Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multy Outlet Pipeline
Uploaded by
hekayat710 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pagesThis document provides standards for above ground, multi-outlet pipelines used for irrigation. It defines the practice as a water distribution system made of aluminum, PVC or polyethylene piping with closely spaced outlets. The purposes are to improve irrigation efficiency, reduce soil erosion and excess runoff. Criteria include minimum pipe sizes, pressure ratings, outlet gate sizing and materials specifications. Considerations for design include protection from corrosion, anchoring, and inclusion of flow measurement devices. Operation and maintenance requirements include flushing, screen cleaning, gate repair and seasonal storage.
Original Description:
Multy Outlet Pipeline
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides standards for above ground, multi-outlet pipelines used for irrigation. It defines the practice as a water distribution system made of aluminum, PVC or polyethylene piping with closely spaced outlets. The purposes are to improve irrigation efficiency, reduce soil erosion and excess runoff. Criteria include minimum pipe sizes, pressure ratings, outlet gate sizing and materials specifications. Considerations for design include protection from corrosion, anchoring, and inclusion of flow measurement devices. Operation and maintenance requirements include flushing, screen cleaning, gate repair and seasonal storage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pagesMulty Outlet Pipeline
Uploaded by
hekayat71This document provides standards for above ground, multi-outlet pipelines used for irrigation. It defines the practice as a water distribution system made of aluminum, PVC or polyethylene piping with closely spaced outlets. The purposes are to improve irrigation efficiency, reduce soil erosion and excess runoff. Criteria include minimum pipe sizes, pressure ratings, outlet gate sizing and materials specifications. Considerations for design include protection from corrosion, anchoring, and inclusion of flow measurement devices. Operation and maintenance requirements include flushing, screen cleaning, gate repair and seasonal storage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
431 - 1
NATURAL RESOURCES CONSERVATION SERVICE
CONSERVATION PRACTICE STANDARD
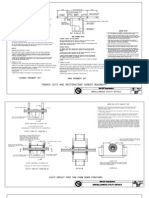
ABOVE GROUND, MULTI-OUTLET PIPELINE
(Ft.)
CODE 431
DEFINITION
A water distribution tubing consisting of
aluminum, PVC, or lay-flat polyethylene pipeline
with closely spaced orifices or gates.
PURPOSE
To increase water use efficiency on irrigated
land.
To reduce irrigation induced soil erosion.
To reduce excessive runoff, flooding, or
ponding associated with inefficient irrigation
water use.
To improve the productivity, health and vigor
of the crop.
To increase the quantity and quality of feed
and forage for domestic animals.
CONDITIONS WHERE PRACTICE APPLIES
The practice applies to irrigable land suited to
surface application methods. This practice shall
not be used in lieu of buried pipelines for
conveyance systems. However, reaches of ungated pipe may be used:
to obtain necessary working pressure for the
system,
to convey water between fields (typically
less than 300 feet),
to convey water to various points within a
field,
for splitting irrigation runs as in surge
irrigation, or
where rock precludes the installation of
buried pipelines.
Water supplies and rates of irrigation delivery for
the area served by the multi-outlet pipeline shall
be sufficient to make irrigation practical for the
crop to be grown and for the method of
application.
CRITERIA
General Criteria Applicable To All Purposes
Pipe Sizes. For durability and transportability,
rigid pipes shall be a minimum of 6 inches in
diameter and not greater than 12 inches in
diameter.
Working pressure. The maximum working
pressure for rigid pipe shall be 10 pounds per
square inch or 23 feet of head. Excess working
pressure shall be reduced to acceptable levels
by installing an appropriate head control
appurtenance.
For lay-flat polyethylene pipe, the
manufacturers recommendations for maximum
allowable working pressure shall be followed. If
the manufacturers recommendations are not
available, the hoop stress formula in National
Engineering Handbook (NEH) Part 636 Chapter
52 shall be used to determine maximum working
pressure, using a safety factor of 1.5.
Friction losses. For design purposes, friction
head losses shall be no less than those
computed by the Hazen-Williams equation,
using roughness coefficients of C=130 for
aluminum pipe and C=150 for plastic or lay-flat
polyethylene pipe. The use of PHAUCET, other
appropriate computer software, or a multiple
outlet factor shall be used in computing losses
when appropriate. Refer to National Engineering
Handbook (NEH), Part 650, EFH Chapter 15:
Irrigation for guidance.
Conservation practice standards are reviewed periodically, and updated if needed. To obtain the current
version of this standard, contact your Natural Resources Conservation Service State Office, or download it
from the electronic Field Office Technical Guide.
NRCS, NHCP
August 2006
431 - 2
Flow velocity. Velocity in the pipeline when
operating at system capacity shall not exceed 7
feet per second unless appropriate surge
protection is accounted for.
diameter and 0.058 inches for 12 inch diameter
pipe.
Capacity. The design capacity of the pipeline
shall be sufficient to deliver an adequate
irrigation stream to the design area for the
planned irrigation method.
conveying water with a copper content
exceeding 0.02 ppm,
in contact with soil having a resistivity of less
than 500 ohm-cm
in contact with soil having a pH less than 4
or greater than 9
Outlet gates. Individual outlet gates shall have
the capacity at design working pressure to
deliver the required flow to a point at least 0.3
feet above the field surface.
Head requirement. The working head shall not
be less than 0.5 feet above outlet gates, unless
a detailed design or manufacturer's literature
indicates that a lower head is adequate to
deliver the required water to the field.
Where either the design working head exceeds
5 feet or where stream flows are erosive, an
effective method of energy dissipation shall be
installed on each gate, or permanent vegetation
shall be planted along the pipeline to provide
erosion control.
Flushing. A suitable outlet shall be installed at
the end of the pipeline, if needed, for flushing
the line free of sediment or other foreign
material.
Materials. Rigid pipe shall be aluminum or
plastic material certified for above ground use.
All fittings and couplers shall equal or exceed
the pressure rating of the pipe with which they
will be used. They shall be made of material that
is recommended by the manufacturer for use
with the pipe
Rigid pipe and appurtenances shall be furnished
with a coupling system that is interchangeable
with the selected pipe material.
Rubber gaskets shall be according to the
manufacturer's standard design dimensions and
tolerances for the pipe material selected. They
shall be of such size and shape as to provide an
adequate compressive force against the spigot
and socket after assembly to effect a positive
seal. The gasket shall be the sole element
depended upon to make the joint flexible and
watertight. The gasket shall be a continuous
elastomeric ring.
Minimum wall thickness for aluminum gated pipe
shall be 0.050 inches for 6 through 10 inches in
NRCS, NHCP
August 2006
Corrosion protection shall be provided for
aluminum pipe when:
Minimum wall thickness of rigid PVC pipe shall
be 0.120 inches. The pressure rating of the pipe
shall be 22 p.s.i. or greater, prior to gate
installation.
Minimum wall thickness of lay-flat polyethylene
pipe shall be 6 mil (.006 inch).
Related structures. An open ditch supply shall
include a permanent water control structure as
the inlet to multi-outlet pipe.
When the water supply for lay-flat polyethylene
pipe is greater than 0.5 feet above ground, a
rigid pipe shall be used to convey water between
the outlet and the coupling of lay-flat
polyethylene pipe.
CONSIDERATIONS
Consider provisions for thrust control at
locations subject to pipe movement.
Consider applicability of future surge or
automation alternatives in preparing the design.
Consider the water source and potential trash
types and amounts when evaluating screen
types and sizes and in the design of an inlet
screen.
Consider effects on the water budget, including
water quality, volume of runoff, and rates of
runoff, in any downstream drainage.
Consider effects on wetlands and water related
wildlife.
Consider effects on water flows and aquifers
and the effects on other water uses and users.
Consider disposal of lay-flat polyethylene pipe
and potential of recycling.
Consider anchoring lay-flat polyethylene tubing
when winds may cause it to move.
431 - 3
Consider including a water measuring device to
assist in irrigation water management.
OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE
PLANS AND SPECIFICATIONS
requirements for flushing pipe,
Plans and specifications shall be prepared to
show site specific details. The drawings and
specifications shall show pipe location(s), pipe
size(s), construction details for the inlet structure
and screen as applicable, sizes and construction
details for head control facilities, and gate
spacing and erosion details as appropriate.
requirements for cleaning and repairing of
screens and structures,
requirements for replacing individual gates
and gaskets,
requirements for off-season storage and
handling of pipe,
If lay-flat polyethylene pipe is included in the
plan, and the manufacturers recommendations
for working pressure are not available, an
appropriate formula or table for determining
maximum working pressure shall be included in
the practice specification.
requirements for anchoring pipe where wind
conditions require, and
recommendation for recycling lay-flat
polyethylene pipe, where recycling is
available.
Plans should also included gate openings or
orifice sizes necessary to deliver the design
flows as determined by appropriate surface
irrigation design procedures.
If the source of water supply is from a water
well, the operation and maintenance plan shall
note that the presence of sand in the pipeline
may indicate problems with the water well.
The operation and maintenance plan for the
system shall include:
NRCS, NHCP
August 2006
You might also like
- Pump Test Pit DesignDocument8 pagesPump Test Pit DesignpostboxsgNo ratings yet
- 16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsFrom Everand16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Contractor's Guide for Installation of Gasketed PVC Pipe for Water / for SewerFrom EverandContractor's Guide for Installation of Gasketed PVC Pipe for Water / for SewerRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Leonard Nadler' ModelDocument3 pagesLeonard Nadler' ModelPiet Gabz67% (3)
- Underground Piping PDFDocument40 pagesUnderground Piping PDFAngelita Qtal100% (2)
- Pipeline Design for Water EngineersFrom EverandPipeline Design for Water EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Coiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!From EverandCoiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationFrom EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- SMAW Pipe Welding TechniquesDocument35 pagesSMAW Pipe Welding Techniquesmiradeel100% (4)
- API 1104 InterpretationDocument6 pagesAPI 1104 Interpretationhekayat71No ratings yet
- API 1104 InterpretationDocument6 pagesAPI 1104 Interpretationhekayat71No ratings yet
- API 570 Chapter10 Asme Ix RevDocument50 pagesAPI 570 Chapter10 Asme Ix RevFabio MiguelNo ratings yet
- Richard IIIDocument36 pagesRichard IIIXuan Mai Nguyen ThiNo ratings yet
- The Role of IT in TQM L'Oreal Case StudyDocument9 pagesThe Role of IT in TQM L'Oreal Case StudyUdrea RoxanaNo ratings yet
- Livestock Watering Fact SheetDocument7 pagesLivestock Watering Fact Sheetapi-228378848No ratings yet
- AED Design Requirements - Water Tanks and System Distribution - Sep09 PDFDocument23 pagesAED Design Requirements - Water Tanks and System Distribution - Sep09 PDFAvonodOiratulcNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Condenser ACC PDFDocument3 pagesAir Cooled Condenser ACC PDFHoney TiwariNo ratings yet
- Water PipelinesDocument8 pagesWater PipelinesBilal AmjadNo ratings yet
- Design PipelineDocument9 pagesDesign Pipelineengr_asad364No ratings yet
- Specifications 1. Tubewell: 1.1 Scope of WorkDocument7 pagesSpecifications 1. Tubewell: 1.1 Scope of WorkanwarNo ratings yet
- Chilled Water System: Part 1: GeneralDocument3 pagesChilled Water System: Part 1: GeneralNoushad P HamsaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Distribution System DesignDocument24 pagesChapter 6: Distribution System DesignChristina Cameron Shane100% (1)
- Section Iii Design Criteria FOR Potable Water Distribution SystemsDocument10 pagesSection Iii Design Criteria FOR Potable Water Distribution SystemsRamces SolimanNo ratings yet
- Ductile Iron Pipe For Wastewater ApplicationsDocument8 pagesDuctile Iron Pipe For Wastewater ApplicationsESiLibraryNo ratings yet
- Culvert ThicknessDocument23 pagesCulvert ThicknessNilaAbubakarNo ratings yet
- SECTION 2 - Design Criteria For Water Distribution Systems - 201304251344365252Document8 pagesSECTION 2 - Design Criteria For Water Distribution Systems - 201304251344365252Harvey Jualo NancaNo ratings yet
- Excerpts From The National Plumbing Code of The Philippines - Sub Topic 3 Sub Topic 4Document7 pagesExcerpts From The National Plumbing Code of The Philippines - Sub Topic 3 Sub Topic 4Sabby SaberonNo ratings yet
- Pacific InstallationDocument9 pagesPacific InstallationMark CaloNo ratings yet
- Instalación de Tuberías EnterradasDocument4 pagesInstalación de Tuberías EnterradasYana ParravanoNo ratings yet
- Sliplining SewersDocument3 pagesSliplining SewersDavid NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Section 02ADocument3 pagesSection 02AFAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Hilton Head Section 05 - Water System DesignDocument8 pagesHilton Head Section 05 - Water System Designlayitdown45No ratings yet
- Piping LayoutDocument16 pagesPiping Layoutsanmiguel000100% (1)
- Technical Specifications and Installation Requirements For Flow MetersDocument12 pagesTechnical Specifications and Installation Requirements For Flow MetersAlaa RamadanNo ratings yet
- Design of Water Supply For PlumbingDocument4 pagesDesign of Water Supply For PlumbingLouie MirandaNo ratings yet
- Plumbing 6Document4 pagesPlumbing 6Stanley Scott ArroyoNo ratings yet
- CWD - Cold Water Pipe SizingDocument82 pagesCWD - Cold Water Pipe SizingSoc SaballaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: House Drains & House SewersDocument5 pagesChapter 12: House Drains & House SewersMr. DummyNo ratings yet
- Design of Water Supply For PlumbingDocument23 pagesDesign of Water Supply For PlumbingssgjmlimNo ratings yet
- Review Materials For PlumbingDocument4 pagesReview Materials For PlumbingMark Anthony Agnes AmoresNo ratings yet
- Pipe Network PDFDocument127 pagesPipe Network PDFlaceydawn100% (1)
- Pipe Layingmanual 2012 EditionDocument127 pagesPipe Layingmanual 2012 EditionSharon LambertNo ratings yet
- Orifice PlatesDocument6 pagesOrifice Plateswsjouri2510No ratings yet
- Soil and Waste PipeDocument28 pagesSoil and Waste PipeRegine Kaye TagurdaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Design Standards and ConsiderationsDocument19 pages3.2 Design Standards and ConsiderationsAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Guide For Installing RTR Pipe Courtesy Bondstrand For InfoDocument4 pagesGuide For Installing RTR Pipe Courtesy Bondstrand For InfoHafiz Ali Alvi100% (1)
- Hydro Testing ProcedureDocument12 pagesHydro Testing ProcedureGaapchuNo ratings yet
- Flowmeter Piping RequirementsDocument4 pagesFlowmeter Piping RequirementsYoke ShuNo ratings yet
- Klargester Percolation Test MethodDocument2 pagesKlargester Percolation Test MethodDoug WeirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Storm DrainageDocument7 pagesChapter 11 Storm Drainageapi-131679190No ratings yet
- SW Manual Chapter 100-700 - Combined - Final - 2022may - Chapter 500Document26 pagesSW Manual Chapter 100-700 - Combined - Final - 2022may - Chapter 500WahidCesarRNo ratings yet
- Tech. Sepc. DescopeDocument21 pagesTech. Sepc. Descoperizwan.khan12345876No ratings yet
- Piping Layout UDLDocument24 pagesPiping Layout UDLLegend Anbu100% (1)
- 606 NHCP CPS Subsurface Drain 2018Document8 pages606 NHCP CPS Subsurface Drain 2018Aibangbee MarkNo ratings yet
- Central Hot Water in HighDocument5 pagesCentral Hot Water in Highexfireex1No ratings yet
- Trench Cuts and Restorations Across Roadways: Flexible Pavement Cut Rigid Pavement CutDocument3 pagesTrench Cuts and Restorations Across Roadways: Flexible Pavement Cut Rigid Pavement CutIqueline JacqelineNo ratings yet
- The Syphonic Roof Drainage System: P. C. Chang, MRDocument12 pagesThe Syphonic Roof Drainage System: P. C. Chang, MRsameeraNo ratings yet
- Underground Piping (U/G) : Cooling Tower PipelineDocument9 pagesUnderground Piping (U/G) : Cooling Tower PipelineMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- Division 16 - Electrical Section 16115 - Underground Conduits and Distribution Duct BanksDocument3 pagesDivision 16 - Electrical Section 16115 - Underground Conduits and Distribution Duct BankskooltahaNo ratings yet
- Pe Handbook Chapter 10 Marine Applications PDFDocument38 pagesPe Handbook Chapter 10 Marine Applications PDFAbhiNo ratings yet
- Water Dist. Sys, Stand Pipe, Drainage Pipe & Sys.Document22 pagesWater Dist. Sys, Stand Pipe, Drainage Pipe & Sys.KevinNavidad100% (3)
- Sewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionFrom EverandSewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsFrom EverandPipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshFrom EverandPneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshNo ratings yet
- StatsDocument1 pageStatshekayat71No ratings yet
- Geroo.netDocument1 pageGeroo.nethekayat71No ratings yet
- Post Weld Heat TreatmentDocument10 pagesPost Weld Heat Treatmentcristian291011No ratings yet
- 2011 AddendaDocument9 pages2011 AddendaMrityunjoy BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Studio LogDocument1 pageStudio Loghekayat71No ratings yet
- Studio LogDocument1 pageStudio Loghekayat71No ratings yet
- 2012 Calendar-Subject OrderDocument1 page2012 Calendar-Subject Orderhekayat71No ratings yet
- Heat TreatmentDocument4 pagesHeat Treatmenthekayat71No ratings yet
- Gas Piping CodeDocument29 pagesGas Piping CodeSenoadji WirosanjoyoNo ratings yet
- S NDocument1 pageS Nhekayat71No ratings yet
- TankDocument20 pagesTankhekayat71No ratings yet
- MPCC 20 WPS12Document3 pagesMPCC 20 WPS12hekayat71No ratings yet
- Oil PipelinesDocument8 pagesOil Pipelineshekayat71No ratings yet
- Ncqz2ethqw6ttlup6bvg 140628221506 Phpapp02Document56 pagesNcqz2ethqw6ttlup6bvg 140628221506 Phpapp02hekayat71No ratings yet
- Applicable To Off Plot Piping Per ASME B31.8: Joint DesignDocument1 pageApplicable To Off Plot Piping Per ASME B31.8: Joint Designhekayat71No ratings yet
- Joint Design Process (Es) : Applicable To Off Plot Piping Per ASME B31.8Document2 pagesJoint Design Process (Es) : Applicable To Off Plot Piping Per ASME B31.8hekayat71No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic TestingDocument15 pagesUltrasonic Testinghekayat71No ratings yet
- HTTPS List1391.3.20Document1 pageHTTPS List1391.3.20hekayat71No ratings yet
- ITP AllDocument1 pageITP AllMuhammadIqbalMughalNo ratings yet
- Melt Flow IndexDocument3 pagesMelt Flow IndexwaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Hosts UmbrellaDocument1 pageHosts UmbrellaFabsor SoralNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Visual Welding InspectionDocument4 pagesThe Importance of Visual Welding Inspectionhekayat71No ratings yet
- مقايسه حد پذيرش عيوب براساس استانداردها PDFDocument1 pageمقايسه حد پذيرش عيوب براساس استانداردها PDFeghashangzadehNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic TestingDocument15 pagesUltrasonic Testinghekayat71No ratings yet
- اتصالات جوش (Arka Ndt.ir)Document20 pagesاتصالات جوش (Arka Ndt.ir)hekayat71No ratings yet
- Case StarbucksDocument3 pagesCase StarbucksAbilu Bin AkbarNo ratings yet
- Epson EcoTank ITS Printer L4150 DatasheetDocument2 pagesEpson EcoTank ITS Printer L4150 DatasheetWebAntics.com Online Shopping StoreNo ratings yet
- Attitude of Tribal and Non Tribal Students Towards ModernizationDocument9 pagesAttitude of Tribal and Non Tribal Students Towards ModernizationAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- COE301 Lab 2 Introduction MIPS AssemblyDocument7 pagesCOE301 Lab 2 Introduction MIPS AssemblyItz Sami UddinNo ratings yet
- IJREAMV06I0969019Document5 pagesIJREAMV06I0969019UNITED CADDNo ratings yet
- IBM Thinkpad Z61 Quanta BW2Document80 pagesIBM Thinkpad Z61 Quanta BW2Abubakar SidikNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Emotional Intelligence Personal DevelopmentDocument19 pagesModule 8 - Emotional Intelligence Personal DevelopmentRoxan Binarao-Bayot60% (5)
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation - DPP 01 (Of Lecture 03) - Lakshya NEET 2024Document3 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and Variation - DPP 01 (Of Lecture 03) - Lakshya NEET 2024sibasundardutta01No ratings yet
- PTD30600301 4202 PDFDocument3 pagesPTD30600301 4202 PDFwoulkanNo ratings yet
- Vialyn Group ResearchDocument17 pagesVialyn Group ResearchVial LynNo ratings yet
- Def - Pemf Chronic Low Back PainDocument17 pagesDef - Pemf Chronic Low Back PainFisaudeNo ratings yet
- Benson Ivor - The Zionist FactorDocument234 pagesBenson Ivor - The Zionist Factorblago simeonov100% (1)
- P&CDocument18 pagesP&Cmailrgn2176No ratings yet
- Directorate of Indian Medicines & Homoeopathy, Orissa, Bhubaneswar Listof The Homoeopathic Dispensaries BhadrakDocument1 pageDirectorate of Indian Medicines & Homoeopathy, Orissa, Bhubaneswar Listof The Homoeopathic Dispensaries Bhadrakbiswajit mathematicsNo ratings yet
- Quiz EditedDocument6 pagesQuiz EditedAbigail LeronNo ratings yet
- LC 67002000 B Hr-Jumbo enDocument2 pagesLC 67002000 B Hr-Jumbo enJulio OrtegaNo ratings yet
- 525 2383 2 PBDocument5 pages525 2383 2 PBiwang saudjiNo ratings yet
- Norm ANSI PDFDocument1 pageNorm ANSI PDFAbdul Quddus Mat IsaNo ratings yet
- System Administration ch01Document15 pagesSystem Administration ch01api-247871582No ratings yet
- Lifecycle of A Frog For Primary StudentsDocument10 pagesLifecycle of A Frog For Primary StudentsMónika KissNo ratings yet
- Revised Exam PEDocument3 pagesRevised Exam PEJohn Denver De la Cruz0% (1)
- Mge - Ex11rt - Installation and User Manual PDFDocument38 pagesMge - Ex11rt - Installation and User Manual PDFRafa TejedaNo ratings yet
- Psyche Finals: Trans 2: Psychotic Disorder: SchizophreniaDocument4 pagesPsyche Finals: Trans 2: Psychotic Disorder: SchizophreniajisooNo ratings yet
- Fisker Karma - Battery 12V Jump StartDocument2 pagesFisker Karma - Battery 12V Jump StartRedacTHORNo ratings yet
- ARRANGING For Marchong or Concert BandDocument13 pagesARRANGING For Marchong or Concert BandCheGus AtilanoNo ratings yet
- A Review On PRT in IndiaDocument21 pagesA Review On PRT in IndiaChalavadi VasavadattaNo ratings yet
- LUNG ARTIFACTSreviewDocument13 pagesLUNG ARTIFACTSreviewMayra ValderramaNo ratings yet