Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Betting System and Method (US Patent 7206762)
Uploaded by
PriorSmart0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
396 views10 pagesU.S. patent 7206762: Betting system and method. Granted to Sireau on 2007-04-17 (filed 2001-01-17) and assigned to Regent Markets Group Ltd.. Currently involved in at least 1 patent litigation: Regent Markets Group, Ltd. v. IG Markets, Inc. (Illinois). See http://news.priorsmart.com for more info.
Original Title
Betting system and method (US patent 7206762)
Copyright
© Public Domain
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentU.S. patent 7206762: Betting system and method. Granted to Sireau on 2007-04-17 (filed 2001-01-17) and assigned to Regent Markets Group Ltd.. Currently involved in at least 1 patent litigation: Regent Markets Group, Ltd. v. IG Markets, Inc. (Illinois). See http://news.priorsmart.com for more info.
Copyright:
Public Domain
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
396 views10 pagesBetting System and Method (US Patent 7206762)
Uploaded by
PriorSmartU.S. patent 7206762: Betting system and method. Granted to Sireau on 2007-04-17 (filed 2001-01-17) and assigned to Regent Markets Group Ltd.. Currently involved in at least 1 patent litigation: Regent Markets Group, Ltd. v. IG Markets, Inc. (Illinois). See http://news.priorsmart.com for more info.
Copyright:
Public Domain
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
«2 United States Patent
Sireau
2
US 7,206,762 B2
Apr. 17, 2007
(10) Patent No.:
45) Date of Patent:
sy
AND METHOD
(73) Inventor: Jean-Yves Sirean, Hong Kong (HK)
(73) Assignee: Regent Markets Group Ltd,
Cyberjaya (MY)
(7) Notice: Subject o any disclaimer, the term ofthis
pateat is extended or adjusted uader 35
USC. 1540) by 1176 days
(21) Appl. No. 097764,778
46325
4641
46328
32000 Vig 705-400
52004 Lallemant 70093
FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS
wo Wossos) ——TI997
wo Woon wip99
WO WODDTIID. KIB
OTHER PUBLICATIONS
Ext Receives Financial Being Licease, PR Newswire, Feb. 18,
(22) Fil: Jan, 17,2001 eae
Engen Pal Of, feisty of Een pt eliion
6) Prior Publication Data ‘No. 00 302 $301-1238, jun. 6, 2003, 57 pages.
US 20010032169 A1 Oa. 18,200 oe
(20) Foreign Application Priority Date Primary Exominr—logishN Patel
aoe tosorsao 74) Atornes, Agent, o Frm—Sioel Rives LLP
‘Ape 27, 2000 (GB) 102107 Gy apsTRAcT
Gh) we
06g 400 (200601) Blac be nen opener
roses oPeable to atcep parame inp bya usr ad eating 1
eu Se TWS/3T; TOSH463; 70526 edolds bet on an aspect of a financial market; and a
(58) Field of Clasifaton Seach ae a eee
a6s26 ceming a finan ns
‘See application file for complete search history. Rancher ie raped ee aed el
9) References Cited of the parameters input by the user and the dita obtained
frm te dit fos
US. PATENT DOCUMENTS
S709785 A 51998 Rowse 46 80 Claims, 1 Drawing Sheet
Un Teminis3
|
Fond te 4d ;
atte] Haat |
ae]
Farm]
coms
commie Newer |
(se |
csingantine | __[ PSone |
am es peesig mie ne
be |
‘alba
stg Fc 8
commas =
Toa cen
[
co
Sunt Naga
‘oer
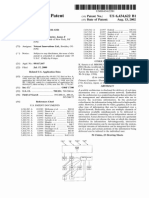
U.S. Patent Apr. 17,2007 US 7,206,762 B2
FIG. 1
r..Ct™~CSY
User Terminals 3
Financial Markets, |
I
Real-Time
Historical
Data Feed $
Second Data
Communications
Network 4
\Data Feed 6
First data
Communications
Network 2
‘Payment
System 9
Central processing machine 1 Data Storage |
[—| Facility 7
I
Third Data
‘Communications
Network 10
‘Accounting
System 11
“Archival Data
Storage Facility 8
Fourth Data,
Communications
‘Network 13
Management
Terminal 12
US 7,206,762 B2
1
BETTING SYSTEM AND METHOD
RELATED APPLICATIONS
‘This application cloims priority from European Patent
Applicaton No. 003025301, filed Ma. 28, 2000, and UK
Patent Application No. 001027017, fed Ape. 27, 2000.
BACKGROUND
“The present diselosure relates to a betting system and
‘method for buying and selling of fixed-odds financial bets
‘Although betting in maay diverse forms has beea in
existence for thousands of years, the concept of a bet onthe
futuee performance of one or more financial market indiea-
torsisa relatively recent one. Such et may tke ne of two
forms, as willbe described.
‘The first form of such a bet (the “spread bet") is one
‘which, ifwon bythe making ofa correc prediction, pays out
sum proportional tothe market Muctuation. For instance, a
speculator may bet that a given stock will fll within a set
period of time, and, if this prediction is corret, may receive
‘Winnings in direet proportion to the amouat by whicl the
stock fas fallen in that period of time.
‘The oer form that such a bet may take is known asthe >
“digital option". Digital bes are of the same form as a
traditional sporting bet in that the speculator predicts a
certain event and receives either a fixed sum of winnings iE
‘that event does occur) or no winnings (ithe event doesnot
‘ceur).Forinstanee, a speculator may bet hata certain stock
index will rise to a certain level by a certain time. Ifthe
‘named index does reach this level, the speculator wins an
‘greed amount of money inrespective of any amount by
\hich the iadex has exceeded the predicted level. It is this,
type of bet that i known asa “fixed odds” bet
However, problems face the individual investor who
wishes to place bots on the financial markets, The wide
‘universe of financial instrments and derivatives products i
typically available ony to professional investors who bave
the financial resources and know-how to access these pro
vt.
Problems also face the bookmaker who wishes to offer
financial bes tothe private investor. These include the fact
that financial bookmaking is labor-intensive, with skilled
staff boing required constantly to adapt the dds offered on
‘an immense variety of possible bets to market conditions
that are changing on a ssinute-by-minute basis,
The average sizeof abet placed by an individval customer
‘will, in general, be very small compared to the average size
of atypical stock market direct iavestment. The potential
profit 1 the bookmaker from sueh small investment ill,
therefore be too small fr it to be evonomically viable to
employ skilled staff to calculate the odds to offer to indi-
vidual speculators sulfciently quickly.
A further problem facing bookmakers is that it is very
ificlt to accurately price complicated or unusual bets, nd
‘bookmakers typically offeronly’a few standard bets ona few
markets,
‘A need exists for a system and method that alleviates
some ofall of the above problems, and which enables a
bookmaker eficienly to offer a wide eange of financial bets
to speculators wishing to place relatively small bets:
SUMMARY.
According to first embodiment, a fixed-odds beting
system comprises a user terminal openble to accept para
x“
8
s
2
ters, input by a user, relating to 2 fixed bet on an
aspect of a financial marke; and a conta processing
‘machine having data feed toa source of data concerning
a financial market and means operable to calculate the ied
‘os forthe bet, base om at feast some ofthe paramcters
fnput by th user and the data obtained fromthe data feed
Aantageously, the user terminal may be operable t
receive and display the odds calcolstad by the central
processing machine
Preferaby, the data fet the source of data concerning
the fancal market comprises at leat a dita feed 10
realtime information concerning the financial markt. Con-
‘venient the data fet the source of data concering the
financial marke may comprise data fed to historical data
concerning the financial market. Advantageously, the data
food is connecied to the source of data concerning the
financial market over a fst data communications netork
Profrably, the fist deta communications networks the
lnvemat oa leased line. The cental processing machine
‘ay bave at least one other daa fed Wo a source of data
concerning one or moe eter financial markets
‘The wserteminal andthe centel processing machine are
preferably connected to one anner via second data
communieations network sucha the Interne
Convent the sytem muy fer comprise payment
system fr dedting payment forthe bet fom the we, he
‘mechanism being linked to the ental processing machine
“The payment system for deducting payment frm the user
say include an E-cash or crit cir payment system.
‘The system may fuer comprise an secountng system
linked to the cenel processing mschine anda management
teminal openble provide information reirding the
operation ofthe Beting system to an administrator thereo.
Advantageously, the parameters for calculating the ods
‘ay include one of more of the following: the relevant
financial marke: the amount tha the user wishes tobe or
the amount thatthe user wishes to win; and one oF mare
ari o target level
‘The system may furher comprise @ storage faiiy for
storing information relating to bes. The etal processing
amschine prfrably inludes means to retrieve information
stored in the storage faciiy, and provide information to a
‘scr cating fo bet proviusy placed hy the see
Preferably, the central processing machine ‘includes
‘means to calculate a price at which to ofc to purchase the
previously placed bet frm the user and to display the price
Calculate by the eental processing machine
In another eubodineat, 2 method of operating a fixed
cds bting system including a cena proessing machine
in communication with a data feed to @ source of dita
concern financial navel, and ower ternal in com-
‘munication with the central processing machine, comprises
accepting fom a user parameters relating 10 ixo-adds bot
oman aspect of fn market receiving one or more of
the parameters at the central processing machine; obsining
data conceming the financial market via the data fod: and
te central processing machine caeulating a fxe-odds
ic forthe bet based on at east one af the parameter input
by the user and the data obtained from the data fed
The metbod may father comprise the steps of displaying
the calculated eds to the user and deducting of receiving
payment from the wer for placing the bet
Preferably, the step of receiving one or more parameters
from the user inclodes the step of receiving infomation
relating to one or more of the following? the relevant
US 7,206,762 B2
3
financial market; the amount that the user wishes to win oF
the amount that the user wishes to bet; ane one or more
barrier or anget levels
“The step ofobiining data concerning he faancial market
‘may include the step of obtaining real-time data relating to
‘one or more of the following: market prices; option quotes,
interest rates and dividend yields,
“The step of obtaining daia concerning a financial market
‘may include the steps of obtaining historical data relating to
‘market prices.
Preferably, the step of calculating the fxed-ads price
‘comprises the step of calculating an estimate ofthe future
volaiity ofthe financial marke.
Conveniently, the method may further comprise the steps
of ehecking the parameters input by the user for logical
inconsistencies therebetween and checking the opening
times ofthe financial market
Preferably, the method further comprises the step of
providing at Teast one other data feed 10-2 source of data
‘concerning ane of more other financial markets.
Conveniently, the step of receiving parameters from the
ser preferably includes the step of receiving parameters
relating to an aspect of the one or more other financial
markets
vo
‘Advantageonsly, the step of calculating the fixedodds *
price for the bet preferably includes the step of calculating
concation matrix containing information concerning the
‘nancial market and the one of more ther fsancial markets
Preferably, dhe system fuser comprises the sep of pro
viding a storage facility, accessible by the central processing
‘machine, for storing information relating to bets,
Conveniently, the step of calculating odds includes the
step of calculating a hedging factor based on information
‘concern previously placed bets obtained from the storage
facility. The method may farther comprise the steps of: (1)
calculating, at the central processing machine, a price at
‘which to olfer to buy a previously placed bet fom the user,
ana proving the price tothe user via the user terminal
In yet another embodiment,» computer program com-
rises computer program code means adapted to: receive
fone or more parameters from a user relating t a fixed-odds
bet on an aspect ofa financial market; obtain data concem-
ing a financial market via a data feed, and calculate a
fixed-odds price for the bet based on at lest one of the
parameters input by the user and the data obtined from the
data feed, The computer program may be embodied on a
computer readable medium or otherwise operable on a
compute,
In sill another embodiment, central processing machine
having a data feed toa source of data concerning 2 financial
:matket is operable to calculate fixed os, based on param
ters input by a user and data obtained fom the data fed
Conveniently, the data feed to the source of data concem-
jing the fizancial market may comprise a data food to
real-time information concerning the financial market,
Advantageously, the data feed to the source of data
‘concerning the financial market may comprise data feed to
at least historical data conceming the financial market
Preferably, the data feed is connected to te souree of data
concerning the financial market over a first data communi
cations network such asthe Internet oF 2 leased line.
‘Advantageously, at least one other data feed may be
provided tea source of data concerning one oF more other
Tinancial marks,
‘The central processing machine may’ further comprise 3
storage facility for storing information relating to bets
s
4
‘The central processing machine may aso have means to
caleulate a price at which to offer to purchase a previously
placed bet from the user.
Advantageously, the central processing machine may
further comprise a management terminal operable to display
information regarding the operation of the betting sytem to
‘an administrator thereo.
Additonal characteristics and advantages will be appar-
cnt trom the following detsiled description of prefered
embodiments which proceeds with reference to the aecom-
paying drawing,
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
FIG. 1 shows a schematic layout ofthe components ofa
‘rating system in aecordance with 2 prefered embodiment
othe present invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED.
EMBODIMENTS,
With reference to FIG, 1, a central processing machine 1
cof a betting system in accordance with a preferred embodi-
‘ment comprises a server running a server operating system
A computer program embodying an aspoct of the beting
system is loaded onto the cental processing machine 1, a8
will be described in greater detail bel.
The central pressing machine 1 is linked vi a fist data
‘communications network 2 oa plurality of wer teinals 3.
Preferably, the fist network 2 is the Internet. The user
terminals comprise PC's, or other suitable machines, ran
fing an appropriate operating system to interlace” with
prospective customers, for inslance a Windows or UNIX
{ype operating system,
“The centeal processing machine 1 is further connected via
second dita communications nesvork 4 1 two data feeds,
‘one of which isa data feed § toa source of realtime market
information, and the other of whichis a data feed 6 to a
source of historical market information. Preferably, the
sacond network 4 s the Internet or a leased ine. Examples
of real-time market quotes data feeds are those provided by
financial information providers such as Reuters, Bloomberg,
‘Bridge, DBC, etc. The primary requirement for this data ink
is that it shouldbe real-time, which isto say thatthe quotes,
retrieved via the data Tink are up-o-thesecond realtime
market quotes.
‘The betting system of FIG. 1 further comprises a data
storage facility 7, comprising a file server operable to store
information conceming placed, pending and expired bets on
‘one of more disks. The data storage facility is connected to
anatchival data storage fcilty 8, which is operable to retain
information oa a plurality of apes or oer long-temn storage
medi
The betting system inchodes an E-cash or ereit card
‘payment system 9, which is inked tothe central processing
‘machine I by a third data communications aetwork 10, Aa
accounting system 11 is also included in the betting system,
this accounting system being direty linked to the een
processing machine 1
‘A management ternal 12 also comprises part of the
betting system. This management terminal 12s linked tthe
central processing machine I via a fouth data communica
tions network 13, which is preferably th Internet
Tn operation, an individual users able to log on tow user
terminal 3 for the purpose of placing a fixed-ods financial
bet. user-id and password, provided (othe individual by
the administrator ofthe betting system, may be required to
US 7,206,762 B2
5
4 so. In practice, the user terminal 3 may comprise a
edicated temninal in a public betting fecilty, or may
alternatively comprise the user's own PC.
‘When the wser attempts to log on to the betting system at
the user terminal 3, the user terminal 3 connec to the
central processing machine 1 via the first network 2. Ifa
password is raquired, the password must be accepted by the
central processing machine I before the user is allowed to
log on to the betting system,
“The user is now able to place a fixed-odds financial bet
using the betting system. The user teminal 3 presents the
user with a suitable interfoe for doing so, this interface
‘comprising & numberof menus othe lke through which the
‘user may navigate to glean information or select bet param
ers. Bet parameters thatthe user may select may include,
among other: the financial marke(s) upon which the bets
to be based (for instance a foreign exchange rate); the
‘amount thatthe user wishes to bet or the amount that the user
wishes to win; or one or more baricr or target levels
(cating to market performance) which seta threshold for
the financial market parameter being monitored, Once the
‘bet parameters are devided upon hy the user, these param
fers are submitted tothe central processing machine I via
the frst network 2
“The fist step performed by the ceatml processing ”
‘machine 1 upon receipt of the bet parameters fom the user
terminal 3 is to ascertain whether or not the bet defined by
the bet parameters is within reasonable reach of current
‘market prices. In order to decide whether or not this isthe
case, the central processing machine 1 gathers information
concerning the current markt prices fom the data fed $10
the souree of real-time market information. If the data
derived thereftom indicates that there is na realistic possi=
bility ofthe market price changing with the rapidity required
by the bet, then the central processing machine 1 will reject
the bet
[Next the bet parameters put by the user are checked by
the central processing machine 1 for logical inconsistencies,
and the bet is rejected if'such inconsistencies are found 1 be
presen. For instance, if @ user has input bet parameters
defining a bet that a certain financial index will remain
‘erwoen a high value of 110 and a low value of 120, the
central processing machine 1 will determine thatthe het is
logically inconsistent and reject te bet.
A further step performed by the central processing
machine 1 on receipt of a set of bet parameters from user
terminal 3 isto check the opening times of the relevant
financial markets. The cetral processing machine 1 has, for
‘his purpose, a link oa source of information containing the
‘opening hours and public holidays of all ofthe markets upon
which bets are offered. Ifa user is allowed to et upon the
performance of a market during @ period for which that
‘markets closed he user gains an uafir advantage and thus
such a bet would be rejected
Once it as been established by the eental processing
‘machine I thatthe bet parameters input by the user define 3
valid bet, the next step isto determine the real-time ra
‘market valves from which to calculate the price of the bet.
Inorder todo ths, the centeal processing machine | accesses
the data foed Sw the source of real-time market information,
‘The data derived thereftom may include current market
prices, option quotes, interest rate levels, dividend yields (in
the case of stocks or stock indices) or carving casts (e.,
storage, delivery or insurance costs inthe case of commod
ties) The central processing machine T may also access the
data feed 6 to the source of historical market infomnation,
s
6
and the data gathered therefrom may include historical
closing prices for the relevant markets
(Once a set of valid bet parameters have been received by
the conta processing machine 1 and the relevant infoma-
tion has been gathered from the data feeds 5,6, the central
processing machine 1 uses the information to caleulate the
‘dds that willbe offered to the user forthe bet.
‘The first step in the process isto calculate the implied
volatility ofthe or each market ypon which the bets based
‘The volatility ofa markets defined as the amount by whieh
the market fluctutes during a given period, and is often
defined as the annualized standard deviation of the natural
Tgarithm ofthe price retums ofthe dey closing values of
the market
‘The implied volatility is the market volatility thatthe
listed options market implies forthe fiture, market volatility
being a major fctor in the determination of the price of an
‘option. Ifthe price of the listed options relating to a given,
‘market for a piven time period is known, this FIGURE can
‘oe reverse-engincerd to calculate the future volatility of the
‘market implied by that option pice, Various techniques exist
for this reverse engineering operation, the most comatoaly
vwsed of which is an algorithm based on the Black and
Scholes option priciag model, however the skilled person
will ealize that any of several alternative algorithms may be
sed instead
‘A standard option priciag model such as the Black and
Scholes model assumes thatthe facial markets fallow a
{og-normal dstibution. This assumption does not, however,
accurately reflect the market panies (like the 1987 stock
‘market crash), which occur witha higher requency than
‘would be expected in a purely lognormal distribution. To
adjust forthe “fatter tls" ofthe real distribution of market
returns, the concept of “volatility smile” is introduced,
‘whereby options with diferent strike prices trae at diferent
implied volailities. Options wit different expiry dates also
trae at different implied volatilities, reflecting diferent
expectations of markot volatility over differen ime poriog
Since there wil likely not be any option with exactly the
sume expiry date and target price as the bet, interpol
‘ill bused to arrive a the best estimate ofthe voat
the bet
To calculate the volatility to be used to price the bet,
options prices are gathered from the data feed § to the
real-time source of market information. The implied vola-
lites ofthe options with strike prices closest othe bartier
for target level ofthe be, and with expiry dates closest tothe
‘expiry date othe bet, ae computed, These implied volatility
poiuls are then interpolated oareve atthe implied volatility
‘most appropiate for the expiry date and barrier or target
level ofthe bet (if the bet has several barir or target levels,
the Kevel that will lad tothe highest selling price for the bet
‘may be nsed) This interpolated implied volatility is used by
the central processing machine Ito calculate the odds forthe
bat
Tis also necessary for the cental pressing machne 1
to take into account the grow of the market oF markets in
question. In order to derive this valu, the intrest rate and
‘other components of the carrying cost for each market
(extracted from the data feed $ to the real-time source of
‘market information are required. For stocks or stock indi-
2s, the growth ofthe market is typically approximated as
‘being te interest rate minus the annualized dividend vio
Ina similar manner to that deseribed above, the interest ite
for an arbitrary time period may be estimated by interpo-
lating between the deposit rates for earlier and later matu-
‘ie o arrive at an appropriate value. For foreign exchange
US 7,206,762 B2
1
‘ates, the grow rates defined as the diference between the
{epost rats in each currency and for other markets such as
commodities, the growth rate incorporates factors such as
storage or dlivery costs, and insurance fees
A complex bet may involve predictions on the perfors s
smanees of several diferent markets, and if such a bet is
placed then correlation muti for these different markets
will need to be computed. Such a conlation matex is
computed by calculating te correlation coefiients of the
relevant markets over a period of historical data cbtained_ 10
from the data feed 6 t0 the source of historical market
information. Ideally, this time period isin proportion to the
Tength of the bet
Once all ofthe necessary information has been gathered
‘or computed by the ceatral processing machine 1, the cena
processing machine I proceeds o calculate the odds forthe
bet defined by the bet parameters, There ae various ways in
\which this may be performed for each type of bet that might.
be placed by the user. Common bets that might be placed
include:
‘an “upidown" bet that a given market will be above oF
below a given level on a given date;
‘an “expiry range” bet tata given markot will be between
two given levels ona given date
a “rainbow” bet, which is essentially a mulkimarket >
expiry range bet;
‘a bullseye” bet that a given market will have an exactly
sven value on a given date:
“one-touch” bet that a given market will touch a given
barrier level at some point before the expiry of the bet,
“noctouch” bet that given marke wll ot tonch a given
barrier level at any point before the expiry of the bet,
‘a“range” bet that a given market wil touch neither of wo
ativen barier levels at ny point before the expiry ofthe bet
“double onetoveh” bet that a given market will touch
both of two given barrier levels at some point before the
expiry ofthe bet:
a “win”, “place” or “show” bet that a market will be
respectively the best, or within the top two best, oop three
‘ost, performing markets (in percentage tems) over a given
period; and
‘a “quinella”, “tierce” or “extota” bet defined from their
rctrack equivalents.
An example of how the price of an expiry range bet might
be caleuated is as follows
‘The formula forthe underiying asset price S is given by:
aS-mssie
8
where ms the grow rate, sis dhe volatility, tis time and
isa variable that follows a Wiener process. The variable 7
‘can be understood by considering the changes in the value
thereof over small intervals of time. Consider a small
interval of time having a duration of dt and define das the
change in during dt. There ae two basi properties that dz
‘must have for2 to he following a Wiener process:
dz must be related to dt by the equation
where € isa random drawing from a standantized normal
istribution (Le, a normal distibution with a mean of 270
and a standard deviation of 10), and the values of dz, forany
to diferent shoe intervals of time dt, must be independent.
Solving this equation, we obtain
«
SiS eager d¥4e00)
8
‘where S( isthe asset price at ime tan S isthe initial asset
price
Lot p be the probability of success ofa bet in this model at
‘expiry time t, Te present value ofthis bet thn hecome:
Prescre
where Ps the present value (oF fair price) of the bel isthe
interest cate, and ti the time to maturity. We denote:
slo
and
‘whore S(t) is the asst price atime isthe time to maturity,
S is the intial asset price, r is the interest rate, g isthe
dividend rate ands is the volaiity.
‘Then, he variable x is defined as
Xow
and is normally distributed with probability density:
mde
tw eat
woe fie
where N(x) is the cumulative probability of the normal
distibution, Let S be the inital market price, and let
eee)
‘where UT and D are the up and down bartiees of the bet
respectively. The peice of the expiry ange bet, defined by U
and D, is then given by:
Gebel
Other formulae for different types of bets may realy be
derived by emplaying the same principles, The type of
forma employed is also not essential to the working ofthe
system—many different methods of caleulating odds exist,
fad any ofthese may’ be use ia the system,
US 7,206,762 B2
9
(Once the price ofthe bet defined by the bet parameters
input by the user is determined, a house mark-up is added
‘and the bet is offered to the user via the user teminal 3,
Since te systom operates on real-time values derived from
the constantly fluctuating markets, the customer is allowed
only a shoct time in which to decide whether or not to
purchase the beta the calculated price. This time period is,
preferably, no more than thisy to sixty seconds, andthe olfer
4s withdeawn after this time.
the user decides vo purchase the bet, he or she will be
prompted to input a username and password (if these were
‘ot input at an earir stag). This information is verified by
the central processing machine 1 and i itis accepted, will,
check the credit balance of the user onthe accounting system,
11, If this reveals that the user has sufficient funds 10
purchase the bet, the transaction with the usr i effected nd
the bet is recorded on the data storage facility 7.
Fach user ofthe system may, on entering his or her valid
‘username and password, view a ist of oustanding bets that
he or she has placed ona user terminal 3. In onder to provide
this list the central processing machine 1 recieves infor.
‘mation regarding the user's previously placed bets from the
ata storage facility 7. The central processing machine 1
snus, for each previously placed bet, determine whether the
bet has: already expired or flilled the conditions ofthe bet.
0 thatthe user has won the bet; sleady expired or cont
‘vened the conditions of the bet so that the user has lost the
bets or has aot yet reached the date or conditions af expiry.
‘The central processing machine 1 derives this information
‘by comparing the bet parameters with both real-time market
information and historical market information for the rel.
‘evant time period obtained via the data feeds 8, 6, The status
‘of each previously placed bet is passed tothe ser terminal
3 for display to the use. IFthe user has won any ofthe bets,
the central processing machine 1 insiicts the accounting
system IT to credit the user's acconnt accoedingly
‘The system may also be provided with a facility to offer
to buy an unexpired bet back from the user. The price that.
is offered for a bet is calelated by fist determining the
value ofthe bet using similar techniques to those desrbed 40
above, witha house mark-up being included in the price. As
eseribed above, the user is given no more than thiety to
sixty seconds to decide whether or aot to aecept the price
offered before the offer is withdrawn.
All of the wansactions between the senttal processing
‘machine 1 and the users ofthe system may be monitored by
an administrator of the system athe management terminal
12. This facility allows the administrator to ensure that the
system is running smoothly and thatthe algorithms and/or
‘models employed by the contal processing machine 1 are
producing appropriate resus
‘Asa frther consideration, the administrator of the system,
:may’be concemed about his or her financial exposure athe
system may accordingly include means to inform the admin
istrawr, in real-time, of the financial exposure via the
‘management terminal 12. This facility allows the adminis-
trator to “hedge” in the futures and options markets, There
are four types of hedging ratio commonly used, namely the
ela, theta, gamma and vega hedging ratios. These ratios,
along with the appeopriate hedging echnigues, are well
‘known in the ar.
In an altomative embodiment, the E-cash or credit card
payment system 9 is replaced by a system that operates with,
“viral” or “fantasy” money instead of real fund. In such
an embodiment, betors are allocated an initial amount of
“fantasy” money to purchase bets, Suevessfl bettors ave
the chance to win prizes or ober benefits
10
As a further consideration, whether or not the payment
system comprises real or fantasy” money, the administrator
of the system may wish 10 ack the bettors who are
consistenily successful at forecasting the direction of the
5 financial markets, The wministator knows that under the
assumption of efficent markets, no person may consistently
forecast the financial markets, and therefore succesful et-
tors are simply those that have beea suocessfl by chance
However, tracking successful bets may provide useful
10 information forthe administrator, such as useful elves for
‘wocking down problems with this embodiment. The admin
istrator may also sell or provide the information comprised
ofthe ongoing bes of the sucessful bettors, o third partes
‘who may choose to use or rely upon this information onthe
1 elif thatthe succesful bettors have a special gift rather
than being simply lucky.
‘The betting system for caleulating the fixed-price odds
that may be offered to a prospective bettor is particularly
‘well-suited to bets placed on the financial markets since the
2 calculation of fixed-price okl is suliciently dial, time
consuming and computationally intensive o make caleula-
tion thereof by humans inefficient forall but the largest of
bots. The systom described herein allows an administrator of
the system to offer reasonable and well-alculated odds in
reabtime to individual speculators beting small sums of
‘money on an almost unlimited number of eventualites,
‘without the need o employ highly-skilled staff to do so, This
servie has not been available in the past
will be obvious to those having skill inthe at that many
‘changes may be made to the deals of the above-described
cembodiments without departing fom the underlying pein-
ciples theroof, The scope of the preset invention should,
therefore, be determined only by the following claims,
“The invention claimed is:
1. A method of operating a fixed-odds betting system
including a cena processing mochine in communication
wit a data feed o a soure of data concerning a financial
‘market, and a user terminal in communication with the
central processing machine, the method comprising the steps
of
Via the user terminal, accepting from a user multiple
parameters relating toa ixed-odls hot on an aspect of
‘financial market:
at the central processing machine, receiving one of more
of the parameters from the user terminal;
atthe central processing machine, obtaining data coacem-
ing the financial market via the data feed;
at the central processing machine, calculating a fhxed-
fodds price for the bet based on at least one of the
parameters ceived from the user terminal and the dsta
obtained from the dat feed; and
communicating the fixed-odds price to the user.
2. A method according to claim 1 further comprising
displaying the calculated fixed-ods price to the user.
3. A method according to claim 1, father comprising:
receiving an authorization from the user to place the bet
‘and
receiving a payment from the user foe placing the bet.
4, A method according to claim 1, futher comprising:
placing the bet; and
crediting an account ofthe user in response to uctation
of said aspect of the fiancial market satisfying the
parameters ofthe bt.
5, A method according to claim 1, wherein the step of
obiaining data concerning the financial market includes
biasing eeul-time data
s
US 7,206,762 B2
aT
6.4 method according to claim 1, wherein the step of
obiaining data concerning a financial market includes
oblaiaing historical data representative ofa history of mar
et prices.
7. A method according to claim 1, wherein the sep of $
calculating the fixed-odds price comprises calculating an
estimate of a future volatility of the financial marke.
8. A.method according to claim 7, whercin:
the sep of obtaining data concerning the financial market
inlides obtaining real-time data concerning the finan-
cial marke; and
the step of caleulating the estimate ofthe fature volatility
‘ofthe fmancial market is at eat partially based on the
realtime data
9, A method according to claim 1, futher comprising:
befor: calculating the fixeddds price, checking the
parameters input by the user fr logical inconsistencies
therebetween,
10. A method according to claim 1, further comprising:
‘before calculating the fxed-odds pice, checking an open
ing time of the fnaneial market
11, A method according to claia 1, wherein
the central processing machine is in communication with,
‘a second dala ead to a source of data concerning a
second financial market different from the financial *
market and
the step of receiving parameters from the user terminal
includes receiving parameters relating to an aspect of
the second financial market.
12. A method secording to claim 1, wherein:
the ceatral processing machine i in communication with
1 second data food to a source of data concerning &
second fnancial market different from the financial
smarket; and
the step of caleuating the fixed-adds price for the het
includes calculating a conelation matrix containing
information concerning the financial market and the
second financial market
13. A method according to claim 1, wherein the system
further includes a data storage facility accessible By the
central processing machine, and furter comprising storing
in the daa storage facility information eating to previously
placed bes
14. A method according to claim 13, fuer comprising
reading from the data storage failty the stored information
relating to previously placed bets, and wherein the step of
caleulating the fixed-odds price for the bet includes ealeu-
lating» hedging factor based on te information concerning
previously placed bets read from the storage facility
15, A.method according to claim 13, futher comprising:
at the central processing machine, calculating a price at
which to oll to buy one or more of the previously
placed bets
16. A method according to claim 18, further comprising
providing the price to the user via the user termi
17. Amethod according 1 claim 1, wherein the financial
‘market includes a foreign cureney market.
18, A method accorting 1 claim 1, wherein the financial
market includes a commodities market
19. A method according t claim 1, wherein the financial
‘market includes a stock market
20, A method according to claim 1, wherein the aspect of
the financial market includes change ina market index.
21. A method according to claim 1, wherein the aspect of
the financial market includes a change ina stock price
x
8
s
12
22. A method acconding to claim 1, wherein the aspect of
‘he financial market includes a change in a foreign currency
exchange ete
23. A method acconling to claim 1, wherein the step of
receiving one or more parameters from the user terminal
includes receiving an identifier of a selected financial mar
et
24, A method acconling to claim 1, wherein the step of
receiving one or more parameters from the user terminal
includes receiving information regarding an amount thatthe
ser wishes to win,
25, A method acconling to claim 1, whercin the step of
receiving one o more parameters from the user terminal
includes receiving 2 target level ofthe aspect of te financial
market.
26. A computer program embodied on a computer read
able medium and operable on a central processing machine
in communication with a data fed, for:
receiving one or more parameter from a use relating 10
a fixed-odds bet on an aspect of financial market;
obtaining dota conceming the financial market vi the
data foods
calelating fixes price for the bet based on at least
‘one of the parameters received from the user aud the
data obiined via the data feed; and
communicating the fixed-odds price to the user.
27.8 computer program according to claim 26, whercia
the step of calculating the fxed-ods price comprises cal~
culating an estimate of a fiture volatility of the financial
market
28. A computer program according to claim 27, wherein:
the data feed includes a realtime data feed: nd
the step of obtaining data concerning the financial market
includes obtaining real-time data conceming the finan-
cial market via the data feed; and
the step of calulating the fixed-odds price is atleast,
partially based om the real-time dat
29. A fixed-odds betting system comprising:
‘means for accepting bet parameters from user relating 0
a fixed-ods bet on an aspect of financial market;
means for obtaining financial market data;
means for calculating a ixed-ods price forthe fined-odds
bet based on at least one ofthe bet parameters from the
user and at least some of the financial market data
obtained; and
means for communicating the fxed-oclds price to the wer.
30. A fixed-odds beting system according to claim 29,
‘wherein at least one of the bet parameters is @ predicted
performance of an aspect of the financial market and further
comprising. means for calculating. a fixed odds for the
predicted performance ofthe financial market
31. A fixed-odds beting system aecording to claim 30,
wherein the predicied performance includes a predicted
‘Muctuation of the aspect of the financial market during abet
period of the bet.
32. A fixed-odds beting system comprising:
‘user terminal operable to accept from a user multiple
parameters relating toa fixed-ods bet on an aspect of
a financial market;
1 data feed to a source of data conceming the financial
market and
‘central processing machine in communication withthe
ata fee aad the user ternal, the central processing
‘machine operable to calculate fxed-odds price forthe
fixed-odds bet based on at Least one of the parameters
‘input by the user and data obtained fom the data feed.
US 7,206,762 B2
13
33. A system according to claim 32, wherein the data feed
includes a real-time data food to a source of real-time data
‘concerning the financial market
34. Asystom according to claim 32, wherein the source of
data conceming the financial market includes a source of
historical data eonceming the finaacil market.
35. A system according to claim 32, wherein the central
processing machine isin communication with the data feed
‘over a data communications network.
36. A.ystem according to claim 32, further comprising a
sevond data feed to a source of data concering a second
Financial marke different from the fsancil market.
37. A sysiem according to claim 36, wherein the central
processing machine is operable to compute a coalation
‘matrix for the financial market and the second financial
market.
238. A system according to claim 32, wherein the central
processing. machine is in communication with the user
terminal over a data communication network.
39. A.gystem according to claim 38, wherein the central
processing machine serves an interface to the user terminal,
And the user teminal is operable to display the interface to
the user for facilitating input ofthe parameters.
40. Asystem according to ela 39, wherein the interface
includes set of menus from which the user ean select at
least some of the parameters,
41 Asystem according to elsim 32, further comprising
data storage fxility aocessible by the central processing
‘machine the data storage fality operable for string iafor-
‘mation regarding previously placed bes.
42, A ystem acconding to claim 32, futher comprising
snultiple other user terminals in communication with the
central processing machine for accepting bets from other
users, and wherein the central processing machine is oper-
able to identity one or more successful users whose bets are
consistently success
43. \ system according to claim 42, further comprising
means for proving toa third party information concerning
bets placed by one or more ofthe succesful users.
44, system according to claim 32, further comprising 8
faciity for buying hack the fixed-odds bet from the usr.
45. A system acconling to claim 32, fuer comprising a
‘payment system in communication with the central process-
ing machine and configured to reeive a payment from the
user forthe Hixed-odd pice.
46. Asystem acconting fo claim 32, futher comprising an
accounting system inked tothe central processing machine
47. Asystem according to claim 46, wherein the ac
{ng gystem maintains an account forthe user and ered the
‘account in response to fuetustion of said aspect of the
financial market satisfying the parameters of the fixedodds
bet
48. A computerimplemented method for beting on a
‘nancial market, comprising:
presenting an interface including a set of memus for
facilitating selection ofa set of parameters fora bet;
receiving the set of parameters from a user via the
imerface;
obtaining financial market data conceming the finsocil
market
caleulating a fxed-odd price forthe bet based on the se
‘of parameters received from the user and ut least some
of the financial market data
offering the bet to the user forthe fixed-odds price: and
receiving from the user an acceptance ofthe oller and a
paymeat of the fixed-adds price,
8
s
14
49. A method according to claim 8, wherein the finan
market includes a foreign cureney market
50. A method according to claim 48, wherein the financial
‘market includes a commodities market.
1. Amethod according to claim 4, wherein the financial
‘market includes stock marke
52. A method acconling to claim 48, wherein the set of
parameters includes a change in a market index.
53. method acconling to claim 48, wherein the set of
parameters includes a change in a stock price
54. A method acconling to claim 48, wherein the set of
parameters includes a change ina foreign curency exchange
rte.
58. A method acconling to claim 48, wherein the set of
parameters includes a selected financial market,
56. A method acconling to claim §8, wherein the set of
parameters includes:
‘target fr the selected financial market:
1 second selected financial market; and
‘target fr the second selected financial market
57. A method according to claim 86, wherein the step of
calculating the fixed-odds price fr the bet includes ealeu-
lating correlation matrix for the selected fiaaacal market
and the second selected financial market.
58. A method acconling to claim 48, wherein the set of
parameters includes a bot period,
59. A metho! acconting.to claim $8, wherein calculating
te fixed-odds price comprises estimating a future volatility
of the faancil market during the bet period
60. A method acconting to elim 48, wherein the set of
parameters includes a bet expiration time:
‘61. A method accondingto claim 60, wherein calculating
the fixed-odds price comprises estimating a fue volatility
of the fmuncial market for @ period preceding the bet
expiration time,
62. Amethod according to claim 48, wherein the financial
‘market data ineludes real-time market data
63. Amethod according to claim 48, wherein the financial
‘market data includes historical market data
64. method acconling to claim 48, wherein the set of
parameters includes a target for an aspect ofthe financial
market
65. A method acconting to claim 64, wherein the target
includes a range.
(6. A method acconting to claim 64, wherein the target
includes a hair
67. Amethod according to claim 64, wherein the finan
‘market includes @ foreign euerency’ market and the target
includes a predicted currency exchange rate
68 A method according to claim 64, wherein the financial
market includes a stock market and the target includes a
predicted stock price,
69, Amethod according to claim 64, wherein the aspect of
the financial market includes a market index.
70. A method according to claim 69, wherein the financial
‘market includes a commodities market.
‘TL-Amethod according to claim 69, wherein the financial
‘market includes a stock mack.
72. A method according to claim 48, futher comprising
‘monitoring the financial market; and
in response to the financial market meeting the set of
parameters, providing a et payollt the ser.
7B. A method acconling to claim 72, wherein the set of
parameters inludes abet period and the step of monitoring
ofthe financial market ineludes obtaining market data for
the bet period
US 7,206,762 B2
15
74. A method according to claim 48, whersin the step of
offering the bot to the use involves offering the bot to the
ser fora limited time.
78. A method according to claim 74, wherein the limited
time is between 30 seconds and 60 seconds.
6. A method ccordng to claim 48, whecn:
the financial market has a growth rate; and
the step of calulating the fixe-odds price is at least
partially based on the growth rate
7A method according to claim 48, wherein the bet has
‘bet expiation time, an, after rceiving the acceptance and
the payment from the user and before the het expiration
‘ime, further comprising:
calulating a cureat value ofthe bet; and
offering to buy the bet from dhe use fra price based on
the Value ofthe bet.
16
78. A method according to claim 48, futher comprising:
storing information conceming the bet and one or more
other previously-ploced bets; and
calculating a hedging factor based on the bet and the
5 previously-placed bets.
79. A method according to claim 48, further compising:
storing predictions made by multiple betors:
‘comping te predictions o outcomes of events to which
the prodictions relate; and
identifying at least one successful bettor whose predic-
tions ar consistently similar to the outcomes
80, A method according to claim 79, further comprising
offering toa third party information comprising subsequent
predictions made by the atleast one succesful bettor
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Like Kind Card Game (US Patent 6193235)Document12 pagesLike Kind Card Game (US Patent 6193235)PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Like Kind Money Board Table Game (US Patent 6186505)Document11 pagesLike Kind Money Board Table Game (US Patent 6186505)PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Method and Apparatus For Retrieving Data From A Network Using Linked Location Identifiers (US Patent 6226655)Document22 pagesMethod and Apparatus For Retrieving Data From A Network Using Linked Location Identifiers (US Patent 6226655)PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Casing Spacer (US Patent 6736166)Document10 pagesCasing Spacer (US Patent 6736166)PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Wine Cellar Alarm System (US Patent 8710985)Document11 pagesWine Cellar Alarm System (US Patent 8710985)PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Modern Telecom Systems LLCDocument19 pagesModern Telecom Systems LLCPriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Cell Regulatory Genes, Encoded Products, and Uses Related Thereto (US Patent 7030227)Document129 pagesCell Regulatory Genes, Encoded Products, and Uses Related Thereto (US Patent 7030227)PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Intelligent User Interface Including A Touch Sensor Device (US Patent 8288952)Document9 pagesIntelligent User Interface Including A Touch Sensor Device (US Patent 8288952)PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- User Interface With Proximity Sensing (US Patent 8035623)Document15 pagesUser Interface With Proximity Sensing (US Patent 8035623)PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Multicasting Method and Apparatus (US Patent 6434622)Document46 pagesMulticasting Method and Apparatus (US Patent 6434622)PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- High-Speed Serial Linking Device With De-Emphasis Function and The Method Thereof (US Patent 7313187)Document10 pagesHigh-Speed Serial Linking Device With De-Emphasis Function and The Method Thereof (US Patent 7313187)PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Casino Bonus Game Using Player Strategy (US Patent 6645071)Document3 pagesCasino Bonus Game Using Player Strategy (US Patent 6645071)PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- TracBeam v. AppleDocument8 pagesTracBeam v. ApplePriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Advance Products & Systems v. CCI Piping SystemsDocument5 pagesAdvance Products & Systems v. CCI Piping SystemsPriorSmartNo ratings yet
- VIA Technologies Et. Al. v. ASUS Computer International Et. Al.Document18 pagesVIA Technologies Et. Al. v. ASUS Computer International Et. Al.PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Senju Pharmaceutical Et. Al. v. Metrics Et. Al.Document12 pagesSenju Pharmaceutical Et. Al. v. Metrics Et. Al.PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Perrie v. PerrieDocument18 pagesPerrie v. PerriePriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Richmond v. Creative IndustriesDocument17 pagesRichmond v. Creative IndustriesPriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Eckart v. Silberline ManufacturingDocument5 pagesEckart v. Silberline ManufacturingPriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Senju Pharmaceutical Et. Al. v. Metrics Et. Al.Document12 pagesSenju Pharmaceutical Et. Al. v. Metrics Et. Al.PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- ATEN International v. Uniclass Technology Et. Al.Document14 pagesATEN International v. Uniclass Technology Et. Al.PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Sun Zapper v. Devroy Et. Al.Document13 pagesSun Zapper v. Devroy Et. Al.PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- GRQ Investment Management v. Financial Engines Et. Al.Document12 pagesGRQ Investment Management v. Financial Engines Et. Al.PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Merck Sharp & Dohme v. Fresenius KabiDocument11 pagesMerck Sharp & Dohme v. Fresenius KabiPriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Mcs Industries v. Hds TradingDocument5 pagesMcs Industries v. Hds TradingPriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Shenzhen Liown Electronics v. Luminara Worldwide Et. Al.Document10 pagesShenzhen Liown Electronics v. Luminara Worldwide Et. Al.PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- TracBeam v. T-Mobile Et. Al.Document9 pagesTracBeam v. T-Mobile Et. Al.PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Dok Solution v. FKA Distributung Et. Al.Document99 pagesDok Solution v. FKA Distributung Et. Al.PriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Merck Sharp & Dohme v. Fresenius KabiDocument10 pagesMerck Sharp & Dohme v. Fresenius KabiPriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Multiplayer Network Innovations v. Konami Digital EntertainmentDocument6 pagesMultiplayer Network Innovations v. Konami Digital EntertainmentPriorSmartNo ratings yet