Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maths I
Uploaded by
Prateek Sharma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views16 pagesAnswers must be written in the medium specified in the Admission Certificate. No marks will be given if the answers are written in a medium other than that specified in the Admission Certificate. The number of marks carried by each qu.eetiori is indicated at the end of the queetio n.
Original Description:
Original Title
MATHS_I
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnswers must be written in the medium specified in the Admission Certificate. No marks will be given if the answers are written in a medium other than that specified in the Admission Certificate. The number of marks carried by each qu.eetiori is indicated at the end of the queetio n.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views16 pagesMaths I
Uploaded by
Prateek SharmaAnswers must be written in the medium specified in the Admission Certificate. No marks will be given if the answers are written in a medium other than that specified in the Admission Certificate. The number of marks carried by each qu.eetiori is indicated at the end of the queetio n.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
i
C.S. (MAIN) EXAM, 2009
Sl. No. 402 C-DTN-J-NUA
MATHEMATICS
Paper—I
Time Allowed : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 300
INSTRUCTIONS
Each question is printed both in Hindi and
in English.
Answers must be written in the medium
specified in the Admission Certificate issued
to you, which must be stated clearly on the
cover of the answer-book in the space
provided for the purpose. No marks will be
given for the answers written in a medium
other than that specified in the Admission
Certificate.
Candidates should attempt Question Nos. 1
and 5 which are compulsory, and any three
of the remaining questions selecting at least
one question from each Section.
The number of marks carried by each
. question is indicated at the end of the
question.
| Assume suitable data if considered necessary
and indicate the same clearly.
Symbols/notations carry their usual
meanings, unless otherwise indicated.
ean é: ages ar feed worn wa ue-wa & fee ye
BT el
Section—A
1. Attempt any five of the following :
(a)
(b)
()
(ad)
fe)
Find a Hermitian and a skew-Hermitian
matrix each whose sum is the matrix
2i 3 =]
ai, 2+3i 2
-i+1 4 Si
Prove that the set V of the vectors
(x1, xg, x3, x4) in R* which satisfy the
equations x,+xX2g+2x3;+x, =O and
2x, +3xy-x3+xX,=0, is a subspace
of R*. What is the dimension of this
subspace? Find one of its bases.
Suppose that f” is continuous on [I, 2]
and that f has three zeroes in the
interval (1, 2). Show that f” has at least
one zero in the interval (1, 2).
If f is the derivative of some function
defined on [a b], prove that there exists
a number né [a, b], such that
frat = sie-a
A line is drawn through a variable point
2 2
on the ellipse ~ +4 =1, z=0 to meet
a? pb?
two fixed lines y = mx, z=c and y =-—mx,
z=-—c. Find the locus of the line
C-DTN-J-NUA/44 2
12
12
12)
12
12
1.
us —A
frafafad 4 fret ata & sax difare :
() we efit sik up fave-efft are orem
Aira, fat at Aefeftaa seg a :
2i 3 -1
1 2+3i 2
-i+1 4 Si
(a) faa Afra fH R* F afexit (x, x, x3, x4) HT
tar @ v, St arent x, + x2 + 2x3 +x4 =0
SN 2x, +3xq—x3 +x4 =O HI UGE wea A,
R* ft um soeste 31 ga sae a ae a
2? gaa ws ste ara Aire
(1) am difite f [1, 2) ef” daa 2 sik stata
(1, 2) 4 / & dm ye 21 eae fe sive
(1, 2) 3” a1 H-8-am Uw Ft 21
(a) af fa, b) 3 cfenfia fet Goa ar smc
@, @ afea He fe wH te dem ne [a, db]
aie 3, a
Lroat= somo-a
2 2
() ariga + Bh z=0 TH Rad fg
a
3 @ ww ta a faa tasit yome, zac
3 y=-mx, z=-c wm fram & fae dik
urdt 21 sa tar & faegaa at ara Ai
12
12
12
12
12
C-DTN-J-NUA/44 3 [ P.T.O.
2. (a)
()
()
3. (a)
Find the equation of the sphere having
its centre on the plane 4x-5y-—z=3,
and passing through the circle
x? +y? +2? -12x-3y+4z+8=0
3x+4y-5z+3=0
Let .#={(1,1,0),(,0,1),(,1,1} and
-# = {(2, 1, 1), (, 2, 1), (-1, 1, I} be the two
ordered bases of R?. Then find a matrix
representing the linear transformation
T:R° R® which transforms # into
%’. Use this matrix representation to
find T(x), where X = (2, 3, 1).
If x=3+0-01 and y=4+0-01, with
approximately what accuracy can you
calculate the polar coordinates r and 8
of the point P(x, y)? Express your
estimates as percentage changes of
the values that r and 6 have at the
point (3, 4).
Find a 2x2 real matrix A which is both
orthogonal and skew-symmetric. Can
there exist a 3x3 real matrix which is
both orthogonal and skew-symmetric?
Justify your answer.
Let L:R*-—R*% be a linear transfor-
mation defined by
L((x,, X2, X3, X4))
= (x3 +%4-%4- XQ, x3 -X—, x4 —%})
Then find the rank and nullity of L
Also, determine null space and range
space of L.
C-DTN-J-NUA/44 4
12
20
20
20
20
ee ——eeses—‘“_Sss—sS
()
(*)
(a)
(7)
(*)
wep ta tie ar aie ara Ais, Brean ax
aad 4x-Sy-z2=3 RF ak A aa
x? 4y? +27 -12x-3y+4z+8=0
3x+4y-5z+3=0
HS Yst we at
eh A= (11,0), 0,0,1),0,,)} aK
8 ={(2,1,1,2,1,-L1493 a wire
ama @ Ro Fl wa we areag +t Te Afar,
Wow 8 iss eciawr 7: Ro Ro a
Fear aon a a1 a Wo woiaita ae 21
sa sreqs Prec ar T(x) eI aa wet} faa
getaret *ifsa, set X = (2, 3, 1) et
aff x =340-013m y=4+0-018, 7 am
fare P(x, y) % gata Résiet r sik 6 ar cert
feat ofgzant aa afta a aad 8? og
amt wet al SA al & festa ufadai
wa 4 orm Afr, vi frg (3, 4) Mr sik OF
al
wh ta 2x2 aeifae Srege A at are aifsre,
St cifee sit fasn-anfita dei a1 aa we
3x3 area sreqe oft a aaa 2%, st cri
ait fase-aafia dei a? acai oe & aa a
acta te Ae
cf 1: R* > Ro om te thas ecie 2,
aT
L(x, X2, X3, X4))
12
20
20
20
= (xg +x4-X1 - XQ, X3-—XQ, Xq — X4)
@ ufone a) aa L at anf sit gpa wt aT
Afr aa a LA as wae sik ake cafe
ar ft Rafer afer)
20
C-DTN-J-NUA/44 Ss [ P.T.O.
4.
()
()
(a)
(b)
Let f:R? —R be defined as
fy
f(y y= Vx +y?
o > if (% y)=(,0)
» if (% y) #(0,0)
Is f continuous at (0,0)? Compute
partial derivatives of f at any point (x, y),
if exist.
A space probe in the shape of the
ellipsoid 4x? +y? +427 =16 enters the
earth’s atmosphere and its surface
begins to heat. After one hour, the
temperature at the point (x, y, z) on the
probe surface is given by
Tix, y, 2) = 8x? +4yz-16z+600
Find the hottest point on the probe
surface.
Prove that the set V of all 3x3 real
symmetric matrices forms a_ linear
subspace of the space of all 3x3 real
matrices. What is the dimension of this
subspace? Find at least one of the bases
for V.
Evaluate
I= Jfdyaz +dzdx + xz? dxdy
$
where S is the outer de of the part of
the sphere x? +y? +z? =1 in the first
octant.
C-DTN-J-NUA/ 44 6
20
20
20
20
(a)
(7)
(*)
(a)
aim f¢:R?2 5R fefafaa & wa 4
uftarfta & :
ww , a (6 y+ 009
fixe W=y 4x? +y?
Oo , af (%,y)=©,0)
am (0, 0) % f aaa 2? fet fag (yg RS
% wiftte sraeasl an ufc aif, afe sat
afer zi!
aegest 4x? +y2 +42? =16 A angie aT
wr sake aaou-am yet & agdea A waa
aaa @ sit seat ye TH aA Te BI GH A
am, wa-a yew fers (x, y, BRAT
T(x, y, 2) = 8x? +4yz-16z+600
gm aa 3) srauo-am & ye a aaa Sarat A
farg ava Fife!
fra Ase fe ait 3x3 areaies aaa seg
az v, ai 3x3 adaa seg & aa a
Utes scene aaa @1 ga soaafe ar saa eT
22 V & feu we-a-an we aren aa Hf
T= ffxdydz+dzdx + xz7dxdy a yeaa
Ss
AR, wel S ved sei F Mae
x? +y? +27 =1% om a aed aed a
20
20
20
20
C-DTN-—J-NUA/44 7 [ P.T.O.
5.
(e)
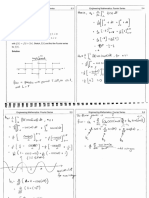
Prove that the normals from the point
(a, B, y) to the paraboloid
lie on the cone
a B | a? —b?
+
- Pa te
x-a y-f Z-¥
Section—B
Attempt any five of the following :
(a)
(b)
(o)
A body is describing an ellipse of
eccentricity e under the action of a
central force directed towards a focus
and when at the nearer apse, the centre
of force is transferred to the other focus.
Find the eccentricity of the new orbit in
terms of the eccentricity of the original
orbit.
Find the Wronskian of the set of
functions
{3x%, [3x9 |}
on the interval [-1,1] and determine
whether the set is linearly dependent on
(-1, 1).
A uniform rod AB is movable about a
hinge at A and rests with one end in
contact with a smooth vertical wall. If
the rod is inclined at an angle of 30°
with the horizontal, find the reaction at
the hinge in magnitude and direction.
C-DTN-J-NUA/44 8
20
12:
i2
12
a fer aa &1 20
wea
5. freafefaa 4 8 fed ata & su dif :
(®) ang fis feet aft A sik fea ue Sea aa
At frat & aitfia sch e a um diga at ter
& Si wa ae We A eafeern He elm 2, da aa
al ee Sa ay oe earaiafta et sitar 81 ag Har
Al Sara A ye wea A seewa H S A ara
Aihara | 12
(@) sage [-1, 1] % Ger &H Se (3x3, (3x5)
a tefa aa fife sik Prater Arie fe ar
@z, [-1, 1] w tana: fete 2 soar ai 21 12
() & wear os AB, fg A fea & seid
Tfesia 2 sik saat wr fa cam fread seater
dan & werk F fer gen 21 af oe fata &
ara 30° & Hm a afiaa A, at fea oe uff
at afta sik feen 4 ara Afra 12
C-DTN-J-NUA/44 9 [ P.T.O.
(d) A shot fired with a velocity V at an
elevation o@ strikes a point P in a
horizontal plane through the point of
projection. If the point P is receding
from the gun with velocity v, show that
the elevation must be changed to 8,
where
sin 20 = sin 2a + * sin 8
12
(e) Show that
div(grad r”) =n(n+1)r"~?
ee
where r =x? +y? +27. 12
() Find the directional derivative of—
@) 4x23 -3x?y?z? at (2,-1,2) along
z-axis;
(ii) x?yz+4xz? at (1,-2,1) in the
direction of 2i —j-2k. 6+6
6. (a) Find the differential equation of the
family of circles in the xy-plane passing
through (-1, 1) and (1, 1). 20
(b) Find the inverse Laplace transform of
F(g)=In( $*2)
s+5S 20
(c) Solve : 20
dy y?(x-
So 2 = yO) =1
dx 3xy? —-x?y-4y
C-DTN-J-NUA/44 10
(a)
@)
(@)
(*)
(a)
@)
an Vv & a 3k Sadi o HH art ag ae,
yao fg & de a gad afaa anda 4
fg Pan aett 21 aff fg P aaqH a aT v
Hwa | sta TT tea A, A aaigu fH saan wt
6 4 ofaffa aon snare erm, wei
sin 20 = sin2a +2¥sine
V 12
aise fe
div(grad r”) = n(n +1)r"~?
wet r= fx? ay? oa? »
Profefiaa feg-stacrs ara Aire: 6+6
@) z-wa m% we-aa (2, -1, 2) %
4x29 -3x7y?2? a
(i) 2i-j-2k A fem Fa, 2, ye
x? yz+4x27 #1
(-1, 1) 3 (1, 1) 4 a SR ge xy-aHTa F
qi-gea sae ater a ara FS! 20
Fs) =1n( S*2) an sft rere stint ara
Afra) 20
ea aif: 20
dy WP K-D yy 1
dx ay? ya
C-DTN-J-NUA/44 11 [ P-T-0.
(b)
(c)
One end of a light elastic string of
natural length I and modulus of
elasticity 2mg is attached to a fixed point
O and the other end to a particle of
mass m. The particle initially heid at
rest at O is let fall. Find the greatest
extension of the string during the
motion and show that the particle will
reach O again after a time
(7 +2-tan7! 2) [2t
Vg
A particle is projected with velocity V
from the cusp of a smooth inverted
cycloid down the arc. Show that the
time of reaching the vertex is
2 [Sexe
‘(a]
where a is the radius of the generating
circle
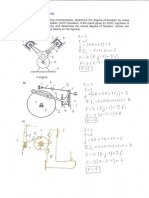
On a_ rigid body, the _ forces
10@+27+2K)N, S(-2i-j+2k)N and
6(2i +27-K)N are acting at points with
position vectors i -j, 2i+5k and 4i-k
respectively. Reduce this system to a
single force R acting at the point (47 +23)
together with a couple G whose axis
passes through this point. Does the
point (47 +2) lie on the central axis?
C-DTN-J-NUA/44 12
De
10
1s
7. (&) veo wea 1 sit yererat Wis 22mg are cH
weit sores So a ws faa faa fg OH GST
ean 2 sit gan fea gee om & UH a TTA
Wego fren tw wa a
fret fen sr 21 af & eam Sto a afta
fier ara Aire sik anise fe ao, aaa
(x +2 -tan7! 2) jak
g
% ara, fx FOR Wa HET! 20
(@) wr agy sfacifta sat Her a us So HT aT
VS a a & Ae A sik waite Pear ara 21
amiga fe vit as aged ar ara
A oof _¥
age (at)
an, ae a sae ga Ht eT 21 10
@) we wz fe um ww fei wn aa
10G+2j7+2K)N, S(-2i-j7+2K)N 3K
62i+2j7-A)N a a @ 2%, fie fea
fem mut: i-j, 245k 3 4i-k 21 a
fara at t@ waa ga Row aaa A, st
fez 4i+2j) wan Ge wa at Hw a,
faa vat ga fag & ate 8 gore a ao fag
(40427) Fa wa a safer 2%? 15
C-DTN-J-NUA/44 13 { P:P.0.
(id
Find the length of an endless chain
which will hang over a circular pulley of
radius a so as to be in contact with
three-fourth of the circumference of the
pulley.
8. (a) Find the work done in moving the
particle once round the ellipse
2
+¥— <1, 2=0 under the field of force
25° 16
given by
F=Qx-y+2i
+(x+y-27)j+(8x-2y+4Qk
(b) Using divergence theorem, evaluate
ff, 4-48
1S
where A= x3i+y%j+z3k and S is the
surface of the sphere x” +y? +z? =a?
(c) Find the value of
ff, OxF)-as
Is
taken over the upper portion of the
surface x? +y?-2ax+az=0 and the
bounding curve lies in the plane z=0,
when
F =(y2 +2? -x?)i
+ (22 +x? -y?) 7+ (x? +y? —27)k
C-DTN-J-NUA/44 14
20
20
(a)
(@)
(1)
ue ta feos oa A oat aa Ae,
fren aft we ada fact at ga yar wet eit
fea ae fect ft afer & cta-steng & serch A at
F=x-y+ai
+(x+y—27)j+@Bx-2y+4gk
2 x? oy? _
BI ved Fe aa & oni dhiga So + tS =
z=0 % ahi sik ao} ue ak gn Ff far
me art at aes fife
sree waa ar gata ae EE ff A-dS #7
ne fanfare, set A = x32 4+y9F429k & atk
Smee x? +4242? =a? a ye a
Je x? +y? -2ax+az=0% at amu far
Tm sit dine am ana z=0 4 fara BAK
fj @xF)-dS a am ara Afsre, wa
F =? +2? -x2)i
+(z? +x? —y?)F +(x? +y? —272)k
y
kk
15
20
20
20
C-DTN-J—NUA/44 15 JS—1000
C-DTN-J-NUA
wea-cqa—I
aaa: a ae yrs : 300
uote wer fet sik stats art tf oa 2)
uel & am set ana Ff fare art alee freer soa
oma waei-aa A fear rar 2, atte ga ne eT TE
aga sya & ga-ye 1 sifea fafée ear 1
fea oat area; sav-wa % sigfaa area
aia ara Pret mera Ff fera me sae OS BT
wet farcry
wet den 1 sik 5 afrard &) art weal Fa nee
wus @ wa-a-ay WH Wer grat fret ater aeit &
ae aifsrey
yer wed %& fer faa ate yea & sia Ff few 7a 8)
afe sravae et, at srg aiiast ar aad Fife Tar
sae fale ifr!
ud /aad watera sat 4 age &, stra fate é1
Note : English version of the Instructions is
printed on the front cover of this
question paper.
You might also like
- IAS Mains Physics 2013Document20 pagesIAS Mains Physics 2013Prateek MudgilNo ratings yet
- IAS Mains Physics 2012Document32 pagesIAS Mains Physics 2012ajay70233No ratings yet
- Fractional Differential Equations: An Introduction to Fractional Derivatives, Fractional Differential Equations, to Methods of Their Solution and Some of Their ApplicationsFrom EverandFractional Differential Equations: An Introduction to Fractional Derivatives, Fractional Differential Equations, to Methods of Their Solution and Some of Their ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- MP PPT Sample Paper-1 (2014 Question Paper)Document64 pagesMP PPT Sample Paper-1 (2014 Question Paper)Firdosh KhanNo ratings yet
- A Trip to China: An Intermediate Reader of Modern Chinese - Revised EditionFrom EverandA Trip to China: An Intermediate Reader of Modern Chinese - Revised EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Chapter 4Document41 pagesChapter 4krothrocNo ratings yet
- Commensurabilities among Lattices in PU (1,n). (AM-132), Volume 132From EverandCommensurabilities among Lattices in PU (1,n). (AM-132), Volume 132No ratings yet
- Eamcet 2010 EngDocument61 pagesEamcet 2010 EngManohar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - PTU B.tech EE-3rd Sem-Applied Mathematics-III (AM-201) Sample Paper 1Document2 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - PTU B.tech EE-3rd Sem-Applied Mathematics-III (AM-201) Sample Paper 1Rajeev KapoorNo ratings yet
- Tables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Second Paper Nambu Part 2Document13 pagesSecond Paper Nambu Part 2rigauxarthurNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 6Document6 pagesHomework 4 6inisdeprawn100% (2)
- 2024 Maths 30 - 5 - 1Document23 pages2024 Maths 30 - 5 - 1TanishNo ratings yet
- Tables of Normalized Associated Legendre Polynomials: Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of Normalized Associated Legendre Polynomials: Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Plane TrigonometryDocument33 pagesPlane TrigonometryDaniel PioquintoNo ratings yet
- Public Admn IDocument8 pagesPublic Admn Iajayrana101No ratings yet
- F-Dtn-M-Nuia Mathematics: Paper-1Document32 pagesF-Dtn-M-Nuia Mathematics: Paper-1Naveen ChNo ratings yet
- EDO Orden 1Document5 pagesEDO Orden 11986daniNo ratings yet
- FourierDocument22 pagesFourierKunal RamnatsingNo ratings yet
- Lok YeeDocument7 pagesLok YeeCHAN LOK YEE陈乐儿No ratings yet
- EXAM, 2010: Cs (Main)Document32 pagesEXAM, 2010: Cs (Main)Naveen ChNo ratings yet
- Xi Hindi 2018Document7 pagesXi Hindi 2018qzdff30No ratings yet
- Crypto Notes 1Document25 pagesCrypto Notes 1kiruthikkumaar2003No ratings yet
- The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianFrom EverandThe Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Persamaan TerbitanDocument31 pagesPersamaan TerbitanWan Habib100% (2)
- Higher Maths 2009Document26 pagesHigher Maths 2009gerryoneil5312No ratings yet
- Jar) 2.F. 2 O2. (Mondq,!J) J'Cope: Of.T - 'Io Excluoll"..!12.Document5 pagesJar) 2.F. 2 O2. (Mondq,!J) J'Cope: Of.T - 'Io Excluoll"..!12.Ryan GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 2010 HSC Mat Term 4 TaskDocument4 pages2010 HSC Mat Term 4 TaskTanishNo ratings yet
- George Arfken - Solutions - 03Document6 pagesGeorge Arfken - Solutions - 03Almaram Aljweher100% (1)
- Factoring Trinomials: Trial and Error and The AC-MethodDocument7 pagesFactoring Trinomials: Trial and Error and The AC-MethodmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Pg76 119Document45 pagesPg76 119ttechindiaNo ratings yet
- Untitled 123Document20 pagesUntitled 123Ajay K. PachauriNo ratings yet
- 2014, APPLIED ECONOMETRICS, Question PaperDocument22 pages2014, APPLIED ECONOMETRICS, Question PapernikhiljoshisrccNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document94 pagesCH 01nhensley17350% (2)
- 12 Physics 2023 24 Pre BoardDocument23 pages12 Physics 2023 24 Pre Boardgiyam75106No ratings yet
- Mathematics 1 - FormulaeDocument31 pagesMathematics 1 - Formulaeiitmmk1981No ratings yet
- MATH2105 - (5) Chain-Rule 1Document15 pagesMATH2105 - (5) Chain-Rule 1Aslı ErenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document49 pagesChapter 3radoslav121No ratings yet
- MECE - 303 - MIDTERM - 1 (2018-2019) Sol'nDocument7 pagesMECE - 303 - MIDTERM - 1 (2018-2019) Sol'nMurat Can YüksekNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Paper 2 2013 Code oDocument24 pagesJee Main Paper 2 2013 Code oAbhishek Kumar100% (2)
- 3S R Sa-H: Xiti3Hi 4'9 W7TfltDocument22 pages3S R Sa-H: Xiti3Hi 4'9 W7TfltDinesh BarwarNo ratings yet
- Ece4721 HW1Document7 pagesEce4721 HW1Yaswanthrao GandhamNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Solution PDFDocument10 pagesCH 9 Solution PDFAndreas ChristoforouNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 0580 Formula SheetDocument9 pagesMathematics 0580 Formula SheetAhmed Qazi80% (5)
- Important PointsDocument18 pagesImportant PointsPrateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Important PointsDocument22 pagesPhysics Important PointsPrateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ch26 2Document12 pagesCh26 2Prateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fpure ch3Document34 pagesFpure ch3itcvadqNo ratings yet
- CA03 5 AsymptoticHandoutDocument5 pagesCA03 5 AsymptoticHandoutPrateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- CA03 5 AsymptoticHandoutDocument5 pagesCA03 5 AsymptoticHandoutPrateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Risk MGMT PlanDocument6 pagesRisk MGMT PlanPrateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Android ActionbarSherlock Nested Fragment Tabs Tutorial - AndroidBeginDocument13 pagesAndroid ActionbarSherlock Nested Fragment Tabs Tutorial - AndroidBeginPrateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Learn Negative Binomial Distribution Tutorial, Definition, Formula, ExamplesDocument2 pagesLearn Negative Binomial Distribution Tutorial, Definition, Formula, ExamplesPrateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- DS BookDocument375 pagesDS BookSnehasis ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Function PointsDocument2 pagesFunction PointsPrateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ist Yr-3-2006Document30 pagesIst Yr-3-2006Prateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dialog Box Using Netbeans (Swing - AWT - SWT Forum at JavaRanch)Document2 pagesDialog Box Using Netbeans (Swing - AWT - SWT Forum at JavaRanch)Prateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dgarg@thapar EduDocument5 pagesDgarg@thapar EduPrateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- LearningDocument16 pagesLearningPrateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dialog Box Using Netbeans (Swing - AWT - SWT Forum at JavaRanch)Document2 pagesDialog Box Using Netbeans (Swing - AWT - SWT Forum at JavaRanch)Prateek SharmaNo ratings yet
- 9 Objectorienteddesignusinguml 120507111037 Phpapp02Document41 pages9 Objectorienteddesignusinguml 120507111037 Phpapp02Prateek SharmaNo ratings yet
![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)