Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thesis 1
Uploaded by
Sarwer Hussain FaisalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thesis 1
Uploaded by
Sarwer Hussain FaisalCopyright:
Available Formats
ELECTRICAL ENERGY GENERATION BASED ON
GYMNASIUM EQUIPMENT
ABSTRACT: The aim of this project is to develop and design a renewable energy source, based on existing
exercise equipment. The energy used in a typical workout at the gym is usually wasted in the mechanics of
the equipment. Among various exercising equipment the main concern is about the stationary bikes, this
converts human muscle power into rotational mechanical power. This project will show how to capture the
mechanical energy of the machine and convert it to electrical energy using a generator-based system.
Produced electrical energy attaching exercise equipment with the shaft of the generator can power a piece
of equipment such as lamp or a computer while exercising. All applicable information regarding the design,
development, and the final product of Human Power Generation project is presented here.
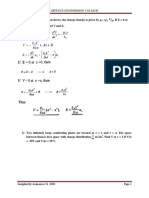
1.
Introduction
Energy is everywhere in the environment
surrounding us and is available in many forms.
Capturing this energy and converting it to
electrical energy has been the subject of many
research investigations. To meet the worlds
increasing
energy
needs,
many
companies around the world are
investing in the research and
development
of
environmentally
sustainable technologies. However,
there exists a large untapped source of
dissipated energy that has potential to
help solve this energy problem. Every day, gym
goers produce lots of energy just by doing their
daily workout on exercise equipment. This
energy, if used as an alternate to fossil fuels could
supply clean sustainable energy. However, this
energy is produced in mechanical form rather
than electrical form, but slight modifications to
the exercise equipment would allow the energy
being produced to be converted to electrical
energy which can be harvested, and stored for a
later time. The concept of harvesting energy from
an exercise machine was introduced by a Hong
Kong gym called California Fitness [1]. Since
then, there have been three establishments in the
United States that have been working to
commercialize this technology [2]. This paper
focuses on large scale power generation from the
gymnasium stationary bicycle and also finds out
its commercial probability as a secondary power
source in local gyms. A field research is done on
different gymnasiums at Chittagong city on the
basis of number of members, working hours,
number of bikes available in the gymnasiums,
secondary power sources used during load
shedding, monthly electric bill, average members
per day, daily load shading time and members
uses the bike etc. detailed design and
construction of the system has been done to
convert the people muscle power into electrical
power. Implementation diagram
The complete system is shown in Fig. 1. Firstly,
the mechanical energy is translated into electrical
energy through the use of coupling belt turning
an alternator. A three phase 500W, 220V, 50Hz
permanent magnet alternator is used due to low
loss and less complexity.
Figure 1: block diagram of human power generation
system
The coupling belt is rubber made to prevent slip
loss. The stationary bike have gear system that
can adjust the range of RPMs and makes initial
pedalling easier. The user is able to start softly
and increase the resistance as momentum is
gained. Secondly, as a 220V alternator is used for
power generation a transformer was needed to
step down the generated voltage to fade into the
charge controller circuit. It has several tapings at
both high voltage and low voltage side. In this
system 220/18V taping is used. A bridge rectifier
circuit is used to converter AC input power into
DC output power.
REFERENCES
[1] N. Prakash, Green gyms, turning sweat into
watts, 2014. [Online] Available:
http://www.thatsfit.com/2011/04/28/green-gymsturning-s weat-into-watts.(May 15,2014).
[2] Arakaki, Justin, P. Lawrence and A.
Nakamura, "Energy Harvesting from Exercise
Machines Cal Poly Recreation Center
Implementation ", unpublished
You might also like
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsFrom EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Paper G Ermie 15-1Document45 pagesPaper G Ermie 15-1abellNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power ProjectDocument12 pagesElectrical Power ProjectsrnkaNo ratings yet
- Matlab-Simulink Controller DesignDocument4 pagesMatlab-Simulink Controller DesignMohamed SomaiNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Project PDFDocument5 pagesPower Factor Project PDFPritam100% (1)
- Design and Analysis of A Dual Input DC-DC Converter For Hybrid Electric VehicleDocument23 pagesDesign and Analysis of A Dual Input DC-DC Converter For Hybrid Electric Vehiclejanga vishwanathNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 LCS 078Document13 pagesLab 6 LCS 078Asad saeedNo ratings yet
- BL0683 6EJ517 Electronic Devices and SystemsDocument19 pagesBL0683 6EJ517 Electronic Devices and Systemskhan aliNo ratings yet
- 11 - AC and DC Equivalent Circuit Modeling of The Discontinuous Conduction ModeDocument29 pages11 - AC and DC Equivalent Circuit Modeling of The Discontinuous Conduction ModeThanh LeNo ratings yet
- EEE 805 Assignment Questions For Chapter 20Document11 pagesEEE 805 Assignment Questions For Chapter 20ayeniNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: 1.1.1 The Principle of WindmillDocument22 pagesChapter-1: 1.1.1 The Principle of WindmillVijay BavikattiNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Solar PV System Under Partial Shading Using Particle Swarm Optimization Based MPPTDocument7 pagesModeling of Solar PV System Under Partial Shading Using Particle Swarm Optimization Based MPPTAnonymous CUPykm6DZNo ratings yet
- Module Information Module Title Electric Drives and Control Module Code MMD2511Document4 pagesModule Information Module Title Electric Drives and Control Module Code MMD2511Ashley KaNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous ChipsDocument25 pagesAsynchronous ChipsAbin Varkey Varghese100% (1)
- A - Generalized - High - Gain - Multilevel - Inverter - For - Small - Scale - Solar - Photovoltaic - ApplicationsDocument15 pagesA - Generalized - High - Gain - Multilevel - Inverter - For - Small - Scale - Solar - Photovoltaic - ApplicationsJamal KhyatNo ratings yet
- Implementation of An Active Battery Balancer Using Fly-Back TransformerDocument4 pagesImplementation of An Active Battery Balancer Using Fly-Back TransformerDebdeep MondalNo ratings yet
- 1.single Phase AC To DC Fully Controlled Converter PDFDocument10 pages1.single Phase AC To DC Fully Controlled Converter PDFAshwin RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Extraction of The Internal Parameters of Solar Photovoltaic Module by Developing Matlab / Simulink Based ModelDocument5 pagesExtraction of The Internal Parameters of Solar Photovoltaic Module by Developing Matlab / Simulink Based Modelzameer05090% (1)
- Wireless Power Transfer SynopsisDocument3 pagesWireless Power Transfer Synopsisa d100% (1)
- Design and Implementation of Water Bill Control System Based GSMDocument5 pagesDesign and Implementation of Water Bill Control System Based GSMPeter MulengaNo ratings yet
- Simulation Modeling of Inverter Controlled BLDC Drive Using Four SwitchDocument18 pagesSimulation Modeling of Inverter Controlled BLDC Drive Using Four SwitchCHEIF EDITORNo ratings yet
- Simulation & Controlling of Brushless DC Motor Using PI/Fuzzy HybridDocument4 pagesSimulation & Controlling of Brushless DC Motor Using PI/Fuzzy Hybridsunil kumarNo ratings yet
- SQL Practice 18-7-14 (Solved)Document4 pagesSQL Practice 18-7-14 (Solved)Rohan Vishwakarma0% (1)
- DC Motor Speed Control Using PWMDocument14 pagesDC Motor Speed Control Using PWMVincent KorieNo ratings yet
- Power Harvesting by Using Human Foot StepDocument2 pagesPower Harvesting by Using Human Foot Stepcamila0% (1)
- Syllabus For Power Electronics and DriveDocument34 pagesSyllabus For Power Electronics and Drivearavi1979No ratings yet
- 1 Comparative Analysis For Various Artificial Intelligence Techniques Applied To Induction Motor DriveDocument12 pages1 Comparative Analysis For Various Artificial Intelligence Techniques Applied To Induction Motor DriveDrPrashant M. MenghalNo ratings yet
- Modeling of DC DC Converter PDFDocument6 pagesModeling of DC DC Converter PDFVishal AryaNo ratings yet
- Passivity Based ControlDocument25 pagesPassivity Based ControlRan HaoNo ratings yet
- Magenetic Chip Collector New 2Document27 pagesMagenetic Chip Collector New 2Hemasundar Reddy JolluNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure of A Power SystemDocument9 pagesBasic Structure of A Power Systembiruke6No ratings yet
- The Copperbelt University School of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Department of Physics PH 110 Introductory PhysicsDocument3 pagesThe Copperbelt University School of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Department of Physics PH 110 Introductory PhysicsLazy BanditNo ratings yet
- Introduction and BackgroundDocument8 pagesIntroduction and Backgroundyohannes getachewNo ratings yet
- Partially Shaded Operation of A Grid-Tied PV SystemDocument9 pagesPartially Shaded Operation of A Grid-Tied PV SystemheanbuNo ratings yet
- PSOC-Lecture NotesDocument130 pagesPSOC-Lecture NotesHemaChandar PNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction To Multilevel InvertersDocument53 pages01 - Introduction To Multilevel Invertersp09el860No ratings yet
- New Contributions To Load Flow Studies by The Method of Reduction and RestorationDocument7 pagesNew Contributions To Load Flow Studies by The Method of Reduction and RestorationncleninNo ratings yet
- Auto Control Design For Power Factor Improvement PDFDocument86 pagesAuto Control Design For Power Factor Improvement PDFDr-Muhammad Aqeel Aslam50% (4)
- Clean Energy Generation, Integration and Storage (Eee-801) : Dr. Abasin Ulasyar Assistant Professor (NUST USPCAS-E)Document12 pagesClean Energy Generation, Integration and Storage (Eee-801) : Dr. Abasin Ulasyar Assistant Professor (NUST USPCAS-E)Malik Shahzeb Ali0% (1)
- Review On Design of Solar Power Tricycle For Physically Handicap PersonDocument7 pagesReview On Design of Solar Power Tricycle For Physically Handicap PersonIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Eee-M.e Ped 3-7-21 An QP R-2017-X86093 (PX5072)Document2 pagesEee-M.e Ped 3-7-21 An QP R-2017-X86093 (PX5072)MR.R. JEBA RAJNo ratings yet
- Power Generation System Through Foot Steps1Document24 pagesPower Generation System Through Foot Steps1Dasari Anuroop ReddyNo ratings yet
- PV-Wind Hybrid SystemsDocument24 pagesPV-Wind Hybrid SystemssahitNo ratings yet
- TP 1800 DC-DC Converter For Hybrid Electric Vehicle and EV ArrowTimesDocument7 pagesTP 1800 DC-DC Converter For Hybrid Electric Vehicle and EV ArrowTimespapipapii100% (1)
- 3 Phase Cascaded H-Bridge InverterDocument7 pages3 Phase Cascaded H-Bridge InverterAnil ShahNo ratings yet
- Psoc Course FileDocument14 pagesPsoc Course Filecholleti sriramNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Protection of The Motor-Generator Pair System For Fault Ride-Through of Renewable Energy Generation SystemsDocument20 pagesIsolation and Protection of The Motor-Generator Pair System For Fault Ride-Through of Renewable Energy Generation SystemsUmesh GowdaNo ratings yet
- DC Link CurrentDocument8 pagesDC Link CurrentsubbannaNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of BLDC Motor For Electric PDFDocument6 pagesSpeed Control of BLDC Motor For Electric PDFtarnaNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Perturb and Observe MPPT of PV System With Direct Control Method Using Boost ConvertersDocument5 pagesImplementation of Perturb and Observe MPPT of PV System With Direct Control Method Using Boost ConvertersRam KumarNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Standalone Hybrid Power System Using Matlab/simulinkDocument6 pagesImplementation of Standalone Hybrid Power System Using Matlab/simulinkIJIERT-International Journal of Innovations in Engineering Research and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Lighting For AutomobileDocument18 pagesAdaptive Lighting For Automobilekavitha mNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset For Temporary Fault and Trip ForDocument16 pagesThree Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset For Temporary Fault and Trip ForFirstLearnNo ratings yet
- rr320206 Utilisation of Electrical EnergyDocument8 pagesrr320206 Utilisation of Electrical EnergySRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- EMS Student CER Examples PDFDocument7 pagesEMS Student CER Examples PDFfuripafNo ratings yet
- Integration of Green and Renewable Energy in Electric Power SystemsFrom EverandIntegration of Green and Renewable Energy in Electric Power SystemsNo ratings yet
- Evsjv 'K E VSK K E VSK: C Avb KVH©VJQDocument1 pageEvsjv 'K E VSK K E VSK: C Avb KVH©VJQSarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- Study On Electricity Distribution, Substation Operation & Maintenance of DESCODocument46 pagesStudy On Electricity Distribution, Substation Operation & Maintenance of DESCOSarwer Hussain Faisal100% (5)
- Thesis BookDocument33 pagesThesis BookSarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- Sarwer Hussain FaisalDocument3 pagesSarwer Hussain FaisalSarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- The Graph Below Shows Information of Employment Rates Across 6 Countries in 1995 and 2005Document1 pageThe Graph Below Shows Information of Employment Rates Across 6 Countries in 1995 and 2005Sarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- Hand Note1Document5 pagesHand Note1Sarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- Internship Report TemplateDocument9 pagesInternship Report TemplateSarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- Hand Note Writing Task - 1Document10 pagesHand Note Writing Task - 1Sarwer Hussain Faisal100% (1)
- Hand Note Writing Task - 1Document1 pageHand Note Writing Task - 1Sarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- Internship Report TemplateDocument5 pagesInternship Report TemplateSarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- Capacitors PDFDocument2 pagesCapacitors PDFSarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- Micro Lab1Document3 pagesMicro Lab1Sarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- Solution of Microprocessor Lab EEE - 410Document13 pagesSolution of Microprocessor Lab EEE - 410Sarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- EENG410 Microprocessors IDocument12 pagesEENG410 Microprocessors ISarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- Important Software KeyDocument11 pagesImportant Software KeySarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- SD2000 GPM InstructionsDocument2 pagesSD2000 GPM InstructionsAkram LamaNo ratings yet
- IEEE STD C37 34 1994 IEEE Standard Test Code For High Voltage Air Switches PDFDocument38 pagesIEEE STD C37 34 1994 IEEE Standard Test Code For High Voltage Air Switches PDFDavid PeredoNo ratings yet
- LANTIN BSEE 2C Electronics Lab2Document11 pagesLANTIN BSEE 2C Electronics Lab2Alwin LantinNo ratings yet
- Chenming-Hu ch2Document24 pagesChenming-Hu ch2Aarthi JayakumarNo ratings yet
- S 4000 Manual PDFDocument55 pagesS 4000 Manual PDFMaría Flores ToledoNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design: Circuits & LayoutDocument48 pagesVLSI Design: Circuits & Layoutchandanayadav8490No ratings yet
- Wave FexDocument22 pagesWave Fexgeremu100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Passive DevicesDocument72 pagesChapter 7 Passive DevicesNikunj ShahNo ratings yet
- Maximum Permissible Voltage DropDocument1 pageMaximum Permissible Voltage DropBaoLCNo ratings yet
- Ta Kmsw500Document24 pagesTa Kmsw500Orangzeb Khan0% (1)
- Eccm in RadarsDocument89 pagesEccm in Radarsjumaah5234100% (4)
- MS3XV357 Hardware 1.3Document214 pagesMS3XV357 Hardware 1.3Lucas VitorNo ratings yet
- Energy Energy Energy: Sector Report Sector Report SectorDocument44 pagesEnergy Energy Energy: Sector Report Sector Report Sectorchengo003No ratings yet
- Abra Electric CoopDocument5 pagesAbra Electric CoopJohn Michael PascuaNo ratings yet
- Philips 42 Inch LCD Power Ic-Fsq510Document14 pagesPhilips 42 Inch LCD Power Ic-Fsq510Raja Pathamuthu.GNo ratings yet
- Digital Pressure Controls: General DescriptionDocument1 pageDigital Pressure Controls: General DescriptionyuyunNo ratings yet
- As 2374.1.2-2003 Power Transformers - Minimum Energy Performance Standard (MEPS) Requirements For DistributioDocument7 pagesAs 2374.1.2-2003 Power Transformers - Minimum Energy Performance Standard (MEPS) Requirements For DistributioSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet TR24-SRDocument3 pagesTechnical Data Sheet TR24-SRManh TuanNo ratings yet
- EPDM Formulations For Electric Wires and Cables: January 2001Document6 pagesEPDM Formulations For Electric Wires and Cables: January 2001Febri Ramdani NugrahaNo ratings yet
- DC Machines: The Action of A CommuttatorDocument5 pagesDC Machines: The Action of A CommuttatorKirk PatrickNo ratings yet
- Ic21 Sect 16 CTRL Circuit ProtDocument30 pagesIc21 Sect 16 CTRL Circuit ProtFawzi AlzubairyNo ratings yet
- 56 TOP Cables - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsDocument14 pages56 TOP Cables - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsJevan A. CalaqueNo ratings yet
- EEE 2019 TEST I 2018 Academic Year (SOLUTIONS) PDFDocument7 pagesEEE 2019 TEST I 2018 Academic Year (SOLUTIONS) PDFCyrus ChartehNo ratings yet
- Imitron: JJS - 600vac, 1-800A, Fast-Acting FusesDocument4 pagesImitron: JJS - 600vac, 1-800A, Fast-Acting FusesErasmo Franco SNo ratings yet
- Chip Package-CodesignDocument46 pagesChip Package-CodesignBilal uddinNo ratings yet
- Applimotion ULT Motor Kits DatasheetDocument2 pagesApplimotion ULT Motor Kits DatasheetElectromateNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Wave Production-Piezoelectric MethodDocument6 pagesUltrasonic Wave Production-Piezoelectric MethodNIKHIL SOLOMON P URK19CS1045No ratings yet
- AND8346/D A519Hrt Hart Modem: Application NoteDocument19 pagesAND8346/D A519Hrt Hart Modem: Application NoteNowan HatsenNo ratings yet
- Sony HCD Gs10 Gs30dab Ver 1 3 SM PDFDocument78 pagesSony HCD Gs10 Gs30dab Ver 1 3 SM PDFClément SaillantNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: NX-340, NX-340 (U)Document42 pagesService Manual: NX-340, NX-340 (U)A&A LABORATORIONo ratings yet