Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5.13.3 WS Solutions
Uploaded by
Sandra Miller0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
372 views2 pagesSolutions for the 5.13.3 worksheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSolutions for the 5.13.3 worksheet
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
372 views2 pages5.13.3 WS Solutions
Uploaded by
Sandra MillerSolutions for the 5.13.3 worksheet
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
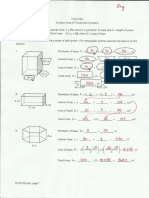
Name kaw s Date Class _
TEKS G8.A
o ism) Practice
Geometric Probability
A point is randomly chosen on AD. Find the
fractional probability of each event.
oes
1. The point is on AB. Bp > 12 2. The point is on BD.
AD Ww
3. The point is on AD. AB > VE >| 4. The point is not on BC. _
AD? S4443=12
Use the spinner to find the fractional probability of each event.
wm 4
5, the pointer landing in region © mor Ss
6. the pointer landing in region A
ow st
7. the pointer not landing in region D A= gp * 32
8. the pointer landing in regions A or 8
1d the probability that a point chosen randomly
4
inside the rectangle is in each given shape. Round eee | — as b0ne2)
answers to the nearest hundredth. se
9. the circle HF = 0.01 one
10. the trapezoid
,
11 the circle o the trapezoid Se ont
12. not the circle and the trapezoid "
Barb is practicing her chip shots on the chipping green at the yA, Hole arew
local golf club. Suppose Barb's ball drops randomly on the chipping | > (8 (w-2.087)
green. The figure shows the chipping green in a grid whose squares | > Aes mnt
have 1-yard sides. There are 18 different 4.5-inch diameter holes
on the chipping green. r2as j Green aren,
Vyd?= 1246 mn = WS yd™
= (apy in”
18, Estimate the probability that Barb will chip her ball into any hole. aus
Round to the nearest thousandth, wiou = 0.0/9
14, Estimate the probability that Barb will chip her ball into the one 228
hole she is aiming for. Round to the nearest thousandth. Taod _* 0-001
15, Estimate how many chip shots Barb will have to take to Wwaoy
ensure that one goes into a randomly selected hole, (228. = 937 shots
16. Barb is getting frustrated, so her shots are even worse. Now
the ball drops randomly anywhere in the grid shown in the figure
Estimate the probability that Barb will miss the chipping green. Round As
to the nearest thousandth. = 20 = OMS
Serer nem nen 60 Holt Geometry
Neen tai i Dap Cage
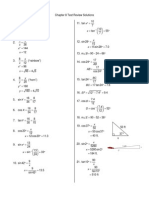
TEKS G.11.D
o Teco Practice Le ah
ine Effects of Changing Dimensions Proportionally
Describe the effect of each change on the area of the given figure.
1. The base of the parallelogram is multiplied by’.
ie 4 teen
2, The length of a rectangle with length 12 yd and width 11 yd is divided by 6
3. The base of a triangle with vertices A(2, 3), B(5, 2),
and C(5, 4) is doubled,
Hiren 1s dovlled
4. The height of a trapezoid with base lengths 4 mm
and 7 mm and height 9 mm is multiplied by 1
In Exercises 5-8, describe the effect of each change on the
perimeter or circumference and the area of the given figure.
5. The length and width of the rectangle are multiplied by ;
oo ¢
6. The base and height of a triangle with base 1.5 m and height 6 m are both tripled.
7. The radius of a circle with center (2, 2) that
passes through (0, 2) is divided by 2.
Larcomberence dured ley 2
Vi
8. The bases and the height of a trapezoid with base lengths
4 in. and 8 in. and height 8 in. are all multiplied by 2.
9. Athombus has an area of 9 om?. The area is multiplied by 5 5 G2
Describe the effects on the diagonals of the rhombus.
> \ fe use de dt
10. Acircle has a circumference of 147 ft. The area is halved,
Desoribe the effects on the circumference of the circle.
Sree Sag Ps rane 59 Holt Geometry
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- 5.13.3 WSDocument5 pages5.13.3 WSSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Geometry Spring Final Review 2016 SolutionsDocument4 pagesGeometry Spring Final Review 2016 SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- 5.13.1 WS SolutionsDocument3 pages5.13.1 WS SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- 6.14.4 WS SolutionsDocument3 pages6.14.4 WS SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- 5.13.6 WS SolutionsDocument4 pages5.13.6 WS SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 6.14.3 Puzzles SolutionsDocument2 pages6.14.3 Puzzles SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- 5.13.4 WS SolutionsDocument5 pages5.13.4 WS SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Astronomy Spring 2016 Semester Exam Review AnswersDocument2 pagesAstronomy Spring 2016 Semester Exam Review AnswersSandra Miller100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- 5.13.5 WS SolutionsDocument6 pages5.13.5 WS SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- 5.13.2 WS SolutionsDocument5 pages5.13.2 WS SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- 6.15.1 WS SolutionsDocument3 pages6.15.1 WS SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Review Packet 2 - Algebra I Notes (2015)Document10 pagesReview Packet 2 - Algebra I Notes (2015)Sandra MillerNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- 6.14.2 WS SolutionsDocument3 pages6.14.2 WS SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Human Space Exploration Book ProjectDocument2 pagesHuman Space Exploration Book ProjectSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Unit 4 Bundle 11 Test Review SolutionsDocument2 pagesUnit 4 Bundle 11 Test Review SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Dead Astronomer SocietyDocument1 pageDead Astronomer SocietySandra MillerNo ratings yet
- 6.14.1 WS SolutionsDocument4 pages6.14.1 WS SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- PAP Geometry 2nd Semester Exam Review SolutionsDocument2 pagesPAP Geometry 2nd Semester Exam Review SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- PAP Chapter 10 Test Review SolutionsDocument2 pagesPAP Chapter 10 Test Review SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Test Review SolutionsDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Test Review SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Polyhedron Template - DecagonDocument1 pagePolyhedron Template - DecagonSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- PAP Chapter 7 Test Review SolutionsDocument2 pagesPAP Chapter 7 Test Review SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Polyhedron Template - Small SquareDocument1 pagePolyhedron Template - Small SquareSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Extra Credit Project - Wheel of TheodorusDocument1 pageExtra Credit Project - Wheel of TheodorusSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- PAP Chapter 5 Test Review SolutionsDocument2 pagesPAP Chapter 5 Test Review SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- PAP Chapter 6 Test Review SolutionsDocument2 pagesPAP Chapter 6 Test Review SolutionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- PAP Geometry 1st Semester Exam Review SolutionsDocument2 pagesPAP Geometry 1st Semester Exam Review SolutionsSandra Miller100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)