Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Sarie LevitaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Sarie LevitaCopyright:
Available Formats
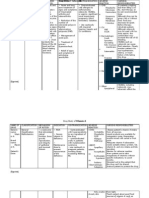
Name of Drug Generic
Route
Dosage/ Frequency 1tab TID
Mechanism of Action > provides elemental iron, an essential component in the formation of hemoglobin
Specific Indication > iron deficiency > as a supplement during pregnancy
Contraindication
Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction > nausea, epigastric pain, vomiting, constipation, black stool, diarrhea, anorexia > temporarily stained teeth from liquid forms
Nursing Consideration > GI upset, maybe related to dose > between meal doses are preferable > drug can be given with some foods although absorption maybe decreased > entericcoated products reduce GI upset but also reduce amount of iron absorbed > monitor
Oral Ferrous sulfate
> contraindicated in patients hemosideorosis, primary hemolytic anemia, deficiency anemia, peptic ulceration, ulcerative colitis, or regional enteritis and in those receiving repeated blood transfusions > use cautiously long-term basis
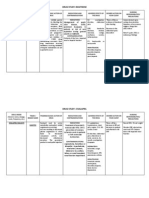
Name of Drug Generic
Route
Dosage/ Frequency 1ampule TIV 30min prior to BT
Mechanism of Action >Diphenhydramine blocks histamine H1-receptors on effector cells of the GI tract, blood vessels and respiratory tract. It also causes sedation and has some anticholinergic action.
Specific Indication > Relief of symptoms associated with perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis; vasomotor rhinitis; allergic conjunctivitis; mild, uncomplicated urticaria and angioedema; amelioration of allergic reactions to blood or plasma; dermatographism ; adjunctive therapy in anaphylactic reactions > Active and prophylactic treatment of motion sickness > Nighttime sleep aid
diphenhydramine TIV
Contraindication Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Hypersensitivity ; > CNS neonates, depression, lactation. dizziness, headache, sedation; paradoxical stimulation in children; dryness of mouth, thickened respiratory secretion, blurring of vision, urinary retention; GI disturbances; blood dyscrasias.
Nursing Consideration Assessment > History: Allergy to any antihistamines, narrow-angle glaucoma, stenosing peptic ulcer, symptomatic prostatic hypertrophy, asthmatic attack, bladder neck obstruction, pyloroduodenal obstruction, third trimester of pregnancy, lactation > Physical: Skin color, lesions, texture; orientation, reflexes, affect; vision examination; P,
> Parkinsonism (including druginduced parkinsonism and extrapyramidal reactions), in the elderly intolerant of more potent drugs, for milder forms of the disorder in other age groups, and in combination with centrally acting anticholinergic antiparkinsonian drugs
BP; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds; prostate palpation; CBC with differential Interventions Monitor patient response, and arrange for adjustment of dosage to lowest possible effective dose.
Name of Drug Generic Calcium Gluconate
Route
Dosage/Frequency
Mechanism of Action > Replaces calcium and maintains calcium level.
Specific Indication > Hypocalcemic emergency > Adjunctive treatment of Magnesium intoxication > Hypophosphatemia > Hyperkalemia with secondary cardiac toxicity
Contraindication
Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction CNS: tingling sensation, syncope with rapid I.V. injection. CV: mild drop in blood pressure, vasodilation, bradycardia, arrhythmias, cardiac arrest with rapid I.V. injection. GI: irritation, constipation, nausea, vomiting, thirst, abd. pain. GU: polyuria, renal calculi. Metabolic: hypercalcemia Skin: local
Nursing Consideration Before: > Make sure prescriber specifies form of calcium to be given; crash carts may contain both calcium gluconate and calcium chloride. > Tell patient to take oral calcium 1 to 1!/2 hours after meals if GI upset occurs. During: > Give I.M. injection in gluteal region in adults and in lateral thigh in infants. Use
TIV
1ampule TIV after BT of 4
reactions, including burning, necrosis, tissue sloughing, cellulites, soft tissue calcification with I.M. use, pain.
I.M. route only in emergencies when no I.V. route is available bec. of irritation of tissue by calcium salts. > Tell patient to take oral calcium with a full glass of water. After: > Monitor calcium levels frequently. Hypercalcemia may result after large doses in chronic renal failure. Report abnormalities.
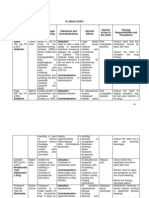
Name of Drug Generic Amlodipine
Route
Dosage/Frequency
Mechanism of Action > inhibits calcium movement across cell membranes of cardiac and vascular smooth muscle. > It dilates coronary arteries, peripheral arteries and arterioles. >Decreases total peripheral vascular resistance by vasodilation.
Specific Indication > Amlodipine is used to manage hypertension, chronic stable angina, and vasospastic angina. > It may be used alone or with other antihypertensives or antianginals.
Contraindication
Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction
Nursing Consideration
oral
1cap BID
> Allergy to amlodipine > Hepatic or renal impairment > Sick sinus syndrome > Heart block > lactation
> Peripheral edema > Headache > Flushing > Dizziness > Palpitations > Nausea > Unusual tiredness or weakness > Chest pain > Bradycardia > Orthostatic Hypotension
> Assess baseline renal and liver function. > Assess blood pressure. > Assess apical pulse. > Assess for peripheral edema behind medial malleolus. > Assess skin for flushing. > Question for headache and weakness. > May be given
without regards to food. Grapefruit juice may increase drug concentration
Name of Drug Conzace
Contents Vit C 5,000 iu Vit E 100 iu Vit C 500 mg Zn sulfate 25 mg
Route Oral
Dosage 1cap TID
Specific Indication > Cellular/tissue maintenance & repair & prevention of premature aging > Maintenance of healthy skin & as adjunct for treatment of various skin disorders
Administration > May be taken w/ meals for better absorption or if GI discomfort occurs
You might also like
- Hesi Exit ExamDocument46 pagesHesi Exit ExamIndia94% (102)
- Internal Medicine Study GuideDocument71 pagesInternal Medicine Study GuideMedicine4theMasses95% (19)
- Nursing Drug CardsDocument32 pagesNursing Drug CardsJenna Rasmussen100% (3)
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipineJulie Aranda Hapin80% (5)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudySarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Pacific RimDocument10 pagesPacific RimSarie Levita100% (1)
- MNT 2 Case StudyDocument14 pagesMNT 2 Case Studyapi-339312954No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular History MindmapDocument12 pagesCardiovascular History MindmapThe_BakerNo ratings yet
- STEMI Complications TreatmentDocument54 pagesSTEMI Complications TreatmentAnonymous CQmrhq1O7100% (1)
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument14 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument10 pagesIschemic Heart Diseaseborn_321118403100% (1)
- Final Drug StudyDocument22 pagesFinal Drug StudyPaula Xavier AlfalahiNo ratings yet
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭No ratings yet
- Drug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument15 pagesDrug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmechachaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Amplodipine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmplodipine Drug StudyRai HanahNo ratings yet
- Antianginal Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii R. Jecino, M.DDocument31 pagesAntianginal Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii R. Jecino, M.DFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- ECLAMPSIA Drug StudyDocument10 pagesECLAMPSIA Drug Studyjessica_omegaNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Medication Classificatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Intervention Generic Name: CNS: GIDocument4 pagesMedication Classificatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Intervention Generic Name: CNS: GIKathleenDawalNo ratings yet
- Drugs Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument7 pagesDrugs Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationPrincess Jenelly CampomanesNo ratings yet
- CHF Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCHF Drug StudyAiza Apelada-NievaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Capitol)Document8 pagesDrug Study (Capitol)Joy CalmerinNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine Hydrochloride: Generic Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Side Effects Nursing ActionsDocument5 pagesRanitidine Hydrochloride: Generic Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Side Effects Nursing ActionsAyanne ArcenaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument7 pagesDrugsEloisa Abarintos RacalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document9 pagesDrug Study 2Justin PasaronNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesDocument18 pagesGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- HEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)Document7 pagesHEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)Leoni HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument70 pagesDrug Studyjahmaicao50% (2)
- 13 Drug StudyDocument6 pages13 Drug StudyRachel Yvonne Cabacungan100% (1)
- Antihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneDocument28 pagesAntihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneLopez JoeNo ratings yet
- Definitions OF DiagnosisDocument25 pagesDefinitions OF DiagnosisGlaire ZarateNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyChristine MatasNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument5 pagesEmergency DrugsArra PlacidesNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument20 pagesDrugsLee Won100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateTempoNo ratings yet
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Dugs CVADocument10 pagesDugs CVAMarie AntoinetteNo ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Amlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventDocument6 pagesAmlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNephrolithiasis - Drug StudyAia JavierNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyChickz HunterNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- Mefenamic Acid Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution MIMS MalaysiaDocument1 pageMefenamic Acid Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution MIMS MalaysianuruladyanisaifuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Drug Study - Psyche (2) DDDDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Psyche (2) DDDAia JavierNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Medcor AguinaldoDocument6 pagesDrug Study Medcor AguinaldoYana PotNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pagesDrug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionOamaga NajlaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Coronary Ward IIDocument7 pagesDrugs Coronary Ward IITimothy Joy VercelesNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocument3 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine BesylateDocument7 pagesAmlodipine BesylatebabuagoodboyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyColleen De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Implication: OB, Lactation, Pedi: GeriDocument29 pagesNursing Implication: OB, Lactation, Pedi: GeriGlyssa CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 68-75Document8 pagesDrug Study 68-75joshua_santiago_5No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyJanine Erika Julom BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Hemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Document4 pagesHemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Stacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudySarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- HIV/AIDSDocument11 pagesHIV/AIDSSarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Medication AdministrationDocument34 pagesMedication AdministrationSarie Levita100% (2)
- Medication AdministrationDocument34 pagesMedication AdministrationSarie Levita100% (2)
- DialysisDocument4 pagesDialysisSarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- N IDocument1 pageN ISarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- CHNDocument14 pagesCHNSarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Health EcoDocument1 pageHealth EcoSarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseJoyVee Pillagara-De LeonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Feu NRMF IcuDocument9 pagesDrug Study Feu NRMF IcuAnne Genesis V. PinedaNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain Notes USMLE Step 3Document3 pagesChest Pain Notes USMLE Step 3kisria100% (1)
- What Is Angina?Document30 pagesWhat Is Angina?Bentoys Street100% (1)
- Cardio DrillDocument22 pagesCardio DrillDemuel Dee L. BertoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Emergency..Document120 pagesCardiovascular Emergency..MarcellRaymondNo ratings yet
- 5605 Nursing DiagnosesDocument51 pages5605 Nursing Diagnoseseericalex100% (2)
- Lecture 11cholesterol ManagementDocument19 pagesLecture 11cholesterol ManagementMahmoud Elamer ElmenshawyNo ratings yet
- CTCAE v4.0Document195 pagesCTCAE v4.0Glauber LeitaoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Risk AssessmentDocument4 pagesCardiac Risk Assessmentmonir61No ratings yet
- 113 Latex Allergy Asthma or Eczema.: FitkitDocument33 pages113 Latex Allergy Asthma or Eczema.: FitkitNeela MukthaNo ratings yet
- Nitroglycerin Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNitroglycerin Drug StudyjuancristoNo ratings yet
- NCP MiDocument8 pagesNCP MiPitaca Madiam Annabehl PaulNo ratings yet
- Smoking, Alcohol, and DrugsDocument13 pagesSmoking, Alcohol, and Drugs'Andi Mursyid Asrarsani'No ratings yet
- Heart Attacks and There Effects On LifeDocument11 pagesHeart Attacks and There Effects On Lifeapi-291565665No ratings yet
- ACS LectureDocument55 pagesACS LectureAyunda AlmiradaniNo ratings yet
- 2015 ESC Guidelines For The ManagementDocument59 pages2015 ESC Guidelines For The ManagementSri WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Quick Management Guide in Emergency Medicine v1.0.25 20111208 (Build13)Document156 pagesQuick Management Guide in Emergency Medicine v1.0.25 20111208 (Build13)Anselm Su100% (14)
- Body MeridianDocument65 pagesBody Meridiandcf67my100% (1)
- Laporan Kasus Kardiovaskuler (Fransiska - C11107156)Document32 pagesLaporan Kasus Kardiovaskuler (Fransiska - C11107156)Fransiska Carmelia SubenoNo ratings yet
- Historia EKGDocument19 pagesHistoria EKGibigrachuNo ratings yet
- CHD PilDocument2 pagesCHD Pilsigit_riyantonoNo ratings yet
- STEMI - Case ReportDocument42 pagesSTEMI - Case ReportWarren LieNo ratings yet