Professional Documents
Culture Documents
External Validity and Sampling
Uploaded by
Jolene TanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
External Validity and Sampling
Uploaded by
Jolene TanCopyright:
Available Formats
COMM II
Sampling and External Validity
Key Terms:
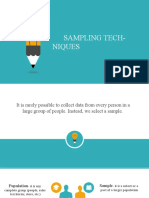
Population - the whole group that you want to study
Sample – subsection of the population, chosen in such a way that their characteristics reflect those of the
group from which they are chosen
Stratum - one or more specifications that divide a population into mutually exclusive segments
Population element - single member of the population
Sampling error - the deviation of the selected sample from the true characteristics, traits, behaviors,
qualities or figures of the entire population.
**recall validity refers to the approximate truth of propositions, inferences, or conclusions.
EXTERNAL VALIDITY
- refers to the approximate truth of conclusions the involve generalizations.
- degree to which the conclusions in your study would hold for other persons in other places and at other
times.
Threats to External Validity: people, place, time
How to improve external validity: replicate study
SAMPLING
- the process of selecting units (e.g., people, organizations) from a population of interest so that by
studying the sample we may fairly generalize our results back to the population from which they were
chosen.
Two types of Sampling: nonprobability and probability
The difference between nonprobability and probability sampling is that nonprobability sampling does not
involve random selection and probability sampling does.
PROBABILITY SAMPLING - any method of sampling that utilizes some form of random selection
Simple Random Sampling – random sample from whole population
Stratified Random Sampling – random sample from identifiable groups or subgroups (stratum)
Cluster Sampling - random samples of successive clusters of subjects (e.g. by institution) until small groups
are shosed as units
Stage sampling – combination of cluster (randomly selecting clusters) and random or stratified random
sampling of individuals
NONPROBABILITY SAMPLING – any method that does not utilize random selection
Purposive sampling – hand-pick subjects on the basis of specific characteristics
Quota Sampling – select individuals as they come to fill a quota by characteristics proportional to
populations
Snowball Sampling – subjects with desired traits or characteristics give names of further appropriate
subjects
Volunteer, Accidental, or Convenience – either asking for volunteers, or the consequence of not all those
selected finally participating, or a set of subjects who just happen top be available
You might also like
- Selecting A Sampling Procedure: (Sample) of A Larger Group (Population)Document4 pagesSelecting A Sampling Procedure: (Sample) of A Larger Group (Population)Shun Dee LebicoNo ratings yet
- PCK5 File 1Document2 pagesPCK5 File 1LichelCaitaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Sampling PDFDocument40 pagesWeek 7 Sampling PDFheyheyNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Prepared By: Nandini Biswas Assistant Professor of Law, UPESDocument19 pagesSampling: Prepared By: Nandini Biswas Assistant Professor of Law, UPESHasta la VistaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Group of ArsadDocument3 pagesAssignment - Group of ArsadElvie CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- Sampling (Statistics) : Probability and Nonprobability SamplingDocument3 pagesSampling (Statistics) : Probability and Nonprobability SamplingAkhil ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- binder edaDocument5 pagesbinder edapalacioaya28No ratings yet
- Statistical Sampling Methods ExplainedDocument5 pagesStatistical Sampling Methods ExplainedmarcoNo ratings yet
- SAMPLING TECHNIQUES HandoutsDocument1 pageSAMPLING TECHNIQUES HandoutsMORENO BACONo ratings yet
- Random SamplingDocument3 pagesRandom SamplingMae TaladtadNo ratings yet
- Sample Design & Sampling MethodsDocument31 pagesSample Design & Sampling MethodsRyans FkdokgiNo ratings yet
- Statistic and Probability ReviewerDocument1 pageStatistic and Probability ReviewerABORDO, JANE ELEONORNo ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument9 pagesSampling TechniquesLovejoylife Castillo RevecheNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument6 pagesStatisticsCyrus Hiedi ViñegasNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology: Research 2 Emmanuel Paciano M. MabulayDocument53 pagesResearch Methodology: Research 2 Emmanuel Paciano M. MabulayRonnie TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology: Research 2 Ma. Daniela Anne B. Samaniego, RPMDocument43 pagesResearch Methodology: Research 2 Ma. Daniela Anne B. Samaniego, RPMMelay LacabaNo ratings yet
- Cluster SamplingDocument2 pagesCluster Samplingas gamingNo ratings yet
- Sampling Methods/Techniques of SamplingDocument3 pagesSampling Methods/Techniques of SamplingShweta B DixitNo ratings yet
- Population - RESEARCHDocument21 pagesPopulation - RESEARCHvrvasukiNo ratings yet
- L5 Research-MethodsDocument43 pagesL5 Research-Methodsmlsobiono2665qcNo ratings yet
- Sampling Techniques: by Fatima NaqviDocument23 pagesSampling Techniques: by Fatima NaqviDania AhmadNo ratings yet
- Sampling Methods ExplainedDocument4 pagesSampling Methods ExplainedMP MagnayeNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Tutor Name: Mr. Rahul BerryDocument18 pagesSampling: Tutor Name: Mr. Rahul BerryAastha PanditNo ratings yet
- Arsh DPT 7th Biostat Lec 6 Sampling TechniqueDocument33 pagesArsh DPT 7th Biostat Lec 6 Sampling TechniqueNovail HashmiNo ratings yet
- Selecting Study Participants for ResearchDocument36 pagesSelecting Study Participants for ResearchRocky R. NikijuluwNo ratings yet
- Population, Sample, Probability&Non-Probability Sampling Technique.Document18 pagesPopulation, Sample, Probability&Non-Probability Sampling Technique.Cikk DedekNo ratings yet
- 05 SamplingDocument49 pages05 Samplinganon_602869128No ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis - Identify VariablesDocument4 pagesStatistical Analysis - Identify VariablesAbigail BantilloNo ratings yet
- 1c - Sampling MethodsDocument35 pages1c - Sampling MethodsNezlyn D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Simple Random SamplingDocument2 pagesSimple Random SamplingMaureen Joy Aguila GutierrezNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Data Collection and Basic Concepts in Sampling DesignDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 3: Data Collection and Basic Concepts in Sampling DesignDominique Anne BenozaNo ratings yet
- Sampling & Sampling TechniquesDocument6 pagesSampling & Sampling TechniquesMavel DesamparadoNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument29 pagesSamplingEsmael AbubakerNo ratings yet
- The logic of sampling techniquesDocument9 pagesThe logic of sampling techniquesrinor ahmetiNo ratings yet
- Sampling MethodsDocument37 pagesSampling MethodsTafsir HossainNo ratings yet
- Sampling Design and Terminology ExplainedDocument27 pagesSampling Design and Terminology ExplainedsannyruraNo ratings yet
- RM Unit 2Document52 pagesRM Unit 2mayankjain08248No ratings yet
- Presented To: Ms. Sukhbir Kaur Presented By: Vandana (843) Reema (829) Mba 2 SemDocument25 pagesPresented To: Ms. Sukhbir Kaur Presented By: Vandana (843) Reema (829) Mba 2 SemVandana InsanNo ratings yet
- Types of SamplingDocument13 pagesTypes of SamplingROSHAN SAFREEN.T 18BBA123100% (1)
- Qualitative Research Method Assignment (Summary) Instructor: DR - Rizwana Raseed Submitted By: Shahzaib Salim (56028)Document6 pagesQualitative Research Method Assignment (Summary) Instructor: DR - Rizwana Raseed Submitted By: Shahzaib Salim (56028)navin aslam jumaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To StatisticsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To StatisticsRifat Hassan RabbyNo ratings yet
- Sampling Theory PPT PresentDocument13 pagesSampling Theory PPT PresentRitam DasNo ratings yet
- Rs SamplingDocument1 pageRs Samplingt7qkd7hv6wNo ratings yet
- (Trochim, 2006) (EBSCO Help, 2017)Document3 pages(Trochim, 2006) (EBSCO Help, 2017)왕JΔIRΩNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of Different Sampling Techniques: Gaganpreet SharmaDocument4 pagesPros and Cons of Different Sampling Techniques: Gaganpreet SharmaKyla RodriguezaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect Data: Lesson 4Document32 pagesUnderstanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect Data: Lesson 4Sam IntongNo ratings yet
- EXT-506 Research Methods On Behavioral Sciences: Term Paper PresentationDocument40 pagesEXT-506 Research Methods On Behavioral Sciences: Term Paper Presentationrachana darigiNo ratings yet
- Sampling Techniques Guide by Dr. MadhumithaaDocument59 pagesSampling Techniques Guide by Dr. MadhumithaaPraveen Kumar MNo ratings yet
- Types Sampling MethodsDocument40 pagesTypes Sampling MethodsRAJESH67% (6)
- Sampling Techniques Explained: Methods, Types and UsesDocument59 pagesSampling Techniques Explained: Methods, Types and UsesAnonymous mzuRnewGNo ratings yet
- Ruhs College of Nursing Sciences, Jaipur: Assignment ON Sampling TechniquesDocument13 pagesRuhs College of Nursing Sciences, Jaipur: Assignment ON Sampling TechniquesDr-Sanjay SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Sampling Distribution - Part 1Document38 pagesSampling and Sampling Distribution - Part 1littlemakzmathNo ratings yet
- Research-reviewerDocument8 pagesResearch-reviewerelecgabrielr.123No ratings yet
- Biostatistics Assignment Sample, Sampling, Population Sample Sampling PopulationDocument3 pagesBiostatistics Assignment Sample, Sampling, Population Sample Sampling Populationsadaf jaan mohammadNo ratings yet
- Sampling Designs ExplainedDocument2 pagesSampling Designs ExplainedVon Valentine MhuteNo ratings yet
- Sampling Techniques for ResearchDocument40 pagesSampling Techniques for ResearchSuhotra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sampling Design: Key ConceptsDocument42 pagesSampling Design: Key ConceptsFaria HossainNo ratings yet
- Example Scenario: Sampling MethodDocument2 pagesExample Scenario: Sampling MethodJoana Marie VelascoNo ratings yet
- Practical ResearchDocument3 pagesPractical ResearchKathNo ratings yet
- Pengembangan Modul Ipa Berbasis Kearifan Lokal Kopi Pada Pokok Bahasan Usaha Dan Energi Di SMPDocument8 pagesPengembangan Modul Ipa Berbasis Kearifan Lokal Kopi Pada Pokok Bahasan Usaha Dan Energi Di SMPAnonymous xXllbGQNo ratings yet
- 2018 Com Module 1 and 2Document6 pages2018 Com Module 1 and 2Anisha BassieNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Symposium: Submitted By: Submitted ToDocument4 pagesAssignment On Symposium: Submitted By: Submitted ToDiksha DuhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Name Grade Topic/Concept Materials/ResourcesDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Name Grade Topic/Concept Materials/Resourcesapi-490250820No ratings yet
- Voices - Extra Resources Info 2022Document2 pagesVoices - Extra Resources Info 2022maig100% (2)
- English Language Arts Standards Writing Grade 7Document10 pagesEnglish Language Arts Standards Writing Grade 7Spectacular TutorNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Commskill - 4Document28 pagesLesson - Commskill - 4HafizaNo ratings yet
- Books That You Should Read For Your Mental FitnessDocument4 pagesBooks That You Should Read For Your Mental FitnessDeepshikha MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Name: Mohammed Aiyaz Pasha Student Id: 982467 Course: Master of Business Subject Title: Management Skills Submitted To: DR Helen GamageDocument9 pagesName: Mohammed Aiyaz Pasha Student Id: 982467 Course: Master of Business Subject Title: Management Skills Submitted To: DR Helen GamagePalak ShahNo ratings yet
- Pakistani TestsDocument5 pagesPakistani TestsHaleema BuTt100% (1)
- Module 1 - Lesson 1 - PR3Document39 pagesModule 1 - Lesson 1 - PR3Cressia Mhay BaroteaNo ratings yet
- Autism: Occupational Therapy's Role WithDocument2 pagesAutism: Occupational Therapy's Role WithStacy Ann VergaraNo ratings yet
- Section 1 What Is ESPDocument6 pagesSection 1 What Is ESPjvafNo ratings yet
- Patient-Centered Care TrainingDocument10 pagesPatient-Centered Care Trainingradomir.boskovicNo ratings yet
- FOCUS-4 kl-12 FIRST PERIOD 2018.2019Document5 pagesFOCUS-4 kl-12 FIRST PERIOD 2018.2019ІванNo ratings yet
- Ged 105 - Main Topic 1Document33 pagesGed 105 - Main Topic 1Dannica Keyence MagnayeNo ratings yet
- Miss Jenelle M. de Vera: English TeacherDocument38 pagesMiss Jenelle M. de Vera: English Teacherromar brionesNo ratings yet
- Fieldwork Experience and Journal EntriesDocument5 pagesFieldwork Experience and Journal Entriesapi-273367566No ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument5 pagesAnnotated BibliographyBrian MaingiNo ratings yet
- Melissa Smith Website ResumeDocument3 pagesMelissa Smith Website Resumeapi-255350959No ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Khan KhanNo ratings yet
- Efforts and Difficulties in Teaching Vocabulary: N. V. F. Liando, J. D. Adam, T. K. LondaDocument5 pagesEfforts and Difficulties in Teaching Vocabulary: N. V. F. Liando, J. D. Adam, T. K. LondaChery BlossomNo ratings yet
- The Elves and the Shoemaker LessonDocument3 pagesThe Elves and the Shoemaker LessonTamiris Silva Codognotto0% (1)
- English Phrases For Meetings - Espresso EnglishDocument8 pagesEnglish Phrases For Meetings - Espresso Englishasamwm.english1No ratings yet
- Strategic Thinking Intuitive Thinking: Subject & Grade/Level Learning CompetencyDocument2 pagesStrategic Thinking Intuitive Thinking: Subject & Grade/Level Learning CompetencySheila Aggarao100% (3)
- A Fuzzy Approach To Text Classification WithDocument4 pagesA Fuzzy Approach To Text Classification WithAvinash NadikatlaNo ratings yet
- Evelyn L. Lazaro BEED 1: Linguistic DimensionsDocument8 pagesEvelyn L. Lazaro BEED 1: Linguistic DimensionsEvelyn LazaroNo ratings yet
- DepEd UpdatedRPMSManualDocument249 pagesDepEd UpdatedRPMSManualJeffrey Farillas100% (3)
- Interpersonal SkillsDocument7 pagesInterpersonal SkillsShivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Functions of LanguageDocument34 pagesExercises: Functions of LanguageЯна ЯрохаNo ratings yet