Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quinine
Uploaded by
DoubleHeartedOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quinine
Uploaded by
DoubleHeartedCopyright:
Available Formats
NAME OF THE DRUG Quinine
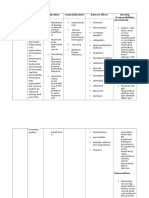
CLASSIFICATION anti-pyretic, antimalarial, analgesic, and antiinflammatory
DOSAGE AND ROUTE
MECHANISM OF ACTION Quinine depresses oxygen uptake and carbohydrate metabolism, elevates pH in intracellular organelles of parasites. It then produces parasitic death. Quinine also relaxes skeletal muscle by increasing the refractory period, decreasing excitability of motor end plates, and affecting the distribution of calcium with muscle fiber.
INDICATIONS Quinine is used to prevent and treat nocturnal recumbent leg cramps. Used alone, or with pyrimethamine and sulfonamide for the treatment of chloroquineresistant falciparum malaria.
CONTRAINDICATIONS Contraindicated to pregnant women,
ADVERSE EFFECTS Nausea Headache Tinnitus Slight visual disturbances Rashes Wheezing Dyspnea Angioedema Cardiac conduction disturbances Decreased hearing
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
Question for possibility of pregnancy prior to initiating therapy. Question for hypersensitivity to quinine, quinidine. Evaluate initial ECG and CBC results. Check for hypersensitivity: flushing, rash/urticaria, itching, dyspnea, and wheezing. Assess level of hearing, visual acuity, presence of headache or tinnitus, and nausea. Report adverse effects promptly
Monitor CBC results for blood dyscrasias Be alert to infection, bleeding or bruising, and unusual tiredness or weakness. Assess pulse and ECG for arrhythmias. Check fasting blood sugar levels; watch out for hypoglycemia.
You might also like
- Drug Study Quinine SulfateDocument7 pagesDrug Study Quinine SulfateKathlyn_Matic_6376No ratings yet
- Chlorthalidone HygrotonDocument2 pagesChlorthalidone HygrotonLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Drug Study: (Celecoxib)Document11 pagesDrug Study: (Celecoxib)Princess Brigitte R. PATE�ANo ratings yet
- SHEENA Clomid Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSHEENA Clomid Drug StudyNur SetsuNo ratings yet
- Pilocarpine (Drug Monograph)Document1 pagePilocarpine (Drug Monograph)Muhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolDocument5 pagesGeneric Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- PiroxicamDocument2 pagesPiroxicamVirginia Aira Lara MarquezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study...Document5 pagesDrug Study...Ezra Dizon ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- Pseudoephedrine HydrochlorideDocument6 pagesPseudoephedrine HydrochlorideAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDocument13 pagesDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- Subcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More CommonDocument2 pagesSubcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More Commonahmad ryanNo ratings yet
- Filgastrim (GCSF)Document3 pagesFilgastrim (GCSF)Kyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Timolol MaleateDocument3 pagesTimolol MaleateAP TOROBXNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida InfectionsDocument1 pageGeneric Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida Infectionscen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- AMINOPHYLLINEDocument2 pagesAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- Ferrous Sulfate - Drug StudyDocument3 pagesFerrous Sulfate - Drug StudyElla Musk100% (1)
- Drug NystatinDocument1 pageDrug NystatinSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Name: Micaela Andrea C. Cielo Date: Year & Section: BS Nursing 2A Drug Study: AlbendazoleDocument2 pagesName: Micaela Andrea C. Cielo Date: Year & Section: BS Nursing 2A Drug Study: AlbendazoleMicaela Andrea CieloNo ratings yet
- Doxazosin MesylateDocument2 pagesDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument1 pageSodium BicarbonateALbinong VelascoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyNikki RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitieskyleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1 (Done)Document3 pagesDrug Study 1 (Done)Otaku MiyoNo ratings yet
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Document4 pagesChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsDocument18 pagesDrug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsJenica ManuntagNo ratings yet
- GENTIMICINDocument1 pageGENTIMICINVinzNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Acute Aspirin ToxicityDocument1 pageGeneric Name: Acute Aspirin ToxicityShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Fansidar Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFansidar Drug StudyjangzieNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComDocument2 pagesCephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComKatyana Cesar100% (1)
- Francis Peteros Drug Study 2 BetamethasoneDocument8 pagesFrancis Peteros Drug Study 2 BetamethasoneFrancis PeterosNo ratings yet
- HYOSCINEDocument1 pageHYOSCINEzyr2189No ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationNicole CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and GastrointestinalDocument64 pagesDrug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and Gastrointestinaljamaica cabrigaNo ratings yet
- ChlorphenamineDocument1 pageChlorphenaminereinaNo ratings yet
- GanciclovirDocument3 pagesGanciclovirRosher Deliman JanoyanNo ratings yet
- MedroxyprogesteroneDocument5 pagesMedroxyprogesteroneunkown userNo ratings yet
- PrimaquineDocument3 pagesPrimaquineVijayakumar NsNo ratings yet
- Glipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardDocument1 pageGlipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Aspirin: Generic NameDocument4 pagesAspirin: Generic NameGwww BabababaNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTramadol Drug StudyTipey Segismundo0% (1)
- Carboprost TromethamineDocument2 pagesCarboprost TromethamineDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- Act Rapid 2Document2 pagesAct Rapid 2Leah Torcelino-InfanteNo ratings yet
- Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Document1 pageCyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Miglitol (Glyset)Document1 pageMiglitol (Glyset)ENo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLDocument6 pagesA Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Amikacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesAmikacin Drug StudyMark Angelo LorzanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefotaximeDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CefotaximeAngel laurestaNo ratings yet
- NalbuphineDocument5 pagesNalbuphineGab PagalilauanNo ratings yet
- Altretamine: Drug DosageDocument16 pagesAltretamine: Drug DosagePrincess CruzNo ratings yet
- DUPHASTON Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDUPHASTON Drug StudyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: AmoxicillinDocument3 pagesDrug Study: AmoxicillinKrzia TehNo ratings yet
- Chymoral PlusDocument3 pagesChymoral PlusNeha SureshNo ratings yet
- LidocaineDocument2 pagesLidocaineAhprelle Quiring Rodiel100% (1)
- Parathyroid Agents PDFDocument32 pagesParathyroid Agents PDFRhodee Kristine DoñaNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Agents PDFDocument32 pagesParathyroid Agents PDFRhodee Kristine DoñaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyVal FielNo ratings yet
- Quinine - Generic, Uses, Side Effects, Dosages, Interactions, WarningsDocument11 pagesQuinine - Generic, Uses, Side Effects, Dosages, Interactions, WarningsAbdulazizMotteNo ratings yet