Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PIHconceptmap
Uploaded by
Christian Paul BolidoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PIHconceptmap
Uploaded by
Christian Paul BolidoCopyright:
Available Formats
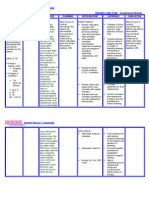
PIH Concept Map
Preeclampsia S/Sx 1. Hypertension- earliest and most dependable sign; 30mm Hg systolic increase or 15mm Hg increase diastolic over baseline; MAP increase 2. Proteinuria- passage of proteins that the tubules cannot reabsorb; excess found in urine; increased serum BUN, creatinine, and uric acid; decrease in urine creatinine clearance 3. Weight gain/Edema- may appear rapidly beginning in lower extremities and moves upward; accumulation of fluid due to decreased blood flow to kidneys causing increased angiotension and aldosterone which trigger the retention of sodium and water Just the facts 1. Hypertensive disease of pregnancy occurring at 20 wks gestation and lasting to 14 wks postpartum 2. Pre-eclampsia- hypertension, proteinuria, and edema 3. Eclampsia- all of the complications of pre-eclampsia plus the presence of convulsions 4. Arteriolar vasospasm and vasoconstriction in the entire body including major organs (multisystem failure disease) Eeclampsia S/Sx 1. All of the clinical manifestations of pre-eclampsia are present (hypertension, proteinuria, and edema) as well as CONVULSIONS 2. Oliguria, edema, excessive weight gain, visual changes, CNS lesions, epigastric pain, visual changes (blurred vision)
Predisposing Factors 1. Primigravida: especially if <17 or >35 years of age 2. Multiple pregnancies: twins, triplets 3. Vascular disease: especially hypertension, renal disease, or diabetes 4. Hydatidiform mole: manifested prior to 20 weeks 5. Dietary deficiencies 6. Drug use- cocaine 7. Family tendency PIH Tx (home management) 1. Decrease activities and bed rest (side lying position) 2. Dietary modifications- protein intake increase 70-80g/day and maintain sodium intake 3. Record fetal activity (kick counts), check urine protein, weigh daily at the same time
Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH)
Nursing Interventions 1. CNS irritability- provide quite environment and rest, comfort measures, assess reflexes administer MgSO4, assess subjective signs (irritability, HA, blurred vision, epigastric pain) 2. Control BP- monitor VS, give antihypertensive drugs, check hematocrit 3. Promote diuresis- dont give diuretics; bed rest (left or right lateral position), check output (foley catheter placement), weigh daily, dipstick for protein 4. Monitor fetal well being- check FHTs, fetal assessment test (OCT) 5. Deliver infant
PIH Tx (hospital management) 1. Administration of MgSO4- calcium channel blocker that interferes with the release of ACH decreasing neuromuscular irritability, and decreasing CNS irritability 2. Respirations must be 14-16, reflexes must be present and urine output must be 100cc in 4 hours (if above is not present hold med and call Dr) 3. Monitor magnesium level- normal 1.5-2.5; therapeutic 4-8; toxicity =>9 4. Labs- CBC, platelets, type and cross match; Renal studies: BUN, creatinine, uric acid; Liver studies: AST, LDH, bilirubin; DIC profile: platelets, fibrinogen, FSP, D-Dimer
Nursing Diagnosis Activity intolerance Anxiety Disturbed sensory perception (visual) Disturbed thought processes Excess fluid volume Fear Impaired urinary elimination Ineffective coping Ineffective tissue perfusion: Cerebral, peripheral Risk for injury
You might also like
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension Nursing Diagnosis NANDADocument9 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension Nursing Diagnosis NANDASanal S SalimNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia Care MapDocument3 pagesPreeclampsia Care Mapapi-38011595475% (4)
- OB Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesOB Nursing Care PlanLiza Marie Cayetano AdarneNo ratings yet
- Precipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryDocument7 pagesPrecipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryLei Ortega100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plane 4 PreeclampsiaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plane 4 PreeclampsiaShamoos Alkhusaibi80% (5)
- HyperbilirubinemiaDocument11 pagesHyperbilirubinemianursereview100% (12)
- Pre EclampsiaDocument13 pagesPre EclampsiaEniamrahs DnalonNo ratings yet
- Cord Prolapse March 23Document2 pagesCord Prolapse March 23Kathleen Vargas100% (1)
- NCP Cough PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCP Cough PneumoniaAirme Raz AlejandroNo ratings yet
- OB Care Plan: Assessment DataDocument12 pagesOB Care Plan: Assessment Dataapi-520985654No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- NCP PediaDocument2 pagesNCP PediaJoey JoseNo ratings yet
- Pre EclampsiaDocument3 pagesPre EclampsiaJon Sayson100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlansDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlansYannah Mae EspineliNo ratings yet
- Ambulatoty CareDocument18 pagesAmbulatoty CareVhince PiscoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For HirschsprungDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For HirschsprungAhmed Altrafe100% (2)
- Drug Card BactrimDocument1 pageDrug Card Bactrimerica2323No ratings yet
- PPH Care PlanDocument4 pagesPPH Care PlanGCNo ratings yet
- BuscopanDocument2 pagesBuscopancen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument16 pagesNursing DiagnosisSi Bunga JonquilleNo ratings yet
- IUFDDocument2 pagesIUFDnurseon0% (1)
- Maternity Case 1: Olivia Jones (Core) : Guided Reflection QuestionsDocument3 pagesMaternity Case 1: Olivia Jones (Core) : Guided Reflection QuestionsDai Nguyen100% (1)
- Nursing Care With EclampsiaDocument40 pagesNursing Care With EclampsiaNadia DesyerianNo ratings yet
- Case Study CS 3Document38 pagesCase Study CS 3tristanpaulNo ratings yet
- Hyperbilirubinemia Case StudyDocument7 pagesHyperbilirubinemia Case Studyr_ramos0759No ratings yet
- Drugs - OBDocument7 pagesDrugs - OBglennarthurNo ratings yet
- Post Test 30 Items OBDocument5 pagesPost Test 30 Items OBJohnasse Sebastian NavalNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placentae Case StudyDocument4 pagesAbruptio Placentae Case StudyMonchee YusonNo ratings yet
- Gestational HypertensionDocument17 pagesGestational HypertensionRubinaNo ratings yet
- CyclosporineDocument2 pagesCyclosporineMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument11 pagesAbruptio PlacentaAlynna ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- NCP Example Pre EclampsiaDocument6 pagesNCP Example Pre EclampsiaChristian Joseph OpianaNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia Eclampsia and Hellp SyndromeDocument24 pagesPreeclampsia Eclampsia and Hellp Syndromeapi-403416350100% (1)
- 01 - Newborn Physical ExamDocument2 pages01 - Newborn Physical Examgerald_valeriano0% (1)
- Reflection 1Document5 pagesReflection 1api-400554289No ratings yet
- Shoulder Dystocia NCPDocument6 pagesShoulder Dystocia NCPNicole Genevie MallariNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDocument30 pagesAmniotic Fluid EmbolismDonmer Ibañez Juan100% (1)
- Case Study BMC-Surgical WardDocument55 pagesCase Study BMC-Surgical WardVirgilio Reyes ManuelNo ratings yet
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocument3 pagesPostpartum HemorrhageClaire Canapi BattadNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa (New) - 1Document32 pagesPlacenta Previa (New) - 1Ibrahim ZainabNo ratings yet
- Case 55 BPHDocument4 pagesCase 55 BPHGetachew Addis75% (12)
- Dalidig - Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDalidig - Drug StudyRaf DalidigNo ratings yet
- CELINDocument9 pagesCELINaikoestrellaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - CvaDocument3 pagesCase Study - CvaJrBong Semanero50% (2)
- Case Study (Aub)Document16 pagesCase Study (Aub)Lucila Lugo0% (2)
- REFERAT - Ppt.pathophysiology of PROM-noviDocument16 pagesREFERAT - Ppt.pathophysiology of PROM-noviFrisma Indah Permatasari100% (1)
- Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Teaching PlanDocument5 pagesHypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Teaching PlanMary Grace Belmonte100% (1)
- Bullets MCNDocument3 pagesBullets MCNAginaya Rein50% (2)
- Nursing Care For Patient With Wilms TumorDocument2 pagesNursing Care For Patient With Wilms TumorAnusha Verghese100% (2)
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus - NISALDocument7 pagesGestational Diabetes Mellitus - NISALKevin de SilvaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Pneumonia With Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument18 pagesNursing Care Plan Pneumonia With Congenital Heart DiseaseKarri Ann Tonel100% (2)
- Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan PDFDocument2 pagesPost Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan PDFA sison100% (1)
- Nursing Crib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionDocument2 pagesNursing Crib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionJustin PasaronNo ratings yet
- Meconium Aspiration SyndromeDocument29 pagesMeconium Aspiration SyndromeAlwin Varghese T0% (1)
- ISBAR Worksheet Olivia Jones Jasgou1752Document1 pageISBAR Worksheet Olivia Jones Jasgou1752Jasmyn Rose100% (1)
- 001hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy PDFDocument23 pages001hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy PDFRosechelle Bas SamsonNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Disorders in PregnancyDocument81 pagesHypertensive Disorders in PregnancyarunshreerajendranNo ratings yet
- Pre EclampsiaDocument179 pagesPre EclampsiaAnton RossiniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 GestosesDocument22 pagesLecture 1 GestosesDrRaghavender ReddyNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study GuideDocument3 pagesExam 1 Study GuideNataraj LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Marine Corps Institute: Semper Fit Advanced Fitness CourseDocument222 pagesMarine Corps Institute: Semper Fit Advanced Fitness CoursesrollinsNo ratings yet
- Crash Course in Dental Management of The Medically Compromised PatientDocument30 pagesCrash Course in Dental Management of The Medically Compromised Patientmazen bokhari100% (1)
- Moh Exam Prep MaterialDocument159 pagesMoh Exam Prep MaterialAbid Ali Khan100% (1)
- Content Outline Content Outline: Certified Crossfit Trainer Certified Crossfit TrainerDocument17 pagesContent Outline Content Outline: Certified Crossfit Trainer Certified Crossfit TrainerMarjoe BianagaNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances - Management Hypertension in PregnancyDocument72 pagesRecent Advances - Management Hypertension in PregnancyMonisha ArulalanNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Eclampsia or PreeclampsiaDocument11 pagesPostpartum Eclampsia or PreeclampsiaAnonymous l6Q1ROq2No ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Activity and SummaryDocument2 pagesReading Comprehension Activity and SummaryTrini YemeNo ratings yet
- Problem Lists Patient PlanDocument1 pageProblem Lists Patient Planangel23No ratings yet
- Metabolic Syndrome: Learning ObjectivesDocument20 pagesMetabolic Syndrome: Learning Objectivesddeeb420% (1)
- Benefits of Sahaja YogaDocument48 pagesBenefits of Sahaja YogaprashantkothariNo ratings yet
- Tivoli: Golf With Class: D. North of The Santo MountainsDocument8 pagesTivoli: Golf With Class: D. North of The Santo MountainsZulfikar YuchaNo ratings yet
- Medline 1 - 100Document133 pagesMedline 1 - 100zionluis007No ratings yet
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument30 pagesMedical Surgical NursingLeila Marquez100% (2)
- Autonomic Dysreflexia in Spinal Cord InjuryDocument5 pagesAutonomic Dysreflexia in Spinal Cord Injuryjulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Wa0001.Document5 pagesWa0001.Santhini PrideepNo ratings yet
- Scientific-Benefits-Of-Meditation-Pdf-Liveanddare ComDocument14 pagesScientific-Benefits-Of-Meditation-Pdf-Liveanddare Comapi-321697736No ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan FinalDocument1 pageFamily Nursing Care Plan FinalKhrisha Anne Davillo100% (1)
- Triplixam 10mg - 2-5mg - 10mg Film Coated Tablets (Perindopril Arginine - Indapamide - Amlodipine)Document8 pagesTriplixam 10mg - 2-5mg - 10mg Film Coated Tablets (Perindopril Arginine - Indapamide - Amlodipine)Sze Wei TanNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Levels For Boys by Age and Height Percentile: BP (Percentile) Systolic BP (MMHG) Diastolic BP (MMHG)Document4 pagesBlood Pressure Levels For Boys by Age and Height Percentile: BP (Percentile) Systolic BP (MMHG) Diastolic BP (MMHG)Annisa NurulNo ratings yet
- Formulary For Cardiology and Hypertension:: Brand Name Generic Name Strength CompanyDocument3 pagesFormulary For Cardiology and Hypertension:: Brand Name Generic Name Strength CompanyDr-Muhammad Junaid Hassan SharifNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Hypertensive Urgency - Group 2 Section 3BDocument48 pagesA Case Study On Hypertensive Urgency - Group 2 Section 3BhernandezmarianneroseNo ratings yet
- Minoxidil MonographDocument39 pagesMinoxidil Monographscrubber100% (1)
- Hypertension Improvement.....Document4 pagesHypertension Improvement.....Ling 보차No ratings yet
- Care During Pregnancy and Childbirth Training Manual For CHO at AB-HWCDocument80 pagesCare During Pregnancy and Childbirth Training Manual For CHO at AB-HWCPranab PalNo ratings yet
- OET Writing ExamplesDocument46 pagesOET Writing Exampleslkdsjfls63% (8)
- Renal Disease in Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma), Including Scleroderma Renal Crisis - UpToDateDocument24 pagesRenal Disease in Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma), Including Scleroderma Renal Crisis - UpToDateBruno José MendesNo ratings yet
- Xavier University-Ateneo de CagayanDocument3 pagesXavier University-Ateneo de CagayanMariano MarbellaNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment SAS Session 14Document9 pagesHealth Assessment SAS Session 14Maria Jub MangrubanNo ratings yet
- Cardivista - Product List - ERDocument2 pagesCardivista - Product List - ERYoussef Kaid0% (1)
- Afsb Psychological Test Book 4TH EditionDocument103 pagesAfsb Psychological Test Book 4TH EditionVictor50% (2)