Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vital Signs Reference Chart - 1
Uploaded by
l10n_assOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vital Signs Reference Chart - 1
Uploaded by
l10n_assCopyright:
Available Formats
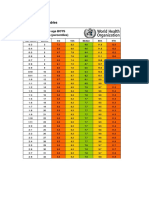
Pediatric Vital Signs Reference Chart
Please note that numerous bodies have created reference ranges, and there may be discrepancies between different
references. This table, along with our detailed references can be found online at http://www.pedscases.com/pediatricvital-signs-reference-chart. For a more detailed approach to this topic, see our podcast on Pediatric Vital Signs.
Heart Rate
Respiratory Rate
Normal Heart Rates By Age (beats/minute)
(Reference: Pediatric Advanced Life Support
Guidelines)
Awake
Sleeping
Age
Rate
Rate
Newborn to 3
85-205
80-160
months
3 months to 2
100-190
75-160
years
2 to 10 years
60-140
60-90
>10 years
60-100
50-90
Normal Respiratory Rate By Age
(breaths/minute)
(Reference: Pediatric Advanced Life Support
Guidelines)
Normal Respiratory
Age
Rate
Infants (<12 months)
30-60
Toddler (1-3 years)
24-40
Preschool (4-5 years)
22-34
School age (6-12
18-30
years)
Adolescence (13-18
12-16
years)
Note: A major 2011 systematic review of pediatric heart rate and respiratory rate suggests that previously
published reference ranges may require updating. Updated centile charts based on this study can be
found here: http://madox.org/tools-and-resources
Blood Pressure
Temperature
Hypotension Reference Ranges
(Reference: Pediatric Advanced Life Support
Guidelines)
Systolic BP in mm
Age
Hg
Term Neonates (0-28
<60
days)
Infants (1-12 months)
<70
< 70 + (age in years
Children 1-10 years
x 2)
Children >10 years
<90
For precise determination of a childs blood
pressure percentile, specific reference tables have
been developed based on a childs age, gender,
and height: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/healthpro/guidelines/current/hypertension-pediatric-jnc4/blood-pressure-tables.
Normal values for temperature do not vary
significantly with age. The type of thermometer will
alter readings, and accuracy.
Temperature Reference Ranges in Children
(Reference: CPS Position Statement on
Temperature Measurement in Pediatrics,
2015)
o
Method
Normal Range ( C)
Rectal
36.6-38
Ear
35.8-38
Oral
35.5-37.5
Axillary
36.5-37.5
The CPS recommends axillary, tympanic and
temporal artery thermometers for screening, and
rectal and oral thermometers for definitive
measurement.
Oxygen Saturation
Normal pediatric pulse oximetry (SPO2) values have not yet been firmly established. SPO2 is lower in the
immediate newborn period. Beyond this period, normal levels are stable with age. Generally, a SPO2 of
<92% should be a cause of concern and may suggest a respiratory disease or cyanotic heart disease.
Developed by Chris Novak for PedsCases.com.
Oct 26, 2015.
You might also like
- HistoryandPhysicalExamDocument105 pagesHistoryandPhysicalExamsilentscream0618No ratings yet
- The OSCE OrientationDocument25 pagesThe OSCE OrientationginadaisluNo ratings yet
- Exams NAC Guideline Rating ScaleDocument2 pagesExams NAC Guideline Rating ScaleM.Dalani100% (1)
- TDM Exam Study Resources PDFDocument5 pagesTDM Exam Study Resources PDFDrosler MedqsNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Skill Labs, Clinical History Taking, and ExaminationDocument84 pagesSkill Labs, Clinical History Taking, and ExaminationJoo Se HyukNo ratings yet
- Paeds Handbook Class2021 1568487638Document30 pagesPaeds Handbook Class2021 1568487638kafosidNo ratings yet
- The 10-Minute Physical Exam: recognizing medical syndromesFrom EverandThe 10-Minute Physical Exam: recognizing medical syndromesNo ratings yet
- 01 Pharmacology PST 05-1Document319 pages01 Pharmacology PST 05-1ambroceNo ratings yet
- OSCE Note 1Document2 pagesOSCE Note 1Presley Omorodion100% (1)
- Basic ECGDocument152 pagesBasic ECGTuấn Thanh VõNo ratings yet
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument30 pagesCase PresentationAmira HelayelNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiology and Pulmonology: A Practically Painless ReviewFrom EverandPediatric Cardiology and Pulmonology: A Practically Painless ReviewNo ratings yet
- NSG 6340 Final Exam 1.........Document9 pagesNSG 6340 Final Exam 1.........Tom0% (1)
- Essential Clinical Cases GP TraineesDocument3 pagesEssential Clinical Cases GP TraineesTahir AliNo ratings yet
- The Nurse Practitioner in UrologyFrom EverandThe Nurse Practitioner in UrologyMichelle LajinessNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics ECG by DR Ali Bel KheirDocument9 pagesPediatrics ECG by DR Ali Bel KheirFerasNo ratings yet
- SyncytiumDocument87 pagesSyncytiumjustin sNo ratings yet
- General Population (No Diabetes or CKD) Diabetes or CKD PresentDocument1 pageGeneral Population (No Diabetes or CKD) Diabetes or CKD PresentMuthia ArsilNo ratings yet
- History Taking in PaediatricsDocument3 pagesHistory Taking in PaediatricsHajar Hanis SofiaNo ratings yet
- History Taking: DR - Ahmed Gaber Ass. Prof of Neurology Ain Shams UniversityDocument81 pagesHistory Taking: DR - Ahmed Gaber Ass. Prof of Neurology Ain Shams UniversityKhaled OssamaNo ratings yet
- 7.8 Collect Data & Come Up With Plan For Day & Nursing Diagnosis Pre-Conference 8-9 Vitals Then Chart, AM Care, StartDocument2 pages7.8 Collect Data & Come Up With Plan For Day & Nursing Diagnosis Pre-Conference 8-9 Vitals Then Chart, AM Care, StartSade' CovingtonNo ratings yet
- History Taking OSCE Example 4Document6 pagesHistory Taking OSCE Example 4worlddoctor2012No ratings yet
- Roughly 50 Medical MnemonicsDocument13 pagesRoughly 50 Medical Mnemonicsmirza_baig_46100% (1)
- Diabetes and Complications: When Documenting Diabetes, It's Important To Note The FollowingDocument2 pagesDiabetes and Complications: When Documenting Diabetes, It's Important To Note The Followingmeikaizen100% (1)
- Aquifer InternalMedicine11 - 45Document8 pagesAquifer InternalMedicine11 - 45JulieNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorders: Advanced Practice Education AssociatesDocument11 pagesMood Disorders: Advanced Practice Education AssociatesAndrea100% (1)
- Lab Values & MeaningDocument1 pageLab Values & MeaningMei SarteNo ratings yet
- Medicine1 Grand PE ScriptDocument10 pagesMedicine1 Grand PE ScriptCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet
- 58 Cases History and Physical Exam BookDocument102 pages58 Cases History and Physical Exam BookeleazarmdNo ratings yet
- The Stages of Prevention - Primer On Public Health PopulationDocument2 pagesThe Stages of Prevention - Primer On Public Health PopulationBSN 201450% (2)
- 2011 09 Medical HistoryDocument52 pages2011 09 Medical HistoryGurpreet CharaNo ratings yet
- Mock Record B-1-2-Well Child VisitsDocument4 pagesMock Record B-1-2-Well Child VisitsaelteeNo ratings yet
- Preventive Care Checklist Form ExplanationsDocument3 pagesPreventive Care Checklist Form ExplanationsKak KfgaNo ratings yet
- Medical Case 1: Language Centre of Malahayati University at 2010Document16 pagesMedical Case 1: Language Centre of Malahayati University at 2010putri1114No ratings yet
- Introduction To History Taking Aims:: Summary of Procedure and NotesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To History Taking Aims:: Summary of Procedure and Notesmj.vinoth@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive H&P Note Template For Phase 1 Spring Assessment 2016Document5 pagesComprehensive H&P Note Template For Phase 1 Spring Assessment 2016Derek JonesNo ratings yet
- Csa - Rams Top Tips Part 1Document7 pagesCsa - Rams Top Tips Part 1Zaheer AliNo ratings yet
- OSCEDocument16 pagesOSCESara KhalidNo ratings yet
- Approach: A. How The Kidney Handle The Proteins?Document9 pagesApproach: A. How The Kidney Handle The Proteins?Rashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- OBGYN HistoryDocument1 pageOBGYN Historysgod34No ratings yet
- PD OSCE GuideDocument19 pagesPD OSCE GuideChorong ParkNo ratings yet
- Quick Hits for Pediatric Emergency MedicineFrom EverandQuick Hits for Pediatric Emergency MedicineCristina M. Zeretzke-BienNo ratings yet
- Blood Sample Normal Panic Values For Abgs: Clinical SignificanceDocument7 pagesBlood Sample Normal Panic Values For Abgs: Clinical SignificancegeonarcisoNo ratings yet
- H&P GuideDocument7 pagesH&P GuideTBWPNo ratings yet
- Classification of Cutaneous LupusDocument5 pagesClassification of Cutaneous Lupusl10n_assNo ratings yet
- Callen2004 Update On The Management of Cutaneous Lupus ErythematosusDocument6 pagesCallen2004 Update On The Management of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosusl10n_assNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kriteria Baru SleDocument10 pagesJurnal Kriteria Baru SleDr Edi HidayatNo ratings yet
- Boeck Ler 2009Document5 pagesBoeck Ler 2009l10n_assNo ratings yet
- Callen2009 Clinically Relevant InformationDocument4 pagesCallen2009 Clinically Relevant Informationl10n_assNo ratings yet
- Beverly J. McCabe, Eric H. Frankel, Jonathan J. Wolfe Handbook of Food-Drug InteractionsDocument1 pageBeverly J. McCabe, Eric H. Frankel, Jonathan J. Wolfe Handbook of Food-Drug Interactionsl10n_assNo ratings yet
- Wozniacka2005 Optimal Use of Antimalarials in TreatingDocument11 pagesWozniacka2005 Optimal Use of Antimalarials in Treatingl10n_assNo ratings yet
- NPPA040112 DecisiontreeDocument1 pageNPPA040112 Decisiontreel10n_assNo ratings yet
- TABLE Boys 3mo To 5yr TRICEPSage PercentileDocument2 pagesTABLE Boys 3mo To 5yr TRICEPSage Percentilel10n_assNo ratings yet
- Bmi For Age Z-ScoreDocument1 pageBmi For Age Z-ScoreTisha Patricia OedoyNo ratings yet
- F E T C: Luid AND Lectrolyte Herapy IN HildrenDocument12 pagesF E T C: Luid AND Lectrolyte Herapy IN HildrenHartantoRezaGazaliNo ratings yet
- Z Score BMI 5-19yearsold Label GirlDocument1 pageZ Score BMI 5-19yearsold Label GirlVienny Widhyanti RosaryaNo ratings yet
- TABLE Boys To 2mo Weight Increment by Birthweight PercentileDocument1 pageTABLE Boys To 2mo Weight Increment by Birthweight Percentilel10n_assNo ratings yet
- BMI For Age 5 19 BoyDocument1 pageBMI For Age 5 19 BoyJustitia LantuNo ratings yet
- GCS PDFDocument1 pageGCS PDFFrincia100% (1)
- Bmifa Boys Z 5 19 LabelsDocument1 pageBmifa Boys Z 5 19 LabelssufigueiraNo ratings yet
- Temperature MeasurementDocument5 pagesTemperature Measurementl10n_ass100% (1)
- CSFDocument1 pageCSFl10n_assNo ratings yet
- Dahlin2005 The Ketogenic Diet Influences The Levels of Excitatory and Inhibitory Amino Acids in The CSF in Children With Refractory EpilepsyDocument11 pagesDahlin2005 The Ketogenic Diet Influences The Levels of Excitatory and Inhibitory Amino Acids in The CSF in Children With Refractory Epilepsyl10n_assNo ratings yet
- CHT Acfa Boys Z 3 5Document1 pageCHT Acfa Boys Z 3 5Rivadin NurwanNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument1 pagePDFl10n_assNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument1 pagePDFl10n_assNo ratings yet
- Lubchenco Curve PDFDocument1 pageLubchenco Curve PDFWarren Lie25% (4)
- CSFDocument1 pageCSFl10n_assNo ratings yet
- Brodie2005 Diagnosing and Predicting Refractory EpilepsyDocument4 pagesBrodie2005 Diagnosing and Predicting Refractory Epilepsyl10n_assNo ratings yet
- Bough2007 Anticonvulsant Mechanisms of The Ketogenic DietDocument16 pagesBough2007 Anticonvulsant Mechanisms of The Ketogenic Dietl10n_assNo ratings yet
- Cross2013 New Research With Diets and EpilepsyDocument6 pagesCross2013 New Research With Diets and Epilepsyl10n_assNo ratings yet
- Cunnane2002 Potential Role of Polyunsaturates in Seizure Protection Achieved With The Ketogenic DietDocument5 pagesCunnane2002 Potential Role of Polyunsaturates in Seizure Protection Achieved With The Ketogenic Dietl10n_assNo ratings yet
- Best2000 Cardiac Complications in Pediatric Patients On The Ketogenic DietDocument3 pagesBest2000 Cardiac Complications in Pediatric Patients On The Ketogenic Dietl10n_assNo ratings yet