Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statistics - Important Notes
Uploaded by
SasquatchCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Statistics - Important Notes
Uploaded by
SasquatchCopyright:
Available Formats
Some Important notes on use of Student’s T-test and Z-test for Hypothesis Testing:
The t-statistic was introduced in 1908 by William Sealy Gosset, a chemist working for
the Guinness brewery in Dublin, Ireland ("Student" was his pen name).
Basic Underlying Assumptions in T-test are:
1) Samples are independent and randomly drawn from a normal population.
2) Sample size is small. (n<=30)
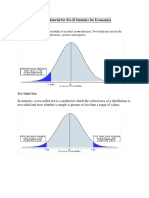
Below are the seven situations which give an idea about when to use T-test or Z-test:
• Situation 1 : Samples are independent and randomly drawn from normal population whose mean
(µ) and standard deviation (σ) are known
Sample size is large i.e. n>=30
Test to be used for Hypothesis testing: Z-test
• Situation 2 : Samples are independent and randomly drawn from normal population whose mean
(µ) and standard deviation (σ) are known
Sample size is small i.e. n<=30
Test to be used for Hypothesis testing: Z-test or T-test
• Situation 3 : Samples are independent and randomly drawn from a normal population whose
mean (µ) is known but standard deviation (σ) is not known
Population size is large
If standard deviation of sample is known then use sample standard deviation as best estimate for
population standard deviation.
Test to be used for Hypothesis testing: Z-test
• Situation 4: Samples are independent and randomly drawn from a Normal population whose
mean (µ) is known but standard deviation (σ) is not known
Population size is small
If standard deviation of sample is known then use sample standard deviation as best estimate for
population standard deviation.
Test to be used for Hypothesis testing: T-test
• Situation 5: Samples are independent and randomly drawn from any population whose standard
deviation (σ) is known and whose sample size is large.
Test to be used for Hypothesis testing: Z-test because of central limit theorem
• Situation 6: Samples are independent and randomly drawn from any population whose standard
deviation (σ) is unknown and whose sample size is large.
Use sample standard deviation to approximate to population standard deviation and use Z-test.
• Situation 7: Samples are independent and randomly drawn from any population whose standard
deviation (σ) is unknown and sample size is small.
In this situation, other test like Wilkokson’s Test is used
You might also like
- Statistical Inference: (Analytic Statistics) Lec 10Document42 pagesStatistical Inference: (Analytic Statistics) Lec 10Nivar selevanayNo ratings yet
- Central Tendency. Hypothesis TestDocument40 pagesCentral Tendency. Hypothesis TestNihal KocheNo ratings yet
- Student's T-Test: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 pagesStudent's T-Test: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaVirender Kumar DahiyaNo ratings yet
- 02 ABE Review - Sampling TechniquesDocument41 pages02 ABE Review - Sampling TechniquesRio Banan IINo ratings yet
- Central Limit TheoremDocument9 pagesCentral Limit TheoremEian InganNo ratings yet
- Sampling MethodDocument23 pagesSampling MethodStar boxNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Parametric and Non Parametric TestsDocument14 pagesHypothesis Testing Parametric and Non Parametric Testsreeya chhetriNo ratings yet
- Q4M2 StatDocument13 pagesQ4M2 StatZeke WeNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. (Hons.) Biotechnology Core Course 13: Basics of Bioinformatics and Biostatistics (BIOT 3013) Biostatistics (BIOT 3013)Document29 pagesB.Sc. (Hons.) Biotechnology Core Course 13: Basics of Bioinformatics and Biostatistics (BIOT 3013) Biostatistics (BIOT 3013)Eugine BalomagaNo ratings yet
- In Hypothesis TestingDocument20 pagesIn Hypothesis TestingDhara TandonNo ratings yet
- Z test: The value of the standard normal random variable Z that cuts off a right tail of area α is denoted zDocument2 pagesZ test: The value of the standard normal random variable Z that cuts off a right tail of area α is denoted zSweta ManandharNo ratings yet
- Sampling Fundamentals ModifiedDocument45 pagesSampling Fundamentals ModifiedArjun KhoslaNo ratings yet
- Sampling Methods and The Central Limit TheoremDocument24 pagesSampling Methods and The Central Limit Theoremiracahyaning tyasNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestDocument23 pagesHypothesis TestAdinaan ShaafiiNo ratings yet
- Assumptions and Properties of Z and T DistributionDocument4 pagesAssumptions and Properties of Z and T DistributionAdnan AkramNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution Theory: Population and SampleDocument8 pagesSampling Distribution Theory: Population and SampleSiddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Testing HypothesisDocument9 pagesTesting HypothesisUsama IqbalNo ratings yet
- DSC1371 - Chapter 8 - Sampling and Sampling DistributionsDocument36 pagesDSC1371 - Chapter 8 - Sampling and Sampling Distributionsammabavani31No ratings yet
- Sampling DistributionDocument29 pagesSampling Distributiondawit tesfaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Research MethodologyDocument5 pagesAssignment 1 Research MethodologybecbellaryNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability T-TestDocument37 pagesStatistics and Probability T-TestR Jibz F HurtzNo ratings yet
- Psda 1 Group 2 StatsDocument21 pagesPsda 1 Group 2 Statsankit varunNo ratings yet
- MS 1724012 Exp8Document13 pagesMS 1724012 Exp8KUNAL DURGANINo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Introduction To The T StatisticDocument42 pagesChapter 9: Introduction To The T StatisticRhaine EstebanNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing and One Sample TestsDocument23 pagesHypothesis Testing and One Sample TestsNina ForliniNo ratings yet
- MB0050 Slides Unit 10Document17 pagesMB0050 Slides Unit 10Yogesh Shinde0% (1)
- Sampling and EstimationDocument15 pagesSampling and EstimationPRIYADARSHI GOURAVNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Quarter 4 - Module 3: Test Statistic On Population Mean Week 3 To Week 4Document20 pagesStatistics and Probability: Quarter 4 - Module 3: Test Statistic On Population Mean Week 3 To Week 4JoshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document47 pagesChapter 5bashatigabuNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument44 pagesHypothesis TestingPartha Pratim TalukdarNo ratings yet
- 10.2 Power PointDocument23 pages10.2 Power PointkrothrocNo ratings yet
- Reviewer CHAPTER 12Document8 pagesReviewer CHAPTER 12Krisha AvorqueNo ratings yet
- Student's T TestDocument12 pagesStudent's T TestZvonko TNo ratings yet
- Forms of Test StatisticDocument31 pagesForms of Test StatisticJackielou TrongcosoNo ratings yet
- Computing of Test Statistic On Population MeanDocument36 pagesComputing of Test Statistic On Population MeanKristoffer RañolaNo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob Q4 Week 3 Module 11 Alexander Randy EstradaDocument21 pagesStat and Prob Q4 Week 3 Module 11 Alexander Randy Estradagabezarate071No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document19 pagesChapter 1camerogabriel5No ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Kakinada: Presented by K.S.S.Prasanthi 14021E0008Document8 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University Kakinada: Presented by K.S.S.Prasanthi 14021E0008Anonymous qroN54rNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument277 pagesHypothesis Testingmeric8669No ratings yet
- Chapter 18. Inference About A Population Mean 1Document9 pagesChapter 18. Inference About A Population Mean 1Muneeza HashmiNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Notes: Hypothesis Testing (p.3) : Testing A Single MeanDocument7 pagesCH 9 Notes: Hypothesis Testing (p.3) : Testing A Single Meansamba684No ratings yet
- Study Material For BA-II Statistics For Economics: One Tailed TestDocument9 pagesStudy Material For BA-II Statistics For Economics: One Tailed TestC.s TanyaNo ratings yet
- Be A 65 Ads Exp 4Document17 pagesBe A 65 Ads Exp 4Ritika dwivediNo ratings yet
- Research Population, Sample Size & Sampling Methods - Quantitative ResearchDocument22 pagesResearch Population, Sample Size & Sampling Methods - Quantitative ResearchJanelle DuranNo ratings yet
- Stat Review Fall 2016Document29 pagesStat Review Fall 2016Aimal khanNo ratings yet
- J. K. Shah Classes Sampling Theory and Theory of EstimationDocument37 pagesJ. K. Shah Classes Sampling Theory and Theory of EstimationGautamNo ratings yet
- 05-06 - BIOE 211 - Supplement Notes of Hypothesis Testing and Inferential StatDocument19 pages05-06 - BIOE 211 - Supplement Notes of Hypothesis Testing and Inferential StatJhelloNo ratings yet
- Testing Two Independent Samples - With Minitab Procedures)Document67 pagesTesting Two Independent Samples - With Minitab Procedures)Hey its meNo ratings yet
- Biostats 2Document7 pagesBiostats 2baf49411No ratings yet
- Research Methodology CH 6Document20 pagesResearch Methodology CH 6heba shhouriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - OverheadsDocument24 pagesChapter 7 - OverheadsMICHAEL TURKSONNo ratings yet
- Bizstat ssn2Document55 pagesBizstat ssn2Fukuri ShikarosNo ratings yet
- 18MAB204T-Module-III (Mathematical Statistics: Tests of Hypothesis)Document33 pages18MAB204T-Module-III (Mathematical Statistics: Tests of Hypothesis)Omisha SingalNo ratings yet
- Sampling & Sampling DistributionsDocument34 pagesSampling & Sampling DistributionsBhagwat BalotNo ratings yet
- 2FAQ in STATISTICS. September 2 2018Document59 pages2FAQ in STATISTICS. September 2 2018PELINA, Carlos Jade L.No ratings yet
- Unit-Six Sampling and Sampling DistributionDocument19 pagesUnit-Six Sampling and Sampling Distributionzeyin mohammed aumerNo ratings yet
- Test On Variables: in Surveys, The Foolish Ask Questions, Wise Cannot AnswersDocument24 pagesTest On Variables: in Surveys, The Foolish Ask Questions, Wise Cannot AnswersNirmal ModhNo ratings yet
- Parametric Tests: DR Heena SharmaDocument60 pagesParametric Tests: DR Heena SharmaBhartiNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 - Continuous ProbabilitiesDocument9 pagesLec 3 - Continuous ProbabilitiesCharles QuahNo ratings yet
- B2B Marketing - SummaryDocument37 pagesB2B Marketing - SummarySasquatch67% (3)
- Amagansett Funds (A)Document8 pagesAmagansett Funds (A)SasquatchNo ratings yet
- Alloy Rods CorporationDocument17 pagesAlloy Rods CorporationSasquatchNo ratings yet
- Li & Fung 2006Document15 pagesLi & Fung 2006Sasquatch100% (1)
- Why Should You Do MBADocument3 pagesWhy Should You Do MBAapi-3719468100% (1)
- Linear Programming Module - A Conceptual FrameworkDocument25 pagesLinear Programming Module - A Conceptual FrameworkSasquatchNo ratings yet
- Sensitivity AnalysisDocument67 pagesSensitivity AnalysisSasquatch100% (1)
- Intel: Building A Technology Brand: by M.Krishnan Sashidharan.S P.VijaykumarDocument16 pagesIntel: Building A Technology Brand: by M.Krishnan Sashidharan.S P.VijaykumarSasquatchNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Logic - Rollnos.43 and 83Document6 pagesFuzzy Logic - Rollnos.43 and 83SasquatchNo ratings yet
- Mountain DewDocument8 pagesMountain DewSasquatch0% (1)
- Automation of Trade SettlementDocument7 pagesAutomation of Trade SettlementSasquatchNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Two Sample TestingDocument100 pagesChapter 8 Two Sample TestingMobasher MessiNo ratings yet
- Homework Problems - Paired Samples T-TestDocument48 pagesHomework Problems - Paired Samples T-TestDevan BhallaNo ratings yet
- A Mathematical Model For COVID-19 To Predict Daily Cases Using Time Series Auto Regressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) Model in Delhi Region, IndiaDocument5 pagesA Mathematical Model For COVID-19 To Predict Daily Cases Using Time Series Auto Regressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) Model in Delhi Region, IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- One Sample Sign TestDocument24 pagesOne Sample Sign TestRohaila RohaniNo ratings yet
- Sta 226Document5 pagesSta 226Kimondo KingNo ratings yet
- Gen StatDocument15 pagesGen StatLugasSetiadjiMarpratamaNo ratings yet
- Grubbs' Outlier TestDocument2 pagesGrubbs' Outlier TestDavid SRNo ratings yet
- Athletically Related Aid and Collegiate Athletic Program SuccessDocument17 pagesAthletically Related Aid and Collegiate Athletic Program SuccessMatthew KlierNo ratings yet
- Course Introduction: Collection and Presentation of Data The Frequency Distribution Graphical Presentation of DataDocument61 pagesCourse Introduction: Collection and Presentation of Data The Frequency Distribution Graphical Presentation of DataShekinah Vingno LingcongNo ratings yet
- Tugas Analisis KuantitatifDocument12 pagesTugas Analisis KuantitatifDoni Palguna 565No ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document5 pagesTutorial 6Quỳnh NgaNo ratings yet
- 10 Seasonal ARIMADocument59 pages10 Seasonal ARIMAjustinlondonNo ratings yet
- Spatial Ecology Mantel TestDocument6 pagesSpatial Ecology Mantel TestrkerstenNo ratings yet
- Central Limit TheoremDocument14 pagesCentral Limit TheoremRakesh Kumar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- A Simple Introduction To Anova: Amemou Franck Elyse Yao, Kaleab Hailemariam Venkat KumarDocument20 pagesA Simple Introduction To Anova: Amemou Franck Elyse Yao, Kaleab Hailemariam Venkat KumarKumar SaiNo ratings yet
- Excel On FinanceDocument8 pagesExcel On Financehiitsds12bNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Fall 2018 - Math 1070 - Elementary StatisticsDocument10 pagesSyllabus Fall 2018 - Math 1070 - Elementary StatisticsQianlong LiuNo ratings yet
- Trial Maths M Term 2 (2014) SmartDocument6 pagesTrial Maths M Term 2 (2014) SmartIrenaeus MartinNo ratings yet
- Child Abuse and Neglect Among Primary SchoolteachersDocument5 pagesChild Abuse and Neglect Among Primary SchoolteachersMarg YatraNo ratings yet
- Practical File Of: "Research Methodology Lab"Document73 pagesPractical File Of: "Research Methodology Lab"Sahil RajputNo ratings yet
- HLM7 PDFDocument366 pagesHLM7 PDFAnonymous tcPTEUOGJNo ratings yet
- SessionDocument128 pagesSessionHarisSuprayogiNo ratings yet
- Distributions of Sample StatisticsDocument112 pagesDistributions of Sample StatisticsebrarrsevimmNo ratings yet
- Question On Inferential StatisticsDocument4 pagesQuestion On Inferential StatisticsOmotosho AdamNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1-Module 1Document39 pagesUNIT 1-Module 1Machel AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Multiple Regression AnalysisDocument3 pagesMultiple Regression AnalysisAleenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Forecasting Solution ManualDocument22 pagesChapter 4 - Forecasting Solution ManualErica Uy44% (9)
- Assignment Report - Predictive Modelling - Rahul DubeyDocument18 pagesAssignment Report - Predictive Modelling - Rahul DubeyRahulNo ratings yet
- 4TH QTR Problem Sets 1 3Document3 pages4TH QTR Problem Sets 1 3Charlotte WennaNo ratings yet
- Local Media1949055759870428644Document6 pagesLocal Media1949055759870428644Ryan Anthony Peñaflor DaynoloNo ratings yet