Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elements of The Weather
Uploaded by
yuenza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
236 views1 pageThe weather is made up of different measurable elements including precipitation, temperature, wind speed and direction, humidity, air pressure, cloud cover, visibility, and sunshine. These elements are measured using instruments like rain gauges, thermometers, anemometers, wind vanes, hygrometers, and barometers, and observations of elements like cloud cover and visibility are recorded. Measurements are used to create climate graphs and weather forecasts.
Original Description:
Original Title
Elements of the Weather
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe weather is made up of different measurable elements including precipitation, temperature, wind speed and direction, humidity, air pressure, cloud cover, visibility, and sunshine. These elements are measured using instruments like rain gauges, thermometers, anemometers, wind vanes, hygrometers, and barometers, and observations of elements like cloud cover and visibility are recorded. Measurements are used to create climate graphs and weather forecasts.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
236 views1 pageElements of The Weather
Uploaded by
yuenzaThe weather is made up of different measurable elements including precipitation, temperature, wind speed and direction, humidity, air pressure, cloud cover, visibility, and sunshine. These elements are measured using instruments like rain gauges, thermometers, anemometers, wind vanes, hygrometers, and barometers, and observations of elements like cloud cover and visibility are recorded. Measurements are used to create climate graphs and weather forecasts.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
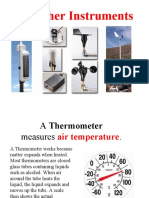
Elements of the Weather
The weather is made up of different elements, which are measured either by
special instruments or are observed by a meteorologist. These
measurements are then recorded and used in the making of climate graphs
and weather forecasts.
The table below shows the weather element details.
Element Description How it is measured Units of measurement
Moisture from the sky
Precipitation By a Rain Gauge Millimetres (mm.)
e.g. rain, snow etc.
By Thermometers,
Temperature How hot or cold it is found inside a Degrees celsius ( c)
Stevenson Screen
How fast the wind is
Wind Speed By an Anemometer Knots, or by the Beaufort Scale
blowing
Points of the compass (north,
Wind Where the wind is
By a Wind Vane north-west etc), or bearing in
Direction blowing from
degrees
Element Description How it is measured Units of measurement
By a Hygrometer (wet Relative Humidity (% of water
The amount of water
Humidity and Dry Bulb vapour that can be held by the
vapour in the air
Thermometers) air at the actual temperature)
The "weight" of the air
Hectopascals (although most
Air Pressure pushing on the surface By a Barometer
people know it as millibars)
of the Earth
The amount of cloud in It is observed by a
Cloud Cover Oktas - eighths of the sky
the sky meteorologist
It is observed by a
Visibility How far you can see Kilometres
meteorologist
Sunshine The hours of sunshine By a Sunshine Recorder Hours and minutes
Element Description How it is measured Units of measurement
You might also like
- Weather Elements (Clouds, Precipitation, Temperature and More): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Earth Sciences Books EditionFrom EverandWeather Elements (Clouds, Precipitation, Temperature and More): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Earth Sciences Books EditionNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - The ElementsDocument22 pagesLesson 1 - The Elementsgw14asamoahpriscillaNo ratings yet
- Clil Measuring The WeatherDocument23 pagesClil Measuring The Weatherapi-618777961No ratings yet
- Geography Note Booklet Grade 9 PDFDocument72 pagesGeography Note Booklet Grade 9 PDFiitope.n.op100% (2)
- Tools in Tracking The Storm: (Names and Uses)Document2 pagesTools in Tracking The Storm: (Names and Uses)Deniel Siapo de SilvaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Climate. Measurement & Representation of Climatic DataDocument29 pagesElements of Climate. Measurement & Representation of Climatic DataVarunNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Weather PowerpointDocument21 pagesMeasuring The Weather PowerpointSUNEEPA ROY CHOUDHURYNo ratings yet
- Q4-DRRR Activity 7 and 8Document3 pagesQ4-DRRR Activity 7 and 8Rhod Manalo SupresenciaNo ratings yet
- Glossary in MeotrologyDocument31 pagesGlossary in Meotrologypanget ako100% (1)
- DRRR g1 PDFDocument39 pagesDRRR g1 PDFxyreneNo ratings yet
- Name: Ni o G. Diestro Date: October 9, 2018 Instructor: Engr. Teresa S. Lumansoc RatingDocument21 pagesName: Ni o G. Diestro Date: October 9, 2018 Instructor: Engr. Teresa S. Lumansoc RatingVerra Myza AratNo ratings yet
- Science Pierre+Document3 pagesScience Pierre+sarah jamesNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Lecture 2Document36 pagesHydrology Lecture 2ben joshua mercadoNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Social Studies Week 18 - 2022 - Consolidated WorksheetDocument10 pagesGrade 5 Social Studies Week 18 - 2022 - Consolidated Worksheetshivanah hunteNo ratings yet
- Glossary Unit 4 GeographyDocument2 pagesGlossary Unit 4 GeographyYolandaNo ratings yet
- Term 1 (Notes)Document4 pagesTerm 1 (Notes)Maria IezhitsaNo ratings yet
- Weather PredictDocument15 pagesWeather PredictMike SyNo ratings yet
- Weather Station Report PDFDocument7 pagesWeather Station Report PDFSunny Sheikh0% (1)
- 17.2 P1 - MeteorologyDocument41 pages17.2 P1 - MeteorologyNelum PereraNo ratings yet
- E-Journal in MeteorologyDocument10 pagesE-Journal in MeteorologycuthNo ratings yet
- Met Ocean 1 Week 2Document33 pagesMet Ocean 1 Week 2JONATHAN LOGOCNo ratings yet
- Weather Station ExperimentDocument6 pagesWeather Station ExperimentSaadFarooqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: PrecipitationDocument14 pagesChapter 2: PrecipitationIbrahim MostazidNo ratings yet
- What Makes Up The WeatherDocument1 pageWhat Makes Up The Weatherapi-310353155No ratings yet
- Weather InstrumentsDocument4 pagesWeather InstrumentsLuisa Del Mundo100% (1)
- Rain Gauge Is An Instrument UsedDocument5 pagesRain Gauge Is An Instrument UsedKathy SarmientoNo ratings yet
- I (Unit-II)Document44 pagesI (Unit-II)TanmaySardanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 FinalDocument8 pagesChapter2 Finalramesh krishnaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report # 2Document6 pagesLab Report # 2zainyousafzai100% (1)
- Obinna Geo 5Document48 pagesObinna Geo 5Obinna RichardNo ratings yet
- Weather Instruments Cut PasteDocument14 pagesWeather Instruments Cut PasteJenniferNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate Yr 8 Lesson NoteDocument12 pagesWeather and Climate Yr 8 Lesson NoteuffiageniusNo ratings yet
- OP Fun Facts Measurements and InstrumentsDocument2 pagesOP Fun Facts Measurements and InstrumentsJuliana RichardNo ratings yet
- DRRR NotesDocument12 pagesDRRR NotesCaoimhe FleurNo ratings yet
- Typical InstrumentsDocument16 pagesTypical Instrumentsssuryaraj911No ratings yet
- Meteorology: Introduction ToDocument34 pagesMeteorology: Introduction ToAndrea FameroNo ratings yet
- What Are The Uses of Meteorological InstrumentsDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Uses of Meteorological InstrumentsCire DuronNo ratings yet
- Name: Neilkrishna Kabara STD: 9 A Roll No.: A914Document24 pagesName: Neilkrishna Kabara STD: 9 A Roll No.: A914greateast anshNo ratings yet
- Geography HYDocument5 pagesGeography HYArpit BarmanNo ratings yet
- Gas NameDocument3 pagesGas NameImamul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Weather Instruments: WEATHER MAPS Indicate Atmospheric Conditions Above A Large PortionDocument3 pagesWeather Instruments: WEATHER MAPS Indicate Atmospheric Conditions Above A Large Portionaljem tubigonNo ratings yet
- ABE 31A - Lab Exercise #1 (Agrometeorological Station Site Visit)Document7 pagesABE 31A - Lab Exercise #1 (Agrometeorological Station Site Visit)RAY MARK ABALAYANNo ratings yet
- College of Agriculture, Forestry, and Environmental SciencesDocument6 pagesCollege of Agriculture, Forestry, and Environmental SciencesZeus CuiNo ratings yet
- 2 MeteorologyDocument93 pages2 MeteorologyMiho BoskovicNo ratings yet
- Weather L4Document30 pagesWeather L4malisaqueen53No ratings yet
- This Cool Little Project That Im Working OnDocument4 pagesThis Cool Little Project That Im Working OnKareem AlhalabiNo ratings yet
- Weather Tools PPTDocument23 pagesWeather Tools PPTconwenaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 MeteorologyDocument4 pagesLecture 5 MeteorologyAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. Relief and ClimateDocument10 pagesUnit 2. Relief and ClimateIrene AragonesesNo ratings yet
- WX ObservationsDocument18 pagesWX ObservationsLouie VerginoNo ratings yet
- Meteorology GNU Free Documentation LicenseDocument18 pagesMeteorology GNU Free Documentation LicenseEdbert TulipasNo ratings yet
- Weather StationDocument1 pageWeather StationAitazaz AhsanNo ratings yet
- Weather InstrumentsDocument12 pagesWeather InstrumentsMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- AnemometerDocument2 pagesAnemometerInesstyNo ratings yet
- Give Us The Different Types of Equipment, Stations or Satellites Used by PAGASA For Weather Determination and ForecastDocument5 pagesGive Us The Different Types of Equipment, Stations or Satellites Used by PAGASA For Weather Determination and ForecastArthNo ratings yet
- Elements of Weather and ClimateDocument6 pagesElements of Weather and ClimateFarheen BanoNo ratings yet
- Weather Cambridge IGCSE Geography (9-1)Document16 pagesWeather Cambridge IGCSE Geography (9-1)Georgina HolmesNo ratings yet
- Shipborne Meteorological Instruments: Activity No. 1-2 AssignmentDocument3 pagesShipborne Meteorological Instruments: Activity No. 1-2 AssignmentKenneth SibonghanoyNo ratings yet
- Components of ClimateDocument8 pagesComponents of ClimateSanghamithra raviNo ratings yet
- Wheater Mind MapDocument1 pageWheater Mind MaparanzazummoraNo ratings yet
- Spill ResponseDocument10 pagesSpill ResponseLittle Holland Pty Ltd100% (1)
- Pollution Control and PreventionDocument4 pagesPollution Control and PreventionPartial DerivativeNo ratings yet
- Basic Guide To Calculating Falls and Gradients For Drainage - Basic Guide To Calculating Falls and Gradients For Drainage - Wyre CouncilDocument6 pagesBasic Guide To Calculating Falls and Gradients For Drainage - Basic Guide To Calculating Falls and Gradients For Drainage - Wyre Councilvenkateswara rao pothinaNo ratings yet
- Gas & Condensate Production Facility Block DiagramDocument5 pagesGas & Condensate Production Facility Block DiagramAswin TrisaktiNo ratings yet
- Method Statement FOR Earthwork: ProjectDocument6 pagesMethod Statement FOR Earthwork: ProjectKelvin Lau Hin HuatNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste ManagementDocument127 pagesSolid Waste ManagementJanna Keziah GambanNo ratings yet
- SRG Slipform Construction 2016 04 e PDFDocument8 pagesSRG Slipform Construction 2016 04 e PDF94738183No ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines: Department of Environmental and Sanitary EngineeringDocument5 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines: Department of Environmental and Sanitary EngineeringAl RomanoNo ratings yet
- ICSE Prelims Geography X ClassDocument4 pagesICSE Prelims Geography X ClassSagar SinghalNo ratings yet
- Sarasota County Comprehensive Plan - Transmittal Draft - Volume 1Document608 pagesSarasota County Comprehensive Plan - Transmittal Draft - Volume 1Suddhasattwa BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Engineering Week 12: Dams and Reservoirs: Dr. M. Mubashir QureshiDocument88 pagesHydraulics Engineering Week 12: Dams and Reservoirs: Dr. M. Mubashir QureshiRana Asad AliNo ratings yet
- DAP CDA BangladeshDocument260 pagesDAP CDA Bangladeshapi-3788255100% (8)
- Shrimp FarmingDocument2 pagesShrimp FarmingNaina Pradeep singhNo ratings yet
- Spar PlatformDocument34 pagesSpar PlatformAmir HazimNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Plumbing DesignDocument60 pagesFundamentals of Plumbing DesignBianca MendozaNo ratings yet
- Grassroots Partcipatory Budgeting FY 2015 - Disaggregated Project List - 81414Document259 pagesGrassroots Partcipatory Budgeting FY 2015 - Disaggregated Project List - 81414Dave Wilson P. TanNo ratings yet
- Underwater WindmillDocument21 pagesUnderwater Windmillbhagyashree behera100% (1)
- Approval From Colombo Municipal CouncilDocument4 pagesApproval From Colombo Municipal CouncilkamaldeshapriyaNo ratings yet
- Queensland Urban Drainage Manual PDFDocument459 pagesQueensland Urban Drainage Manual PDFAnthony Nguyen89% (9)
- Merck - CromatografiaDocument406 pagesMerck - CromatografiaechorossiNo ratings yet
- Slop Oil and Oily Sludge Recovery Brochure - tcm11 68550Document16 pagesSlop Oil and Oily Sludge Recovery Brochure - tcm11 68550Irelena RomeroNo ratings yet
- River Training Works: GabionsDocument15 pagesRiver Training Works: GabionsFITSUM BerheNo ratings yet
- Aeration IEEEDocument7 pagesAeration IEEEdragh meh downNo ratings yet
- Building Maintenance ChecklistDocument5 pagesBuilding Maintenance ChecklistNur MajNo ratings yet
- Coal Runoff Analysis Complete ReportDocument32 pagesCoal Runoff Analysis Complete ReportArif SusetyoNo ratings yet
- ESS 4 StandardDocument7 pagesESS 4 StandardLineth DomingoNo ratings yet
- Arsenic in RiceDocument5 pagesArsenic in RiceMadurosNo ratings yet
- Sheringham Geography CourseworkDocument7 pagesSheringham Geography Courseworkf5d7ejd0100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet Rust Remover: Revision Date: 12/05/2015 Revision: 5 Supersedes Date: 02/06/2014Document9 pagesSafety Data Sheet Rust Remover: Revision Date: 12/05/2015 Revision: 5 Supersedes Date: 02/06/2014FahrezaNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant Unit Lab ReportDocument19 pagesRefrigerant Unit Lab Reportakmal100% (2)