Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Notes 3.1.3 Plant & Animal Cell Overview
Uploaded by
Kari Kristine Hoskins BarreraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Notes 3.1.3 Plant & Animal Cell Overview
Uploaded by
Kari Kristine Hoskins BarreraCopyright:
Available Formats
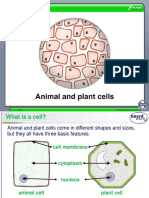
Plant and Animal Cell Overview: The Basics
! Both plant and animal cells, which are eukaryotes, have cell features in common:
• Both plant and animal cells are bound by plasma membranes that enable the
regulation of materials passing into and out of the cell.
• Compartmentalization is the process by which cells have evolved organelles,
membrane-enclosed structures that perform specific functions, to increase the
efficiency of cell metabolism.
• The surface-area-to-volume ratio is used to measure cell efficiency. It is
calculated by dividing a cell’s surface area (in square units) by the volume (in cubic
units).
An outer plasma membrane binds both (b)
plant and (a) animal cells. The membrane
allows regulation of material passing in and
out of the cell. Generalized plant and animal
cells—including cell membranes—are depicted
in illustrations on the left.
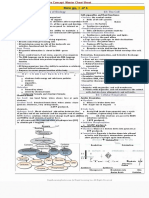
(a) Cell compartmentalization can be likened
to the division of labor by society. Compart-
mentalization enables cell organelles to
specialize in one activity and thereby increase
productivity. The illustrations on the left show
that in both (b) plant and (a) animal cells, cell
processes are compartmentalized into
organelles, the main units of cell function.
(b)
Cell membrane
The illustration on the left presents the
surface-area-to-volume ratios of three
hypothetical cube sizes. As overall cube (cell)
size increases, surface-area-to-volume ratio
decreases. A higher surface-area-to-volume
ratio is more efficient for cellular activity.
www.thinkwell.com info@thinkwell.com
Copyright © 2000, Thinkwell Corp., All Rights Reserved. 031500bio062
You might also like
- FIRST Expo 2013 PDFDocument1 pageFIRST Expo 2013 PDFKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Last Snake RunnerDocument4 pagesLast Snake RunnerKari Kristine Hoskins Barrera100% (1)
- Pose Id OnDocument21 pagesPose Id OnKari Kristine Hoskins Barrera100% (1)
- To The TeacherDocument1 pageTo The TeacherKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Prometheus EnrichmentDocument11 pagesPrometheus EnrichmentKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- AHEC Ravens FEC Program DescriptionsDocument5 pagesAHEC Ravens FEC Program DescriptionsKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- AHERT Robotics Camp Spring 2013Document2 pagesAHERT Robotics Camp Spring 2013Kari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Pandora EnrichmentDocument9 pagesPandora EnrichmentKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Odyssey Book 10Document11 pagesOdyssey Book 10Kari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Native AmericanDocument9 pagesNative AmericanKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Olympian OverviewDocument23 pagesOlympian OverviewKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Norse Mythology 2Document17 pagesNorse Mythology 2AtraNo ratings yet
- Olympian Gods PacketDocument194 pagesOlympian Gods PacketKari Kristine Hoskins Barrera80% (5)
- In The Beginning, Zeus, HestiaDocument30 pagesIn The Beginning, Zeus, HestiaKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- General ActivitiesDocument21 pagesGeneral ActivitiesKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Microbe MomentsDocument2 pagesMicrobe MomentsKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- HermesDocument11 pagesHermesKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Her ADocument5 pagesHer AKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- NYS Regents Physics Reference TablesDocument6 pagesNYS Regents Physics Reference Tablesfizxtchr100% (2)
- Iliad Book 1Document17 pagesIliad Book 1Kari Kristine Hoskins Barrera100% (1)
- Hep Ha Est UsDocument7 pagesHep Ha Est UsKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Hades, DemeterDocument22 pagesHades, DemeterKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Regents Examination in Geometry Test Sampler FallDocument32 pagesRegents Examination in Geometry Test Sampler FallKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Microbial Evolution ActivityDocument24 pagesMicrobial Evolution ActivityKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Microbes Too Smart For AntibioticsDocument5 pagesMicrobes Too Smart For AntibioticsFederico LeonNo ratings yet
- Scientific NotationDocument1 pageScientific NotationAlejandro AguilarNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Regents January 2009Document28 pagesEarth Science Regents January 2009Bilawal Nasir RajaNo ratings yet
- LabsDocument49 pagesLabsKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Science Graph ExerciseDocument11 pagesScience Graph ExerciseKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Microbial GrowthDocument48 pagesMicrobial Growthdreamrose100% (14)
- Dna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 3Document6 pagesDna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 3afeuettkk100% (1)
- Biology 5090-Diffusionosmosis-And-Active-Transport - pptx-1Document36 pagesBiology 5090-Diffusionosmosis-And-Active-Transport - pptx-1Saba AnjumNo ratings yet
- Blood Practice TestDocument13 pagesBlood Practice Testching chongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document7 pagesChapter 06Teehee Jones100% (5)
- Stage 2 Sace Biology: TOPIC 1: DNA and Proteins Chapter 1.1 DNA StructureDocument41 pagesStage 2 Sace Biology: TOPIC 1: DNA and Proteins Chapter 1.1 DNA StructureKassyKasNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIDocument110 pagesAnimal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIYash Soneji100% (2)
- Literature Please Refer To Included For Correct: Principles & Practice of Diffusion & OsmosisDocument30 pagesLiterature Please Refer To Included For Correct: Principles & Practice of Diffusion & OsmosisrezamaulanaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Quiz L 9Document2 pagesThe Cell Quiz L 9moutaz bedeweyNo ratings yet
- 1841846791Document600 pages1841846791Mohammed Hussein100% (1)
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument8 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsQueenie Marie Obial AlasNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Diagrams WorksheetDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Diagrams WorksheetG Meera Prem Kumar20% (5)
- Apoptosis: Dr. Prabesh K Choudhary Final Year Resident MD PathologyDocument47 pagesApoptosis: Dr. Prabesh K Choudhary Final Year Resident MD PathologyAhmed BioNo ratings yet
- Animation: Mitosis and CytokinesisDocument10 pagesAnimation: Mitosis and CytokinesisTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Code ZOOL Course DetailsDocument33 pagesCode ZOOL Course DetailssaqikhanNo ratings yet
- RNA Structure and TypesDocument39 pagesRNA Structure and Typesshubham sachdeva100% (1)
- Biology QuizDocument36 pagesBiology QuizNikko CarilloNo ratings yet
- Effect of PH On The Activity of Potato CatalaseDocument1 pageEffect of PH On The Activity of Potato CatalaseNathuAndrews50% (2)
- Unit 01 - Pharmacognosy - 4th Semester Question BankDocument3 pagesUnit 01 - Pharmacognosy - 4th Semester Question Bankgaurav saxenaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of The Cell: ProteinsDocument121 pagesMolecular Biology of The Cell: ProteinsparaclitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NeuronDocument49 pagesChapter 2 NeuronNithinNo ratings yet
- Report BioDocument2 pagesReport BioJay BNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2157646 20210113110650Document3 pagesLab Report 2157646 20210113110650marlon molinaNo ratings yet
- BP504 T. (Pharmacognosy AND Phytochemistry II (Theory) )Document11 pagesBP504 T. (Pharmacognosy AND Phytochemistry II (Theory) )gaurav saxenaNo ratings yet
- Joe Tippens' Protocol and Scientific Backing PDFDocument2 pagesJoe Tippens' Protocol and Scientific Backing PDFkodia Kodia80% (5)
- Yumpu PDF DownloaderDocument14 pagesYumpu PDF DownloaderPoc Vezem0% (1)
- Expression of Cloned Proteins in Animal Cells PDFDocument2 pagesExpression of Cloned Proteins in Animal Cells PDFFeliciaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: MeiosisDocument24 pagesCell Division: MeiosisErnest De Mesa MendozaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Blood: DR - Ayana WasseDocument87 pagesPhysiology of Blood: DR - Ayana WasseEyachew TewabeNo ratings yet
- Protein-Amino AcidsDocument59 pagesProtein-Amino AcidsAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet