Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Living Planet: Key Ecology Terms
Uploaded by
hirmannazif72410 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesInteractions Within Communities Food Chain Model for feeding relationships. Symbiosis Close relationship between species. Mutualism Both species benefit from relationship and other is not affected. Parasitism one organism benefits and one is harmed in relationship.
Original Description:
Original Title
6REcologyVocab
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInteractions Within Communities Food Chain Model for feeding relationships. Symbiosis Close relationship between species. Mutualism Both species benefit from relationship and other is not affected. Parasitism one organism benefits and one is harmed in relationship.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesLiving Planet: Key Ecology Terms
Uploaded by
hirmannazif7241Interactions Within Communities Food Chain Model for feeding relationships. Symbiosis Close relationship between species. Mutualism Both species benefit from relationship and other is not affected. Parasitism one organism benefits and one is harmed in relationship.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Living Planet
Part of Earth that supports life
Biosphere (top crust, water, atmosphere).
Makes environments.
Living and nonliving parts in an
Ecosystem environment.
Study of interactions between
Ecology organisms and environment.
Organisms of the same species
Population living in an area.
Community All populations in an ecosystem.
Place where an organism lives
Habitat (food, shelter, moisture,
temperature).
Populations
Organisms seek same resource.
Competition Limits population size.
Most intense within same species.
Population Size of a population in an area.
Density
Restricts the number of the
population.
Limiting Example: lack of rain, lack of
Factor food, habitat destruction,
temperature change.
Largest number of one species
Carrying an ecosystem can support.
Capacity
Birth and death rates.
Change in
Population Moving.
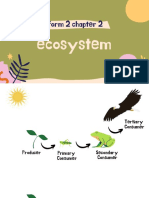
Interactions Within Communities
Outside energy source (sun)
to make food (photosynthesis).
Producers Green plants.
Cannot make their own food.
Obtain energy by eating other
Consumers organisms.
Herbivores, carnivores,
omnivores, decomposers.
Herbivore Eats plants.
Carnivore Eats animals.
Omnivore Eats plants and animals.
Decomposer Eats waste and dead organisms.
Interactions Within Communities
Food Chain Model for feeding relationships.
Close relationship between
Symbiosis species.
Both species benefit from
Mutualism relationship.
One organism benefits from
relationship and other is not
Commensalism affected.
One organism benefits and one
Parasitism is harmed in relationship.
Interactions Within Communities
Organism’s role (job) in the
Niche environment.
Predators Consumers eating consumers.
Prey Food of consumer.
You might also like
- Interactions in EcosystemsDocument42 pagesInteractions in EcosystemsJeanelle AlbertNo ratings yet
- Microbial Ecosystem Narrative ReportDocument4 pagesMicrobial Ecosystem Narrative ReportJeane Klaire ObadoNo ratings yet
- Interactions: Environment and OrganismsDocument33 pagesInteractions: Environment and OrganismsAngelica MartinNo ratings yet
- Ecology RevDocument46 pagesEcology RevrivaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Species and PopulationDocument52 pages2.1 Species and PopulationAgormahNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Community InteractionDocument95 pages3.0 Community InteractionAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAONo ratings yet
- Biology ecosystem notesDocument8 pagesBiology ecosystem notesChamsNo ratings yet
- Ecology & Ecosystems - Understanding Interactions Between Organisms & EnvironmentsDocument21 pagesEcology & Ecosystems - Understanding Interactions Between Organisms & EnvironmentsRisshi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Ecology Notes: Species, Populations, Communities, EcosystemsDocument41 pagesEcology Notes: Species, Populations, Communities, EcosystemsManish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 11-Ecology Notes PDFDocument41 pages11-Ecology Notes PDFShubham MandalNo ratings yet
- Species Interactions & Community Ecology ExplainedDocument51 pagesSpecies Interactions & Community Ecology Explainedpepody11No ratings yet
- 6th Grade Ecosystem VocabularyDocument2 pages6th Grade Ecosystem Vocabularyapi-262495543No ratings yet
- Sample Notes EnvironmentDocument8 pagesSample Notes Environmentpradeep aryaNo ratings yet
- Ecology - Vocabulary ListDocument4 pagesEcology - Vocabulary ListBrandon ShevelevNo ratings yet
- Attributes-to-ecosystem-and-biodiversityDocument8 pagesAttributes-to-ecosystem-and-biodiversityGORDO, JANELLE L.No ratings yet
- Ecology Review NotesDocument6 pagesEcology Review NotesMaKylah ClevelandNo ratings yet
- Ecology & Conservation Chapter 26 GuideDocument19 pagesEcology & Conservation Chapter 26 GuideShawn ChenNo ratings yet
- Community CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesCommunity CharacteristicsChristine ApriyaniNo ratings yet
- Principles of Ecology, Interaction of Organisms Within The EnvironmentDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Ecology, Interaction of Organisms Within The EnvironmentdinakahNo ratings yet
- EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE KEY TERMSDocument20 pagesEARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE KEY TERMSFat AjummaNo ratings yet
- Understanding EcosystemsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding EcosystemsPak ToursNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial Ecology Notes1Document130 pagesTerrestrial Ecology Notes1api-265611555No ratings yet
- Interdependence Among Living Organism S and The EnvironmentDocument33 pagesInterdependence Among Living Organism S and The EnvironmentHuda WahabNo ratings yet
- Main Points On Organism Interact in EcosystemDocument3 pagesMain Points On Organism Interact in EcosystemZyrone Uriarte Generoso RNNo ratings yet
- Symbiotic Relationship and Its TypesDocument33 pagesSymbiotic Relationship and Its TypesMayuri Vohra0% (1)
- Concept of Ecosystem Producers Consumers and DecomposersDocument9 pagesConcept of Ecosystem Producers Consumers and DecomposersShiv RajNo ratings yet
- Modules 3 & 4 2019Document14 pagesModules 3 & 4 2019ChamsNo ratings yet
- Mejia Ecology NotesDocument27 pagesMejia Ecology NotesThien TranNo ratings yet
- The Ecosystem: Biotic and Abiotic FactorsDocument24 pagesThe Ecosystem: Biotic and Abiotic FactorsJericho MangubatNo ratings yet
- Community Ecology Community Ecology Looks at The InteractionsDocument5 pagesCommunity Ecology Community Ecology Looks at The InteractionsLeah MacalipayNo ratings yet
- Ess 5Document17 pagesEss 5Apollonia VitelliNo ratings yet
- Ecology 3 Column NotesDocument2 pagesEcology 3 Column Notesmceldownea100% (1)
- Rev Notes ch19 eDocument13 pagesRev Notes ch19 eEdgar LeungNo ratings yet
- Biology Biology: Chapter 9: EcosystemDocument14 pagesBiology Biology: Chapter 9: EcosystemazraNo ratings yet
- ECOLOGYDocument34 pagesECOLOGYRachelle MamarilNo ratings yet
- Ex3 Interspecific InteractionsDocument28 pagesEx3 Interspecific InteractionsPrincess RomoNo ratings yet
- Biology Term 4Document6 pagesBiology Term 4ghfh9mn5f6No ratings yet
- EcologyDocument12 pagesEcologyapi-254474797No ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument56 pagesEcosystemEvangeline BocasasNo ratings yet
- Interaction and InterdependenceDocument36 pagesInteraction and InterdependenceLouNo ratings yet
- Module 2-Ge Elect PesDocument10 pagesModule 2-Ge Elect PesDivine Grace CincoNo ratings yet
- Insects and The Biotic EnvironmentDocument4 pagesInsects and The Biotic Environmentirfan khanNo ratings yet
- Interdependence Among Organisms and Their EnvironmentDocument13 pagesInterdependence Among Organisms and Their EnvironmentNantha KumaranNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Habitat Species Population Community Ecosystem NicheDocument3 pagesEcosystem Habitat Species Population Community Ecosystem NicheMuhammad Riefdy Asas 1 Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Ekjot Study SheetDocument3 pagesEkjot Study Sheetapi-302396873No ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 4Document13 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 4EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 EcosystemDocument60 pagesChapter 2 EcosystemJu WenNo ratings yet
- Scientific Study of The Interactions Between Organisms and Their EnvironmentsDocument54 pagesScientific Study of The Interactions Between Organisms and Their EnvironmentsNurul Safiah SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Sci7 Studytnotes Jan. 16,2023-Science7Document4 pagesSci7 Studytnotes Jan. 16,2023-Science7lucky laguraNo ratings yet
- SZL202 Topic One Components of An EcosystemDocument5 pagesSZL202 Topic One Components of An Ecosystemmarubegeoffrey41No ratings yet
- Inter Specific InteractionDocument7 pagesInter Specific InteractionSandeep kumar SathuaNo ratings yet
- Science Notes 1Document4 pagesScience Notes 1Neptune LopezNo ratings yet
- Ecology DiscussionDocument31 pagesEcology DiscussionAl Marjorie Abrasaldo TatingNo ratings yet
- Species Interaction and EcologyDocument62 pagesSpecies Interaction and EcologyAmit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Ste Lesson On Ecology 2018Document61 pagesSte Lesson On Ecology 2018Laurel S. MedinaNo ratings yet
- Ecology Reading and ReviewDocument8 pagesEcology Reading and Reviewjohan preciadoNo ratings yet
- Population Limit Factors Carrying Capacity SymbiosisDocument35 pagesPopulation Limit Factors Carrying Capacity Symbiosisjoe doeNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life 1Document61 pagesEarth and Life 1Glyneth Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Niche & Community Interactions NicheDocument4 pagesNiche & Community Interactions Nichesiti nurhalizahNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: Explore the Diversity of Life on Earth with Environmental Science Activities for KidsFrom EverandBiodiversity: Explore the Diversity of Life on Earth with Environmental Science Activities for KidsNo ratings yet
- The Pitch CanvasDocument2 pagesThe Pitch CanvasDimas Wichaksono75% (4)
- The Pitch CanvasDocument2 pagesThe Pitch CanvasDimas Wichaksono75% (4)
- Arahan Teknik (Jalan) 2A-85Document3 pagesArahan Teknik (Jalan) 2A-85mohdnizamNo ratings yet
- BookcaseDocument19 pagesBookcasehirmannazif7241No ratings yet
- Stavic PriceListDocument1 pageStavic PriceListhirmannazif7241No ratings yet
- Am Bon Use CatalogueDocument30 pagesAm Bon Use Cataloguehirmannazif7241No ratings yet
- Stavic PriceListDocument1 pageStavic PriceListhirmannazif7241No ratings yet
- Rextron PricelistDocument1 pageRextron Pricelisthirmannazif7241No ratings yet
- Cell Division QuestionDocument18 pagesCell Division Questionhirmannazif72410% (1)
- Official Game GuideDocument30 pagesOfficial Game GuideHhfugNo ratings yet
- WasdabDocument13 pagesWasdabfakhri84No ratings yet
- PPEsDocument11 pagesPPEsPrithivirajan CuddaloreNo ratings yet
- Traceability Summary - Supplies July 2015 - June 2016: PT Multimas Nabati Asahan, Kuala TanjungDocument4 pagesTraceability Summary - Supplies July 2015 - June 2016: PT Multimas Nabati Asahan, Kuala TanjungAbu KhalidNo ratings yet
- تحليل البول بالصور والشرحDocument72 pagesتحليل البول بالصور والشرحDaouai TaaouanouNo ratings yet
- Desensitization ProtocolsDocument28 pagesDesensitization ProtocolsAnonymous 9dVZCnTXSNo ratings yet
- YUMMY TUMMY - Beef Biryani Recipe - Beef Dum Biryani RecipeDocument48 pagesYUMMY TUMMY - Beef Biryani Recipe - Beef Dum Biryani RecipeWilliam Cj LyngdohNo ratings yet
- Natalia Mooting QDocument1 pageNatalia Mooting QPok Nik LiNo ratings yet
- Effects of Climate ChangeDocument10 pagesEffects of Climate ChangeJan100% (1)
- t-47 Residential Real Property Affidavit - 50108 ts95421Document1 paget-47 Residential Real Property Affidavit - 50108 ts95421api-209878362No ratings yet
- Police Log January 23, 2016Document9 pagesPolice Log January 23, 2016MansfieldMAPoliceNo ratings yet
- Cognitive and Psychopathological Aspects of Ehlers DanlosDocument5 pagesCognitive and Psychopathological Aspects of Ehlers DanlosKarel GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Basseri TribeDocument3 pagesBasseri TribeMaddah HussainNo ratings yet
- Duty Resume ReportDocument1 pageDuty Resume ReportaleemuddinNo ratings yet
- Stakeholders in The Iep Process JDocument9 pagesStakeholders in The Iep Process Japi-546526887No ratings yet
- Habit TrackersDocument38 pagesHabit Trackersjesus100% (1)
- Energy Certification of Buildings and Nearly Zero-Energy BuildingsDocument70 pagesEnergy Certification of Buildings and Nearly Zero-Energy BuildingsOgnjen BobicicNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDocument8 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood IllnessSehar162No ratings yet
- 01 Basic Design Structure FeaturesDocument8 pages01 Basic Design Structure FeaturesAndri AjaNo ratings yet
- Boiler BlowdownDocument2 pagesBoiler BlowdownbaratheonNo ratings yet
- CAUTI Surveillance FormDocument2 pagesCAUTI Surveillance FormJiansong ChangNo ratings yet
- Modified Micro Marsupialization in Pediatric Patients: A Minimally Invasive TechniqueDocument4 pagesModified Micro Marsupialization in Pediatric Patients: A Minimally Invasive TechniquerinahpsNo ratings yet
- Pathway StemiDocument2 pagesPathway StemiIntan Nurulita SariNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equation CalculationsDocument6 pagesChemical Equation CalculationsHera RiegoNo ratings yet
- Guerra, Germae Joyce - Media JournalDocument2 pagesGuerra, Germae Joyce - Media JournalGERMAE JOYCE GUERRANo ratings yet
- Flow Meter SpecificationDocument2 pagesFlow Meter SpecificationDan4ChristNo ratings yet
- Pnp-MemorandumDocument9 pagesPnp-MemorandumraalphNo ratings yet
- DIAGEO2Document12 pagesDIAGEO2Tatiana Zuleta RojasNo ratings yet
- Guidance Counseling EssentialsDocument2 pagesGuidance Counseling EssentialsElizabeth E. FetizaNo ratings yet
- Product BrochureDocument2 pagesProduct BrochureNoel RodríguezNo ratings yet