution. (Most of the time it is expressed in terms of moles [Mol].)
II.
Solution equilibrium is reached when the physical state in which the opposing process of dissolution and
crystallization of a solute occurs at equal rates.
III.
Insolubility is the inability of one substance to dissolve in another substance. (For example, oil will not
dissolve in water.)
IV.
Saturated vs Unsaturated Solutions:
A. Saturated Solutions - a solution that contains the maximum amount of dissolved solute is described as a
saturated solution.
B. Unsaturated Solutions - a solution that contains less solute than a saturated solution under the existing
conditions is an unsaturated solution.
C. Supersaturated Solutions - a supersaturated solution is a solution that contains more dissolved solute
than a saturated solution under the same conditions.
You might also like
- The Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Lesson No.4: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)Document5 pagesLesson No.4: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)Franklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Solutions and Solubility NotesDocument2 pagesSolutions and Solubility Noteshimani bhandariNo ratings yet
- Solubility and Distribution PhenomenaDocument28 pagesSolubility and Distribution PhenomenaArchie Cabachete100% (1)
- Grade 7 Mixtures and Solutions Full ReviewDocument28 pagesGrade 7 Mixtures and Solutions Full Reviewblackcat657No ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 5 Water and Solution 2Document79 pagesForm 2 Chapter 5 Water and Solution 2KERTHIGA A/P VIJAYAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Mixture - SolutionDocument12 pagesMixture - Solutionmenaga ilangkovanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Solutions: Material Downloaded From SUPERCOPDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Solutions: Material Downloaded From SUPERCOPNothing is ImpossibleNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 7 Test BankDocument3 pagesScience Grade 7 Test BankAlisha EnguanchoNo ratings yet
- KSSM Form 2 Chapter 5 Water and SolutionDocument65 pagesKSSM Form 2 Chapter 5 Water and SolutionCikgu Rahmat NBJ67% (9)
- Solubility in Inorganic ChemistryDocument17 pagesSolubility in Inorganic ChemistryGessa GelocaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 SolutionsDocument11 pagesChapter 16 SolutionsMarco VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Lesson 3: Factors Affecting SolubilityDocument4 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Lesson 3: Factors Affecting SolubilityAJ ALMODANo ratings yet
- 2.solutions FDocument33 pages2.solutions Fshrutianand8915No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledAzenith CastroNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument8 pagesSolutionTamia ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Activity On SolutionsDocument7 pagesActivity On SolutionsPequiro, Dielle Ana ZilphaNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument61 pagesColligative PropertiesSubhasish Sau100% (1)
- Science q1 w3 Factors Affecting SolubilityDocument20 pagesScience q1 w3 Factors Affecting SolubilityMallen MallenNo ratings yet
- 5 Weeks: Chemistry The Central Science. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, Pp. 474-475Document4 pages5 Weeks: Chemistry The Central Science. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, Pp. 474-475Toh YangNo ratings yet
- 7aed7d83 457f 4522 9c06 40e9f10536d6 Introduction To SolutionsDocument3 pages7aed7d83 457f 4522 9c06 40e9f10536d6 Introduction To SolutionsHarvexxNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument32 pagesSolutionsMayuresh PanseNo ratings yet
- Solubility of Drugs PDFDocument66 pagesSolubility of Drugs PDFPrabhas MeherNo ratings yet
- Class Xii 1,2,3 SolutionDocument50 pagesClass Xii 1,2,3 SolutionSubhasish SauNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and Solutions LPDocument8 pagesMixtures and Solutions LPapi-247784082No ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument10 pagesSolutionsaubrey caresusaNo ratings yet
- Perpetual Succour Academy, Inc.: Teacher-Made Learner's Home TaskDocument3 pagesPerpetual Succour Academy, Inc.: Teacher-Made Learner's Home TaskMa. Joan FerrolinoNo ratings yet
- Solubility and Distribution PhenomenaDocument89 pagesSolubility and Distribution Phenomenadesekar sejati100% (2)
- 8 Mixtures and Solutions (Revised)Document44 pages8 Mixtures and Solutions (Revised)Janna May ManliguezNo ratings yet
- Module 4 in Physical ScienceDocument10 pagesModule 4 in Physical ScienceDarlyn MontillaNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument6 pagesSolutionsKathryne May JinonNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch02 SolutionsDocument5 pages12 Chemistry Notes Ch02 SolutionsHimanshu DixitNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1601430625143 6716886876762277304Document16 pagesOrca Share Media1601430625143 6716886876762277304Neil MaglalangNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document1 pageWeek 6Michelle Diaz DonaireNo ratings yet
- Perpetual Succour Academy, Inc.: National RD., Poblacion Dos, Malabuyoc, CebuDocument3 pagesPerpetual Succour Academy, Inc.: National RD., Poblacion Dos, Malabuyoc, CebuMa. Joan FerrolinoNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument18 pagesSolutionbam sygNo ratings yet
- All ExperimentsDocument42 pagesAll ExperimentsSAMAIRA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 5 Water and Solution 2Document82 pagesForm 2 Chapter 5 Water and Solution 2Anis HairiahNo ratings yet
- Solutions and SolubilityDocument28 pagesSolutions and SolubilityMhimi ViduyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Solutions Reading NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 15 - Solutions Reading Notescaffeinewriter100% (1)
- Solubility and Distribution Phenomena: Aseel SamaroDocument89 pagesSolubility and Distribution Phenomena: Aseel Samaroveneta gizdakovaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Saidane Lecture Notes Properties of Solutions: Chem 200Document10 pagesDr. Saidane Lecture Notes Properties of Solutions: Chem 200Marko QuebralNo ratings yet
- 4th Qtr. Module Week 4Document3 pages4th Qtr. Module Week 4Avirel Reynante PodadorNo ratings yet
- Physically CombinedDocument82 pagesPhysically CombinedRonalyn CariñoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 SolutionDocument2 pagesModule 2 SolutionLJ Valdez100% (1)
- Lecture 3 - Solubility & DissolutionDocument16 pagesLecture 3 - Solubility & DissolutionSHANJIDA ALI RIANo ratings yet
- G7 Science Q1 - Week 6-Unsaturated and Saturated SolutionDocument14 pagesG7 Science Q1 - Week 6-Unsaturated and Saturated SolutionJessa-Bhel AlmueteNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Biology 8Document9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Biology 8hanieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document6 pagesChapter 7Hina RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Solutions and SolubilityDocument9 pagesSolutions and SolubilityDarrell W. GarwayNo ratings yet
- Inbound 3037901320309779520Document40 pagesInbound 3037901320309779520Erica Eunice ChavezNo ratings yet
- Physiochemical and Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument10 pagesPhysiochemical and Colligative Properties of SolutionsAhmad ButtNo ratings yet
- 10 SolutionsDocument1 page10 SolutionsJessica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chem M7 SolutionsDocument27 pagesChem M7 SolutionsDiana Dealino-Sabandal100% (1)
- Larutan 1 PDFDocument21 pagesLarutan 1 PDFAnonymous 2xr3Y5VNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument32 pagesSolutionsAditya PandeyNo ratings yet
- SamiDocument13 pagesSamiTolex MelakuNo ratings yet
- Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Substances Lesson 2 PropertiesDocument95 pagesChapter Introduction Lesson 1 Substances Lesson 2 PropertiesDavid Berl100% (1)
- Solutions (Chemistry)Document11 pagesSolutions (Chemistry)Carlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- 5 3 Characteristics of GasesDocument1 page5 3 Characteristics of Gasesapi-272358521No ratings yet
- 5 1 Math - The Language of ScienceDocument2 pages5 1 Math - The Language of Scienceapi-272358521No ratings yet
- Unit 10: Electricity & Magnetism Content Outline: Electromagnetism (10.4) I. ElectromagnetismDocument1 pageUnit 10: Electricity & Magnetism Content Outline: Electromagnetism (10.4) I. Electromagnetismapi-272358521No ratings yet
- Work, Then Out of The Device by A Wire, and Back To The SourceDocument1 pageWork, Then Out of The Device by A Wire, and Back To The Sourceapi-272358521No ratings yet
- 5 4 Pressure and GasesDocument1 page5 4 Pressure and Gasesapi-272358521No ratings yet
- 4 5 Molarity 1Document1 page4 5 Molarity 1api-272358521No ratings yet
- Rates of Reactions 3 5Document1 pageRates of Reactions 3 5api-272358521No ratings yet
- 4 4 Acids Bases BuffersDocument2 pages4 4 Acids Bases Buffersapi-272358521No ratings yet
- Chemical Nomenclature 3 2Document1 pageChemical Nomenclature 3 2api-272358521No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions 3 4Document2 pagesChemical Reactions 3 4api-272358521No ratings yet
- Atomic Theory Project 2 1Document2 pagesAtomic Theory Project 2 1api-272358521No ratings yet
- Sound Waves 9 2Document2 pagesSound Waves 9 2api-272358521No ratings yet
- Subatomic Particles 2 4 1Document2 pagesSubatomic Particles 2 4 1api-272358521No ratings yet
- Atomic Model 2 2Document2 pagesAtomic Model 2 2api-272358521No ratings yet
- Properties of Matter NotesDocument2 pagesProperties of Matter Notesapi-272358521100% (2)
- Optics 9 7Document1 pageOptics 9 7api-272358521No ratings yet
- RubegoldbergprojectDocument2 pagesRubegoldbergprojectapi-272358521No ratings yet
- Fluids OutlineDocument3 pagesFluids Outlineapi-272358521No ratings yet