Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kimia F4 Akhir Tahun SBP 2008
Uploaded by
Mustakimah MuhamadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kimia F4 Akhir Tahun SBP 2008
Uploaded by
Mustakimah MuhamadCopyright:
Available Formats
MOZ@C
SULIT 4541/1
4541/1
KIMIA
Kertas 1
Oktober
2008
1¼ hrs
BAHAGIAN PENGURUSAN
SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH DAN SEKOLAH KLUSTER
SEKTOR OPERASI PENDIDIKAN
KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA
______________________________________________
PEPERIKSAAN SELARAS DIAGNOSTIK TINGKATAN 4 2008
KIMIA
Kertas 1
Satu jam lima belas minit
JANGAN BUKA KERTAS SOALAN INI HINGGA DIBERITAHU
1. Kertas soalan ini mengandungi 50 soalan.
2. Jawab semua soalan
3. Jawab dengan menghitamkan ruangan yang betul pada kertas jawapan
4. Bagi setiap soalan hitamkan satu ruangan sahaja
5. Sekiranya anda hendak menukar jawapan, padamkan tanda yang telah dibuat.
Kemudian hitamkan jawapan yang baru.
6. Rajah yang mengiringi soalan tidak dilukiskan mengikut skala.
7. Anda dibenarkan menggunakan kalkulator saintifik yang tidak boleh
diprogramkan.
Kertas soalan ini mengandungi 20 halaman bercetak
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR1SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
1 Which of the following substances contain molecules?
A Zinc
B Ethanol
C Sodium chloride
D Magnesium oxide
2 Which of the following is the correct formula for barium hydroxide?
A BaOH
B Ba2OH
C Ba(OH)2
D BaOH2
3 Which of the following set of elements consist of all non metals?
A Chlorine, Nitrogen and Sulphur
B Oxygen, Hydrogen and Lithium
C Phosphorus, Lead and Carbon
D Carbon, Iodine and calcium
4 Which of the following compounds have electrostatic forces between the particles?
A Ammonia
B Naphthalene
C Iodine
D Potassium oxide
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR2SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
5 Which of the following is the energy change that occurs in the process of electrolysis?
A electrical energy heat energy
B potential energy chemical energy
C electrical energy chemical energy
D chemical energy electrical energy
6 The properties of acids are due to the presence of
A hydrogen ion
B hydroxide ions
C hydrogen atoms
D hydrogen molecules
7 Which of the following statements is correct?
A All carbonate salts are soluble in water
B All chloride salts are soluble in water
C All nitrate salts are soluble in water
D All sulphate salts are soluble in water
8 The National Monument is made of bronze. Which is the main metal in bronze?
A Aluminium
B Iron
C Tin
D Copper
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR3SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
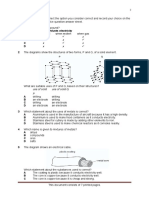
9 An enclosed cylinder is filled with helium atoms. Which diagram shows the arrangement
of the helium atoms ?
10 The formula of a substance is written as FeSO4. What is the name of the compound
according to the IUPAC system?
A Iron sulphate
B Iron(II) sulphate
C Iron(III) sulphate
D Iron(II) sulphite
11 The element which does not form compound with other elements is likely to have proton
number of
A 4
B 8
C 10
D 16
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR4SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
12 Which of the following represents the electron arrangement for sodium chloride, NaCl?
[Proton number; Na, 11; Cl, 17]
13 Electrolytes are able to conduct electricity because they
A have low melting point and boiling point
B contain freely moving ions
C contain freely moving electron
D contain freely moving molecules
14 Which of the following statement describes the property of hydrochloric acid?
A It reacts with any metal to give hydrogen
B It liberates ammonia from ammonium salts
C It causes colour of litmus paper to change from red to blue
D It reacts with any bases to produce a salt.
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR5SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
15 Insoluble salts can be prepared through
A Precipitation Reaction
B Neutralization Reaction
C Crystallization
D Recrystallization
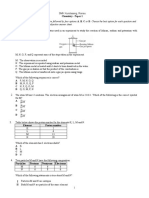
16 Haber Process can be represented by the following equation:
N2 (g) + H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g)
What is the catalyst, temperature and pressure used in this process?
Catalyst Temperature(˚C) Pressure (atm)
A Iron 450 200
B Platinum 900 150
C Platinum 800 10
D Iron 200 1050
31 32
17 The atoms P and S have the same
15 16
A number of protons
B number of neutrons
C number of electrons
D nucleon number
18 The ion of a newly discovered metal M has the symbol M3+ . What will be the formula of
its chloride?
A MCl
B M2Cl3
C MCl3
D M3Cl
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR6SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
19 The property of an element which cannot be predicted from the position of an element in
the Periodic Table of Elements is
A the charge of its ion.
B the formula of its oxide
C the number of isotopes it has.
D the acidic or basic nature of its oxide.
20 Table 1 shows the proton number of elements M and N.
Element Proton number
M 3
N 17
TABLE 1
Which of the following is true of the compound formed between elements M and N?
Compound formula Type of bond
A MN Ionic bond
B MN Covalent bond
C M2N3 Ionic bond
D M3N2 Covalent bond
21 Which of the following voltaic cells produces the highest voltage?
A Iron - copper cell
B Zinc - copper cell
C Aluminium - zinc cell
D Magnesium - copper cell
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR7SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
22 Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Based on the equation above we can conclude that
[Relative atomic mass: Zn, 65; H,1; O,16; S, 32]
I 1 mol of sulphuric acid will produce 1 mol of zinc sulphate
II 1 mol of zinc will react with 1 mol of sulphuric acid
III 100 cm3 sulphuric acid 1 mol dm-3 will produce 16.1 g zinc sulphate if the zinc
used is in excess.
IV The total volume of hydrogen gas liberated will be determined by the amount of
zinc and sulphuric acid reacted.
A II and IV only
B I, II and III only
C I, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
23 Which of the following ions would liberate a gas that turns damp red litmus paper blue
when added with sodium hydroxide solution and then heated?
A H+
B NH4+
C Zn2+
D Fe2+
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR8SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
24 Table 2 shows the pairs of polymer and monomer.
Polymer Monomer
I Carbohydrate Glucose
II Polyvinyl chloride Chloroethene
III Protein Amino acid
IV Natural rubber Neoprene
TABLE 2
Which of the following pairs of polymer and monomer are correct ?
A I and II only
B I, II and III only
C II, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
25 Which of the following diagram represents magnesium oxide?
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR9SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
26 How many molecules of bromine are there in 0.045 mol of bromine?
[Avogadro Constant ; 6.02 X 1023 ]
A 2.7 X 1022
B 3.3 X 1023
C 7.9 X 1024
D 1.2 X 1025
27 An element X requires two electrons to form a stable negative ion. Which group is X
located in the Periodic Table of Elements?
A 2
B 16
C 17
D 18
28 The electron arrangement of atoms P and Q are 2.8.4 and 2.6 respectively.
Which of the following statement is true about the formation of a compound between P
and Q ?
A Each atom Q receives an electron from one atom P
B Each atom P receives four electrons from one atom Q
C Each atom P combines with two atoms Q by sharing of electrons
D Each atom P combines with one atom Q by transfer of electrons
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR10SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
29 Silver nitrate solution of 1 mol dm-3 is electrolysed by using silver electrodes. Which of the
following half equations occur at the anode and cathode respectively?
Anode Cathode
A 4OH- O2 + 2H2O+ 4e 2H+ + 2e H2
B 4OH- O2 + 2H2O+ 4e Ag+ + e Ag
C Ag Ag+ + e Ag+ + e Ag
D Ag Ag+ + e 2H+ + 2e H2
30 Sulphuric acid is a diprotic acid because
A sulphuric acid has the properties of acid and also a dehydrating agent.
B one mole of sulphuric acid can neutralise two moles of bases.
C one molecule of sulphuric acid contains two moles OH- ions.
D one molecule of sulphuric acid produces two H+ ions in water.
31 The following equation represents the reaction between copper(II) oxide and nitric acid.
CuO + 2HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + H2O
Calculate the mass of copper(II) nitrate formed when 6.4g of copper (II) oxide powder
reacts with excess nitric acid.
[ Relative atomic mass: Cu,64; N,14; O,16]
A 4.96g
B 5.04g
C 7.52g
D 15.04g
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR11SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
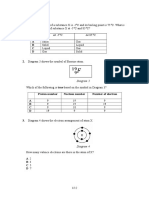
32 Diagram 1 below shows the atom arrangement in brass that is represented by atom P and
atom Q. Atom P
Atom Q
DIAGRAM 1
Which of the following represents metals P and Q?
P Q
A Copper Zinc
B Tin Copper
C Zinc Carbon
D Zinc Copper
7
33 An element represented by the symbol X
3
A has three valence electrons
B forms a positively charged ion.
C is located in Group 17 of the Periodic Table.
D has 3 protons and 7 neutrons.
34 8 atoms of element Z have the same mass as in 1 atom of tellurium, Te.
Based on the statement above, what is the relative atomic mass of element Z?
[Relative atomic mass : Te, 128 ]
A 8
B 16
C 32
D 64
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR12SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
35. Which of the following locations are correct of an element with a proton number of 7 in
the Periodic Table of Elements?
I Period 2
II Period 5
III Group 15
IV Group 2
A I and III only
B II and IV only
C I and IV only
D II and III only
36 Diagram 2 shows the electron arrangement in a molecule formed between two Z atoms.
Z Z
DIAGRAM 2
Which of the following statements is true about molecule Z2?
A Exists as solid at room temperature.
B Conducts electricity in molten state.
C Has a low melting point.
D Dissolves in water.
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR13SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
37 Substance X in the molten form is electrolysed using carbon electrodes. After 10 minutes,
a brown solid is deposited at the cathode and a greenish yellow gas is released at the
anode. What is substance X?
A Lead (II) chloride
B Lead (II) bromide
C Copper (II) bromide
D Copper (II) chloride
38 Which of the following solutions has the lowest pH value?
A 0.1 mol dm-3 sulphuric acid, H2SO4
B 0.1 mol dm-3 ethanoic acid, CH3COOH
C 1.0 mol dm-3 aqueous ammonia, NH4OH
D 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide solution, NaOH
39 Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Based on the equation above, calculate the volume of hydrogen gas released at room
conditions when 1.3 g of zinc powder reacts with excess hydrochloric acid.
[ Molar volume : 24 dm3mol-1 at room conditions, Relative atomic mass: H,1; Cl, 35.5;
Zn, 65]
A 120 cm3
B 240 cm3
C 360 cm3
D 480 cm3
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR14SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
40 The manufacturing of sulphuric acid involves several reactions. Which of the following
equations represents the reaction that requires the use of vanadium(V)oxide as catalyst?
A S + O2 → SO2
B 2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
C SO3 + H2SO4 → H2S2O7
D H2S2O7 + H2O → 2H2SO4
41 Which of the following graphs shows the temperature (T) against time (t) when a mixture
of pentane (boiling point 36oC) and hexane (boiling point 70oC) is distilled?
42 A hydrocarbon has the empirical formula of CH3 with a molar mass of 30 g mol-1. Which
of the following is the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon?
[Relative atomic mass : H, 1; C,12 ]
A CH3
B C2H6
C C3H9
D C4H12
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR15SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
43 Element X reacts with cold water to form alkaline solution while element Y reacts with
water to form acidic solution. Which of the following is the correct group of X and Y in
the Periodic Table of Elements?
X Y
A 1 14
B 2 15
C 1 17
D 3 17
44 Table 3 shows the proton number of three elements X, Y and Z.
Element X Y Z
Proton Number 12 8 17
TABLE 3
What is the formula of the substance and the type of bond formed between X, Y and Z?
Formula Type of Bond
I XY Covalent
II YZ2 Covalent
III XZ2 Ionic
IV Z2 Covalent
A IV only
B III and IV only
C II, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR16SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
45 Diagram 3 shows the set up of the apparatus of a simple voltaic cell. The reading on
the voltmeter is 0.3 V.
Zinc plate
Iron plate
Iron (II) sulphate
solution
DIAGRAM 3
Which of the following statements will increase the reading of the voltmeter?
I Increase the volume of iron (II) sulphate solution
II Substitute the iron plate with a silver plate
III Use a more dilute iron (II) sulphate solution
IV Substitute the zinc plate with a magnesium plate
A I and II only
B I and III only
C II and IV only
D II, III and IV only
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR17SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
46 Neutralization reaction between nitric acid and calcium hydroxide is shown in the
chemical equation below.
2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
What is the minimum volume of nitric acid of 0.2 mol dm-3 needed to completely
neutralise 50 cm3 calcium hydroxide solution 0.05 mol dm-3.
A 12.5 cm3
B 25.0 cm3
C 37.5 cm3
D 50.0 cm3
47 When sodium hydroxide is added dropwise until in excess to a solution, a white
precipitate which is soluble in excess is formed. The ions that could be present in the
solution are
I Al3+
II Zn2+
III Mg2+
IV Pb2+
A I and II only
B III and IV only
C I, II, and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR18SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
48 Which of the following properties of ceramics are correctly matched to the ceramic
articles?
Ceramic articles Properties of ceramic
I Tiles Resistant to chemical reactions
II Spark plug High melting point
III Superconductor Low electrical resistance
IV Electrical cable holder Good conductor of electricity
A I and II only
B II and III only
C I, II and III only
D II, III and IV only
49 Elements P, Q and R are in the same group in the Periodic Table of Elements. Table 4
shows the observation for the reaction of the elements with chlorine and the formula of the
chloride formed.
Reaction with chlorine Formula of chloride
P Burns brightly PCl
Q Burns very brightly QCl
R Burns most brightly RCl
TABLE 4
Which of the following statements is correct?
A P, Q, R are earth metals
B The atomic radius increases from P to Q to R
C The elements form ion with univalent negative charge
D Their reactivity decreases down the group
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR19SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
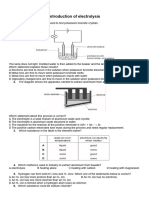
50 Diagram 4 below shows the set up of the apparatus for the electrolysis of concentrated
sodium chloride solution.
DIAGRAM 4
Which of the following formulas shows the products formed at the anode and the
cathode respectively?
Anode Cathode
A O2 H2
B Cl2 H2
C Cl2 Na
D O2 Cl2
END OF QUESTION PAPER
4541/1 SMS MUZAFFAR20SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
Nama: .................................................... Tingkatan: ..............................
SULIT
4541/2
Kimia
Kertas 2
Oktober
2008
2 ½ jam
BAHAGIAN PENGURUSAN
SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH / KLUSTER
SEKTOR OPERASI PENDIDIKAN
KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA
PEPERIKSAAN SELARAS DIAGNOSTIK TINGKATAN 4 2008
KIMIA
Kertas 2
Dua jam tiga puluh minit
JANGAN BUKA KERTAS SOALAN INI SEHINGGA DIBERITAHU
1. Tuliskan nama dan tingkatan pada
ruang yang disediakan. Bahagian Soalan Markah Markah
2. Jawab semua soalan daripada penuh diperoleh
Bahagian A. Tuliskan jawapan anda 1 10
dalam ruang yang disediakan
2 10
3. Jawab satu soalan daripada Bahagian
B dan satu soalan daripada Bahagian 3 10
C.Jawapan kepada bahagian B dan A 4 10
Bahagian C hendaklah ditulis pada 5 10
kertas tulis.
6 10
4. Anda diminta menjawab dengan lebih
terperinci untuk Bahagian B dan B 7 20
Bahagian C. Jawapan mestilah jelas 8 20
dan logik. Persamaan, gambar rajah, 9 20
jadual, graf dan cara lain yang sesuai C 10 20
untuk menjelaskan jawapan anda boleh
digunakan.
5. Anda hendaklah menyerahkan kertas Jumlah
tulis dan kertas tambahan, jika
digunakan bersama-sama dengan
kertas soalan.
6. Penggunaan kalkulator saintifik yang
tidak boleh diprogramkan adalah
dibenarkan.
Kertas soalan ini mengandungi 16 halaman bercetak
[lihat sebelah
SULIT
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
1. Diagram 1.1 shows the symbols for atoms of elements X, Y and Z.
24 28 19
X Y Z
12 14 9
DIAGRAM 1.1
(a) (i) Write the electron arrangement of atom Z.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(ii) What is the number of neutrons for atom Y?
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(iii) What is the atomic mass of atom X?
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(b) Diagram 1.2 shows the set up of the apparatus of an experiment where a drop of bromine
liquid is dropped into a gas jar and is left for a few minutes.
bromine
gas
DIAGRAM 1.2
(i) State one observation in the gas jar after a few minutes.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
[1 mark]
(ii) Name the process that occurred in the gas jar.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[1mark]
4541/2 2 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
(iii) Name the type of particles that exist in bromine.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[1 mark]
(iv) State the change of state of bromine that occurred in the gas jar.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[1 mark]
(v) The change of state in (b) (iv) can occur at room temperature. Explain why
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
[1 mark]
(c) Substance X has a melting point of 79oC . Draw the particles arrangement of substance X at
60oC and at 80oC.
At 60oC At 80oC
[2 marks]
4541/2 3 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
2. An experiment was carried out in the school laboratory to determine the empirical formula of an
oxide of copper by flowing hydrogen gas over heated copper oxide. Table 2 shows the results
obtained.
Description Mass (g)
Combustion tube + asbestos paper 36.20
Combustion tube + asbestos paper + copper oxide 39.40
Combustion tube + asbestos paper + copper 38.76
TABLE 2
(a) What is meant by ‘empirical formula’ ?
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(b) Draw a labelled diagram to show the set up of the apparatus that can be used to carry out
the experiment above.
[2 marks]
(c) State one precautionary step to be taken when carrying out the experiment above.
……………………………………………………………………………………...............
[1 mark]
4541/2 4 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
(d) Based on the results obtained,
(i) calculate the mass of copper and oxygen that have reacted.
[1 mark]
(ii) determine the ratio of moles of copper atom to oxygen atom.
[Relative atomic mass: Cu, 64; O, 16]
[1 mark]
(iii) determine the empirical formula of the copper oxide
[1 mark]
(e) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between copper oxide and hydrogen.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(f) Can the empirical formula of magnesium oxide be determined through the experiment
above? Give one reason for your answer.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[2 marks]
4541/2 5 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
3. Diagram 3 shows the position of several elements in the Periodic Table of Elements.
The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
P U V
Q T
R S W
DIAGRAM 3
(a) Using the letters in Diagram 3, answer the following questions.
(i) Choose an element that is monoatomic.
……………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(ii) Which element forms an amphoteric oxide?
……………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(iii) Which element is a halogen?
……………………………………………………………………………………..
[1 mark]
(b) Write the formula for the ion formed from an atom of element P.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(c) Which element has the biggest atomic radius?
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(d) (i) Why are elements Q and R placed in the same group?
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
4541/2 6 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
(ii) When a small piece of element Q is put into water, a type of solution is formed.
Name the type of solution formed.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(iii) Compare the reactivity of the reaction towards water between elements Q and R.
……….……………………………………………………………………………………..
[1 mark]
(e) Arrange P, U, V and T according to the increase in size of atoms.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(f) State one special characteristic of element S.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
4541/2 7 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
4. Diagram 4 shows the set up of the apparatus for the electrolysis of copper(II) sulphate solution
using copper as electrodes.
U T
copper(II) sulphate
solution
DIAGRAM 4
(a) State which electrode acts as the anode.
……………………………………………………………………………………................
[1 mark]
(b) Name all the ions present in the solution.
………………………………………………………………………………………............
[1 mark]
(c) (i) State the observation at electrode T .
………..………………………………………………………………………………..........
[1 mark]
(ii) Write the half equation for the reaction at electrode T.
………..……………………………………………………………………………………..
[1 mark]
(d) (i) State the colour change (if any) to the copper (II) sulphate solution.
……….……………………………………………………………………………………..
[1 mark]
4541/2 8 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
(ii) Explain your answer in (d)(i)
……….……………………………………………………………………………………
………..……………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
[2 marks]
(f) The above experiment is repeated by using carbon electrodes to replace the copper
electrodes.
(i) Name the product formed at electrode U.
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
[1 mark]
(ii) Describe how you could verify the product formed in f(i)
…….………………………………………………………………………………………..
…….………………………………………………………………………………………..
…….………………………………………………………………………………………..
[2 marks]
4541/2 9 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
5. Diagram 5 shows the set up of the apparatus and the magnification of the burette reading for the
titration of 25.0 cm3 of potassium hydroxide solution and 1.0 mol dm-3 of hydrochloric acid
using phenolphtalein as indicator.
0 25
1 26
Potassium
hydroxide
Initial titration solution Final titration
DIAGRAM 5
(a) Complete the table below.
Final burrett reading/cm3
Initial burrette reading/cm3
Volume of acid/cm3
[2 marks]
(b) State the change of colour to the phenolphtalein indicator in the titration.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(c) Write the chemical equation for the neutralisation reaction.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(d) Calculate the concentration of the potassium hydroxide solution in mol dm-3.
4541/2 10 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
[3 marks]
(e) The experiment above is repeated by using 1.0 mol dm-3 of sulphuric acid to replace the
hydrochloric acid to titrate the 25.0 cm3 potasssium hydroxide solution.
(i) State the volume of the sulphuric acid needed to titrate the potassium hydroxide solution.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 mark]
(ii) Explain your answer in (e) (i).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[2 marks]
6. Diagram 6 shows the flow chart for the industrial manufacture of sulphuric acid.
Sulphur + O2 Sulphur dioxide + O2 Sulphur trioxide
Heat Step X
Step Y + H2SO4
Sulphuric acid Oleum
DIAGRAM 6
(i) Name the process of manufacturing sulphuric acid.
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
[1 mark]
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation for Step X and Step Y.
Step X: …………………………………………………………………………………………
Step Y: …………………………………………………………………………………………
[2 marks]
4541/2 11 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
(iii) State the three conditions required for the reaction in Step X.
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
[3 marks]
(b) Sulphuric acid reacts with aqueous ammonia to form ammonium sulphate, (NH4)2SO4 salt.
(i) Name the reaction.
...................……………………………………………………….........................................
[1 mark]
(ii) State one use of ammonium sulphate in daily life?
……………………………………………………………………………............…….......
[1 mark]
(iii) Calculate the percentage of nitrogen in ammonium sulphate.
[Relative atomic mass : H, 1; O, 16; N, 14; S, 32 ]
[2 marks]
4541/2 12 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
Section B ( 20 marks )
Answer any one question from this section.
The suggested time to answer section B is 30 minutes.
7. Diagram 7 shows the formulae of 4 types of gases released during the eruption of a volcano.
N2 CO2 H2S H2O
DIAGRAM 7
(a) Calculate the molar mass of each gas shown in Diagram 7.
[Relative atomic mass : H, 1; C, 12; O, 16; N, 14; S, 32 ]
[4 marks]
(b) Show that 0.9 g of water vapour contains the same number of molecules as in 2.2 g of
carbon dioxide.
[Relative atomic mass: H, 1; C, 12; O, 16; Avogadro Constant, NA = 6.02 X 1023]
[4 marks]
(c) A sample contains 0.1 mol carbon dioxide gas at room temperature and pressure.
[Relative atomic mass : C, 12; O, 16; 1 mol of gas occupies a volume of 24 dm3 at room
temperature and pressure; Avogadro Constant,NA = 6.02 X 1023]
Calculate:
(i) the volume,
(ii) the mass,
(iii) the number of molecules and
(iv) the number of atoms
of the 0.1 mol carbon dioxide gas in the sample.
[5 marks]
(d) At very high temperature, hydrogen sulphide gas released from the eruption of the
volcano will react with oxygen in the air to produce sulphur dioxide and water vapour.
Referring to the information above,
(i) write a balanced chemical equation to represent the reaction.
(ii) calculate the maximum mass of sulphur dioxide produced if 952 g of hydrogen
sulphide is released from the volcanic eruption.
[7 marks]
4541/2 13 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
8. Table 8.1 shows the electron arrangement for atoms P, Q dan R.
Element Electron arrangement
P 2.8.1
Q 2.8.7
R 2.4
TABLE 8.1
(a) The reaction between atoms of P and Q form an ionic compound whereas the reaction between
atoms of Q and R forms a covalent compound. Based on the above statement, explain how
these ionic and covalent compounds are formed.
[12 marks]
(b) Table 8.2 shows the melting point and boiling point of two chemical compounds at room
temperature.
Compound Melting Point (OC) Boiling Point (OC)
M - 23 76.8
N 2030 2970
TABLE 8.2
Explain the differences in the melting point and boiling point of compound M and N with respect
to the types of particles present and the types of bonding.
[ 8 marks]
4541/2 14 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
Section C ( 20 marks )
Answer any one question from this section.
The suggested time to answer section C is 30 minutes.
9. (a) What is the meaning of electrolyte?
[2 marks]
(b) Lead(II) bromide powder cannot conduct electricity
but molten lead(II) bromide can conduct electricity.
Explain the above statement.
[4 marks]
(c) A student has a spoon made of iron. He intends to beautify the spoon by electroplating it
with a suitable metal.
Design a laboratory experiment to electroplate the iron spoon.
Your answer should consist of the following:
Chemicals required
Procedures of the experiment
Diagram showing the set-up of the apparatus
Half-equations involved in the reaction
Observation
[10 marks]
(d) Electrolytic cell and voltaic cell are two types of cells.
Draw one example of a voltaic cell and write the half equation for the reaction that occurs at
the anode and cathode.
[4 marks]
4541/2 15 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
10. (a) Describe an experiment to prepare a dry zinc nitrate.
Your answers should include the equations involved.
[10 marks ]
(b) Diagram 10 shows the arrangement of atoms in pure copper and brass.
pure copper
brass
DIAGRAM 10
(i) What is the meaning of alloy?
[1 mark]
(ii) State the three aims of alloying
[3 marks]
(iii) Brass is harder than pure copper. Explain.
[6 marks]
4541/2 16 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C 4541/2
4541/2 17 [Lihat sebelah]
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
MOZ@C
Name :………………………………………………………… Class: ………….………
4541/3
KIMIA
Kertas 3
Oktober
2008
1½ Jam
BAHAGIAN PENGURUSAN
SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH DAN SEKOLAH KLUSTER
SEKTOR OPERASI PENDIDIKAN
KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA
_______________________________________________
PEPERIKSAAN SELARAS DIAGNOSTIK TINGKATAN 4 2008
KIMIA
KERTAS 3
Satu jam tiga puluh minit
JANGAN BUKA KERTAS SOALAN INI SEHINGGA DIBERITAHU
1. Tuliskan nama dan tingkatan anda pada
Untuk Kegunaan Pemeriksa
ruangan yang disediakan.
2. Kertas soalan ini adalah dalam Soalan Markah Markah
dwibahasa. Penuh Diperoleh
3. Soalan dalam Bahasa Inggeris 1 15
mendahului soalan yang sepadan dalam
Bahasa Melayu.
2 18
4. Calon dikehendaki membaca maklumat
di halaman 2 kertas soalan ini.
3 17
Jumlah 50
Kertas soalan ini mengandungi 10 halaman bercetak
SMS MUZAFFAR SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES
MAKLUMAT UNTUK CALON
1. This question paper consists of three questions. Answer all questions.
Kertas soalan ini mengandungi tiga soalan. Jawab semua soalan.
2. Write your answers for Question 1 and Question 2 in the spaces provided in the
question paper.
Tuliskan jawapan bagi Soalan 1 dan Soalan 2 dalam ruang yang disediakan
dalam kertas soalan.
3. Write your answers for Question 3 on the lined pages at the end of the question
paper in detail. You may use equations, diagrams, tables, graphs and any other
suitable methods to explain your answer.
Tuliskan jawapan bagi Soalan 3 pada halaman bergaris di bahagian akhir kertas
soalan ini dengan terperinci. Anda boleh menggunakan persamaan, gambar
rajah, jadual, graf dan cara lain yang sesuai untuk menjelaskan jawapan anda.
4. Show your working. It may help you to get marks.
Tunjukkan kerja mengira, ini membantu anda mendapatkan markah.
5. If you wish to change your answer, neatly cross out the answer you have done.
Then write down the new answer.
Sekiranya anda hendak menukar jawapan, batalkan jawapan yang telah dibuat.
Kemudian tulis jawapan yang baru.
6. Diagrams in the questions are not drawn to scale unless stated.
Rajah yang mengiringi soalan tidak dilukis mengikut skala kecuali dinyatakan
sebaliknya.
7. Marks allocated for each question or part questions are shown in brackets.
Markah yang diperuntukkan bagi setiap soalan atau ceraian soalan ditunjukkan
dalam kurungan.
8. Time suggested for answering Question 1 and Question 2 is 45 minutes and
Question 3 is 45 minutes.
Masa yang dicadangkan untuk menjawab Soalan 1 dan Soalan 2 ialah 45 minit
dan Soalan 3 ialah 45 minit.
9. You may use a non-programmable scientific calculator.
Anda dibenarkan menggunakan kalkulator saintifik yang tidak boleh
diprogramkan.
10. Hand in this question paper at the end of the examination.
Serahkan semua kertas jawapan anda di akhir peperiksaan.
4541/3 SMS MUZAFFAR2SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C
Marks awarded:
Mark Description
3 Excellent: The best response
2 Satisfactory : An average answer
1 Weak : An inaccurate response
0 No response or wrong response
Pemberian Markah:
Skor Penerangan
3 Cemerlang: Respons yang paling baik
2 Memuaskan: Respons yang sederhana
1 Lemah: Respons yang kurang tepat
0 Tiada respons atau respons salah
4541/3 SMS MUZAFFAR3SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C
For Answer all questions
examiner’s
use
1. An experiment was carried out by a group of students to determine the melting point
of acetamide. Diagram 1 shows the thermometer reading at the 4th and the 6th minute
of the experiment when acetamide was heated in a boiling tube until above its
melting point.
100 100
90 90
80 80
Thermometer reading at Thermometer reading at
the 4th minute the 6th minute
DIAGRAM 1
(a)
Time /min
0 ½ 1 1½ 2 2½ 3 3½
Temperature/o C
27.0 36.0 50.0 66.0 82.0 82.0 82.0 82.0
Time /min
4 4½ 5 5½ 6
Temperature/o C
84.0 88.0 92.0
TABLE 1
1(a) Table 1 shows the results of the experiment. Based on Diagram 1, complete the
table to show the temperature at the 4th and the 6th minute.
[3 marks]
1(b) (b) On the graph paper provided, draw the graph of temperature against time based
on the collected data.
[3 marks]
4541/3 SMS MUZAFFAR4SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C
4541/3 SMS MUZAFFAR5SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C
For
examiner’s
use
(c) Use the graph in (b) , to determine the melting point of acetamide. Show on the
graph how you determine this melting point.
1(c) ………………………………………………………………………………
[3 marks]
(d) The temperature did not change from the 2nd minute until the 4th minute.
Explain why.
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
1(d)
…………………………………………………………………………………
[3 marks]
(e) Acetamide is an example of a covalent compound and sodium chloride is an example of
an ionic compound. Classify the following compounds into covalent compounds and
ionic compounds.
Magnesium chloride Carbon dioxide
Tetrachloromethane Methylbenzene
Zinc sulphate Copper(II) nitrate
1(e)
[3 marks]
4541/3 SMS MUZAFFAR6SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C
2. The reactivity of alkali metals with water depends on their position in Group 1 of the
Periodic Table of the Elements. Diagram 2 below shows the set up of the apparatus
for an experiment to determine the reactivity of the alkali metals with water.
alkali metal
basin filled with
water
DIAGRAM 2
The experiment is carried out by using lithium, sodium and potassium to react with
water respectively. Observation of the experiment is shown in Table 2.1 below.
ALKALI METAL OBSERVATION
The lithium metal moves slowly on the surface of the
Lithium water.
The sodium metals moves faster on the surface of the
Sodium
water with “hissing” sound.
The potassium metal moves the fastest on the surface
Potassium
of the water.
TABLE 2.1
4541/3 SMS MUZAFFAR7SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C
For
examiner’s (a) Complete Table 2.2 below based on the experiment.
use
Name of variables Action to be taken
(i) Manipulated variable (i) The way to manipulate variable
............................................................ ........................................................
............................................................ .........................................................
............................................................ .........................................................
(ii) Responding variable (ii) What to observe in the
............................................................ responding variable
............................................................ .........................................................
............................................................. ..........................................................
(iii) Fixed variable (iii) The way to maintain the fixed
............................................................. variable
............................................................. .........................................................
............................................................ .........................................................
2(a)
[6 marks]
TABLE 2.2
(b) State the hypothesis for the experiment above.
2(b) ……………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………..
[3 marks]
(c) Based on Table 2.2, arrange the alkali metals in descending order of reactivity
of the metals with water.
2(c)
………………………………………………………………………………
[3 marks]
4541/3 SMS MUZAFFAR8SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C
For
examiner’s
use
(d) The proton number of the alkali metals increase in the order:
Lithium → Sodium → Potassium
State the relationship between the position of the alkali metals in Group 1
and their reactivity.
…………………………………………………………………………..................
……………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………….. 2(d)
[3 marks]
(e) Rubidium is an alkali metal located below potassium in Group 1 . Predict the
reactivity of rubidium with water.
……………………………………………………………………………… 2(e)
[3 marks]
4541/3 SMS MUZAFFAR9SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C
3.
The distance of pairs of metals in the electrochemical
series influenced the voltage values in different
electrochemical cells.
Based on the statement above, plan a laboratory experiment to construct an
electrochemical cell to determine the factor that influences the differences in the voltage
values.
Your planning should include the following:
(i) Statement of the problem
(ii) All the variables
(iii) Hypothesis
(iv) List of materials and apparatus
(v) Procedure
(vi) Tabulation of data
[17 marks]
END OF QUESTION PAPER
4541/3 SMS MUZAFFAR10SYAH , MELAKA SULIT
SULIT MOZ@C
SULIT 4541/1/2/3
4541/1
Kimia
Oktober
2008
BAHAGIAN PENGURUSAN
SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH DAN SEKOLAH KLUSTER
SEKTOR OPERASI PENDIDIKAN
KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA
PEPERIKSAAN SELARAS DIAGNOSTIK TINGKATAN EMPAT 2008 SBP
KIMIA
Peraturan pemarkahan Kertas 1, 2 dan 3
SMS MUZAFFAR1SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
Paper 1
1 B 21 D 41 B
2 C 22 D 42 B
3 A 23 B 43 C
4 D 24 B 44 C
5 C 25 C 45 C
6 A 26 A 46 B
7 C 27 B 47 C
8 D 28 C 48 C
9 D 29 C 49 B
10 B 30 D 50 B
11 C 31 D
12 D 32 A
13 B 33 B
14 D 34 B
15 A 35 A
16 A 36 C
17 B 37 D
18 C 38 A
19 C 39 D
20 A 40 B
SMS MUZAFFAR2SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
Marking Scheme Paper 2
Section A
No MARKING CRITERIA MARK
SUB TOTAL
1(a)(i) 2.7 1
(ii) 14 1
(iii) 24 1 3
1(b)(i) Reddish brown gas formed 1
(ii) Diffusion 1
(iii) Molecules 1
(iv) Liquid → gas 1
(v) Bromine has low boiling point 1 5
1(c)
1 2
10
2(a) A chemical formula that gives the simplest whole number ratio 1 1
of atoms of each element in the compound.
2(b)
Burning excess hydrogen
Oxide of copper
Dry
hydrogen
gas
Heat
- functional 1
- label( oxide of copper, dry hydrogen gas and heat) 1 2
SMS MUZAFFAR3SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
2(c) ●Remove all the air from the apparatus before the oxide of
copper is heated
●The flow of hydrogen gas is continued throughout the cooling of
the product
Any one answer correct 1 1
2 d(i) mass of copper : 38.76 – 36.20 = 2.56g
mass of oxygen : 39.40 – 38.76 = 0.64g
Calculation + mass including unit 1
2 d(ii) Cu : O
2.56/64 : 0.64/16
0.04 : 0.04 1
1 : 1
2d(iii) CuO 1 3
2(e) CuO + H2 Cu + H2O 1 1
2(f) No. 1
Magnesium is more reactive than hydrogen.// Magnesium is
above hydrogen in the Reactivity Series. 1 2
10
3(a) W 1
T 1
V 1 3
3 (b) P2+ 1 1
3(c) R 1 1
3(d) ● The atoms have the same valence electron. 1
● alkaline 1
● R is more reactive than Q 1 3
SMS MUZAFFAR4SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
3(e) V, U, P and T 1 1
3(f) Forms coloured compound/ion//can act as catalyst//has variable 1 1
oxidation number
10
4(a) U 1 1
4(b) copper (II) ion, suphate ion,hydrogen ion,hydroxide ion 1 1
a: symbol
4(c)(i) brown solid is deposited//electrode T becomes thicker 1
(ii) Cu2+ + 2e Cu 1 2
4(d) (i) The intensity of blue colour solution remains unchanged 1
(ii) The rate of Cu2+ ion discharged at the cathode same with the rate
of Cu2+ ion formed at the anode 1
The concentration / no.of Cu2+ ion remains unchanged 1 3
4(f)(i) oxygen gas 1
(ii) Put a glowing wooden splinter near/into the mouth of the test tube 1
lighted up/rekindled 1 3
10
5(a)
Final burrett reading/cm3 25.55 1
Initial burrette reading/cm3 0.55 1 2
Volume of acid/cm3 25.00
5(b) pink to colourless 1 1
5(c) HCl + KOH → KCl + H2O 1 1
5(d) MaVa = 1 1
MbVb 1
1
1.0 x 25.0 = 1
Mb x 25.0 1
1 3
Mb = 1.0 mol dm-3
SMS MUZAFFAR5SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
5(e) 12.5 cm3 1
Sulphuric acid is a diprotic acid. 1
has 2 times the concentration of H+ ions compared to 1 3
hydrocholric acid.
10
6(a)(i) Contact Process 1
(ii) 2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3 1
(iii) SO3 + H2SO4 → H2S2O7 1
(i)
Catalyst: vanadium (V) oxide 1
Temperature: 450oC – 550oC 1
Pressure : 1 atm 1 6
6(b) (i) Neutralization 1
(ii) Fertilizer 1
(iii) % of Nitrogen = 14X2
--------------------------- X 100
14(2)+1(8)+32+16(4) 1
= 28
----- X 100
32 1 4
= 21.21%
10
SMS MUZAFFAR6SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
Section B
No MARKING CRITERIA MARK
SUB TOTAL
7 (a) 1. N2 : 2 X 14 = 28 1
2. CO2 : 12 + 2(16) = 44 1
3. H2S : 2(1) + 32 = 34 1
4. H2O : 2(1) + 16 = 18 1 4
7(b) 1 moles of water vapour = 0.9
18
= 0.05 1
2 no. of molecules = 0.05 moles X 6 X 1023
= 3 x 10 22
1
3 moles of CO2 = 2.2
44
= 0.05 moles 1
4 no. of molecules = 0.05 moles X 6 x 1023
= 3 x 10 22 1 4
7(c)(i) Volume = 0.1 X 24
= 2.4 dm3// 2400cm3 1
(ii) Mass = 0.1 X 44 1
= 4.4g
(iii) No. of molecules = 0.1 X 6.02 X 1023 1
= 6.02 X 1022
(iv) No. of atom = 3 X 0.1 X 6.02 X 1022 1
= 1.806 X 1023 1 5
7d(i) 2 H2S + 3 O2 → 2SO2 + 2H2O
Correct formula of reactant and product 1
Correct no. of mol of reactant 1
Correct no. of mol of product 1
(ii) 1. Moles of H2S = 952
34 1
= 28
2. 2 moles of H2S produced 2 moles SO2 1
28 moles of H2S produced 28 moles of SO2 1
3. mass of SO2 = 28 x [ 32 + 2(16) ] 1 7
= 1792 g
SMS MUZAFFAR7SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
20
8(a) Between P and Q
1
Atom P has 1 valence electron
Atom P loses/donates/transfers 1 electrons to form P+ ion 1
//
P P+ + e- and attain stable octet electron arrangement
Atom Q has 7 valence electrons 1
Atom gains/receives/accept 1 electron to formQ ion//-
Q + e-Q- 1
attain the stable /octet electron arrangement
1
The two oppositely-charged ions// the P+ and Q- ion are
bonded together by a strong electrostatic force 1
To form a ionic compound with the formula PQ //
Diagramn 1
Between Y and Z
Atom R has 4 valence electrons and atom Q has 1 valence
1
electrons
One atom R contributes 4 electrons and (each) atom Q
1
contributes one electron for sharing
Atom R shared 4 pairs of electron with 4 atoms Q 1
to attain a octet /stable electron arrangement respectively 1
Diagram
1
SMS MUZAFFAR8SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
R Q
Q
12
8(c) Compound M is an ionic compounds 1
Compound N is a covalent compounds 1
Compound M has high melting and boiling point 1
Compound N has low melting and boiling point 1
Strong electrostatic force of attraction exists between
1
the ions /the oppositely-charged ions in compound M
Weak intermolecular forces //held together by weak (Van
1
der Waals) force of attractions between molecules in
compound N
A lot of heat energy // high of energy is required to break 1
the strong forces in the compound M
● little heat energy //low energy is needed to overcome the 1
8
weak forces in the compound N
20
SMS MUZAFFAR9SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
Section C
No MARKING CRITERIA MARK
SUB TOTAL
9(a) 1.Electrolyte is an ionic compound that can conduct electricity 1
2.in the molten state or aqueous solution. 1 2
9(b) 1. In powdered form, lead(II) ions and Bromide ions cannot move 1
freely.
2. The ions are held together with strong electrstatic forces 1
3. In molten state, the ions can move freely. 1
4. The free moving ions carry the electrical charges. 1 4
9(c) 1. Chemicals required: silver nitrate solution, silver plate, 1
Procedures:
2. [50 – 200]cm3 of [0.5 – 2.0] mol dm-3 of silver nitrate solution 1
is poured into a beaker.
3. The silver plate is the anode and the iron spoon is the cathode. 1
4. The silver plate and the iron spoon are connected to the battery 1
with the connecting wires. 1
5. The silver plate and the iron spoon are then dipped into the 1
silver nitrate solution.
6. [complete and functional set-up of apparatus] 1
7. [labels: at anode: silver plate, at cathode: iron spoon,
electrolyte: silver nitrate solution} 1
8. Half equation at anode: Ag → Ag+ + e 1
9. Half equation at cathode: Ag+ + e → Ag 1 10
10. Observation: iron spoon is covered with grey, silvery/shiny
deposit.
9(d) 1. [one example of voltaic cell with complete and functional set-up 1
of apparatus:
2. [Labels: at anode: more electropositive metal,eg. Zinc
at cathode: less electropositve metal, eg. Copper] 1
a suitable electrolyte, eg. Copper(II) sulphate solution] 1
3. Half-equation at anode: Zn → Zn2+ + 2e 1
4. Half-equation at cathode: Cu2+ + 2e → Cu 4
20
SMS MUZAFFAR10SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
No MARKING CRITERIA MARK
SUB TOTAL
10(a) 1 Name of suitable reactant e.g: zinc/zinc oxide/zinc carbonate 1
and nitric acid
2 [50-200] cm3 of [0.1-2.0 ]moldm-3 of nitric acid is poured into a 1
beaker
3 Heat /Warm the acid 1
4 Add in zinc/zinc oxide/zinc carbonate into the acid bit by bit 1
until in excess/ no longer dissolves
5 Stir the mixture and filter 1
6 The filtrate is poured into an evaporating dish. 1
7 heat until saturated 1
8 The solution is allowed to cool 1
9 The crystals formed are filtered and by compressing/pressing 1
between 2 sheets of filter paper.
10 Suitable chemical equations e.g ; 1 10
ZnCO3 + 2HNO3 Zn(NO3)2 + H2O + CO2
10b(i) An alloy is a mixture of two or more elements with a certain fixed
composition in which the major component is a metal 1
(ii) To increase the strength/ hardness of a pure metal To 1
increase the resistance to corrosion of a pure metal 1
To improve the appearance of a pure metal 1
(iii) In pure copper,atoms are of the same size 1
atoms are orderly arranged in layers 1
the layers of atoms can slide over each one another when a force is 1
applied
In brass, atoms of tin and copper have different size 1
the presence of tin atoms disrupt the orderly arrangement of the
copper atoms. 1
The layers of copper atoms are more difficult to slide over each 1
other.
10
20
SMS MUZAFFAR11SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
Marking Scheme Paper 3
1 (a) KK0503 – Measuring and using numbers
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to write both temperatures with correct to 1 decimal place] 3
temperature reading : 82.0 °C
temperature reading : 97.0 °C
[Able to record all the volumes accurately but without decimal place] 2
temperature reading : 82
temperature reading : 97
[Able to write at least one reading of the temperature accurately] 1
No response given / wrong response 0
1 (b) KK0506 – Communicating
EXPLANATION SCORE
[ Able to draw a graph of temperature against time of the experiment on
the same axes with all the 4 items below correctly ]
(i) axes labelled correctly with units
(ii) suitable scale used
(iii) all points plotted correctly
(iv) smooth curve of graph and more than ½ size of graph paper 3
[ Able to draw a graph of temperature against time of the experiment on 2
the same axes with all the 3 items correctly ]
[ Able to manipulate two items correctly ] 1
No response or wrong response 0
SMS MUZAFFAR12SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
1 (c)KK0505 – Predicting
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to state the temperature correctly and able to show the how the melting 3
point is determined on the graph]
Answer: 82 .0
82oC
melting
point
[Able to state the temperature but without unit and did not label melting point 2
on the graph correctly]
Answer: 82
Melting point
[Able to state the temperature but without unit and did not show the melting 1
point on the graph]
Answer: 82
No response given / wrong response 0
1 (d) KK0508 – Interpreting Data
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to interpret the data accurately] 3
Suggested answer:
The heat energy absorbed is used to overcome the forces of attraction/bonds
between the molecules of acetamide
[Able to give correct interpretation but less accurate] 2
Suggested answer:
The heat energy is used to overcome the forces of attraction of molecules /
particles of acetamide
[Able to give an idea] 1
Suggested answer:
The heat energy is used / absorbed.
No response given / wrong response 0
SMS MUZAFFAR13SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
1 (e) KK0505 – Classifying
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to classify the ionic and covalent compounds correctly] 3
Ionic Covalent
Magnesium chloride Methylbenzene
Copper(II) nitrate Tetrachloromethane
Zinc sulphate Carbon dioxide
[Able to state at least two pairs correctly // correct grouping but wrong 2
heading or vice versa ]
[Able to state one pair correctly in a correct grouping] 1
No response given / wrong response 0
2(a) KK0510 - State the variables
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to state the three variables and action to be taken correctly] 6
Name of variables Action to be taken
(i) Manipulated variable: (i) The way to manipulate
Type of group 1 metals variable:
used Use lithium, sodium and
potassium metal for each
experiment.
(ii) Responding variable: (ii) What to observe in
the responding variable:
Rate of reaction//Reactivity of
the reaction The movement of metal on
the water surface.
(iii) Fixed variable: (iii) The way to maintain
the fixed variable:
Quantity/size of metal used. Use the same quantity/size
of metal.
[Able to state any five items correctly] 5
[Able to state any four items correctly] 4
[Able to state any three items correctly] 3
[Able to state any two items correctly] 2
[Able to state any one item correctly] 1
No response given / wrong response 0
SMS MUZAFFAR14SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
2 (b) KK0512 – Stating hypothesis
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to state the relationship between manipulated variable and 3
responding variable correctly]
Suggested answer:
The metal which is below in Group 1 is more reactive in the reaction with
water//The lower the metal in Group 1 the more reactive is the reaction
with water.
[Able to state the relationship between manipulated variable and 2
responding variable but in the opposite direction]
Suggested answer:
The more reactive the reaction, the lower the position of the metal in Group 1
[Able to state an idea of the hypothesis] 1
Suggested answer:
Metals in Group 1 can react with water
No response given / wrong response 0
2(c) KK 0508 – Interpreting Data
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to arrange the metals in descending order based on their reactivity] 3
Suggested answer:
K, Na, Li
[Able to arrange the metals in ascending order based on their reactivity] 2
Answer:
Li, Na, K,
[Able to arrange the position of at least two metals in descending/ascending] 1
Suggested answer:
Na, Li, K// Li, K, Na// Na, K, Li
No response given / wrong response 0
2(d) KK0507- Making relationship
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to state the relationship accurately] 3
Suggested answer:
The lower the position of the metal in Group 1, the higher the reactivity of the
metal.
[Able to state the relationship correctly but less accurate] 2
Suggested answer:
The reactivity of the metals is inversely proportional to their position in the
group.
[Able to state an idea of a relationship] 1
Suggested answer:
Position of metals affect the reactivity
No response given / wrong response 0
SMS MUZAFFAR15SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
c2(e) KK 0508 – Predicting
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to predict the reactivity of rubidium correctly] 3
Suggested answer:
The reaction of Rubidium is most reactive among lithium, sodium and
potassium when react with water
[Able to predict the arrangement of the metals based on their reactivity] 2
Suggested answer:
The reaction of Rubidium is most reactive.
[Able to give an idea 1
Suggested answer:
Rubidium is a reactive metal
No response given / wrong response 0
3.(a) KK051021 – Statement of the problem
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to make a correct statement of problem] 3
Suggested answer:
Does the distance between two/ pair of metals in the electrochemical series
give different voltage values?
[Able to make a statement of the problem or suitable aim] 2
Suggested answer:
Does the distance between two /pair of metals give different voltage values?//
Distance between two/pair of metals in the electrochemical series gives
different voltage values.
[Able to state an idea of statement of problem or aim] 1
Metals influence the voltage values
No response given / wrong response 0
3 (b) KK051202 – Stating variables
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to state all the three variables correctly] 3
Suggested answer:
Manipulated variable : types of pairs of metals
Responding variable: voltage values//potential difference
Constant variable : electrolyte used such as copper(II) sulphate solution.
[Able to state any two of the variables correctly] 2
[Able to state one of the variables correctly or state idea regarding 1
variable]
No response given / wrong response 0
SMS MUZAFFAR16SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
3(c) KK051202 – Stating hypothesis
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to state the relationship between manipulated variable and 3
responding variable correctly]
Suggested answer:
The further the distance/position between two metals in the electrochemical
series, the bigger the voltage value.
[If the responding variable comes first, the score is 2]
[Able to state the relationship between manipulated variable and 2
responding variable]
Suggested answer:
The further the distance /position between two metals, the bigger the
voltage value//vice versa
[Able to state an idea of the hypothesis] 1
Suggested answer:
Metals influence the voltage value
No response given / wrong response 0
3(d) KK051205 – List of materials and apparatus
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to state the list of materialss and apparatus correctly and completely] 3
Suggested answer:
Beaker, connecting wires, crocodile clips, voltmeter, sand paper, [magnesium
ribbon, zinc strip,lead strip, copper strip], [copper(II) sulphate solution]
[Able to state the list of substances and apparatus correctly but not 2
completely]
Suggested answer:
Beaker, connecting wires, voltmeter, [magnesium ribbon, zinc,
copper],[copper(II) sulphate solution]
[Able to state an idea about the list of substances and apparatus] 1
Suggested answer:
Beaker, metals, voltmeter, electrolyte, wire.
No response given / wrong response 0
SMS MUZAFFAR17SYAH , MELAKA
SULIT MOZ@C
3(e) KK051204 –Procedure
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to state a complete experimental procedure] 3
Suggested answer:
1. [30 -200] cm3 of copper(II) sulphate solution is poured into a beaker.
2. Magnesium ribbon and copper strip are cleaned with the sand paper.
3. Magnesium and copper are dipped into the copper(II) sulphate solution.
4. Both metals are connected to a voltmeter.
5. The voltmeter reading is recorded.
6. The circuit is completed.
7. Steps 1 to 6 are repeated by using different of metals to pair with
copper.
[Able to state the procedure which include the following steps] 2
Answer: Steps 1,3,4,5,6
[Able to state an idea of procedure] 1
Answer: Steps 3,5
No response given / wrong response 0
3(f) Tabulation of data
EXPLANATION SCORE
[Able to exhibit the tabulation of data correctly ]
Pairs of metals Voltage/V Negative terminal
[Able to exhibit the tabulation of data less accurately ] 2
Pairs of metals Voltage
[Able state an idea about the tabulation of data] 1
Metals Voltage
No response given / wrong response 0
END OF MARKING SCHEME
SMS MUZAFFAR18SYAH , MELAKA
You might also like
- Iron Metabolism: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical ConsequencesFrom EverandIron Metabolism: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical ConsequencesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SULIT 4541/1 Chemistry Paper 1 Mei 2007Document22 pagesSULIT 4541/1 Chemistry Paper 1 Mei 2007AMINNo ratings yet
- Kimia P1 SBP Mid Year SPM 2008Document44 pagesKimia P1 SBP Mid Year SPM 2008adeebspark100% (1)
- 638b7346d28d9Document20 pages638b7346d28d9HC GamerNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972From EverandCoordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972A. B. P. LeverNo ratings yet
- Klks 9 Test-LatihanDocument6 pagesKlks 9 Test-LatihankrisnuNo ratings yet
- Progress in Reaction Kinetics: Volume 6From EverandProgress in Reaction Kinetics: Volume 6K. R. JenningsNo ratings yet
- NL MCQ Challenge 03Document5 pagesNL MCQ Challenge 03Alvin Lee100% (1)
- Photochemistry – 6: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Sixth International Symposium on Photochemistry, Aix-En-Provence, France, 19-23 July, 1976From EverandPhotochemistry – 6: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Sixth International Symposium on Photochemistry, Aix-En-Provence, France, 19-23 July, 1976A. GilbertNo ratings yet
- 10chemistry General Trial Test AnsDocument6 pages10chemistry General Trial Test AnsMNo ratings yet
- 12.1 ExerciseDocument8 pages12.1 ExerciseDakarirayi MutenherwaNo ratings yet
- NL MCQ Timed Practice 08 (R10)Document4 pagesNL MCQ Timed Practice 08 (R10)Alvin LeeNo ratings yet
- 2020 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Ngee Ann SecondaryDocument35 pages2020 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Ngee Ann SecondaryDORA SIN YU KWOKNo ratings yet
- GZB Xii Ws-9 Chemistry D & F Block Elements October Sarita KhokharDocument4 pagesGZB Xii Ws-9 Chemistry D & F Block Elements October Sarita KhokharSaman PanwarNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions.: Section A (15 Marks)Document7 pagesAnswer All Questions.: Section A (15 Marks)chee pin wongNo ratings yet
- Jar 1 Jar 1 Lid Air: A B C DDocument7 pagesJar 1 Jar 1 Lid Air: A B C DaaryavaminNo ratings yet
- Exam Chew 1Document7 pagesExam Chew 1ThilagaNo ratings yet
- NL MCQ Timed Practice 02 (R01)Document4 pagesNL MCQ Timed Practice 02 (R01)Alvin LeeNo ratings yet
- Uppp2 Sem 2 2017Document5 pagesUppp2 Sem 2 2017Loh Wai YeeNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument33 pagesElectrolysisborglingchompersNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/23Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/23shabanaNo ratings yet
- Yr10 Chemistry Paper 2 YE22Document14 pagesYr10 Chemistry Paper 2 YE22Ern QiNo ratings yet
- Read These Instructions FirstDocument6 pagesRead These Instructions FirstSalman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- Blackened The Corresponding Space On The Objective Answer SheetDocument9 pagesBlackened The Corresponding Space On The Objective Answer SheetSJD KimNo ratings yet
- 4024q1 Specimen PaperdocxDocument12 pages4024q1 Specimen PaperdocxLeses MayNo ratings yet
- Topik 6 ElectrochemistryDocument27 pagesTopik 6 ElectrochemistryJaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Kertas 1 SoalanDocument28 pagesKertas 1 SoalanZakaria Md SaadNo ratings yet
- 2019f5s9ex4chemistry 1Document13 pages2019f5s9ex4chemistry 1Dania NatashaNo ratings yet
- Metals MCQ PDFDocument21 pagesMetals MCQ PDFMunshatia Islam MerryNo ratings yet
- 12.3 ExerciseDocument15 pages12.3 ExerciseDakarirayi MutenherwaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument41 pagesCHEMISTRYLindsayyNo ratings yet
- AHS Prelim 2014 P1Document11 pagesAHS Prelim 2014 P119Y1H GAO CHENZHANGNo ratings yet
- Pre IG 0.14 (Night), Chemistry, Monthly TestDocument8 pagesPre IG 0.14 (Night), Chemistry, Monthly TestHtet Wai Yan AungNo ratings yet
- Parwah Intelek Kimia Paper 1 2013Document22 pagesParwah Intelek Kimia Paper 1 2013Jamuna RaniNo ratings yet
- There Are 50 Questions in This Paper. Choose The Best Answer For Each QuestionDocument21 pagesThere Are 50 Questions in This Paper. Choose The Best Answer For Each Questionapi-19650882No ratings yet
- Name: Class: I/C NoDocument19 pagesName: Class: I/C NopermatasemarakNo ratings yet
- Bahagian A 1. The Melting Point of A Substance X Is - 2: Diagram 3Document12 pagesBahagian A 1. The Melting Point of A Substance X Is - 2: Diagram 3ndianaoNo ratings yet
- 2004 MRSM Without AnswerDocument49 pages2004 MRSM Without AnswerChoong Wen JianNo ratings yet
- 2019 Sec 4 Science Chemistry SA2 Singapore Sports SchoolDocument30 pages2019 Sec 4 Science Chemistry SA2 Singapore Sports School19Y1H GAO CHENZHANGNo ratings yet
- 2019 Sec 4 Science Chemistry SA2 Singapore Sports SchoolDocument30 pages2019 Sec 4 Science Chemistry SA2 Singapore Sports School19Y1H GAO CHENZHANGNo ratings yet
- Part 1: Multiple-Choice Questions (20 Marks)Document11 pagesPart 1: Multiple-Choice Questions (20 Marks)kahguaNo ratings yet
- Review SheetDocument15 pagesReview Sheetmtayyab zahidNo ratings yet
- Singles 11Document4 pagesSingles 11Nagendra BharadwazNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level Chemistry Paper 1 Multiple Choice May/June 2005 1 HourDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level Chemistry Paper 1 Multiple Choice May/June 2005 1 Hourkaran79No ratings yet
- Class X ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesClass X ElectrolysisvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document15 pagesPaper 1SitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- AA Chem CW (2nd Term) (9) 2nd - InddDocument3 pagesAA Chem CW (2nd Term) (9) 2nd - InddTing TCNo ratings yet
- Trial STPM Term2 2015Document8 pagesTrial STPM Term2 2015Earliany Mohd ShahriNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education Chemistry Paper 1 Multiple Choice October/November 2006 45 MinutesDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education Chemistry Paper 1 Multiple Choice October/November 2006 45 MinutesVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- 962/1 Trial STPM 2010: Confidential / SulitDocument15 pages962/1 Trial STPM 2010: Confidential / SulitDiong JayhueyNo ratings yet
- O-Levels Chemistry ExemplarDocument40 pagesO-Levels Chemistry Exemplartendaisithole02No ratings yet
- LW F6 Chem Mock Exam P1 1718 PDFDocument23 pagesLW F6 Chem Mock Exam P1 1718 PDFVincent haNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Electrochemistry Text Book ExerciseDocument31 pagesChapter 10 Electrochemistry Text Book ExerciseshahidkakaNo ratings yet
- SMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang STPM Trial Exam Term 2 2019 (Chemistry)Document7 pagesSMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang STPM Trial Exam Term 2 2019 (Chemistry)AlyciaLeeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/23Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/23mercy.cyfn.109No ratings yet
- Kedah 2018 P1Document25 pagesKedah 2018 P1hassan ukongNo ratings yet
- Test Topic: Atomic Structure, Formula Writing and Balancing Equation, Bonding and Structure, Redox, ElectrolysisDocument11 pagesTest Topic: Atomic Structure, Formula Writing and Balancing Equation, Bonding and Structure, Redox, ElectrolysisArham Tamim100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/22ZubairHassanNo ratings yet
- The Internet of ThingsDocument33 pagesThe Internet of ThingsKaedara KazuhaNo ratings yet
- Think Feel DoDocument3 pagesThink Feel DoHardik MehtaNo ratings yet
- God Reborn - The Birth of God and The Creation of The UniverseDocument204 pagesGod Reborn - The Birth of God and The Creation of The UniverseTony Bermanseder100% (1)
- Minglana-Mitch-T-Answers in Long QuizDocument9 pagesMinglana-Mitch-T-Answers in Long QuizMitch MinglanaNo ratings yet
- MHD Exam 6 MaterialDocument179 pagesMHD Exam 6 Materialnaexuis5467100% (1)
- Instant Download The Practice of Creative Writings 3rd Edition Ebook PDF PDF FREEDocument32 pagesInstant Download The Practice of Creative Writings 3rd Edition Ebook PDF PDF FREEbarbara.ward425100% (46)
- 61-Article Text-180-1-10-20170303 PDFDocument25 pages61-Article Text-180-1-10-20170303 PDFSOUMYA GOPAVARAPUNo ratings yet
- HRIRDocument23 pagesHRIRPhuong HoNo ratings yet
- SB Roadmap B1 1Document161 pagesSB Roadmap B1 1Carmen Flores AloyNo ratings yet
- List of Marketing Metrics and KpisDocument5 pagesList of Marketing Metrics and KpisThe KPI Examples ReviewNo ratings yet
- CSMP77: en Es FRDocument38 pagesCSMP77: en Es FRGerson FelipeNo ratings yet
- C779-C779M - 12 Standard Test Method For Abrasion of Horizontal Concrete SurfacesDocument7 pagesC779-C779M - 12 Standard Test Method For Abrasion of Horizontal Concrete SurfacesFahad RedaNo ratings yet
- HimediaDocument2 pagesHimediaWiwit MarianaNo ratings yet
- Final Report of BBSMDocument37 pagesFinal Report of BBSMraazoo1967% (9)
- Syntax Ps4Document6 pagesSyntax Ps4blue_child86% (7)
- Assignment Brief - Starting A Business and Fundamental of MarketingDocument7 pagesAssignment Brief - Starting A Business and Fundamental of Marketingmd rahimNo ratings yet
- Restoring PH Balance in The BodyDocument6 pagesRestoring PH Balance in The Bodycinefil70No ratings yet
- Infoblatt Skischulen Trends Port eDocument18 pagesInfoblatt Skischulen Trends Port eAustrian National Tourism BoardNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Absence of Conflict of InterestDocument1 pageDeclaration of Absence of Conflict of InterestJvhelcoronacondat CondatNo ratings yet
- Dispersion Relation of Electromagnetic WavesDocument2 pagesDispersion Relation of Electromagnetic WavesFidel SouzaNo ratings yet
- Preparatory Newsletter No 3 2013Document22 pagesPreparatory Newsletter No 3 2013SJC AdminNo ratings yet
- Lier Upper Secondary SchoolDocument8 pagesLier Upper Secondary SchoolIES Río CabeNo ratings yet
- TSR 9294 DLA3 Dragons RestDocument78 pagesTSR 9294 DLA3 Dragons RestLéo Duarte100% (4)
- Learner Cala Guide: PART A: Identification of Knowledgeable Elderly Part BDocument5 pagesLearner Cala Guide: PART A: Identification of Knowledgeable Elderly Part BPrimrose MurapeNo ratings yet
- Study of Noise Mapping at Moolchand Road Phargang New DelhiDocument10 pagesStudy of Noise Mapping at Moolchand Road Phargang New DelhiEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- SIRMDocument9 pagesSIRMshailendra369No ratings yet
- Ellis Lived ExperiencesDocument31 pagesEllis Lived ExperiencesJeanny Mae PesebreNo ratings yet
- Forklift Driver Card and Certificate TemplateDocument25 pagesForklift Driver Card and Certificate Templatempac99964% (14)
- Free DMAIC Checklist Template Excel DownloadDocument5 pagesFree DMAIC Checklist Template Excel DownloadErik Leonel LucianoNo ratings yet
- New York LifeDocument38 pagesNew York LifeDaniel SineusNo ratings yet