Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter6 Answers
Uploaded by
Sammy AhmedOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter6 Answers
Uploaded by
Sammy AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6: The Cell 1. How do biologists isolate cell components?
- The goal of cell fractionation is to take cells apart and separate the major organelles from one another. - Uses an ultracentrifuge which spins as fast as 130,000 rpm. Forces of gravity separate cell components. 2. What are four things all cells have in common? - Golgi Apparatus - Ribosomes - Mitochondrion - Endoplasmic Reticulum 3. How do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ? - Only Bacteria and Archaea consists of prokaryotic cells. Protists, fungi, animals, and plants consist of eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic: DNA contained in the nucleoid which has no membrane to separate it form the rest of the cell. Eukaryotic: DNA contained in a membrane-bound nucleus; bigger.
4. What is a limiting factor to cell size? - Cellular metabolism. 5. How do ribosomes differ in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
6. What is the adaptive value of the endomembrane system?
7. For each of the cellular structures, indicate a few significant aspects. Include major functions and structures.
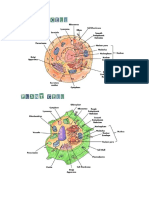
Nuclear Membrane Nuclear Pores Nuclear Lamina Chromatin Nucleolus Ribosome Smooth ER only found in animal cells; encloses the nucleus and sepearates it from the cytoplasm. line each pore of the nuclear envelope and regulate the entry and exit of certain large macromolecules and particles. netlike array of protein filaments that maintains the shape of the nucleus by mechanically supporting the nuclear envelope. complex of proteins and DNA that makes up chromosomes. synthesizes rRNA; found inside the nucleus. particles made of rRNA and protein; carry out protein synthesis. differs from rough ER because it lacks ribosomes; makes lipids; metabolizes carbohydrates; detoxifies drugs and poisons.
Rough ER Golgi Apparatus Lysosome Vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplast Peroxisome Cytoskeleton Microtubule Microfilament Intermediate Filament Extracellular Matrix Plasmodesmata Tight Junction Desmosomes Gap Junctions
has ribosomes; synthesizes secretory proteins; produces membranes like phospholipids. composed of cisternae; has 2 poles - a cis face and a trans face which receive and expel ribosomes. membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that an animal cell uses to digest all kinds of macromules. prominent in older plant cells; used for energy storage, breakdown of waste products, hydrolysis of macromules, plant growth. site of cellular respiration (creation of ATP by extracting energy from sugars, fats, and other fuels). found only in plants; site of photosynthesis (conversion of solar energy to chemical energy). microbody containing enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen, producing and then degrading hydrogen peroxide network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm; organizes structure and activities of the cell; composed of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. hollow tubes in the cytoskeleton; maintain cell shape; moves chromosomes in cell division. two intertwined strands of actin in the cytoskeleton; maintains or changes cell shape; muscle contraction; cleavage formation in cell division. proteins coiled into thicker cables in the cytoskeleton; maintains cell shape; anchors nucleus; forms nuclear lamina. in animal cells only; composed of glycoproteins like collagen; equivalent to a plant cell's adjacent cell wall. channels in plant cells that connect one cell to another. in animals; membranes of neighboring cells are very tightly pressed against each other; prevent leakage of extracellular fluid across a layer of epithelial cells. in animals; fasten cells together into strong sheets. in animals; provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to an adjacent cell; necessary for communication between cells in many types of tissues.
8. Trace the path of production of a protein-based secretion from a secretory cell. (List the organelles involved.) - Bound ribosomes made out of RNA and a protein are synthesized by the Rough ER. - Golgi apparatus takes the products in through its cis face. - Proteins are sent through its cisternae, which pinches off into vesicles containing the proteins. - Vesicles exit out the trans face of the Golgi in their vesicles which transports them to a place in the cell where they are needed for secretion.
You might also like
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- CH 6 A Tour of The CellDocument7 pagesCH 6 A Tour of The Cellwil7verNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Function and PropertiesDocument10 pagesCell Structure Function and PropertiesWanda JohnNo ratings yet
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocument30 pagesLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument108 pagesBiochemJangNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9. Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument35 pagesLecture 9. Cell and Cell OrganellesSaksham JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Review - CellsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Review - Cellsmari coboNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesDocument34 pagesCells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesJeffrey100% (1)
- Week 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021Document4 pagesWeek 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021yui kirigayayuukiNo ratings yet
- Nature of CellsDocument7 pagesNature of CellsAdrian Lee VannorsdallNo ratings yet
- 0-Introduction NotesDocument7 pages0-Introduction Notesjimmy.bousaba27No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells: ProkaryotesDocument8 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells: Prokaryotesdavid tsaiNo ratings yet
- Cells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsDocument10 pagesCells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsHassinMarkLariosaNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell Membrane: Patricia Caldani MSDocument51 pagesCell and Cell Membrane: Patricia Caldani MSkittypattyNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- Lecture 2ALevels of Organization in Animal ComplexityDocument15 pagesLecture 2ALevels of Organization in Animal ComplexityElleNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellPrincess MillanNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument36 pagesThe CellSam MumoNo ratings yet
- Biokim 4 - Bu Asih - sEL 2019Document74 pagesBiokim 4 - Bu Asih - sEL 2019Rizky NNo ratings yet
- As OCR Biology Revision PackDocument28 pagesAs OCR Biology Revision PackJoel TrelivingNo ratings yet
- Cells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsDocument8 pagesCells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsRameesha RanaNo ratings yet
- MCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLDocument9 pagesMCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLGabi taofeekatNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellDocument8 pagesGrade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellOlayinka SalmonNo ratings yet
- Ans 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument33 pagesAns 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsAdewaleNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument4 pagesBiochemistryAaliyah Ashley CerboNo ratings yet
- Bio Exam 2 Study GuideDocument6 pagesBio Exam 2 Study GuidekecordovaNo ratings yet
- LESSONS in BIOCHEMDocument39 pagesLESSONS in BIOCHEMMikhael Jay IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Describe Animal Cell Seen Under The Light MicroscopeDocument21 pagesDescribe Animal Cell Seen Under The Light MicroscopetasmiahNo ratings yet
- Phospholipids (Fats With Phosphorous Attached), Which at Body Temperature AreDocument7 pagesPhospholipids (Fats With Phosphorous Attached), Which at Body Temperature AreCmae VidadNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Theory: Heba Abd El Fattah May 2011 Biology SL CellsDocument8 pages2.1 Cell Theory: Heba Abd El Fattah May 2011 Biology SL Cellsansarish94No ratings yet
- Topic 3 Cell Structure and MitosisDocument10 pagesTopic 3 Cell Structure and MitosisdaniaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2.2 Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument11 pagesMODULE 2.2 Cellular Level of OrganizationKate Andrea PanizalesNo ratings yet
- Biology F4 Teaching ModuleDocument13 pagesBiology F4 Teaching ModuleNurfatin Jamaludin100% (1)
- CellDocument17 pagesCellAaliyah Quesha LadjamatliNo ratings yet
- 6.1-How Are Cells Studied?: Magnification Resolution Contrast Electron Microscope (EM)Document7 pages6.1-How Are Cells Studied?: Magnification Resolution Contrast Electron Microscope (EM)Sadasivarao GaddeNo ratings yet
- The Cell Theory of BiologyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Theory of BiologyFrezelVillaBasiloniaNo ratings yet
- Unit I Cell & Subcellular Organelles, Cell Mem & Transport BDSDocument48 pagesUnit I Cell & Subcellular Organelles, Cell Mem & Transport BDSshafrasimin22No ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument4 pagesCell BiologyasadzamanchathaNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument6 pagesCell Biologyakash kumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The CELLDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The CELLlorelie asisNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Structure and TaxonomyKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Cell and Molecular Biology 1Document38 pagesLecture 1 Cell and Molecular Biology 1Martin HangasNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)Document46 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)MeryemNo ratings yet
- Membrane Main Article: Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesMembrane Main Article: Cell MembraneAriella ZoeyNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.2 - Ultrastructure of CellsDocument56 pagesTopic 1.2 - Ultrastructure of CellsAhmed IqbalNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Document8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Saurav SoniNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument6 pagesBIOLOGYKiana BNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument25 pagesCell StructuresAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- The CellDocument17 pagesThe CelluissojohnyzNo ratings yet
- BIO 1 The CellDocument54 pagesBIO 1 The CellElyNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures: The BasicsDocument4 pagesCell Structures: The BasicsParama CinthyaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology and Genetics Notes On All Lectures PDFDocument62 pagesCell Biology and Genetics Notes On All Lectures PDFMR ManalangNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument10 pagesCELLMAAYER MUHAMMADNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument18 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellssalahuddin_md5935100% (1)
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesCell - The Unit of Lifelpc4944No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument22 pagesCell Structure and FunctionRavi DesaiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Interactive Reading QuestionsDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Interactive Reading QuestionsJoshua LagonoyNo ratings yet
- Measure For Measure AngeloDocument1 pageMeasure For Measure AngeloRoger Knight100% (1)
- WWW - Ib.academy: Study GuideDocument122 pagesWWW - Ib.academy: Study GuideHendrikEspinozaLoyola100% (2)
- Oration For Jon Kyle ValdehuezaDocument2 pagesOration For Jon Kyle ValdehuezaJakes ValNo ratings yet
- Radiopharmaceutical Production: History of Cyclotrons The Early Years at BerkeleyDocument31 pagesRadiopharmaceutical Production: History of Cyclotrons The Early Years at BerkeleyNguyễnKhươngDuyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 (B)Document6 pagesCHAPTER 4 (B)Jon Lester De VeyraNo ratings yet
- RPT Form 2 2023Document7 pagesRPT Form 2 2023NOREEN BINTI DOASA KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- FreeMarkets: Procurement & Outsourcing StrategiesDocument44 pagesFreeMarkets: Procurement & Outsourcing StrategiesFarhaad MohsinNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 5Document3 pagesDLL Week 5Nen CampNo ratings yet
- Organigation DeveDocument3 pagesOrganigation Devemerin sunilNo ratings yet
- Articles 62 & 63: Presented By: Muhammad Saad Umar FROM: BS (ACF) - B 2K20Document10 pagesArticles 62 & 63: Presented By: Muhammad Saad Umar FROM: BS (ACF) - B 2K20Muhammad Saad UmarNo ratings yet
- Man Is Made by His BeliefDocument2 pagesMan Is Made by His BeliefLisa KireechevaNo ratings yet
- Not For Profit Governance WeilDocument224 pagesNot For Profit Governance WeillkjhmnvbNo ratings yet
- American RunwayDocument26 pagesAmerican RunwayGayathri SuriyaNo ratings yet
- Character Sketch of Elizabeth BennetDocument2 pagesCharacter Sketch of Elizabeth BennetAiman AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Ernesto Sirolli - Eenterprise FacilitationDocument300 pagesErnesto Sirolli - Eenterprise FacilitationFrancis James Leite Marques PereiraNo ratings yet
- Spyderco Product Guide - 2016Document154 pagesSpyderco Product Guide - 2016marceudemeloNo ratings yet
- Binding of IsaacDocument10 pagesBinding of IsaacBraz SouzaNo ratings yet
- Oleracea Contain 13.2% Dry Matter, 15.7% Crude Protein, 5.4% Ether ExtractionDocument47 pagesOleracea Contain 13.2% Dry Matter, 15.7% Crude Protein, 5.4% Ether ExtractionJakin Aia TapanganNo ratings yet
- Confidential Recommendation Letter SampleDocument1 pageConfidential Recommendation Letter SamplearcanerkNo ratings yet
- CURRICULUM VITAE Kham Khan Suan Hausing, PHDDocument8 pagesCURRICULUM VITAE Kham Khan Suan Hausing, PHDCinpu ZomiNo ratings yet
- Su Jok, Twist Therapy AND Smile MeditationDocument7 pagesSu Jok, Twist Therapy AND Smile MeditationprateekNo ratings yet
- Different Departments Required in A HospitalDocument11 pagesDifferent Departments Required in A HospitalEdsel Dudes AbanteNo ratings yet
- Summarized ACLS ScriptDocument7 pagesSummarized ACLS Scriptnc.angel.niceNo ratings yet
- 1929 Davos DisputationDocument20 pages1929 Davos DisputationEstevao Cruz100% (1)
- COMM 103 Floyd Chapters Study GuideDocument4 pagesCOMM 103 Floyd Chapters Study GuideMad BasblaNo ratings yet
- Scribe FormDocument2 pagesScribe FormsiddharthgamreNo ratings yet
- LET Facilitating Learning EDITED3Document12 pagesLET Facilitating Learning EDITED3Likhaan PerformingArts HomeStudio100% (5)
- Task Basis JurisprudenceDocument10 pagesTask Basis JurisprudenceKerwin LeonidaNo ratings yet
- Fortune 2010Document14 pagesFortune 2010Stefan JenkinsNo ratings yet