Professional Documents
Culture Documents
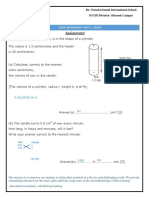
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices
Uploaded by
DeepanshuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices
Uploaded by
DeepanshuCopyright:
Available Formats
Analytics: Application Developer (Siebel 7.
7)
Module 16: Design Principles
and Best Practices
Module Objectives
After completing this module you will be able to:
Identify recommended design principles and best
practices related to the presentation of information in
Intelligence Dashboards
Why you need to know:
As an analytics application developer, you want to ensure
that your users are able to use the data effectively and
that the applications’ performance is optimized
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 2 of 17
0/4
Dashboard Design Tips
Performance
Readability
Security
Filtering
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 3 of 17
1/5
Performance
Avoid designing Dashboards that return too much data
Avoid designing requests that use overly complex queries
Use smaller requests that link to other requests for additional
detail
Use Guided Navigation to link smaller Dashboards
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 4 of 17
2/5
Readability
Use fewer columns
More columns in a request are not necessarily better
Simplicity can tell the reader what is going on in one look
Use charts to simply views of data
Use conditional formatting to focus attention on data outside
given parameters
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 5 of 17
3/5
Security
Use security groups to filter out irrelevant or unwanted
Dashboards for users
Organize Dashboards by user role to help users locate the data
they are interested in
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 6 of 17
4/5
Filtering
Ensure global filters have a default value
Setting value to nothing or all will return all the data and impact
performance
Setting a default value creates a smaller data set
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 7 of 17
0/8
Charting Design Tips
Pie
Bar
Line
Funnel
Pareto
Scatter
Area
Radar
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 8 of 17
1/8
Pie
Pie charts are used to portray the contribution of the parts to a
whole
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 9 of 17
2/8
Bar
Bar charts draws comparisons between items, but not to a
whole
Horizontal bar charts imply an emphasis on time
Vertical bar charts remove the emphasis on time
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 10 of 17
3/8
Line
Line charts show one variable changing over time
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 11 of 17
4/8
Funnel
Funnel charts are used to graphically represent data that
changes over different periods or stages
Funnel charts are well-suited for showing actual compared to
targets for data where the target is known to decrease (or
increase) significantly per stage, such as a sales pipeline
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 12 of 17
5/8
Pareto
Pareto charts used to ranking causes from most significant to
least significant (80/20 rule or Pareto Principle)
Bars on left relatively more important than those on right
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 13 of 17
6/8
Scatter
Scatter charts show the correlation of two sets of numbers by
plotting where the variables intersect.
Scatter charts are useful when the coordinates on the horizontal
scale, often time intervals, are irregular
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 14 of 17
7/8
Area
Area charts shows the relative importance of values over a
period of time
Similar to a line chart, but emphasizes the amount of change
(magnitude of values) rather than the rate of change
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 15 of 17
8/8
Radar
Radar charts are a graphical display of the differences between
actual and ideal performance
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 16 of 17
Summary
This module showed you how to:
Identify recommended design principles and best
practices related to the presentation of information in
Intelligence Dashboards
Module 16: Design Principles and Best Practices 17 of 17
You might also like
- Design ExpertDocument19 pagesDesign ExpertMoreNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics for Managers: Taking Business Intelligence Beyond ReportingFrom EverandBusiness Analytics for Managers: Taking Business Intelligence Beyond ReportingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 10 Rules For Better Dashboard DesignDocument1 page10 Rules For Better Dashboard Designjwpaprk1100% (1)
- Logi Ebook DashboardDesign FinalDocument28 pagesLogi Ebook DashboardDesign FinaldoddyNo ratings yet
- Agile by Design: An Implementation Guide to Analytic Lifecycle ManagementFrom EverandAgile by Design: An Implementation Guide to Analytic Lifecycle ManagementNo ratings yet
- Strucanalysis Wiki Index - PHP Title Chapter 1Document17 pagesStrucanalysis Wiki Index - PHP Title Chapter 1sumitroy89No ratings yet
- Rewired: The McKinsey Guide to Outcompeting in the Age of Digital and AIFrom EverandRewired: The McKinsey Guide to Outcompeting in the Age of Digital and AIRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- OBIEE - Dashboard Tips and Best Practice GuidelinesDocument6 pagesOBIEE - Dashboard Tips and Best Practice GuidelinesPani GummadiNo ratings yet
- The Informed Company: How to Build Modern Agile Data Stacks that Drive Winning InsightsFrom EverandThe Informed Company: How to Build Modern Agile Data Stacks that Drive Winning InsightsNo ratings yet
- Xcelsius Essentials - SGTDocument63 pagesXcelsius Essentials - SGTJesus SanchezNo ratings yet
- The Analytics Lifecycle Toolkit: A Practical Guide for an Effective Analytics CapabilityFrom EverandThe Analytics Lifecycle Toolkit: A Practical Guide for an Effective Analytics CapabilityNo ratings yet
- Ansys Tips and Ansys TricksDocument62 pagesAnsys Tips and Ansys TricksSelva GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Complex Mapping DesignDocument2 pagesComplex Mapping DesignSurup SAmbitNo ratings yet
- Reading Sample Sap Press Designing Dashboards With Sap Analytics CloudDocument24 pagesReading Sample Sap Press Designing Dashboards With Sap Analytics CloudSalah BAKIRNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Architectural Design 1 3/16/17Document59 pagesChapter 6 Architectural Design 1 3/16/17daniel whitelyNo ratings yet
- School Management System": Title of The ProjectDocument18 pagesSchool Management System": Title of The ProjectreenasameerNo ratings yet
- Run ChartDocument3 pagesRun ChartmosatNo ratings yet
- ANSYS - Tips and TricksDocument84 pagesANSYS - Tips and Tricksmanel_drNo ratings yet
- 11 Designing Form and ReportsDocument35 pages11 Designing Form and Reportsnazmul_hasan_16No ratings yet
- 31 SAP ABAP Interview Questions With Answers For Freshers and ExperiencedDocument17 pages31 SAP ABAP Interview Questions With Answers For Freshers and ExperiencedSahil MalhotraNo ratings yet
- ANSYS DesignXplorerDocument4 pagesANSYS DesignXplorerVasundhara Kumari PeddintiNo ratings yet
- Ansys TipsDocument79 pagesAnsys TipsMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Tableau Certification Study GuideDocument26 pagesTableau Certification Study Guidecancelthis0035994100% (1)
- Concepts in Enterprise Resource Planning: Third EditionDocument49 pagesConcepts in Enterprise Resource Planning: Third EditionAbdoosh F-eNo ratings yet
- Statistical Software For Microcomputers: AMOS 4.0: Book ReviewDocument4 pagesStatistical Software For Microcomputers: AMOS 4.0: Book ReviewTrần Tiến QuangNo ratings yet
- Tableau Course Content: Duration: 24 Hours Who Should Learn The Tableau Course?Document7 pagesTableau Course Content: Duration: 24 Hours Who Should Learn The Tableau Course?Ramkoti VemulaNo ratings yet
- OBIEE 10G/11G Dashboard Tips and Best Practice Guidelines: SearchDocument4 pagesOBIEE 10G/11G Dashboard Tips and Best Practice Guidelines: SearchAzhar MullaNo ratings yet
- Training Transcript:: Planning For A Successful DashboardDocument4 pagesTraining Transcript:: Planning For A Successful DashboardEko Aji SaputraNo ratings yet
- Mphasis An HP Company: ERP / SAP OverviewDocument74 pagesMphasis An HP Company: ERP / SAP OverviewmeddebyounesNo ratings yet
- Unit 4:OLAP: Online Analytical ProcessingDocument34 pagesUnit 4:OLAP: Online Analytical ProcessingHansica MadurkarNo ratings yet
- Faq in Sap - AbapDocument4 pagesFaq in Sap - AbapSripriya GunaNo ratings yet
- SAP TPM Excel CapabilitiesDocument43 pagesSAP TPM Excel CapabilitiesMamta Saboo Chakraborty100% (1)
- UADE 2021 - TIC 4 - Data VisualizationDocument30 pagesUADE 2021 - TIC 4 - Data VisualizationDamián Eduardo RamírezNo ratings yet
- WWW Qualityfoundation in Sqc7 Basic Qctools HTMLDocument14 pagesWWW Qualityfoundation in Sqc7 Basic Qctools HTMLfahadfiazNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 DSDLCDocument32 pagesChapter3 DSDLCJason Rocima PartaNo ratings yet
- Modern Systems Analysis and DesignDocument43 pagesModern Systems Analysis and DesignRoel PalmairaNo ratings yet
- Secrets To Unlocking Tableau's Hidden Potential PDFDocument15 pagesSecrets To Unlocking Tableau's Hidden Potential PDFtsoh100% (1)
- Practice: A Generic ViewDocument18 pagesPractice: A Generic ViewTaqi ShahNo ratings yet
- Internship Report (Waseem)Document66 pagesInternship Report (Waseem)idrees aliNo ratings yet
- Dashboard Design & Data Visualization RequirementDocument3 pagesDashboard Design & Data Visualization RequirementInfoCepts IncNo ratings yet
- P-Dmaic Roadmap r2 From SSIDocument1 pageP-Dmaic Roadmap r2 From SSIShiva KumarNo ratings yet
- 15 03 12 Planning Tips and TricksDocument43 pages15 03 12 Planning Tips and TricksparmitchoudhuryNo ratings yet
- IM - BUMA 30083 - Fundamentals of Prescriptive Analytics (BSBA-MM TG 4-1) - Week 5Document9 pagesIM - BUMA 30083 - Fundamentals of Prescriptive Analytics (BSBA-MM TG 4-1) - Week 5SteveN.MalunesNo ratings yet
- ABAP Training For Functional Consultants 60Document62 pagesABAP Training For Functional Consultants 60abbas910% (1)
- Pitfalls For Real Time Software Developer - 2Document11 pagesPitfalls For Real Time Software Developer - 2phamvan_tuongNo ratings yet
- Trends in System Development: Systems Analysis and Design in A Changing WorldDocument23 pagesTrends in System Development: Systems Analysis and Design in A Changing Worldgaurav2300500No ratings yet
- Top 25 Excel Dashboard Tips SheetDocument2 pagesTop 25 Excel Dashboard Tips SheetClerenda McgradyNo ratings yet
- Modeling PerspectivesDocument17 pagesModeling Perspectivesashscribd_idNo ratings yet
- Key Pain Points of OBIEE Users: BI ImplementationDocument12 pagesKey Pain Points of OBIEE Users: BI ImplementationAnil GonuguntaNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Tips and ANSYS TricksDocument74 pagesANSYS Tips and ANSYS Tricksjulio1114No ratings yet
- Beginners Guide To Dashboards PDFDocument12 pagesBeginners Guide To Dashboards PDFSynkroMax BiotechNo ratings yet
- Pattern Recognition Software GuideDocument21 pagesPattern Recognition Software GuideRenéNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Consejos y Trucos - Peter BudgellDocument74 pagesANSYS Consejos y Trucos - Peter BudgellFREDDY PINTONo ratings yet
- Testing Your DashboardDocument19 pagesTesting Your DashboardMazhar MahadzirNo ratings yet
- Performance Monitoring 2016Document53 pagesPerformance Monitoring 2016Luca Ele Ale Stefi100% (1)
- Course Code and Title: ENTERPRISE ARCHITECTURE Lesson Number: Lesson 3 (Week 3) Topic: Enterprise Architecture Tool Part 2Document19 pagesCourse Code and Title: ENTERPRISE ARCHITECTURE Lesson Number: Lesson 3 (Week 3) Topic: Enterprise Architecture Tool Part 2Allysa Cebeda PascasioNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Data Modeling - Lecture 1Document21 pagesDimensional Data Modeling - Lecture 1Arijit BiswasNo ratings yet
- SWE 205 - Introduction To Software Engineering: - User Interface Design (Chapter 16)Document27 pagesSWE 205 - Introduction To Software Engineering: - User Interface Design (Chapter 16)matthewluiNo ratings yet
- Module 12: Administering Siebel Analytics ApplicationsDocument23 pagesModule 12: Administering Siebel Analytics ApplicationsDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- App DevDocument1 pageApp DevDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Module 14: Using Siebel DeliversDocument23 pagesModule 14: Using Siebel DeliversDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Module 15: Siebel Analytics Applications OverviewDocument20 pagesModule 15: Siebel Analytics Applications OverviewDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Module 13: Deploying Disconnected AnalyticsDocument18 pagesModule 13: Deploying Disconnected AnalyticsDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- 17AD WrapUpDocument12 pages17AD WrapUpDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- 05AD AnswersDocument30 pages05AD AnswersDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Module 9: Integrating Intelligence Dashboards Into Siebel ApplicationsDocument23 pagesModule 9: Integrating Intelligence Dashboards Into Siebel ApplicationsDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Guided NavigationDocument13 pagesGuided Navigationgagan1667No ratings yet
- Module 7: Creating Intelligence DashboardsDocument15 pagesModule 7: Creating Intelligence DashboardsDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Module 8: Configuring Intelligence DashboardsDocument13 pagesModule 8: Configuring Intelligence DashboardsDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- ModelDocument2 pagesModelDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Module 10: Customizing The Analytics Web User InterfaceDocument11 pagesModule 10: Customizing The Analytics Web User InterfaceDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Module 6: Views and Charts in RequestsDocument20 pagesModule 6: Views and Charts in RequestsDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Query PerformanceDocument2 pagesQuery PerformanceDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Siebel Analytics ArchitectureDocument29 pagesModule 3: Siebel Analytics ArchitectureDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Module 4: Analytics Repository BasicsDocument18 pagesModule 4: Analytics Repository BasicsDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Business Objects Concepts Snow FlakesDocument1 pageBusiness Objects Concepts Snow FlakesDeepanshu100% (1)
- Introduction To EIMDocument15 pagesIntroduction To EIMDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- EIm 1Document33 pagesEIm 1DeepanshuNo ratings yet
- OLTP Vs OLAPDocument2 pagesOLTP Vs OLAPDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Olap Tool Market ShareDocument1 pageOlap Tool Market ShareDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Star SchemaDocument1 pageStar SchemaDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- OBIEE ExploringAnalyticsUIDocument18 pagesOBIEE ExploringAnalyticsUIDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- LogicaL Data MODELDocument3 pagesLogicaL Data MODELDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Fact and Fact Types DWH CONCEPTDocument2 pagesFact and Fact Types DWH CONCEPTDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- DWH Site MapDocument1 pageDWH Site MapDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Data Warehousing Dimensional Data ModelDocument2 pagesData Warehousing Dimensional Data ModelDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- DBA FundamentalsDocument1 pageDBA FundamentalsDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Epson WorkForce Pro WF-C878-879RDocument8 pagesEpson WorkForce Pro WF-C878-879Rsales2 HARMONYSISTEMNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: BTY351 Plant Biotechnology LaboratoryDocument40 pagesLaboratory Manual: BTY351 Plant Biotechnology LaboratoryRetik KoulNo ratings yet
- 1SFC132367M0201 PSE Internal Modbus RTUDocument22 pages1SFC132367M0201 PSE Internal Modbus RTUAhmed OsmanNo ratings yet
- Varargout Tugas - GUI (Varargin) : FunctionDocument7 pagesVarargout Tugas - GUI (Varargin) : FunctionDwi Lestari dwi375ft.2019No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document23 pagesChapter 3pganoelNo ratings yet
- Bootloader3 PDFDocument18 pagesBootloader3 PDFsaravananNo ratings yet
- SPE-183743-MS Maintaining Injectivity of Disposal Wells: From Water Quality To Formation PermeabilityDocument19 pagesSPE-183743-MS Maintaining Injectivity of Disposal Wells: From Water Quality To Formation PermeabilityAminNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Monopole Circularly Polarised Microstrip Patch Antenna Using HFSSDocument17 pagesDesign and Analysis of Monopole Circularly Polarised Microstrip Patch Antenna Using HFSSKashif FurkanNo ratings yet
- Big Data Analytics & Technologies: HbaseDocument30 pagesBig Data Analytics & Technologies: HbaseWong pi wenNo ratings yet
- Articles On SidisDocument146 pagesArticles On SidisMircea492003100% (1)
- RRB JE CBT-2 Electronics Tech Paper With Key 31-8-2019 1st ShiftDocument55 pagesRRB JE CBT-2 Electronics Tech Paper With Key 31-8-2019 1st ShiftKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Sympoly Toolbox IssuesDocument7 pagesSympoly Toolbox IssuesAli FahemNo ratings yet
- Fiber SyllabusDocument1 pageFiber SyllabusPaurav NayakNo ratings yet
- Body Deassembly 9 Interior TrimDocument7 pagesBody Deassembly 9 Interior TrimCarlos TecnicNo ratings yet
- MathDocument2 pagesMathWessam ElmongyNo ratings yet
- C191HM Powermeter and Harmonic Manager CommunicationsDocument30 pagesC191HM Powermeter and Harmonic Manager CommunicationsRoberto GarridoNo ratings yet
- CSC:361-Software Engineering: Semester: Fall2020Document39 pagesCSC:361-Software Engineering: Semester: Fall2020hamsfayyazNo ratings yet
- 3 DB RDMDocument49 pages3 DB RDMfaisal shahzadNo ratings yet
- Excel NotesDocument9 pagesExcel NotesAhnNo ratings yet
- CHM170L Exp3 Surface TensionDocument5 pagesCHM170L Exp3 Surface TensionKaiser SaltoNo ratings yet
- CSIE Fisa Disciplina - Baze de DateDocument4 pagesCSIE Fisa Disciplina - Baze de DateCostin CheluNo ratings yet
- Sap SCM TrainingDocument5 pagesSap SCM TrainingGLOBAL TEQNo ratings yet
- Symmetries and Conservation Laws-Consequences of Noether TheoremDocument8 pagesSymmetries and Conservation Laws-Consequences of Noether TheoremmastinaropuruNo ratings yet
- Sample Chapter - Oil and Gas Well Drilling Technology PDFDocument19 pagesSample Chapter - Oil and Gas Well Drilling Technology PDFDavid John100% (1)
- Chem 1211 Lab ReportDocument9 pagesChem 1211 Lab Reportansleybarfield0% (1)
- Sewage: Vag Hade Flap ValveDocument4 pagesSewage: Vag Hade Flap ValveAhmedRamadanNo ratings yet
- Bubble Sort ExampleDocument7 pagesBubble Sort Examplenur_anis_8No ratings yet
- Workshop 2 Electrical Installations Single PhaseDocument3 pagesWorkshop 2 Electrical Installations Single PhaseDIAN NUR AIN BINTI ABD RAHIM A20MJ0019No ratings yet
- Class - B Complementary Symmetry Power AmplifierDocument3 pagesClass - B Complementary Symmetry Power AmplifierAnonymous SH0A20No ratings yet