Professional Documents
Culture Documents
gr6 Waves and Currents
Uploaded by
api-3182579100 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
142 views2 pagesEnergy travels in waves, and electric current is the constant flow of electric energy. Light, sound, mechanical energy all travel in waves. A wave can be measured based on a comparison of its highest point (crest) and lowest point (trough)
Original Description:
Original Title
gr6 waves and currents
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEnergy travels in waves, and electric current is the constant flow of electric energy. Light, sound, mechanical energy all travel in waves. A wave can be measured based on a comparison of its highest point (crest) and lowest point (trough)
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
142 views2 pagesgr6 Waves and Currents
Uploaded by
api-318257910Energy travels in waves, and electric current is the constant flow of electric energy. Light, sound, mechanical energy all travel in waves. A wave can be measured based on a comparison of its highest point (crest) and lowest point (trough)
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Name: ______________________________
Waves &
Currents
When you hear the words waves and
currents, your brain might immediately make
you think about the ocean, or at least some
form of water. Thats natural, since that is
probably what you have experienced the most
in connection to those two words. But waves
and currents can be talking about energy as
well. Energy travels in waves, and electric
current is the constant ow of electric energy.
A wave, whether it is in the ocean, on land,
or in the air, is simply the movement that
takes energy from one place to another. Many
kinds of energy travel in waves. Light, sound,
An ocean wave is an
and mechanical energy all travel in waves.
example
of how energy
Sound waves, for example, are produced by
moves through water.
the vibration of particles. Plucking a string
on a guitar or violin makes the air around the
string move back and forth.
A wave can be measured based on a comparison of its highest point
(crest) and lowest point (trough). The distances between troughs and the
distance between crests are called wavelengths. You can use a timer to see
how many crests happen in a certain amount of time, and that will tell you
the frequency of a wave.
The constant ow of charged particles is an electric current. Negatively
charged particles move toward positively charged particles. Electric current
needs an unbroken path, or circuit. A circuit is made of wires, an energy
source and something that requires energy. Then the current can ow!
Understanding the Terms
1. What is a wave? How are ocean waves and sound waves similar?
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
2. What is a trough? How is it different than a crest?
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
3. What is the name for the ow of charged particles?
______________________________________________________________________________________
Copyright 2012 K12reader.com. All Rights Reserved. Free for educational use at home or in classrooms.
www.k12reader.com
Name: ______________________________
Waves &
Currents
When you hear the words waves and
currents, your brain might immediately make
you think about the ocean, or at least some
form of water. Thats natural, since that is
probably what you have experienced the most
in connection to those two words. But waves
and currents can be talking about energy as
well. Energy travels in waves, and electric
current is the constant ow of electric energy.
A wave, whether it is in the ocean, on land,
or in the air, is simply the movement that
takes energy from one place to another. Many
kinds of energy travel in waves. Light, sound,
An ocean wave is an
and mechanical energy all travel in waves.
example
of how energy
Sound waves, for example, are produced by
moves through water.
the vibration of particles. Plucking a string
on a guitar or violin makes the air around the
string move back and forth.
A wave can be measured based on a comparison of its highest point
(crest) and lowest point (trough). The distances between troughs and the
distance between crests are called wavelengths. You can use a timer to see
how many crests happen in a certain amount of time, and that will tell you
the frequency of a wave.
The constant ow of charged particles is an electric current. Negatively
charged particles move toward positively charged particles. Electric current
needs an unbroken path, or circuit. A circuit is made of wires, an energy
source and something that requires energy. Then the current can ow!
Understanding the Terms
1. What is a wave? How are ocean waves and sound waves similar?
A wave is the movement of energy from one place to another. Both ocean
______________________________________________________________________________________
waves and sound waves show the movement of energy. Energy travels
______________________________________________________________________________________
through water to make ocean waves. Sound waves are energy moving
______________________________________________________________________________________
through air.
______________________________________________________________________________________
2. What is a trough? How is it different than a crest?
A trough is the lowest point of a wavelength. A crest is the opposite of
______________________________________________________________________________________
a trough, because a crest is the highest point of a wavelength.
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
3. What is the name for the ow of charged particles?
An electric current
______________________________________________________________________________________
Copyright 2012 K12reader.com. All Rights Reserved. Free for educational use at home or in classrooms.
www.k12reader.com
You might also like
- Traveling To The Distant West: Changing Transportation NeedsDocument1 pageTraveling To The Distant West: Changing Transportation NeedsYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Whats The ForecastDocument1 pageWhats The ForecastYanny WongNo ratings yet
- What Is Tribal GovernmentDocument1 pageWhat Is Tribal GovernmentYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Tell Tale Heart CharacterDocument2 pagesTell Tale Heart CharacterYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Taiga EcosystemsDocument2 pagesTaiga EcosystemsYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Theodore RooseveltDocument2 pagesTheodore RooseveltYanny WongNo ratings yet
- ShakespeareDocument2 pagesShakespeareYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Main Idea - Tom SawyerDocument2 pagesMain Idea - Tom SawyerYanny Wong100% (1)
- Main Idea - Magna CartaDocument2 pagesMain Idea - Magna CartaYanny Wong100% (1)
- Self ReflectionDocument2 pagesSelf ReflectionYanny WongNo ratings yet
- National SymbolsDocument2 pagesNational SymbolsYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Main IdeaDocument2 pagesMain IdeaYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Pearl HabourDocument2 pagesPearl HabourYanny Wong100% (1)
- Ransom of Red ChiefDocument2 pagesRansom of Red ChiefYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Main Idea 2Document2 pagesMain Idea 2Yanny WongNo ratings yet
- Main Idea - Sleeping HollowDocument2 pagesMain Idea - Sleeping HollowYanny Wong100% (1)
- Main Idea - Solar EclipseDocument2 pagesMain Idea - Solar EclipseYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Main Idea - Moby DickDocument2 pagesMain Idea - Moby DickYanny Wong0% (1)
- Main Idea - Romeo and JulietDocument2 pagesMain Idea - Romeo and JulietYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Main Idea - David CopperfieldDocument2 pagesMain Idea - David CopperfieldYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Main Idea - Mississippi RiveDocument2 pagesMain Idea - Mississippi RiveYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Main Idea - O PioneerDocument2 pagesMain Idea - O PioneerYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Main Idea - Little WomenDocument2 pagesMain Idea - Little WomenYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Main Idea - 20000 Leaugues Under The SeaDocument2 pagesMain Idea - 20000 Leaugues Under The SeaYanny Wong100% (1)
- Inference - The Wonderful Wizard of OzDocument2 pagesInference - The Wonderful Wizard of OzYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Main Idea - Call of The WildDocument2 pagesMain Idea - Call of The WildYanny WongNo ratings yet
- Main Idea - Ben FranklinDocument2 pagesMain Idea - Ben FranklinYanny Wong33% (3)
- Main Idea - Art MovemenDocument2 pagesMain Idea - Art MovemenYanny WongNo ratings yet
- gr6 Limited ResourcesDocument1 pagegr6 Limited Resourcesapi-233355650No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Analysis of Long Term Ecological Monitoring Through Leaf Surface Temperature Parameters in Selected Evergreen and Deciduous Plants of Kodappali.Document29 pagesAnalysis of Long Term Ecological Monitoring Through Leaf Surface Temperature Parameters in Selected Evergreen and Deciduous Plants of Kodappali.Classic PrintersNo ratings yet
- Stefan-Boltzmann Law: 2 H C Exp 1Document16 pagesStefan-Boltzmann Law: 2 H C Exp 1RonyVargasNo ratings yet
- Chitendai LTD Iradiance Vs Silicon Solar PanelDocument4 pagesChitendai LTD Iradiance Vs Silicon Solar PanelRamon CuevasNo ratings yet
- EVS Lecture II 5 ValuesofBiodiversityDocument7 pagesEVS Lecture II 5 ValuesofBiodiversityBalpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Hydropower Development in NepalDocument34 pagesHydropower Development in NepalKapil Pudasaini100% (2)
- Thermodynamics by Hipolito Chapter 1Document10 pagesThermodynamics by Hipolito Chapter 1Nash Fernandez100% (6)
- Geography Form 1 Schemes of WorkDocument15 pagesGeography Form 1 Schemes of WorkOMONDI VICTOR OUMA100% (1)
- NGL Recovery ProcessesDocument16 pagesNGL Recovery ProcessesChris Richard0% (1)
- Introduction: The Formation of Deep EcologyDocument48 pagesIntroduction: The Formation of Deep EcologySRIKANTA MONDALNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography A Landscape Appreciation 9Th Edition Mcknight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument57 pagesPhysical Geography A Landscape Appreciation 9Th Edition Mcknight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFlegacycuttinglkhd100% (6)
- Experimento # 7Document3 pagesExperimento # 7GodVegeta 28 TorresNo ratings yet
- Geography ProjectDocument16 pagesGeography ProjectJai KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry f4 Mid-Year ExamDocument13 pagesChemistry f4 Mid-Year ExamWindy SanNo ratings yet
- AP Physics B Electrostatics Coulomb Law Test of TimingDocument3 pagesAP Physics B Electrostatics Coulomb Law Test of Timingsobre1982No ratings yet
- Final Class 8 Science 20230828084415550Document5 pagesFinal Class 8 Science 20230828084415550aryantomar5112No ratings yet
- SCI03 - PPT - CO4.1D - Drought El Nino La NinaDocument30 pagesSCI03 - PPT - CO4.1D - Drought El Nino La NinaEdward SnowdenNo ratings yet
- Drainage Master Plan FordelhiDocument20 pagesDrainage Master Plan FordelhiLovenish BhagatNo ratings yet
- Pressure Swing Adsorption in The Unit Operations LaboratoryDocument8 pagesPressure Swing Adsorption in The Unit Operations Laboratorydilip matalNo ratings yet
- TurbinesDocument39 pagesTurbinesHmaedNo ratings yet
- (Environmental and Microbial Biotechnology) Ram Prasad, Shi-Hong Zhang - Beneficial Microorganisms in Agriculture-Springer (2022)Document356 pages(Environmental and Microbial Biotechnology) Ram Prasad, Shi-Hong Zhang - Beneficial Microorganisms in Agriculture-Springer (2022)paulocesarNo ratings yet
- BoW - Science 7Document3 pagesBoW - Science 7John EviotaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 (Topic: Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation)Document1 pageActivity 1 (Topic: Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation)John JohnnyNo ratings yet
- 6.thermo TD Relations Objective by RajputDocument3 pages6.thermo TD Relations Objective by RajputMuruganantham MajesticNo ratings yet
- Chemical Vapour DepositionDocument10 pagesChemical Vapour Depositionkarthik sampathNo ratings yet
- Science Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03Document4 pagesScience Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Extreme Environments: Raina M. MaierDocument12 pagesExtreme Environments: Raina M. MaierEğitim ParaylaNo ratings yet
- TurbinDocument3 pagesTurbinRafliNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Majola Recycling V4Document50 pagesBusiness Plan Majola Recycling V4Darlington DhanahNo ratings yet
- Types of DistillationDocument6 pagesTypes of Distillationravi2007No ratings yet
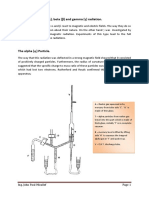
- The Nature of Alpha (Repaired) PDFDocument7 pagesThe Nature of Alpha (Repaired) PDFKeith Zammit TaboneNo ratings yet