Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anaphylaxis Algo
Uploaded by
zacklim_2000Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anaphylaxis Algo
Uploaded by
zacklim_2000Copyright:
Available Formats
Resuscitation Council (UK)
Anaphylaxis
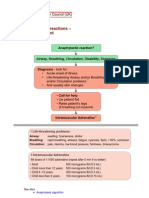
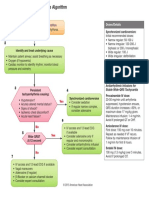
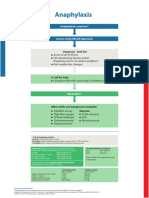
algorithm Anaphylactic reaction?
Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, Exposure
Diagnosis - look for:
• Acute onset of illness
• Life-threatening Airway and/or Breathing
1
and/or Circulation problems
• And usually skin changes
• Call for help
• Lie patient flat
• Raise patient’s legs
2
Adrenaline
When skills and equipment available:
• Establish airway
• High flow oxygen Monitor:
3
• IV fluid challenge • Pulse oximetry
4
• Chlorphenamine • ECG
5
• Hydrocortisone • Blood pressure
1 Life-threatening problems:
Airway: swelling, hoarseness, stridor
Breathing: rapid breathing, wheeze, fatigue, cyanosis, SpO2 < 92%, confusion
Circulation: pale, clammy, low blood pressure, faintness, drowsy/coma
2 Adrenaline (give IM unless experienced with IV adrenaline) 3 IV fluid challenge:
IM doses of 1:1000 adrenaline (repeat after 5 min if no better) Adult - 500 – 1000 mL
• Adult 500 micrograms IM (0.5 mL) Child - crystalloid 20 mL/kg
• Child more than 12 years: 500 micrograms IM (0.5 mL)
Stop IV colloid
• Child 6 -12 years: 300 micrograms IM (0.3 mL)
if this might be the cause
• Child less than 6 years: 150 micrograms IM (0.15 mL) of anaphylaxis
Adrenaline IV to be given only by experienced specialists
Titrate: Adults 50 micrograms; Children 1 microgram/kg
4 Chlorphenamine 5 Hydrocortisone
(IM or slow IV) (IM or slow IV)
Adult or child more than 12 years 10 mg 200 mg
Child 6 - 12 years 5 mg 100 mg
Child 6 months to 6 years 2.5 mg 50 mg
Child less than 6 months 250 micrograms/kg 25 mg
See also: ► Anaphylactic reactions – Initial treatment
You might also like
- Time Table FCCS OB 13 - 14 Maret SbyDocument4 pagesTime Table FCCS OB 13 - 14 Maret SbyLina SusantiNo ratings yet
- Treatment Algorithm for AnaphylaxisDocument1 pageTreatment Algorithm for AnaphylaxisLidya YudithNo ratings yet
- Resuscitation Council Uk Anaphylaxis AlgorithmDocument1 pageResuscitation Council Uk Anaphylaxis Algorithmbrianed231100% (1)
- Diagnosis Dan Resusitasi Pada Pasien Syok Perdarahan & Syok DehidrasiDocument29 pagesDiagnosis Dan Resusitasi Pada Pasien Syok Perdarahan & Syok DehidrasiAris Dwi RahimNo ratings yet
- ACOG Guidance Update - Diagnosis and Management of PROM (Prelabor Rupture of Membranes) - The ObG ProjectDocument8 pagesACOG Guidance Update - Diagnosis and Management of PROM (Prelabor Rupture of Membranes) - The ObG Projectteresita vargasNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana ACS HUT Harkit 2015Document35 pagesTatalaksana ACS HUT Harkit 2015Muhammad Jahari SupiantoNo ratings yet
- CamScanner Document ScansDocument66 pagesCamScanner Document ScansAdif FlysNo ratings yet
- Framingham Risk ScoreDocument2 pagesFramingham Risk ScoreAsyiqin NasirNo ratings yet
- TREATMENT OF 71 YEAR OLD GRANNY WITH STAGE II HYPERTENSION AND HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIADocument13 pagesTREATMENT OF 71 YEAR OLD GRANNY WITH STAGE II HYPERTENSION AND HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIAagathaaveonitaNo ratings yet
- EBPH Evidence Tentang Dukungan Sosial bagi Pasien HIVDocument11 pagesEBPH Evidence Tentang Dukungan Sosial bagi Pasien HIVSeptantri HandayaniNo ratings yet
- PERDICIDocument31 pagesPERDICIDeya PrastikaNo ratings yet
- Assessing Potential Harm in Healthcare Interventions and PoliciesDocument10 pagesAssessing Potential Harm in Healthcare Interventions and PoliciesMuhammad HidayatNo ratings yet
- Tabel Konversi FiO2Document2 pagesTabel Konversi FiO2arie_yuliantoNo ratings yet
- Hasil UKMPPD Feb 2015 SignedDocument36 pagesHasil UKMPPD Feb 2015 SignedMuhammad Rifki El-MuammaryNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading Muhamad Fakhri PPDS JantungDocument24 pagesJournal Reading Muhamad Fakhri PPDS JantungLycka AkaishaNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading AminophyllineDocument76 pagesJournal Reading AminophyllinePandhu Suprobo100% (1)
- Jurnal TBCDocument6 pagesJurnal TBCLorinsya Ollin100% (1)
- Integrated Emergency and Disaster Management System in DIYDocument49 pagesIntegrated Emergency and Disaster Management System in DIYHari Mas KuncoroNo ratings yet
- Tesis Terapi Batuk DarahDocument10 pagesTesis Terapi Batuk DarahAnonymous DxYXYkjTo5No ratings yet
- Bab I-V Jurding Infanticide EditedDocument62 pagesBab I-V Jurding Infanticide EditedS FznsNo ratings yet
- Mmas+kuesioner Kepatuhan Minum ObatDocument9 pagesMmas+kuesioner Kepatuhan Minum Obatdesti purnama sariNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Obat Analgesik, Anti Piretik & Anti Inflamasi: Andri Tilaqza, M.Farm., AptDocument45 pagesFarmakologi Obat Analgesik, Anti Piretik & Anti Inflamasi: Andri Tilaqza, M.Farm., AptDark BlueNo ratings yet
- Radiologi Peritonitis Dan Perforasi IhsanDocument9 pagesRadiologi Peritonitis Dan Perforasi IhsanCharles Patrice Isaupu GansangNo ratings yet
- Laporan Case 4 - Burn InjuryDocument37 pagesLaporan Case 4 - Burn InjuryAnna Rahmania SariNo ratings yet
- Validity and importance of harm resultsDocument2 pagesValidity and importance of harm resultsFekhaza AlfarissiNo ratings yet
- Buku Panduan Pengayaan OSCE UKMPPD 2Document130 pagesBuku Panduan Pengayaan OSCE UKMPPD 2jayanti100% (1)
- RBCH - PHT Aminophylline Loading Dose GuidelinesDocument2 pagesRBCH - PHT Aminophylline Loading Dose GuidelinesAdrian PrasetioNo ratings yet
- Surat Pengantar Dan Proposal ACSA 2023 IAIDocument20 pagesSurat Pengantar Dan Proposal ACSA 2023 IAIEtikNo ratings yet
- Slide PPT PrismaDocument31 pagesSlide PPT PrismaUlul Azmi AdnanNo ratings yet
- Dyspepsia PDFDocument14 pagesDyspepsia PDFCdma Nastiti FatimahNo ratings yet
- Soac 2021 First AnnouncementDocument13 pagesSoac 2021 First AnnouncementHendi PrihatnaNo ratings yet
- Tehnik - Tehnik Analgesia Post OperasiDocument32 pagesTehnik - Tehnik Analgesia Post OperasiGuntur Aryo PuntodewoNo ratings yet
- Acute Life Threatening Events Management PDFDocument58 pagesAcute Life Threatening Events Management PDFAlice Valeria WiyonoNo ratings yet
- PENATALAKSANAAN ASMA JANGKA PANJANGDocument81 pagesPENATALAKSANAAN ASMA JANGKA PANJANGbotolkecapNo ratings yet
- Refreshing DHFDocument13 pagesRefreshing DHFNia Nurhayati ZakiahNo ratings yet
- Guideline Stroke Perdossi 2007Document15 pagesGuideline Stroke Perdossi 2007Saut 'tetZ' PurbaNo ratings yet
- Hidayaturromi-Jurnal Ileus Obstruktif PDFDocument4 pagesHidayaturromi-Jurnal Ileus Obstruktif PDFHerman HermanNo ratings yet
- Rca KarsDocument75 pagesRca KarsAnonymous 12i1wlaALNo ratings yet
- Lamp.2 Sop Evakuasi MedisDocument2 pagesLamp.2 Sop Evakuasi MedisUci HasbullahNo ratings yet
- D 031026Document8 pagesD 031026RifqiNo ratings yet
- JNC 6 Vs 7Document2 pagesJNC 6 Vs 7Diwan AyuNo ratings yet
- Konas Perdatin 2019Document66 pagesKonas Perdatin 2019Akreditasi RSPC19No ratings yet
- PhotokeratitisDocument15 pagesPhotokeratitisSelase Di MariaNo ratings yet
- Original Research Abstract AFCC ASMIHA 2019Document82 pagesOriginal Research Abstract AFCC ASMIHA 2019Program Studi Kardiologi100% (1)
- Risk Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Lung CancerDocument6 pagesRisk Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Lung CancerAsdar Raya RangkutiNo ratings yet
- Revisi Final Skripsi Tes Jalan 6 MenitDocument83 pagesRevisi Final Skripsi Tes Jalan 6 MenitagungNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Asma Gina 2015Document34 pagesKlasifikasi Asma Gina 2015Roni Ardian100% (1)
- Saran Hasil Mcu InggrisDocument3 pagesSaran Hasil Mcu Inggrisapril babyNo ratings yet
- Relationship between surgical duration and shivering in spinal anesthesia patientsDocument9 pagesRelationship between surgical duration and shivering in spinal anesthesia patientsariefNo ratings yet
- Heidi's Epinephrine and Amiodarone Infusion for Edema and Doris' TreatmentDocument13 pagesHeidi's Epinephrine and Amiodarone Infusion for Edema and Doris' TreatmentSavero Evan AbishaNo ratings yet
- 2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmDocument1 page2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmRyggie ComelonNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana PneumoniaDocument37 pagesTatalaksana PneumoniaAnindya AgrasidiNo ratings yet
- Dr Suvianto Scan Report May 2009Document55 pagesDr Suvianto Scan Report May 2009Denny LukasNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lecture Assignments for Inborn Errors of MetabolismDocument2 pagesPre-Lecture Assignments for Inborn Errors of MetabolismclementNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Ujian Sidang Periode 112 TGL 26-27 Juni 2021 (Rev)Document9 pagesJadwal Ujian Sidang Periode 112 TGL 26-27 Juni 2021 (Rev)Yohan Nafisa NetNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Syndrome Workshop Tig2010Document41 pagesGeriatric Syndrome Workshop Tig2010Fadhilah MuthiNo ratings yet
- Anapost1 PDFDocument1 pageAnapost1 PDFIvana Vučić KlarićNo ratings yet
- AnafilaxisDocument1 pageAnafilaxisalkutbiNo ratings yet
- Poster SpecCircs Anaphylaxis Treatment Algorithm ENG V20151001 HRES Site PDFDocument1 pagePoster SpecCircs Anaphylaxis Treatment Algorithm ENG V20151001 HRES Site PDFnamja07No ratings yet
- Emergency Treatment of Anaphylactic ReactionsDocument31 pagesEmergency Treatment of Anaphylactic Reactionsmaed78No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Challenges in Cervical Lymphadenitis TBDocument19 pagesDiagnostic Challenges in Cervical Lymphadenitis TBAstriTaufiRamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Knot Tying ManualDocument50 pagesKnot Tying ManualAdriana Vick100% (1)
- The 2015 Bls Acls Guidelines EnaDocument36 pagesThe 2015 Bls Acls Guidelines EnaAstriTaufiRamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Berita Acara Presentasi PortofolioDocument7 pagesBerita Acara Presentasi PortofolioAstriTaufiRamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument60 pagesBlood PressureEnerolisa ParedesNo ratings yet