Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Schizophrenia Concept Map
Uploaded by
Gabrielle FranklinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Schizophrenia Concept Map
Uploaded by
Gabrielle FranklinCopyright:
Available Formats
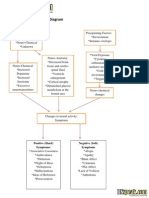
Disorder/Dx:
Schizophrenia
Risks
Biological Factors: genetic, neurobiological, brain structure abnormalities Psychological and Environmental factors: prenatal stressors, psychological stressors, and environmental stressors
Nursing Process
Assessment
Medications
Conventional antipsychotics treat positive symptoms only (i.e.) Chlorpromazine (Thorazine), Thioridazine (Mellaril), Loxapine (Loxitane), Thiothixene (Navene) Atypical antipsychotics treat positive and negative symptoms (i.e.) Aripiprazole (Abilify), Clozapine (Clozaril), Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Paliperidone (Invega), Quetiapine (Seroquel)
S/S:
positive, negative, cognitive, and affective symptoms --- signs include the four As, affect, associative looseness, autism, ambivalence
A B C T
S/S for Mgt
Positive symptoms: presence of something that is not normally present (hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behavior, paranoia Negative symptoms: absence of something that should be present but is not (lack of motivation, anhedonia, and poor thought processes) Cognitive symptoms: abnormalities in how a person thinks Affective symptoms: symptoms involving emotions and their expression
Nsg Dx Distorted Thought Self Control Pt Goals/Expected Outcomes
Maintains affect consistent with mood, interacts appropriately, reports decrease in hallucinations or delusions, asks for validation of reality
Nursing Interventions: ID Risks Screening Manage S/S Rx Administer and Monitor Meds Report S/E
Evaluation Goals/Expected Outcomes Reached?
You might also like
- Notes, Vibrational Frequencies, Chakras, Elements, Colours, Emotional HealingDocument1 pageNotes, Vibrational Frequencies, Chakras, Elements, Colours, Emotional HealingIsaiyah Carmona100% (3)
- Major Depression NCPDocument2 pagesMajor Depression NCPSeann LorescoNo ratings yet
- Psych Careplan For PaperDocument18 pagesPsych Careplan For PaperUSMCDOC100% (2)
- Psych Med ChartsDocument5 pagesPsych Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotes100% (5)
- Addiction Treatment Homework Planner PracticeplannersDocument61 pagesAddiction Treatment Homework Planner Practiceplannersjames.keeter43297% (34)
- Mental Health Nursing HandoutDocument27 pagesMental Health Nursing HandoutKim Ramos100% (26)
- Psychiatric NursingDocument21 pagesPsychiatric NursingFreeNursingNotes92% (38)
- Concept Map of DepressionDocument2 pagesConcept Map of DepressionJu Lie AnnNo ratings yet
- Pocket Tutor Understanding ABGs and Lung Function TestsDocument170 pagesPocket Tutor Understanding ABGs and Lung Function Testsdanelv100% (1)
- SCHIZOPHRENIADocument16 pagesSCHIZOPHRENIAapi-382243367% (3)
- Outpatient Procedures MasterDocument67 pagesOutpatient Procedures MasterSteveNo ratings yet
- Psych Drugs NursingDocument7 pagesPsych Drugs Nursinglisa100% (2)
- Psychiatric NurseslabsDocument28 pagesPsychiatric NurseslabsStephanie Villanueva AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Seroquel (Quetiapine)Document3 pagesSeroquel (Quetiapine)E100% (1)
- Psych DrugsDocument3 pagesPsych Drugsdcabeguin100% (1)
- S H Z P R N A: Colegio de Sta. Lourdes of Leyte Foundation, Inc. College of Nursing Tabontabon, LeyteDocument74 pagesS H Z P R N A: Colegio de Sta. Lourdes of Leyte Foundation, Inc. College of Nursing Tabontabon, LeyteGlenn ChavezNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Mental HealthDocument117 pagesNCLEX Mental HealthMikhaila Rutherford100% (7)
- Schizophrenia Care Plan RNDocument8 pagesSchizophrenia Care Plan RNlisa75% (4)
- Case 3 - Sinus HeadacheDocument6 pagesCase 3 - Sinus HeadacheJohn FightakisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Concept Map for Diabetes Patient ManagementDocument1 pageNursing Concept Map for Diabetes Patient ManagementSev Kuzmenko0% (1)
- Abnormal Psychology: Definitions, Perspectives, and ClassificationDocument53 pagesAbnormal Psychology: Definitions, Perspectives, and ClassificationcipaxobNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Maladaptive Pattern of Behavior NCM 105 LectureDocument70 pagesCare of Clients With Maladaptive Pattern of Behavior NCM 105 LectureMay June100% (1)
- Varcolis FUNDAMENTAL OF PSY - NURSING - NCLEX RNDocument20 pagesVarcolis FUNDAMENTAL OF PSY - NURSING - NCLEX RNisapatrick8126100% (1)
- Psych Nursing Practice ExamsDocument44 pagesPsych Nursing Practice ExamsJesie Mel BacenaNo ratings yet
- ATI Mental Health ReviewDocument30 pagesATI Mental Health ReviewTee Wood100% (10)
- Schizophrenia MapDocument1 pageSchizophrenia Mapjchase936267% (3)
- Psychopathology Paranoid SchizophreniaDocument2 pagesPsychopathology Paranoid SchizophreniaPrincess Joy T. Catral57% (7)
- Chapter 19 Substance AbuseDocument8 pagesChapter 19 Substance AbuseCatia Fernandes100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of SchizophreniaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Schizophreniasarzlasco090% (1)
- Psych Care PlanDocument3 pagesPsych Care Plancwarrington0967% (3)
- Mental Health Nursing Practice Test 3Document16 pagesMental Health Nursing Practice Test 3Dr. Jayesh Patidar100% (4)
- PSYCH Care Plan 3Document15 pagesPSYCH Care Plan 3USMCDOC100% (10)
- Psychology 101: The Study of Mind and BehaviorDocument34 pagesPsychology 101: The Study of Mind and BehaviorDaniel Berthier100% (2)
- Schizophrenia Concept MapDocument1 pageSchizophrenia Concept MapAlma Janella TOSINO100% (2)
- Chapter 14 Anxiety and Anxiety DisordersDocument4 pagesChapter 14 Anxiety and Anxiety DisordersCatia Fernandes100% (2)
- Jesse Bishop Process Recording FormDocument8 pagesJesse Bishop Process Recording FormVijaya Rani100% (1)
- Case Study (Mrs. Greene)Document9 pagesCase Study (Mrs. Greene)Trina Joy DomantayNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageSchizophrenia Schematic DiagramCyrus De AsisNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Concept MapDocument3 pagesBipolar Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (2)
- Bipolar Disorder Concept MapDocument1 pageBipolar Disorder Concept Mapashleydean100% (1)
- Care Plan For Schizoaffective Disorder Bipolar TypeDocument4 pagesCare Plan For Schizoaffective Disorder Bipolar TypeAlrick Asentista100% (2)
- Psychopathologies and Their TreatmentsDocument47 pagesPsychopathologies and Their TreatmentsLuther BlissettNo ratings yet
- Responding to Psychiatric PatientsDocument11 pagesResponding to Psychiatric Patientsobgynsoon100% (1)
- Bipolar Concept MapDocument3 pagesBipolar Concept MapMeghan Cannon57% (7)
- A Beautiful Mind MSEDocument10 pagesA Beautiful Mind MSECarla Rosyl Fuentes100% (3)
- Process RecordingDocument8 pagesProcess Recordingapi-340063062No ratings yet
- Additional Nursing Care Plans - SchizophreniaDocument26 pagesAdditional Nursing Care Plans - SchizophreniaJasmin Jacob100% (4)
- Brittany Thompson IprDocument4 pagesBrittany Thompson Iprapi-257869281100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Bipolar DisorderDocument20 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Bipolar Disordermjk2100% (4)
- Chapter 7 Clients Response To IllnessDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Clients Response To IllnessCatia FernandesNo ratings yet
- Substance DependenceDocument16 pagesSubstance Dependencemardsz94% (18)
- Chapter 4 Treatment Settings and Theraputic PRogramsDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Treatment Settings and Theraputic PRogramsCatia Fernandes100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans For Acute ConfusionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plans For Acute Confusionynecesity75% (4)
- The Royal Children HospitalDocument8 pagesThe Royal Children HospitalrenystrawberryNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Bipolar DisorderbeshyNo ratings yet
- Medication SheetDocument4 pagesMedication SheetJasleen AilenNo ratings yet
- Aa Na Observation Reflection TemplateDocument3 pagesAa Na Observation Reflection Templateapi-426049026No ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Schematic Diagram: Positive (Hard) Symptoms: Negative (Soft) SymptomsDocument1 pageSchizophrenia Schematic Diagram: Positive (Hard) Symptoms: Negative (Soft) SymptomsLovely Acabado Tampoco100% (1)
- PMH Nursing Care Plan 01112017Document19 pagesPMH Nursing Care Plan 01112017api-371817203No ratings yet
- TMendoza CriticalCareConceptMap2Document5 pagesTMendoza CriticalCareConceptMap2Theresa Fernandez Mendoza0% (1)
- Depression Symptoms Beck's Cognitive Triad Suicide Risk FactorsDocument9 pagesDepression Symptoms Beck's Cognitive Triad Suicide Risk FactorswatchNo ratings yet
- Bmed Concept MapDocument2 pagesBmed Concept Mapapi-247954649No ratings yet
- Patient Education schiZOphreniaDocument2 pagesPatient Education schiZOphreniarinkai13100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Bipolar DisorderGab Abalos100% (2)
- Psychopathologies Models and DSM-5Document13 pagesPsychopathologies Models and DSM-5jin jinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PsychosisDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Psychosisمحمد القرنيNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument28 pagesSchizophreniawizborrlyzo006No ratings yet
- Metastase Bone DiseaseDocument20 pagesMetastase Bone DiseasedrkurniatiNo ratings yet
- Vertical Humeral Osteotomy For Stem Revision in Total Shoulder ArthroplastyDocument5 pagesVertical Humeral Osteotomy For Stem Revision in Total Shoulder ArthroplastyngoyalnNo ratings yet
- Meal Plan Medyo FinalDocument14 pagesMeal Plan Medyo FinalJasha MaeNo ratings yet
- A New Understanding and A Minimalist Approach For.17Document9 pagesA New Understanding and A Minimalist Approach For.17diego.guerra.smithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document38 pagesChapter 1MarjoriePoticanoNo ratings yet
- The Residency Towers: 15 - 16 SeptemberDocument10 pagesThe Residency Towers: 15 - 16 SeptembervamshidhNo ratings yet
- Orthognathic surgery treatment stagesDocument92 pagesOrthognathic surgery treatment stagesishtiiiNo ratings yet
- Mims Indonesia - June.2015.en - SampleDocument1,786 pagesMims Indonesia - June.2015.en - SampleHendryFransiskus50% (2)
- December 30, 2015 Tribune-PhonographDocument15 pagesDecember 30, 2015 Tribune-PhonographcwmediaNo ratings yet
- Speech and language disorders explainedDocument22 pagesSpeech and language disorders explainedJaren NadongNo ratings yet
- Intra Articular Growth Factors and Cartilage Repair. Henrique JonesDocument9 pagesIntra Articular Growth Factors and Cartilage Repair. Henrique JonesNuno Craveiro LopesNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Foot Wound OffloadingDocument8 pagesDiabetic Foot Wound OffloadingTBNo ratings yet
- Nucleus DropDocument1 pageNucleus DropYovinus DenyNo ratings yet
- Shannonresume 2018 ADocument1 pageShannonresume 2018 Aapi-400871779No ratings yet
- Blue Baby SyndromeDocument6 pagesBlue Baby SyndromeHerryanto AgustriadiNo ratings yet
- Gregory Classification, and These Two Classifications Will Give UsDocument15 pagesGregory Classification, and These Two Classifications Will Give Usapi-19840404No ratings yet
- Kasus 2Document3 pagesKasus 2Amalia RisnaNo ratings yet
- LGD-4033 ENDO 2011 Poster FinalDocument1 pageLGD-4033 ENDO 2011 Poster FinaleverstrongNo ratings yet
- Mcguinness2020 - SulforaphaneDocument12 pagesMcguinness2020 - SulforaphaneSITI KHOLIFAHNo ratings yet
- Wound Bed PreparationDocument18 pagesWound Bed PreparationSaurabh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Rifaximin For The Treatment of TDDocument11 pagesRifaximin For The Treatment of TDAnkur AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Hospital Pharmacy ManagementDocument17 pagesHospital Pharmacy ManagementMuhammad MuhlisNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Revascularization in Stable Patients With Diabetes Mellitus - UpToDateDocument22 pagesCoronary Artery Revascularization in Stable Patients With Diabetes Mellitus - UpToDateAnca StanNo ratings yet