Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Liver Cirrhosis Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Caren ReyesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Liver Cirrhosis Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Caren ReyesCopyright:
Available Formats
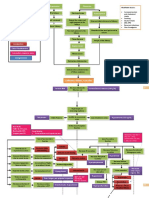
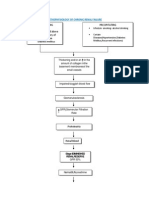
LIVER CIRRHOSIS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
chronic alcoholism
toxins from alcohol:
release of acetyldehyde
↑ AST, ALT,
damage hepatocytes
alkaline,
phophatase, GGT
necrosis of hepatocytes
fibrosis obstruction in
blood flow
↓ liver function liver cells regenerate PORTAL
in abnormal pattern HYPERTENSION
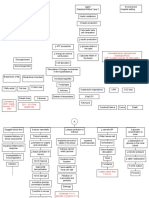
liver cells loaded with fat
enlargement
irritates the Glisson capsule
PAIN
↑ glycogenesis ↓ production ↓ CHON ↓ production ↓ metabolism of ↓ metabolism ↓ stores of vitamins obstruction of bile flow
↓ glycogenolysis, of albumin synthesis of clotting ammonia drugs and minerals
glucogenesis (in factors
↓ colloidal general) drug toxicity ↓ fat ↓ bilirubin bile reabsorbed in
↑ ammonia
altered glucose osmotic altered clotting absorption in GIT the blood
levels
metabolism pressure altered studies ↓ RBC ↓ energy ↓ energy
immune production production ↓ Vitamin K bilirubin in
↓ energy bleeding hepatic production
edema, function absorption feces bile salts in jaundice ↑ bile in
tendendcies encephalopathy
ascites and altered skin kidney
anemia ↓ energy
healing ↓ clotting clay-colored
blood loss feces pruritus production
factors dark-colored
changes in coma
susceptibility urine
anemia coordination,
to infection bleeding/
memory, death
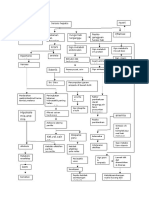
anemia ↑ bilirubin level
↓ metabolism of steroid hormone orientation
asterixis, fetor
estrogen, progesterone, aldosterone hepaticus
testosterone
Na and water ↑ K+ and H+
male female retention excretion
loss of male loss of feminine edema, ascites alkalosis
characteristics characteristics
and and hypokalemia
development of development of
some feminine some male
characteristics characteristics
You might also like
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument1 pageChronic Renal Failurejj_cuttingedges100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of PUDDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PUDdeoxis1933% (3)
- Acute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyJanica Marinas100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Liver Cirrhosisgaelty100% (4)
- CKD PathoDocument5 pagesCKD PathoJohn MIchael AusaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisDocument4 pagesPathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisCyrus Ortalla RobinNo ratings yet
- Liver Patho and EcoDocument10 pagesLiver Patho and EconeeckoiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument1 pagePathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology CHFKim Franzel M. Rabe100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormPen MontanteNo ratings yet
- PUD PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePUD PathophysiologyHerbert A Serquina100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of CholelithiasisSherilNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- Liver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorDocument22 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorJorie RocoNo ratings yet
- Nstemi PathoDocument2 pagesNstemi PathoSheana TmplNo ratings yet
- IV. The PATIENTS ILLNESS (Nephrolithiasis) Pathophysiology (Book-Based)Document3 pagesIV. The PATIENTS ILLNESS (Nephrolithiasis) Pathophysiology (Book-Based)wapakalypseNo ratings yet
- Laennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesLaennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyTrixie Al Marie100% (3)
- Final patho-HCVDDocument2 pagesFinal patho-HCVDAlvin RamirezNo ratings yet
- My Case Study of Liver CirrhosisDocument13 pagesMy Case Study of Liver Cirrhosisdysphile100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CHFPerry Oliver AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
- Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERDocument1 pageGroup 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERArisa VijungcoNo ratings yet
- ARF PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesARF Pathophysiologykathy100% (9)
- Ovarian Cancer, The NEw PathophyDocument3 pagesOvarian Cancer, The NEw PathophylieselannjacobNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureIvana Yasmin Bulandres100% (2)
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 pagesAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CVADocument1 pagePathophysiology CVANenette Aquino100% (2)
- Liver Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageLiver Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (4)
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument2 pagesCholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramChristyl CalizoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisAprille Rose UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Liver Cancer 2Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Liver Cancer 2Charis Paroginog92% (12)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis: A Case Study OnDocument31 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: A Case Study OnCharmaine del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Liver Cirrhosis - MercyDocument7 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Liver Cirrhosis - Mercymersenie_TheovercomerNo ratings yet
- Copd PathoDocument1 pageCopd PathoRey AngeloNo ratings yet
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypertension PathophysiologyZaida Eunice EstabayaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsYuyu Tulawie100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Alcoholic Liver Diseaseshailendra tripathiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Document1 pagePathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsReina SamsonNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiologybilliam123100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverKenneth Lagman100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Peptic Ulcer Disease: 55 Y/o Female)Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Peptic Ulcer Disease: 55 Y/o Female)kristian markus delos santos100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- Diagram of Pathophysiology CancerDocument5 pagesDiagram of Pathophysiology CancerKristaMaeC.Lazo0% (3)
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAngina Pectoris Pathophysiologydana86% (7)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Chronic Renal FailureBettinaFernando80% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureTrixia Almendral100% (2)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia PathophysiologyDarla SaulerNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology ESRDDocument9 pagesPathophysiology ESRDJaye DangoNo ratings yet
- Precipitating Factors: Alcoholism Diet ( FAT) Hypertension Predisposing FactorsDocument1 pagePrecipitating Factors: Alcoholism Diet ( FAT) Hypertension Predisposing FactorsKevin Jade HerreraNo ratings yet
- DIabetes Mellitus ! Patho (Complete)Document8 pagesDIabetes Mellitus ! Patho (Complete)freyaNo ratings yet
- Endo ShortlistingDocument3 pagesEndo ShortlistingMamoona RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Anemia PathoDocument1 pageAnemia PathoKathleen EvizaNo ratings yet
- Increased Serum Glucose Level (Hyperglycemia) 278.14 MG/DL (Normal: 70-100 MG/DL)Document3 pagesIncreased Serum Glucose Level (Hyperglycemia) 278.14 MG/DL (Normal: 70-100 MG/DL)Angel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- AlgoDocument1 pageAlgoErrold Joseph LahaganNo ratings yet
- PathwayDocument1 pagePathwayVinda NurdianaNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Study GuideDocument34 pagesNCLEX Study GuideCaren Reyes100% (1)
- 2011 Full Page Calendar - TomKat StudioDocument12 pages2011 Full Page Calendar - TomKat StudioThe TomKat StudioNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer NCPDocument1 pageCervical Cancer NCPCaren ReyesNo ratings yet
- High Risk PregnancyDocument2 pagesHigh Risk PregnancyCaren ReyesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - HyperthyroidismDocument2 pagesPathophysiology - HyperthyroidismCaren Reyes100% (5)
- RE Operative ARE: 06 September 2010 Perioperative Nursing Elvira LimDocument4 pagesRE Operative ARE: 06 September 2010 Perioperative Nursing Elvira LimCaren ReyesNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageLiver Cirrhosis PathophysiologyCaren ReyesNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes - Urinary AlterationsDocument13 pagesFluid and Electrolytes - Urinary AlterationsCaren ReyesNo ratings yet
- DR - Datis - Kharrazian Gut Bacteria TranscriptDocument35 pagesDR - Datis - Kharrazian Gut Bacteria TranscriptGreg Wolfe100% (4)
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia With Myelodysplasia RelatedDocument6 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia With Myelodysplasia RelatedAgus WiniNo ratings yet
- SPINAL NERVE Presentation Completed-2Document51 pagesSPINAL NERVE Presentation Completed-2Sheikh Muhammad MuhallilNo ratings yet
- Lembar Usg Iota Onkologi KebidananDocument1 pageLembar Usg Iota Onkologi KebidananAhmad NazharNo ratings yet
- DiGeorge SyndromeDocument11 pagesDiGeorge SyndromeRupesh MohandasNo ratings yet
- Definition and Management of Odontogenic MaxillaryDocument11 pagesDefinition and Management of Odontogenic MaxillaryAlleste OrenNo ratings yet
- 9 - Clinical Management (STRATOG 2015 SBAs)Document12 pages9 - Clinical Management (STRATOG 2015 SBAs)w yNo ratings yet
- Oral CandidiasisDocument4 pagesOral CandidiasisAnish RajNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Anemia Algorithm HandoutDocument2 pagesDiagnosing Anemia Algorithm HandoutValentino Farroñay TafurNo ratings yet
- CCRN Test Prep PDFDocument135 pagesCCRN Test Prep PDFreneecoleman100% (5)
- Libro The Molecular Basis of Human Cancer William B. Coleman PHD, Gregory J. Tsongalis PHDDocument580 pagesLibro The Molecular Basis of Human Cancer William B. Coleman PHD, Gregory J. Tsongalis PHDBerenice LoredoNo ratings yet
- DRUG NAME: Methotrexate: Synonym (S) : Common Trade Name (S) : ClassificationDocument16 pagesDRUG NAME: Methotrexate: Synonym (S) : Common Trade Name (S) : ClassificationChandanaSanjeeNo ratings yet
- Exceptional DevelopmentDocument12 pagesExceptional DevelopmentMa. IvoryVan SantillanNo ratings yet
- Immunology of The SkinDocument505 pagesImmunology of The SkinDan Stein100% (2)
- Bone PDFDocument14 pagesBone PDFVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Cmucat Reviewer 1Document16 pagesCmucat Reviewer 1Cylit Jhames SalomonNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument48 pagesNervous SystemSuvalari Mimi JonathanNo ratings yet
- Bibliografia 2222Document28 pagesBibliografia 2222francivan111No ratings yet
- Aortic RegurgitationDocument18 pagesAortic RegurgitationAbdur RaqibNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Artery DiseaseDocument42 pagesPeripheral Artery Diseaseadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria PDFDocument15 pagesMitochondria PDFCafassoAndrea100% (1)
- BoardsBeyond23C Checklist 2020 2Document7 pagesBoardsBeyond23C Checklist 2020 2Mahmoud AbouelsoudNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Solved Past Papers by Med-Com PDFDocument123 pagesPharmacology Solved Past Papers by Med-Com PDFAmeer AslamNo ratings yet
- 1.psychiatric Neuroscience - Incorporating Pathophysiology Into Clinical Case Formulation - ClinicalKeyDocument43 pages1.psychiatric Neuroscience - Incorporating Pathophysiology Into Clinical Case Formulation - ClinicalKeyClaudia0% (1)
- G2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFDocument1 pageG2015 Adult Tachycardia PDFibbs91No ratings yet
- Drug Study IsoniazidDocument3 pagesDrug Study IsoniazidJamil Lorca100% (4)
- Canine Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca Current Concepts in Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument7 pagesCanine Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca Current Concepts in Diagnosis and TreatmentAgeng prasetyo100% (1)
- Nervous System: Nur Nabilah Binti Abdullah Nur Izyan Shahirah Binti Mohd BakriDocument67 pagesNervous System: Nur Nabilah Binti Abdullah Nur Izyan Shahirah Binti Mohd BakriNur NabilahNo ratings yet
- BPH and Urethral StrictureDocument25 pagesBPH and Urethral Stricturezaminazz100% (1)
- Absolute Dermatology Review - Mastering Clinical Conditions On The Dermatology Recertification Exam (PDFDrive)Document461 pagesAbsolute Dermatology Review - Mastering Clinical Conditions On The Dermatology Recertification Exam (PDFDrive)mogoscristina100% (1)