Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evans - The Respiratory System
Uploaded by
Cassidy_0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views2 pagesThe respiratory system is responsible for providing oxygen and removing carbon dioxide. It does this through breathing. When we breathe, we inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide follows the same path out of the lungs when we exhale. The bronchi are formed by the trachea diving into two main bronchi (the right and left) the right bronchi is shorter and wider than the left bronchi it also subdivides into three lobar bronchi while the left stays
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe respiratory system is responsible for providing oxygen and removing carbon dioxide. It does this through breathing. When we breathe, we inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide follows the same path out of the lungs when we exhale. The bronchi are formed by the trachea diving into two main bronchi (the right and left) the right bronchi is shorter and wider than the left bronchi it also subdivides into three lobar bronchi while the left stays
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views2 pagesEvans - The Respiratory System
Uploaded by
Cassidy_The respiratory system is responsible for providing oxygen and removing carbon dioxide. It does this through breathing. When we breathe, we inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide follows the same path out of the lungs when we exhale. The bronchi are formed by the trachea diving into two main bronchi (the right and left) the right bronchi is shorter and wider than the left bronchi it also subdivides into three lobar bronchi while the left stays
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
The Respiratory System
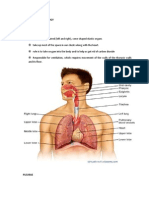
Human lungs are paired with the left being divided into two lobes
and the right divided into three lobes. The left lung is slightly
smaller than the right lung and they are protected by your rib cage.
The respiratory system means of getting oxygen to the blood.
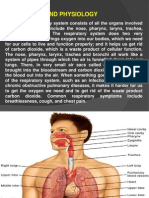
The respiratory system is responsible for
providing oxygen and removing carbon
dioxide. The primary function of the
respiratory system is to supply the
blood with oxygen in order for the
blood to deliver the oxygen to the
rest of the body. It does this
through breathing. When we
breathe, we inhale oxygen and
exhale carbon dioxide.
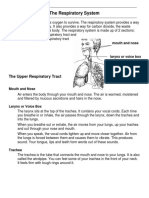
Oxygen enters the respiratory
system through the mouth and the
nose internally and externally. When
you breathe through your nostrils the
nasal hairs act as a filter from dust it
warms and moistens the air.
The oxygen then passes through the larynx which is muscle and
cartilage that contains the vocal cords commonly known as a
person’s voice box, and the trachea known as the windpipe which is a
tube that enters the chest cavity it’s filled with cartilage which
makes it flexible to stop it from collapsing. The trachea then splits
into two smaller tubes called the bronchi it then divides again
forming bronchial tubes leading to the lungs where they divide into
smaller tubes again connected to alveoli.
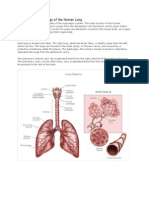
The Bronchus are formed by the trachea diving into two main
bronchi (the right and left) The right bronchi is shorter and wider
than the left bronchi it also subdivides into three lobar bronchi
while the left stays as two. The bronchus carries air into the lungs.
The alveoli are air sacs that hold oxygen. The oxygen molecules
diffuse from the alveolus in the capillaries then they attach to the
deoxygenated rich blood cells then they get breathed out as carbon
dioxide.
The inhaled oxygen passes into the alveoli and then diffuses
through the capillaries into the arterial blood. Meanwhile, the
waste-rich blood from the veins releases its carbon dioxide into the
alveoli. The carbon dioxide follows
the same path out of the lungs when
you exhale. As the diaphragm
contracts and relaxes, breathing
takes place.
(www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alve
olus_diagram)
(www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Gray961)
Bibliography
•www.fi.edu/learn/heart/systems/respiration.html
•www.dentalarticles.com/images/respiratory-system
•www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alveolus_diagram
•www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_lung
You might also like
- Pathophy of CapDocument4 pagesPathophy of CapKatzii FranciaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the LungsDocument1 pageAnatomy and Physiology of the LungsBranzuela ChristineNo ratings yet
- Vi. Anatomy and Physiology The Lungs StructureDocument5 pagesVi. Anatomy and Physiology The Lungs StructureJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Vi. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesVi. Anatomy and PhysiologyJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Human Lung Anatomy & RespirationDocument2 pagesHuman Lung Anatomy & Respirationhoneydine_03No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageRespiratory SystemSharm ManlangitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 46: The Circulatory and Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesChapter 46: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systemapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemVin EighteenthNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory System ExplainedDocument6 pagesThe Human Respiratory System ExplainedshashaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology PneumoniaDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology PneumoniaJohnson MallibagoNo ratings yet
- DiscussionDocument26 pagesDiscussionCHARMAINE ORUGANo ratings yet
- Respiration Is A Chemical Reaction That Happens in All Living CellsDocument3 pagesRespiration Is A Chemical Reaction That Happens in All Living CellsKani KurmanbekovaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesThe Respiratory SystemRoland Jacques AlconisNo ratings yet
- LO4 - Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesLO4 - Respiratory SystemCHR1555No ratings yet
- LO4 - Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesLO4 - Respiratory SystemCHR1555No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory and Cardiovascular SystemsDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systemsbryan leguiabNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument5 pagesRespiratoryKintina MorataNo ratings yet
- Body Systems: Respiratory System: Oxygen Delivery SystemDocument2 pagesBody Systems: Respiratory System: Oxygen Delivery SystemKathiresan KathirNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMDocument6 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMCarlos Alfonso Borromeo AmoresNo ratings yet
- Circulatory and Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory and Respiratory Systemclarisse100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument1 pageAnatomy and PhysiologyDian Rose Sebanes MamintaNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 9 Learning Activity Sheets on Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument18 pagesScience Grade 9 Learning Activity Sheets on Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsAngel88% (8)
- Air We BreathDocument2 pagesAir We BreathLorraineNo ratings yet
- Science Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument13 pagesScience Respiratory and Circulatory SystemElisha Kate AmitNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Respiratory TractsDocument2 pagesRespiratory TractsMervis ChandaNo ratings yet
- A New BookDocument8 pagesA New Bookapi-327183872No ratings yet
- Science 9 Week 1 and 2Document6 pagesScience 9 Week 1 and 2Cherry Beth PagenteNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesScience Reviewer - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemMaribeth Villanueva100% (2)
- CVS&RespDocument8 pagesCVS&RespmaniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemchacameroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs: How They WorkDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Lungs: How They WorkMayownski TejeroNo ratings yet
- Breathing Process PDFDocument3 pagesBreathing Process PDFDianeNo ratings yet
- Topics To Read While On DemoDocument3 pagesTopics To Read While On DemoAmelia Angelisa CatimbangNo ratings yet
- 025735919Document3 pages025735919Vinz JaneNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System Aniket DasDocument11 pagesHuman Respiratory System Aniket DasChep KepNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: PHYSIOLOGY-the Branch of Biology That Deals With The Internal Workings ofDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: PHYSIOLOGY-the Branch of Biology That Deals With The Internal Workings ofshonievin100% (2)
- RespirationDocument8 pagesRespirationAwn Tarek AmmariNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMDocument13 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMANAMAZING CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Dayacus, Nicole T.: Prof. Irene Aquino: Beed 2B: Topic 6 TsegDocument3 pagesDayacus, Nicole T.: Prof. Irene Aquino: Beed 2B: Topic 6 TsegNicole VerdaderoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System OverviewDocument19 pagesRespiratory System OverviewTsume ShoutaroNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiratory Systemwilmarmendejar02No ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and the LungsDocument21 pagesHuman Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and the LungsEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Chapter II - Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesChapter II - Respiratory SystemIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Ii Anatomy+and+physiologyDocument2 pagesIi Anatomy+and+physiologybillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesThe Respiratory SystemNada RonaldNo ratings yet
- 34-2 Respiratory SystemDocument19 pages34-2 Respiratory Systemnancie8No ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: Mouth and NoseDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory System: Mouth and NoseKyle NoolNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System in Human BeingsDocument11 pagesRespiratory System in Human BeingsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY Study Lower Respiratory TractDocument3 pagesANATOMY Study Lower Respiratory TractLP BenozaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: What Is Respiration?Document25 pagesRespiratory System: What Is Respiration?Perla AlejandresNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory Systemcharamina13No ratings yet
- Respiratory System BpeDocument2 pagesRespiratory System BpeRam AugustNo ratings yet
- Review in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryDocument3 pagesReview in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryElvie Jane P. MolatoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemUzumaki Naruto (NARUTADIKS)No ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument17 pagesCardiopulmonary ResuscitationRisavina Dorothy CondorNo ratings yet
- LungsDocument5 pagesLungsTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesRespiratory SystemSudip NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument11 pagesAnatomy of The Respiratory SystemHaris MunandarNo ratings yet
- ANCFGBLOODBANK 0216 FinalDocument5 pagesANCFGBLOODBANK 0216 FinalShan AhmadNo ratings yet
- HUMAN-ORGAN-SYSTEM, RR11Am (LEC) 2021-NCMC101 (Pelausa, Joel C.)Document19 pagesHUMAN-ORGAN-SYSTEM, RR11Am (LEC) 2021-NCMC101 (Pelausa, Joel C.)Joel PelausaNo ratings yet
- Changes in Different Health Dimensions During AdolescenceDocument1 pageChanges in Different Health Dimensions During AdolescenceJinky Verano CortezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Blue BoxesDocument19 pagesUnit 2 Blue Boxesstarblue265100% (1)
- Roles of Hormones in Menstrual CycleDocument17 pagesRoles of Hormones in Menstrual CycleLeena Muniandy100% (1)
- NeuroDocument317 pagesNeuroNela Popa100% (2)
- JPAC (/) : 3.3: Blood ProductsDocument12 pagesJPAC (/) : 3.3: Blood Productsanwar1971No ratings yet
- Dragons Touch - Weaknesses of HumanDocument6 pagesDragons Touch - Weaknesses of Humanprakharmishra902No ratings yet
- Orthodontics - Preparatory Manual For Undergraduates - E Book PDFDocument1,384 pagesOrthodontics - Preparatory Manual For Undergraduates - E Book PDFJustin Kimberlake64% (14)
- Trans Chapter 16Document5 pagesTrans Chapter 16رجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- COMPLICATIONS OF ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERYDocument38 pagesCOMPLICATIONS OF ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERYFebryantiPBundaayabariqNo ratings yet
- Matrix Gel System PDFDocument49 pagesMatrix Gel System PDFArchi Claresta AprilinoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1Document6 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1warren macraisinNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Parts and FunctionsDocument3 pagesDigestive System Parts and Functionsshindou ai67% (3)
- Coreection Du TD D'anglais 21-22Document13 pagesCoreection Du TD D'anglais 21-22Issouf BertheNo ratings yet
- 4 - TissuesDocument103 pages4 - TissuesAngel Alexis BiasonNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Test Cranial Nerve I: OlfactoryDocument2 pagesCranial Nerve Test Cranial Nerve I: OlfactoryjisooNo ratings yet
- Kamila HarDocument3 pagesKamila HarIoana Maria DănilăNo ratings yet
- Class HolothuroideaDocument2 pagesClass HolothuroideaSecretsoushiNo ratings yet
- Ethier Introductory Bio Mechanics From Cells To Organisms Cambridge 2007Document545 pagesEthier Introductory Bio Mechanics From Cells To Organisms Cambridge 2007hoplala100% (1)
- MBBS Assignment on Histology of Spleen and Lymph NodesDocument3 pagesMBBS Assignment on Histology of Spleen and Lymph NodesAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System LabDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System Labapi-253801731No ratings yet
- Endocrine System Chapter SummaryDocument6 pagesEndocrine System Chapter SummaryShiny ChenNo ratings yet
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypertension PathophysiologyTiffany Blanca Evangelista RaiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory Systemtarunesh1No ratings yet
- Treatment TimingDocument35 pagesTreatment Timingramya0% (2)
- Molar UprightingDocument8 pagesMolar UprightingNguyen AnhNo ratings yet
- Nakamura IIDocument10 pagesNakamura IIMairaMaraviChavezNo ratings yet
- Bases Neurobiologicas Dificultades Aprendizaje PDFDocument5 pagesBases Neurobiologicas Dificultades Aprendizaje PDFMacarena MartínezNo ratings yet
- Chronic Hyperplastic PulpitisDocument30 pagesChronic Hyperplastic PulpitisGlory Pohan67% (3)