Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics
Uploaded by
zachriggleOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics
Uploaded by
zachriggleCopyright:
Available Formats
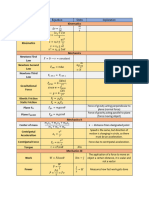
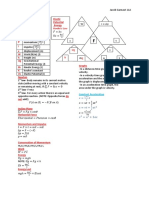
Gravity Circular Motion
,force of gravity Angular Vars Definition Linear Variable
Angular Position
Angular Velocity
Acceleration of gravity at height h from Earthʼs surface
Angular
Acceleration
Force of gravity at distance R from earth
, Mass of earth inside radius r, with density Potential Energy
Gravitational P.E. between 2 objects. r=distance between objects
height H r > radius of earth spring
, Escape velocity. Obj1 often=Earth, so one of the
cancels, and and
. Minimum velocity to escape orbit. G=G. M=mass. R=radius.
, Keplerʼs Law
= density.
m = mass of an object.
r = distance between objects, radius.
Power + Work
, average power
, raise/lower , variable vector Force
, work with an angle:
Kinetic Energy
, max drop height (given max N); p = inertia
Impulse and Momentum
|| , momentum is parallel to velocity
, impulse is change in momentum
,average force over time
Rotation
, sigma=rotational velocity.
Eqns of Motion Definition Linear Variable
Acceleration
Velocity
Position
Collisions - Elastic
special case when
*Note: Above is also true for velocity, just swap out p with v.
Collisions - Partially Inelastic
, Change/loss in kinetic energy
Collisions - Part Inelastic w/ Walls
Friction
, Static Friction
, Kinetic Friction
You might also like
- Engineering Dynamics: Chapter - Kinetics ParticlesDocument17 pagesEngineering Dynamics: Chapter - Kinetics ParticlesAbdillah AbassNo ratings yet
- Downloadfile 1 PDFDocument104 pagesDownloadfile 1 PDFBrianChanNo ratings yet
- System Force (F) Displacement Work (W) MKS Newton (N) Meters (M) N-M or J CGS Dyne CM Dyne-Cm or Erg English LB FT FT-LB Hooke's' LawDocument4 pagesSystem Force (F) Displacement Work (W) MKS Newton (N) Meters (M) N-M or J CGS Dyne CM Dyne-Cm or Erg English LB FT FT-LB Hooke's' LawAdriangelo Apud AngelesNo ratings yet
- Learnfast Review and Tutorial Hub Nmat Reviewer Velocity Acceleration Force Work PDFDocument5 pagesLearnfast Review and Tutorial Hub Nmat Reviewer Velocity Acceleration Force Work PDFBib SeñoNo ratings yet
- All Engphys FormulasDocument5 pagesAll Engphys FormulasCres Dan Jr. BangoyNo ratings yet
- General Physics ReviewerDocument15 pagesGeneral Physics ReviewerArviNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer: Concepts of Motion - An Object Is Said in Motion If It ChangesDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer: Concepts of Motion - An Object Is Said in Motion If It ChangesDark3126 Tower1008No ratings yet
- Learnfast Review and Tutorial Hub - Nmat Reviewer: Velocity, Acceleration, Force WorkDocument8 pagesLearnfast Review and Tutorial Hub - Nmat Reviewer: Velocity, Acceleration, Force WorkEllah Gutierrez50% (2)
- Gravitational Fields - AllDocument27 pagesGravitational Fields - AlleugeniawijonoNo ratings yet
- Physics - Gravitaional FieldDocument3 pagesPhysics - Gravitaional FieldArafat HossainNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument30 pagesGravitationSamiyah Irfan 2023243No ratings yet
- Roller Coaster ProjectDocument35 pagesRoller Coaster ProjectVanitta RangsitananNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument33 pagesGravitationDebayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Circular MotionDocument2 pagesTopic 2 - Circular Motionmariam hNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 1&2 Formula SheetDocument2 pagesPhysics Unit 1&2 Formula SheetDivit RajputNo ratings yet
- P.E. MGH M Mass G Gravity H HeightDocument3 pagesP.E. MGH M Mass G Gravity H HeightzhiyinNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula, Glossary, Exam PapersDocument19 pagesPhysics Formula, Glossary, Exam Papersanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Dynamics: Second Semester 1442HDocument37 pagesDynamics: Second Semester 1442HKhalid AlqahtaniNo ratings yet
- Liviabrookes MechanicsDocument2 pagesLiviabrookes Mechanicsengg filesNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument44 pagesWork Energy and PowerBea OquendoNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - FINAL - AAE343Document2 pagesFormula Sheet - FINAL - AAE343Nouman1203No ratings yet
- Gravity OrigDocument60 pagesGravity OrigMjNnKmNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhysics ReviewerROEB AIREE MUEGANo ratings yet
- Physics Definition by Vasumitra GajbhiyeDocument3 pagesPhysics Definition by Vasumitra GajbhiyeHuzaifa ImranNo ratings yet
- 6351PHY3 Unit 3 Cheat SheetDocument2 pages6351PHY3 Unit 3 Cheat Sheetmonika durairajNo ratings yet
- Ch.3 - RotationRigidBodyDocument9 pagesCh.3 - RotationRigidBodyPhương Trâm TrầnNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision Set 2Document2 pagesPhysics Revision Set 2Shi Kai TengNo ratings yet
- G-Potential EnergyDocument2 pagesG-Potential EnergySung ParkNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Potential NOTESDocument2 pagesGravitational Potential NOTESKimberly MutangaNo ratings yet
- 2 Orbital MechanicsDocument59 pages2 Orbital MechanicsabdishNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Potential EnergyDocument8 pagesGravitational Potential EnergyHaar TambalusiNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument6 pagesPhysics ReviewerKimberley MendozaNo ratings yet
- CH 3 & 5 & 6 Vectors, Newton's Laws, & Applications of Newton's LawsDocument4 pagesCH 3 & 5 & 6 Vectors, Newton's Laws, & Applications of Newton's LawsMelindaNo ratings yet
- Physics 2305 Equation Sheet - Test 2Document2 pagesPhysics 2305 Equation Sheet - Test 2Michael MorrisonNo ratings yet
- Physics Summarisation: Chapter One. Motion and RelativityDocument16 pagesPhysics Summarisation: Chapter One. Motion and RelativityYM GaoNo ratings yet
- ConceptMap PDFDocument8 pagesConceptMap PDFWongXinXinNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument12 pagesGravitationskumar123846No ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics-Formula SheetDocument2 pagesIGCSE Physics-Formula SheetPraveen PeterNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula SheetDocument12 pagesPhysics Formula SheetGiulia CostantiniNo ratings yet
- Gravitation TheoryDocument16 pagesGravitation TheoryC.Madan KumarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Knowledge Mat Topic 8 Energy Forces Doing Work V1 2Document4 pagesEdexcel Knowledge Mat Topic 8 Energy Forces Doing Work V1 2NetkoNo ratings yet
- Ch2 CheatSheets MergedDocument5 pagesCh2 CheatSheets Mergedfreya screepNo ratings yet
- All Physics Formulas For O Levels Physics by Ethan Wu: Celsius To KelvinDocument6 pagesAll Physics Formulas For O Levels Physics by Ethan Wu: Celsius To KelvinReuben CachiaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Igcse Physics 4ph1 TheoryDocument21 pagesEdexcel Igcse Physics 4ph1 Theorysammam mahdi samiNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion: Round and RoundDocument6 pagesCircular Motion: Round and RoundFarogh HamidNo ratings yet
- A2 Phy Chapterwise NotesDocument72 pagesA2 Phy Chapterwise Notesiqra farooqNo ratings yet
- ΙΒ PHYSICS CHAPTER 6 and 10 Circular Motion and Gravitation HLDocument19 pagesΙΒ PHYSICS CHAPTER 6 and 10 Circular Motion and Gravitation HLAnastasia VergouNo ratings yet
- PhET Interactive Physics Simulations For IB DP Physics (SL & HL)Document7 pagesPhET Interactive Physics Simulations For IB DP Physics (SL & HL)sam mirisonNo ratings yet
- 4th GRADING SCIENCE 3Document6 pages4th GRADING SCIENCE 3Azlynn Courtney FernandezNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument16 pagesCircular MotionSamiyah Irfan 2023243No ratings yet
- Forces and Motion Cheat SheetDocument1 pageForces and Motion Cheat SheetmifewpmfewpoNo ratings yet
- 7.rotational MechanicsPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae SheetDocument4 pages7.rotational MechanicsPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae Sheetma joNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion: Day FiveDocument8 pagesCircular Motion: Day FiveKalyan RangavajjalaNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Fields ResumeDocument4 pagesGravitational Fields ResumeAmri Ramadhan D'classicNo ratings yet
- SVRphy18 PDFDocument1 pageSVRphy18 PDFanoetaNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy vs. Kinetic Energy - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPotential Energy vs. Kinetic Energy - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Functionally Graded Materials 2017Document118 pagesFunctionally Graded Materials 2017alfonsoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 MAT283Document2 pagesAssignment 1 MAT283meiofaunaNo ratings yet
- DM1 315S6 75,0kWDocument3 pagesDM1 315S6 75,0kWJohnny Diaz VargasNo ratings yet
- CT Analyzer User Manual ESPDocument178 pagesCT Analyzer User Manual ESPmendezhanda100% (1)
- State Space Model Nptel ModDocument30 pagesState Space Model Nptel ModBarathNo ratings yet
- 6th Year Chemistry The Gas LawsDocument31 pages6th Year Chemistry The Gas LawsAnusia ThevendaranNo ratings yet
- Flowizard 3.1Document4 pagesFlowizard 3.1Antonio MezzopreteNo ratings yet
- 1978 Fairchild Optoelectronics Data Book PDFDocument300 pages1978 Fairchild Optoelectronics Data Book PDFItseed Corca0% (1)
- Diagram Fasa Fe-CDocument12 pagesDiagram Fasa Fe-CRudi HirarkiNo ratings yet
- Group1 Lab1b ReportDocument13 pagesGroup1 Lab1b ReportMark Allen FacunNo ratings yet
- United State Pharmacopoea 1st EditionDocument294 pagesUnited State Pharmacopoea 1st EditionNehruRogerNo ratings yet
- JgyugufDocument47 pagesJgyugufMarcoNo ratings yet
- Astm D 3612 - 01Document24 pagesAstm D 3612 - 01mtuankctNo ratings yet
- Iris RecognitionDocument21 pagesIris RecognitionRahul100% (1)
- 1 Outrigger and Belt Wall SystemDocument24 pages1 Outrigger and Belt Wall SystemBurhan NasutionNo ratings yet
- 9ABS301 Mathematics - IIDocument8 pages9ABS301 Mathematics - IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Application of Fuzzy Logic in Electrical Discharge Machining (Edm)Document37 pagesA Case Study On Application of Fuzzy Logic in Electrical Discharge Machining (Edm)TanviNo ratings yet
- BSOSR6X0907Document20 pagesBSOSR6X0907xuanhungyteNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Tutorial 1Document11 pagesAbaqus Tutorial 1Dg IRfan100% (1)
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Jean100% (1)
- K FactorDocument3 pagesK FactorAnonymous hISvHbfiB1No ratings yet
- 120:360 - Biochemistry Fall 2015 Sample Questions For Exam 1Document5 pages120:360 - Biochemistry Fall 2015 Sample Questions For Exam 1BluedevNo ratings yet
- Physics - Lab ReportDocument26 pagesPhysics - Lab ReportBAUAN Al DominicNo ratings yet
- Geologos 15 1soft SeddeformationsDocument54 pagesGeologos 15 1soft SeddeformationsM HakimNo ratings yet
- Pressosmart Alfa LAvalDocument4 pagesPressosmart Alfa LAvalCostichiNo ratings yet
- ICP OES Maintenance Troubleshooting PDFDocument39 pagesICP OES Maintenance Troubleshooting PDFmiftahchemNo ratings yet
- Geologic Processes On EarthDocument38 pagesGeologic Processes On EarthTrisha May Flores100% (2)
- Engine Lubrication SystemDocument29 pagesEngine Lubrication SystemAnonymous xjV1llZSNo ratings yet
- Elementary General Thermodynamics - Martin V. Sussman PDFDocument464 pagesElementary General Thermodynamics - Martin V. Sussman PDFGrigore VladNo ratings yet
- F1 Flow Measurement in Closed ConduitDocument5 pagesF1 Flow Measurement in Closed ConduitSzeQiLungNo ratings yet