Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pa Tho Physiology Final
Uploaded by
rhan0330Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pa Tho Physiology Final
Uploaded by
rhan0330Copyright:
Available Formats
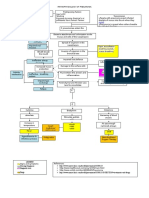
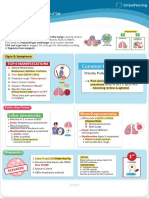
VII.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Precipitating Factors
Predisposing Factor Frequent contact with people
Physiologic (Immunity) who have the disease
Poor ventilation
Crowded/
Low Socioeconomic Status
System
Involved
Respiratory System
Etiology/ Cause
Air droplets from a cough or
sneeze of an infected person
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.
tuberculosis)
Molecular Changes Gross Anatomical
Air droplets from a cough or sneeze of Changes
an infected person
Productive Phlegm
Tubercle bacilli invasion in the apices Lesions on the lung tissues
of the
Lungs or near the pleurae of the lower Calcification of the affected
lobes lung tissues
Ineffective Gas exchange
Bronchopneumonia develops in the
brought by damaged
lung tissue
bronchioles
(Phagocytosed tubercle bacilli are
ingested by macrophages or the pus
Weight Loss
formation)
Necrotic Degeneration occur
Drainage of necrotic materials into the
tracheobronchial tree
Lesions may calcify (Ghon’s Tubecle)
Tubercle bacilli immunity develop
Acquired immunity leads to further
growth
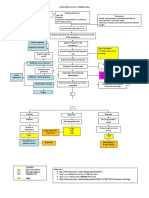
Lab
Physiologic Manifestation on Findings
Positive
Effect on Bodily Function Mantoux test
Fever Positive Sputum
Productive Phlegm Exam
Lesions on the lung tissues
Calcification of the affected lung tissues
Ineffective Gas exchange brought by
damaged bronchioles Radiological
Rapid Respiration to compensate with Studies
inadequate bronchioles Positive X-ray
Chest Pain Results
Weight Loss
Complications
Clinical Manifestation Skeletal Tuberculosis
Patient Productive Phlegm Genital Tract Tuberculosis
Compensates/ Weight Loss Urinary tract Tuberculosis
Fever CNS Tuberculosis
Recover/ Client’s GI Tuberculosis
Chest Pain
Manifestation Adrenal Tuberculosis
Body Malaise Scrofula Tuberculosis
Improved Fatigue Cardiac Tuberculosis
Negative X-ray
Final Diagnosis
Pulmonary
Tuberculosis
Category 1
You might also like
- Pulmonary Infection in the Immunocompromised Patient: Strategies for ManagementFrom EverandPulmonary Infection in the Immunocompromised Patient: Strategies for ManagementCarlos AgustiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Genitourinary TuberculosisDocument8 pagesPathophysiology of Genitourinary Tuberculosisace_51891No ratings yet
- Book Based: Etiology: Tubercle Bacilli Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsDocument7 pagesBook Based: Etiology: Tubercle Bacilli Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsIrish EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Koch's Disease (Tuberculosis) : Primary InfectionDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Koch's Disease (Tuberculosis) : Primary InfectionbijelNo ratings yet
- Path o Physio TB EffusionDocument2 pagesPath o Physio TB EffusionSergi Lee OrateNo ratings yet
- Conceptmap Oct 12Document1 pageConceptmap Oct 12Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Neonatal Sepsis Secondary To Neonatal PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Neonatal Sepsis Secondary To Neonatal Pneumoniapaul andrew laranjo asuncion80% (5)
- WK 3 Assignment Lrti - OtedaDocument8 pagesWK 3 Assignment Lrti - Otedakyle otedaNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: Republic of The Philippines San Fabian, Echague, Isabela Activity 2 Medical-Surgical NursingDocument9 pagesIsabela State University: Republic of The Philippines San Fabian, Echague, Isabela Activity 2 Medical-Surgical Nursingpinoy HubNo ratings yet
- GRANDPAR-PATHOPHYSIOLOGY-4 (1) Pertusis Whooping Cough Secondary To PneumoniaDocument5 pagesGRANDPAR-PATHOPHYSIOLOGY-4 (1) Pertusis Whooping Cough Secondary To PneumoniaJustin AlejoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of TBDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of TBEddie Lou GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PcapDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of PcapThomas joshua QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaMaria Cristina100% (1)
- PCAP Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPCAP Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYCHRISTIE MONTANO25% (4)
- Patient Based PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPatient Based PathophysiologyDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Etiology PCAPDocument2 pagesEtiology PCAPClark SavageNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Pathophysiology (Book Based) : Non-Modifiable: ModifiableDocument2 pagesPneumonia Pathophysiology (Book Based) : Non-Modifiable: ModifiableYVETTE CLAIRE BORRESNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis: PGI Leichel Ann N. AlbertoDocument82 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis: PGI Leichel Ann N. AlbertoLeichel AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaJuneNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaJesselle LasernaNo ratings yet
- B. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyDocument3 pagesB. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyKenneth Torres100% (1)
- Pneumonia in Children: Monocytogenes, Chlamydia TrachomatisDocument1 pagePneumonia in Children: Monocytogenes, Chlamydia TrachomatisAlcala, Mariaden A.100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaJeffrey Ramos100% (1)
- Concept MapDocument4 pagesConcept MapMersiya SarapuddinNo ratings yet
- I. Definition: Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument6 pagesI. Definition: Pulmonary Tuberculosisjulie-pearl-6329No ratings yet
- Patient Based PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPatient Based PathophysiologyJeizel IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsDocument6 pagesPredisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsKen SimonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Pneumoniaoxidalaj97% (31)
- Asia Pacific College of Advanced StudiesDocument4 pagesAsia Pacific College of Advanced Studiesaella gracieNo ratings yet
- Copd TBDocument1 pageCopd TBnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaAzria John DemetriNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of TuberculosisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of TuberculosisFirenze Fil96% (56)
- Pcap - PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesPcap - PathophysiologyAyla Mar100% (1)
- Asma Dan COPDDocument52 pagesAsma Dan COPDArga Krittas MaranNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Patho & SignsDocument1 pagePneumonia Patho & SignsVishalNo ratings yet
- Simple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaDocument1 pageSimple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaJason A. AdoyoganNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Pathophysiology (Patient Based) : Non-Modifiable: ModifiableDocument2 pagesPneumonia Pathophysiology (Patient Based) : Non-Modifiable: ModifiableYVETTE CLAIRE BORRESNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia Concept MapDocument1 pageCommunity Acquired Pneumonia Concept MapSebastianNo ratings yet
- Chart - Respiratory Infections BacteriaDocument4 pagesChart - Respiratory Infections BacteriaRedNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and TuberculosisDocument1 pageSchematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and Tuberculosispragna novaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pott'S DiseaseDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Pott'S Diseasee3runeNo ratings yet
- Final PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesFinal Pathophysiologyemely p. tangoNo ratings yet
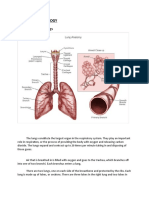
- Anatomy of The Lungs: Viii. PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Lungs: Viii. PathophysiologyShin EscaresesNo ratings yet
- Alinsangao, Nashwa N. BSN 3B - SIC (Pathogenesis & Life Threatening Pathways)Document5 pagesAlinsangao, Nashwa N. BSN 3B - SIC (Pathogenesis & Life Threatening Pathways)NASHWA NASLUN. ALINSANGAONo ratings yet
- San Gabriel, GMA, Cavite College of Nursing: Iv. Pathophysiology by The BookDocument2 pagesSan Gabriel, GMA, Cavite College of Nursing: Iv. Pathophysiology by The BookSTEPHANIE LIBO-ONNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology PneumoniaSheila Mae Escalante67% (3)
- NCM 112 Respiratory HandoutDocument7 pagesNCM 112 Respiratory HandoutissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Age - Weather: Aspiration of Secretions Containing MicrobesDocument4 pagesAge - Weather: Aspiration of Secretions Containing Microbeslouie john abilaNo ratings yet
- Patho of Pott's DiseaseDocument2 pagesPatho of Pott's DiseaseIris Balino100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Shortness of Breathing Crackles and Wheezes Dull PercussionDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Shortness of Breathing Crackles and Wheezes Dull Percussionjudith dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Chemical Mediators of the Acute Inflammatory Reaction: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: Modern Trends in Physiological SciencesFrom EverandChemical Mediators of the Acute Inflammatory Reaction: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: Modern Trends in Physiological SciencesNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Biochemical Pharmacology: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesFrom EverandFundamentals of Biochemical Pharmacology: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesNo ratings yet
- CitationDocument1 pageCitationJennifer A. IñigoNo ratings yet
- Answer: D: ExplanationDocument33 pagesAnswer: D: Explanationjaime costaNo ratings yet
- Byzantium Notes CultureDocument6 pagesByzantium Notes Culturepatrick cairoliNo ratings yet
- Application Note Assessing Flow Accelerated Corrosion With Pulsed Eddy CurrentDocument2 pagesApplication Note Assessing Flow Accelerated Corrosion With Pulsed Eddy CurrentZoran TripunovskiNo ratings yet
- Fluphenazine Drug Study!Document3 pagesFluphenazine Drug Study!EmJay Balansag100% (3)
- Imovie 2020 PDF Guide PDFDocument2 pagesImovie 2020 PDF Guide PDFTanushka MalhotraNo ratings yet
- The Sparrow: Srijani Bhowmick Class VDocument12 pagesThe Sparrow: Srijani Bhowmick Class VsgphycoNo ratings yet
- From The Explorer's DaughterDocument2 pagesFrom The Explorer's DaughterMisho DragnevNo ratings yet
- Reheating and Preheating After Inflation: An IntroductionDocument9 pagesReheating and Preheating After Inflation: An IntroductionSourav GopeNo ratings yet
- GP150 PDFDocument125 pagesGP150 PDFBf Ipanema100% (1)
- Proposed USG Boral Ceiling System For Tropicana MiyuDocument5 pagesProposed USG Boral Ceiling System For Tropicana MiyuLorraineNo ratings yet
- Outsourcing-Insourcing CriteriaDocument8 pagesOutsourcing-Insourcing CriteriaGuadagustinNo ratings yet
- School Action Plan in IctDocument1 pageSchool Action Plan in IctMcDaryl Mateo100% (3)
- Designation Order SicDocument3 pagesDesignation Order SicMerafe Ebreo AluanNo ratings yet
- Subject - Monetary Economics: MoneyDocument4 pagesSubject - Monetary Economics: MoneyRajat LonareNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1: Course Plan / OutlineDocument3 pagesLecture-1: Course Plan / OutlineNaiem IslamNo ratings yet
- MIS Downloads Requirement Specification Document Example 2Document14 pagesMIS Downloads Requirement Specification Document Example 2Rajashree PatilNo ratings yet
- Architecture Building Services: Assignment-1Document36 pagesArchitecture Building Services: Assignment-1santhu majiNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument22 pagesIonic EquilibriumbeherasubhammikunNo ratings yet
- LDK8000Document110 pagesLDK8000asjoben1002No ratings yet
- Nakul VermaDocument112 pagesNakul VermaNakul VermaNo ratings yet
- Interdependence and The Gains From TradeDocument30 pagesInterdependence and The Gains From TradeAnusree P hs20h011No ratings yet
- Avy eDocument11 pagesAvy emsvkumar0% (1)
- Blast Injury ManagementDocument16 pagesBlast Injury Managementheart wisdomNo ratings yet
- Quiz ErrorsDocument5 pagesQuiz Errorsanon_843459121No ratings yet
- Surveying Lesson 6 To 10 PDFDocument68 pagesSurveying Lesson 6 To 10 PDFNadane AldoverNo ratings yet
- Backup of DB2Document1,297 pagesBackup of DB2Kamakshigari SureshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 OptimizationDocument41 pagesLecture 6 Optimizationaku_la100% (2)
- À Bout de Souffle (Breathless) : Treatment by François TruffautDocument10 pagesÀ Bout de Souffle (Breathless) : Treatment by François TruffautAlex KahnNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Badminton - Fundamental SkillsDocument45 pagesModule 7 - Badminton - Fundamental SkillsJoshua AltamiranoNo ratings yet