Professional Documents
Culture Documents
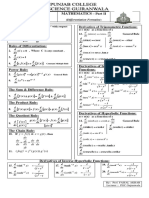
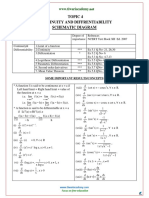
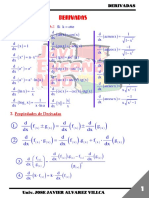
Derivatives - Important Formulae
Uploaded by
gnathwCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Derivatives - Important Formulae
Uploaded by
gnathwCopyright:
Available Formats
Nath’s Tutorial
10-3-309/C,Masab Tank,Hyderabad-28.
Ph : 9246159181.
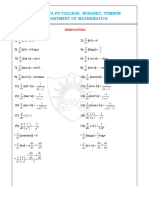
Important Definitions and Formulae in Derivatives
I. Derivatives:
1.Derivative :- Let y = f(x) be a function. If h is any change in x, then the
Lt f(x h) - f(x)
corresponding change in y is f(x+h) – f(x).If h 0 h
exists, then f(x) is said to be differentiable at x. The limit is called the
derivative of f(x) and it is denoted by f ′(x) or y ′ or y1 .
d du
2. If k is any constant and u is a function of x, then dx
{ku} k
dx .
3. If u and v are two functions of x, then
d du dv d dv du v du u dv
i) {u v} ii) {uv} u v iii) d { u } dx dx
dx dx dx dx dx dx
dx v v2
d d
4. dx (c) = 0. where c is a constant. 5. dx (xn) = n x n-1
d 1 d
6. dx (logx) = x 7. dx (ex) = ex
d d 1
8. dx ( ax) = ax log a 9. dx ( x )= 2 x
d x x d
10. dx = x 11. dx (sin x) = cos x
d d
12. dx (cos x) = - sin x 13. dx (tan x) = sec2x
d d
14. dx (cot x) = - cosec2x 15. dx ( sec x) = sec x tan x
d d
(sin-1x) =
1
16. dx (cosec x) = - cosec x cot x 17. dx 1 x
2
d 1 d
18. dx ( cos-1x) = - 2 19. dx (tan-1x) = 1
1 x 2
1 x
d d 1
20. dx (cot-1x) = - 1 1x 2 21. dx (sec-1x) = x 1 x2
d 1
22. dx (cosec-1x) = - x x2 1
You might also like
- Calculus Cheat Sheet DerivativesDocument4 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Derivativeshyd arnes100% (4)
- Castel - From Dangerousness To RiskDocument10 pagesCastel - From Dangerousness To Riskregmatar100% (2)
- Derivatives Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesDerivatives Cheat SheetalexNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Notes On The Life and Works of Jose Rizal - IncompleteDocument15 pagesNotes On The Life and Works of Jose Rizal - Incompleteblock_me_please50% (2)
- PrintDocument5 pagesPrintxewoj59015No ratings yet
- Formulas for DifferentiationDocument11 pagesFormulas for DifferentiationManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Derivatives of Basic Elementary FunctionsDocument7 pagesDerivatives of Basic Elementary Functionsi Don't knowNo ratings yet
- Formula 2Document2 pagesFormula 2randhawa03023No ratings yet
- Formulario 2 Páginas 15 16 FusionadoDocument4 pagesFormulario 2 Páginas 15 16 FusionadoCarlos RuizNo ratings yet
- Basic Differentiation Formulas - 1Document1 pageBasic Differentiation Formulas - 1HowNo ratings yet
- DiffDocument3 pagesDiffVishwa NathNo ratings yet
- Formulas of Differentiation and IntegrationDocument3 pagesFormulas of Differentiation and Integrationm.o.ren.je.n.l.yNo ratings yet
- Review of DifferentiationDocument3 pagesReview of DifferentiationMark SmithNo ratings yet
- 21 IntegralDocument24 pages21 IntegralgeniNo ratings yet
- Derivatives and integrals formulasDocument2 pagesDerivatives and integrals formulasExodusNo ratings yet
- Differentiation (Day-5)Document4 pagesDifferentiation (Day-5)Faizan AnsariNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Formula SheetDocument1 pageDerivatives Formula SheetCG DroñgêrNo ratings yet
- Math (Differentiation Notes)Document2 pagesMath (Differentiation Notes)Satyam ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Differentiation & Int All in OneDocument3 pagesDifferentiation & Int All in OneJASKIRAT GOGIANo ratings yet
- Derivatives: Definition and NotationDocument4 pagesDerivatives: Definition and NotationHarsh VyasNo ratings yet
- Hand Out Continuity and DifferentiabilityDocument3 pagesHand Out Continuity and DifferentiabilityKriti SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document13 pagesLecture 2James KarenNo ratings yet
- RulesDocument1 pageRulesBil's Top 5No ratings yet
- Techniques of Differentiation-1Document3 pagesTechniques of Differentiation-1lqmandyNo ratings yet
- 01 - Differentiation - ADocument38 pages01 - Differentiation - ASpandan BhutkarNo ratings yet
- Mat1322NotesS19 Part1Document27 pagesMat1322NotesS19 Part1dongmianjunNo ratings yet
- 12 Maths Chapter 5 Assignments 2Document6 pages12 Maths Chapter 5 Assignments 2JayeshNo ratings yet
- FormularioDocument3 pagesFormularioAraceli González ReséndizNo ratings yet
- Differential CalculusDocument25 pagesDifferential CalculusSamNo ratings yet
- Calc Form SheetDocument4 pagesCalc Form Sheet17090 Ashikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Integration Theory Module-5Document13 pagesIntegration Theory Module-5Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Formulaphase 2Document1 pageFormulaphase 2nagham khaledNo ratings yet
- Class XII - Math Chapter: Differential Calculus: X C X C +Document5 pagesClass XII - Math Chapter: Differential Calculus: X C X C +sudha.kriNo ratings yet
- Mathematics DerivativesDocument4 pagesMathematics DerivativesmontuNo ratings yet
- List of Formulas Engineering Mathematics Table of Derivatives & Integrations I Derivatives Ii Integrations 1. 1Document3 pagesList of Formulas Engineering Mathematics Table of Derivatives & Integrations I Derivatives Ii Integrations 1. 1nicromiteNo ratings yet
- Formula RioDocument10 pagesFormula RioJorge AdánNo ratings yet
- Formulas in Differential CalculusDocument2 pagesFormulas in Differential CalculusIvory Leigh Suguitan AntoniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Differentiations - Questions - Class 12 Maths Question Bank With Solutions CBSE - PDF Download (2023-2024)Document9 pagesChapter 10 - Differentiations - Questions - Class 12 Maths Question Bank With Solutions CBSE - PDF Download (2023-2024)rajatv271722No ratings yet
- IntegrationsDocument10 pagesIntegrationsjohnNo ratings yet
- Integration TargetDocument138 pagesIntegration Targetipsita londheNo ratings yet
- All Calc 2 Integration Techniques: (50 Integrals For Calc 2 Students)Document5 pagesAll Calc 2 Integration Techniques: (50 Integrals For Calc 2 Students)吴绍轩No ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument15 pagesChapter ThreeMustafa SagbanNo ratings yet
- Derivadas e IntegralesDocument2 pagesDerivadas e IntegralesARIZACA SILVESTRE JUAN GABRIELNo ratings yet
- FORMULARIO DE DERIVADAS E INTEGRALESDocument2 pagesFORMULARIO DE DERIVADAS E INTEGRALESGary PomaNo ratings yet
- Derivatives: Concept of DerivativeDocument4 pagesDerivatives: Concept of Derivativesunny rathodNo ratings yet
- Additional Math Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAdditional Math Cheat SheetKiro HeadsifterNo ratings yet
- DC & Ic Formulae-2016Document2 pagesDC & Ic Formulae-2016adhityaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives PDFDocument4 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives PDFShivamNo ratings yet
- MATERI KULIAH MATEMATIKA II TEKNIK SIPIL USAKTIDocument27 pagesMATERI KULIAH MATEMATIKA II TEKNIK SIPIL USAKTIHafidz NurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Review of Calculus Techniques for Solving ODE ProblemsDocument3 pagesReview of Calculus Techniques for Solving ODE Problemsahmed salymNo ratings yet
- 12th DIFFERENTIATION: - Theory & ProblemsDocument11 pages12th DIFFERENTIATION: - Theory & Problemsarjun sabuNo ratings yet
- Derivatives: Basic Properties/Formulas/RulesDocument4 pagesDerivatives: Basic Properties/Formulas/RulesjonahNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument2 pagesCalculusdissipog1932No ratings yet
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970From EverandNonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Louis B. RallNo ratings yet
- II Assignment Problems: M-I Unit - IVDocument2 pagesII Assignment Problems: M-I Unit - IVgnathwNo ratings yet
- II Assignment Problems: M-I Unit - IIIDocument1 pageII Assignment Problems: M-I Unit - IIIgnathwNo ratings yet
- Assignment Problems: M-III Unit-VIDocument2 pagesAssignment Problems: M-III Unit-VIgnathwNo ratings yet
- Royal Institute of Technology and Science: Assignment Problems: M-III Unit-VDocument1 pageRoyal Institute of Technology and Science: Assignment Problems: M-III Unit-VgnathwNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - IDocument6 pagesMathematics - IgnathwNo ratings yet
- Assignment Problems: M - III Unit/-VDocument1 pageAssignment Problems: M - III Unit/-VgnathwNo ratings yet
- Assignment Problems: M-III Unit-VIIDocument1 pageAssignment Problems: M-III Unit-VIIgnathwNo ratings yet
- II Assignment Problems: M-I Unit - IIIDocument1 pageII Assignment Problems: M-I Unit - IIIgnathwNo ratings yet
- II Assignment Problems: M-I Unit - IIIDocument1 pageII Assignment Problems: M-I Unit - IIIgnathwNo ratings yet
- Assignment Problems: M-I Unit-IIDocument1 pageAssignment Problems: M-I Unit-IIgnathwNo ratings yet
- Assignment Problems: M - I Unit-IDocument1 pageAssignment Problems: M - I Unit-IgnathwNo ratings yet
- Assignment Problems: M-I Unit-IDocument2 pagesAssignment Problems: M-I Unit-IgnathwNo ratings yet
- m3 Regular Jntu Question Papers 2008Document7 pagesm3 Regular Jntu Question Papers 2008anjaneyuludNo ratings yet
- Royal Institute of Technology and Science: Assignment Problems: M-III Unit-VDocument1 pageRoyal Institute of Technology and Science: Assignment Problems: M-III Unit-VgnathwNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - III AssignmentDocument2 pagesMathematics - III AssignmentgnathwNo ratings yet
- M - III Assignment IIDocument1 pageM - III Assignment IIgnathwNo ratings yet
- MM Assignment - IIIDocument1 pageMM Assignment - IIIgnathwNo ratings yet
- M-III Practice ProblemsDocument1 pageM-III Practice ProblemsgnathwNo ratings yet
- M-I Assignment - IIIDocument1 pageM-I Assignment - IIIgnathwNo ratings yet
- M1 Practice Problems - 2Document1 pageM1 Practice Problems - 2gnathwNo ratings yet
- M1 - Assignment-II (2) For Rits CSE / EIE / Civil StudentsDocument1 pageM1 - Assignment-II (2) For Rits CSE / EIE / Civil StudentsgnathwNo ratings yet
- MM Practice Problems-1Document2 pagesMM Practice Problems-1gnathwNo ratings yet
- Mathematics-I Question Bank For First Year Students of RitsDocument2 pagesMathematics-I Question Bank For First Year Students of RitsgnathwNo ratings yet
- M-I: Practice Problems - 1: N N N N N NDocument1 pageM-I: Practice Problems - 1: N N N N N NgnathwNo ratings yet
- M-I Assignment - II (1) For CSE/EIE/CivilDocument1 pageM-I Assignment - II (1) For CSE/EIE/CivilgnathwNo ratings yet
- M-I: Practice Problems - 1: N N N N N NDocument1 pageM-I: Practice Problems - 1: N N N N N NgnathwNo ratings yet
- Rits MM QB For Mid IDocument2 pagesRits MM QB For Mid IgnathwNo ratings yet
- Mathematics-I Question Bank For First Year Students of RitsDocument2 pagesMathematics-I Question Bank For First Year Students of RitsgnathwNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - III Assignment II For EEE/EIE Students of RITSDocument1 pageMathematics - III Assignment II For EEE/EIE Students of RITSgnathwNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2018-2019 Term 1Document205 pagesLesson Plan 2018-2019 Term 1Athlyn DurandNo ratings yet
- Relay Coordination Using Digsilent PowerFactoryDocument12 pagesRelay Coordination Using Digsilent PowerFactoryutshab.ghosh2023No ratings yet
- Interna Medicine RheumatologyDocument15 pagesInterna Medicine RheumatologyHidayah13No ratings yet
- PowerhouseDocument10 pagesPowerhouseRanjan DhungelNo ratings yet
- MSC Euribia - 2023-06-01Document2 pagesMSC Euribia - 2023-06-01蔡國懷No ratings yet
- C11 RacloprideDocument5 pagesC11 RacloprideAvina 123No ratings yet
- EG-45-105 Material Information Sheet (Textura) V2Document4 pagesEG-45-105 Material Information Sheet (Textura) V2GPRNo ratings yet
- Startups Helping - India Go GreenDocument13 pagesStartups Helping - India Go Greensimran kNo ratings yet
- 9AKK101130D1664 OISxx Evolution PresentationDocument16 pages9AKK101130D1664 OISxx Evolution PresentationfxvNo ratings yet
- CHB 2Document15 pagesCHB 2Dr. Guruprasad Yashwant GadgilNo ratings yet
- Intec Waste PresiDocument8 pagesIntec Waste Presiapi-369931794No ratings yet
- 67c Series Bulletin 08 04 PDFDocument12 pages67c Series Bulletin 08 04 PDFnight wolfNo ratings yet
- Philippine College of Northwestern Luzon Bachelor of Science in Business AdministrationDocument7 pagesPhilippine College of Northwestern Luzon Bachelor of Science in Business Administrationzackwayne100% (1)
- Ipo Exam Revised SyllabusDocument1 pageIpo Exam Revised Syllabusজ্যোতিৰ্ময় বসুমতাৰীNo ratings yet
- Critique On A Film Director's Approach To Managing CreativityDocument2 pagesCritique On A Film Director's Approach To Managing CreativityDax GaffudNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Information Technology and Innovation To Improve Business Performance Through Marketing Capabilities in Online Businesses by Young GenerationsDocument10 pagesThe Impact of Information Technology and Innovation To Improve Business Performance Through Marketing Capabilities in Online Businesses by Young GenerationsLanta KhairunisaNo ratings yet
- CCEE SWD Basic Levers ToolDocument28 pagesCCEE SWD Basic Levers ToolDivina Margarita Gómez AlvarengaNo ratings yet
- Hardware Purchase and Sales System Project ProfileDocument43 pagesHardware Purchase and Sales System Project Profilesanjaykumarguptaa100% (2)
- National Products Classification Code For Services in IndiaDocument92 pagesNational Products Classification Code For Services in Indiakalanemi0% (2)
- The Emperor Jones: What's Inside in ContextDocument27 pagesThe Emperor Jones: What's Inside in ContextHarshvardhan RaiNo ratings yet
- Ilham Bahasa InggrisDocument12 pagesIlham Bahasa Inggrisilhamwicaksono835No ratings yet
- Fda PDFDocument2 pagesFda PDFVictorNo ratings yet
- ChE 135 Peer Evaluation PagulongDocument3 pagesChE 135 Peer Evaluation PagulongJoshua Emmanuel PagulongNo ratings yet
- EMECH 2 MarksDocument18 pagesEMECH 2 MarkspavanraneNo ratings yet
- STEM Spring 2023 SyllabusDocument5 pagesSTEM Spring 2023 SyllabusRollins MAKUWANo ratings yet
- Learn Square Roots & Plot on Number LineDocument11 pagesLearn Square Roots & Plot on Number LineADAM CRISOLOGONo ratings yet
- SIM5320 - EVB Kit - User Guide - V1.01 PDFDocument24 pagesSIM5320 - EVB Kit - User Guide - V1.01 PDFmarkissmuzzoNo ratings yet