Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of Fracture
Uploaded by
Marion Mendez100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
27K views1 pageCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
27K views1 pagePathophysiology of Fracture
Uploaded by
Marion MendezCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
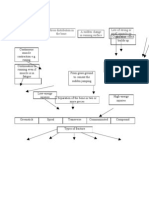
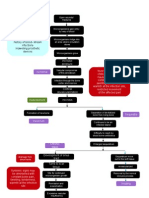
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF FRACTURE
Stress placed on a bone,
exceeds the bone ability to absorb it
Injury in the bone
Disruption in the continuity of bone
Disruption of muscle and blood vessels attached
to the ends of the bone
Soft tissue damage
Bleeding
Hematoma forms in medullary canal
Bone tissue surround the fractured site dies
Inflammatory response
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of FractureLawrence Espinosa78% (9)
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of FractureVenus Tagaan UcatNo ratings yet
- Post Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPost Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyRizalyn QuindipanNo ratings yet
- Iii. Clinical Discussion of The Disease A. Pathophysiology of Fracture I. (Book Based)Document4 pagesIii. Clinical Discussion of The Disease A. Pathophysiology of Fracture I. (Book Based)Lemuel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Fracture PathophysiologyDocument1 pageFracture PathophysiologyIrene Joy Gomez100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of FractureAnne Lorraine Bringas93% (27)
- Bone Fracture PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBone Fracture PathophysiologyRay Mahawi100% (2)
- Pathophysiology FracturesDocument2 pagesPathophysiology FracturesSewyel Garburi71% (7)
- Pathophysiology Bone Fracture (Tibia)Document1 pagePathophysiology Bone Fracture (Tibia)Brainan Aquino0% (2)
- Osteoarthritis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesOsteoarthritis PathophysiologyJona Suarez70% (10)
- Pathophysiology OsteosarcomaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology OsteosarcomaVernadeth Dumagat50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument1 pagePathophysiology of FractureShayne Jessemae Almario100% (3)
- OsteomyelitisDocument1 pageOsteomyelitisJohara Mae De RamaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology OsteosarcomaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology OsteosarcomaGladys Barcelona0% (1)
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologyRj MagpayoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of OsteoarthritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of OsteoarthritisMae Layug100% (2)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMaDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMakyawNo ratings yet
- Potts Disease Case Study OLGCDocument15 pagesPotts Disease Case Study OLGChomermanlapaz100% (2)
- Chronic Cholecystitis With Cholelithiasis PathoDocument2 pagesChronic Cholecystitis With Cholelithiasis PathoBill Clinton Lamira BabanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of OsteomyelitisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of OsteomyelitisJhon Jerric Pante Aguinaldo100% (1)
- Case Study - FractureDocument35 pagesCase Study - FractureJo-anne Cordero100% (3)
- Case of OsteosarcomaDocument25 pagesCase of Osteosarcomadocs2009100% (3)
- Osteomyelitis Case StudyDocument41 pagesOsteomyelitis Case StudyJohn Bernard Ting Tizon100% (2)
- Fracture at Right Femur - Orif Case StudyDocument16 pagesFracture at Right Femur - Orif Case StudyKaloy Kamao100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury 1Document1 pagePathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury 1kristel_nicole18yaho60% (5)
- Pathophysiology VolvulusDocument2 pagesPathophysiology VolvulusHyacinth Bueser Bondad0% (2)
- Cellulitis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCellulitis PathophysiologyWilfredo Mata Jr.100% (8)
- Discharge PlanningDocument5 pagesDischarge PlanningNoora KhalidNo ratings yet
- Nursing Priorities: 8 Fracture Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document10 pagesNursing Priorities: 8 Fracture Nursing Care Plan (NCP)PagodNo ratings yet
- Common Cause or Etiology of Pott's DiseaseDocument5 pagesCommon Cause or Etiology of Pott's DiseaseStan Aves GarciaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Open FractureDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Open FracturegiffersonbNo ratings yet
- Electrical Burn PathophysiologyDocument1 pageElectrical Burn PathophysiologydanicaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Pott's DiseaseDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Pott's Diseasederic95% (21)
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of AppendicitisAbbie Tantengco100% (3)
- Orthopedic HardwareDocument36 pagesOrthopedic HardwareMarivic Diano100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Osteomyelitis DiagramDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Osteomyelitis DiagramKim Enrico JumarangNo ratings yet
- Pott's Disease NCPDocument7 pagesPott's Disease NCPkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Fractures, PathophysiologyDocument1 pageFractures, Pathophysiology4kscribdNo ratings yet
- Management For OsteosarcomaDocument2 pagesManagement For OsteosarcomakyawNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AGE With DHNDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AGE With DHNFarr Krizha Tangkusan50% (2)
- Case Study HemorrhoidsDocument4 pagesCase Study HemorrhoidsTeanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAppendicitis PathophysiologyitsmeayaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal TractionDocument7 pagesSkeletal TractionAnnalyn Austria100% (2)
- Potts DiseaseDocument5 pagesPotts Diseasemyla-elmarie100% (1)
- Multiple Physical Injuries Secondary To Vehicular AccidentDocument31 pagesMultiple Physical Injuries Secondary To Vehicular AccidentAnton Laurenciana50% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAnne Marie Angelica BilonoNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Open Tibial FractureDocument48 pagesCase Study On Open Tibial FractureOmotosho AlexNo ratings yet
- Fracture !!!!!!Document31 pagesFracture !!!!!!Maryjoy MertallaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain OsteosarcomaDocument8 pagesAcute Pain OsteosarcomaMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- NP Motor Vehiculr AccidentDocument16 pagesNP Motor Vehiculr AccidentAngelie Joy100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of PeritonitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PeritonitisLeslie PaguioNo ratings yet
- Pott's DiseaseDocument30 pagesPott's DiseaseLucila Lugo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology On Fracture of Left Femoral Head: Precipitating Factor Predisposing FactorDocument2 pagesPathophysiology On Fracture of Left Femoral Head: Precipitating Factor Predisposing FactorEsther Mendez CatubigNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorscadayNo ratings yet
- PathooDocument1 pagePathooMary Louise LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiologygoodie1988No ratings yet
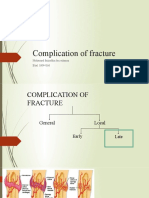
- Complication of FractureDocument18 pagesComplication of FractureJoni NeohNo ratings yet
- Ortho PAthoDocument4 pagesOrtho PAthoCheriz LukbanNo ratings yet
- Muscle Skeletal Trauma For EMSDocument79 pagesMuscle Skeletal Trauma For EMSPaulhotvw67100% (4)
- Pa Tho Physiology of OsteomyelitisDocument4 pagesPa Tho Physiology of OsteomyelitisninasaguidNo ratings yet
- PES Early EnrolmentDocument2 pagesPES Early EnrolmentMarion MendezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Type II Diabetes MellitusDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Type II Diabetes MellitusMarion Mendez100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebral PalsyDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Cerebral PalsyMarion MendezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CapDocument1 pagePathophysiology of CapMarion MendezNo ratings yet