Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chi Square IPA
Uploaded by
Dave HallmonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chi Square IPA
Uploaded by
Dave HallmonCopyright:
Available Formats
Hallmon, David. (Summer 2008) C&I 557 Mid-Term. Two Task Analysis of the Chi-Square Method.
Southern Illinois University-Carbondale.
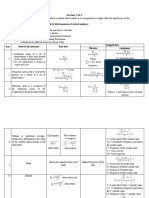
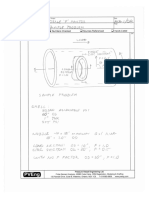
Information Processing Analysis of the Chi-Square Method
Start End
A
Enter with previously unseen data set Chi-Square Method not Locate the df value in the
2 applicable.
& a Chi-Square x Table of statistical 2
appropriate column of the x Table.
significance.
No
Recall the definition of nominal Locate the value closest to your
categorical: Data is not represented in 2
Is the data sets level calculated x on that df row.
scale, order, or intervals. Data is only in
of measurement observed categories with one variable.
nominal categorical?
Move up the column and determine
Recall the Chi-Square Formula: your probability p value.
Yes
x2 = ∑ (fo - fe)2 / fe ,
Multiply the p value by 100 to
Determine the null hypothesis by dividing the determine the percentage %
total sample numbers N by the total number of Recall determining
probability that any deviation from
the null hypothesis: expected is only due to chance.
categories k to determine what the expected
frequency fe would be if due to chance.
fe = N / k
Calculate the difference between 2 Is the p value for Yes
observed frequency fo of a category and Recall part of the x 2
2 the calculated x
the expected fe & square the amount. formula: (fo - fe)
is p > 0.05?
Accept your null
Divide the calculated difference by the 2 No hypothesis. The results
expected frequency fe. Recall part of the x
2 are not statistically
formula: (fo - fe) / fe significant
Reject your null
hypothesis. The results
are statistically
significant. Other factors
Record as Category1 c1 or subsequent are involved!
Recall categories: End
categories c2, c3, c4…
c1= (fo - fe)2 / fe
c2= (fo - fe)2 / fe
End
Yes
Additional categories
in sample?
No
Recall summation of
Sum ∑ all categories in sample categories formula:
c1 + c2 + c3 + … x2 = ∑ c1 + c2 +…
Complete calculations to 4
significant digits. Round off
answer to 3 significant digits.
Recall degrees of freedom
Determine the degrees of freedom formula: df = k -1
df A
You might also like
- Week 6 Homework Chi-Square TestsDocument58 pagesWeek 6 Homework Chi-Square TestsJasonNo ratings yet
- Unit FP1 Further Pure Mathematics 1Document5 pagesUnit FP1 Further Pure Mathematics 1Nushran NufailNo ratings yet
- Math Note - STATISTICS - FORMULASDocument4 pagesMath Note - STATISTICS - FORMULASNesrine LaradjiNo ratings yet
- Chi-square goodness of fit test templateDocument4 pagesChi-square goodness of fit test templateSAT1243No ratings yet
- Appendix: 12.1 Inventory of DistributionsDocument6 pagesAppendix: 12.1 Inventory of DistributionsAhmed Kadem ArabNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Statistics and Probability PDFDocument27 pagesUnit 4 Statistics and Probability PDFcodieNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Chi Squae ApplicationsDocument7 pagesLesson 1 Chi Squae ApplicationsVanessa PuaNo ratings yet
- FRM 2019 Part II - Quicksheet PDFDocument6 pagesFRM 2019 Part II - Quicksheet PDFswetha reddy100% (2)
- Areas Under A Normal DisctributionDocument16 pagesAreas Under A Normal Disctributionvincent.dequit77No ratings yet
- Introduction to Descriptive StatisticsDocument23 pagesIntroduction to Descriptive StatisticsKARAN SINGH-MBANo ratings yet
- M6 2020 Normal Distribution Lecture NotesDocument31 pagesM6 2020 Normal Distribution Lecture Notescoyite8695No ratings yet
- A 18-Page Statistics & Data Science Cheat SheetsDocument18 pagesA 18-Page Statistics & Data Science Cheat SheetsAniket AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Generalised Linear Models and Bayesian StatisticsDocument35 pagesGeneralised Linear Models and Bayesian StatisticsClare WalkerNo ratings yet
- StatisticssheetDocument6 pagesStatisticssheetmohNo ratings yet
- MA8452 PIT - by EasyEngineering - Net 2Document74 pagesMA8452 PIT - by EasyEngineering - Net 2YUVARAJ YUVANo ratings yet
- Rational Equations, Functions and InequalitiesDocument9 pagesRational Equations, Functions and InequalitiesRain VicenteNo ratings yet
- Gen Math M1W2Document10 pagesGen Math M1W2datumanongnormalahNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Two Way Tables Analysis of Two-Way TablesDocument44 pagesAnalysis of Two Way Tables Analysis of Two-Way Tablesuday369No ratings yet
- Reviewer in Statistics and Probability: Measures of Central Tendencies Constructing Probability DistributionDocument2 pagesReviewer in Statistics and Probability: Measures of Central Tendencies Constructing Probability DistributionHyana Imm MedalladaNo ratings yet
- 2016 FRMPart 2 Quick SheetDocument6 pages2016 FRMPart 2 Quick SheetGaurav BansalNo ratings yet
- TI-84 Skills For The IB Maths SL: Zeros (Document4 pagesTI-84 Skills For The IB Maths SL: Zeros (buruh garmentNo ratings yet
- Volker BlobelDocument27 pagesVolker Blobelfetiviw298No ratings yet
- Eng 2015 Prelims ReviewerDocument11 pagesEng 2015 Prelims ReviewerJERICHO ESTIALBONo ratings yet
- Solve, Differential/Quadratic Differential, Integration, Maximum/Minimum Value, and CalculationsDocument16 pagesSolve, Differential/Quadratic Differential, Integration, Maximum/Minimum Value, and Calculationsathembo georgeNo ratings yet
- Notes 2016 FRM Quick SheetDocument6 pagesNotes 2016 FRM Quick SheetJoannaNo ratings yet
- MMW Complete ModuleDocument39 pagesMMW Complete ModuleKristel Joy BelgicaNo ratings yet
- Data Science CheatsheetDocument4 pagesData Science CheatsheetAditiNo ratings yet
- Chap 2:: 4 Levels of MeasurementDocument13 pagesChap 2:: 4 Levels of MeasurementThi Thi PhamNo ratings yet
- Lec17 PriorModelingDocument37 pagesLec17 PriorModelinghu jackNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Quarter 2 Week 3 Test of HypothesisDocument6 pagesStatistics and Probability: Quarter 2 Week 3 Test of HypothesisArth LubayNo ratings yet
- Function Reminders PriDocument32 pagesFunction Reminders PriCarla Itzel GtzNo ratings yet
- Confidence Intervals For Normal Samples PDFDocument8 pagesConfidence Intervals For Normal Samples PDFSahas ParabNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Measures of DispersionDocument10 pagesLesson 4 - Measures of DispersionEdward NjorogeNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency Lec 2Document5 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency Lec 2elakkiyaNo ratings yet
- Equations ConfIntDocument1 pageEquations ConfIntNguyễn TrangNo ratings yet
- Data Science CheatsheetDocument4 pagesData Science Cheatsheet8s97d6ty6pNo ratings yet
- Chi-Square Distribution PropertiesDocument7 pagesChi-Square Distribution PropertiesMohammedseid AhmedinNo ratings yet
- Statistics PacketDocument17 pagesStatistics Packetmafroosahamed73No ratings yet
- Theory of Estimation Ama 4306Document4 pagesTheory of Estimation Ama 4306Shedrine WamukekheNo ratings yet
- Num PyDocument3 pagesNum PyFlávio CrispinNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document4 pagesLab 4Mian BlalNo ratings yet
- Learning Modules: DhayfullahDocument9 pagesLearning Modules: DhayfullahJennan DaraganganNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work: Hrs Units Notes Examples ReferencesDocument17 pagesScheme of Work: Hrs Units Notes Examples ReferencesOluseye AkinNo ratings yet
- 21 20s hw5 PDFDocument5 pages21 20s hw5 PDFkjhgNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan Explore: V Xi8Kkbxh65GDocument9 pagesLearning Plan Explore: V Xi8Kkbxh65GRojelyn ConturnoNo ratings yet
- Modeling Failure Data with a Mixture of Two Weibull DistributionsDocument12 pagesModeling Failure Data with a Mixture of Two Weibull DistributionsSatyam SwarupNo ratings yet
- x (sample mean) is the most unbiased estimate for the population mean μ p= x nDocument5 pagesx (sample mean) is the most unbiased estimate for the population mean μ p= x nelleNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Variance of The Sample Mean Population Standard Deviation of The Sampling DistributionDocument5 pagesStatistics and Probability: Variance of The Sample Mean Population Standard Deviation of The Sampling DistributionAndrea GamutanNo ratings yet
- University of Palestine Gaza Strip Civil Engineering College Numerical Analysis CIVL 3309 Dr. Suhail LubbadDocument36 pagesUniversity of Palestine Gaza Strip Civil Engineering College Numerical Analysis CIVL 3309 Dr. Suhail LubbadHazem AlmasryNo ratings yet
- 2basic Statistics FormulaDocument24 pages2basic Statistics Formulatexmart vzmNo ratings yet
- S1-In A NutshellDocument12 pagesS1-In A NutshelldaliatarekboushraNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Advanced Exam PrepDocument14 pagesArithmetic Advanced Exam Prepmoviestp0No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Polynomial PacketDocument28 pagesUnit 3 Polynomial PacketHaileyNo ratings yet
- Caie A2 Biology 9700 Practical v1Document10 pagesCaie A2 Biology 9700 Practical v1ARMANI ROYNo ratings yet
- Statistics Notes DLDocument7 pagesStatistics Notes DLShannon LimNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1658406732618 6955861992247277741Document3 pagesOrca Share Media1658406732618 6955861992247277741Rowena Thet BulayNo ratings yet
- SS - 3 - Mindmaps - Quantitative MethodsDocument30 pagesSS - 3 - Mindmaps - Quantitative Methodshaoyuting426No ratings yet
- 1 - Roots of Algebraic EquationsDocument7 pages1 - Roots of Algebraic Equationsvnchougule8738No ratings yet
- Checklist s2Document3 pagesChecklist s2Arwa HamdiNo ratings yet
- COAP 2000 Summer Syllabus 2014 HallmonDocument13 pagesCOAP 2000 Summer Syllabus 2014 HallmonDave HallmonNo ratings yet
- Brandt2014 Teaching FestivalDocument1 pageBrandt2014 Teaching FestivalDave HallmonNo ratings yet
- Howald2014 Teaching FestivalDocument1 pageHowald2014 Teaching FestivalDave HallmonNo ratings yet
- COAP 2000 Fall 1 2013 Creating Web Pages With Advanced CSS Dave Hallmon Webster University Week 6 Lesson Fall1 2013Document122 pagesCOAP 2000 Fall 1 2013 Creating Web Pages With Advanced CSS Dave Hallmon Webster University Week 6 Lesson Fall1 2013Dave HallmonNo ratings yet
- Course Term Instructor Name: Email: Catalog Description: Math & Computer Science Department Course SyllabusDocument11 pagesCourse Term Instructor Name: Email: Catalog Description: Math & Computer Science Department Course SyllabusDave HallmonNo ratings yet
- Webster's Online Learning Center in A NutshellDocument21 pagesWebster's Online Learning Center in A NutshellDave HallmonNo ratings yet
- COAP 2000 Fall 1 2013 Creating Web Pages With Multimedia, Attracting Visitors, & Finishing Term Projects Dave Hallmon Webster University Week 7 Lesson Fall1 2013Document135 pagesCOAP 2000 Fall 1 2013 Creating Web Pages With Multimedia, Attracting Visitors, & Finishing Term Projects Dave Hallmon Webster University Week 7 Lesson Fall1 2013Dave HallmonNo ratings yet
- COAP 2000 Fall 1 2013 Week 4 Lesson Creating Web Pages With Tables, CSS, & Utilizing Adobe Kuler + Midterm Exam (Dave Hallmon) Webster Universityk4 Lesson Fall1 2013Document62 pagesCOAP 2000 Fall 1 2013 Week 4 Lesson Creating Web Pages With Tables, CSS, & Utilizing Adobe Kuler + Midterm Exam (Dave Hallmon) Webster Universityk4 Lesson Fall1 2013Dave HallmonNo ratings yet
- Coap 2000 Summer 2013 HallmonDocument13 pagesCoap 2000 Summer 2013 HallmonDave HallmonNo ratings yet
- COAP 2000 Fall 1 2013 Week 3 Lesson Creating Web Pages With Text, Links, & Images (Dave Hallmon) Webster UniversityDocument104 pagesCOAP 2000 Fall 1 2013 Week 3 Lesson Creating Web Pages With Text, Links, & Images (Dave Hallmon) Webster UniversityDave HallmonNo ratings yet
- COAP 2000 Fall 1 2013 Creating Web Pages With Image Maps & Forms (Dave Hallmon) Webster University Week 5 Lesson Fall1 2013Document87 pagesCOAP 2000 Fall 1 2013 Creating Web Pages With Image Maps & Forms (Dave Hallmon) Webster University Week 5 Lesson Fall1 2013Dave HallmonNo ratings yet
- COAP2000 Fall 1 2012 Week 6 Lesson Creating Web Pages With Advanced CSS & Term Project Drafts (Dave Hallmon)Document108 pagesCOAP2000 Fall 1 2012 Week 6 Lesson Creating Web Pages With Advanced CSS & Term Project Drafts (Dave Hallmon)Dave HallmonNo ratings yet
- Course COAP 2000: Introduction To Web Programming Term Site InstructorDocument13 pagesCourse COAP 2000: Introduction To Web Programming Term Site InstructorDave HallmonNo ratings yet
- COAP 2000 Fall 1 2013 Week 1 Lesson Introduction To HTML and The Web Development Cycle (Dave Hallmon) Webster UniversityDocument72 pagesCOAP 2000 Fall 1 2013 Week 1 Lesson Introduction To HTML and The Web Development Cycle (Dave Hallmon) Webster UniversityDave HallmonNo ratings yet
- COAP2000 Fall 1 2012 Week 7 Lesson Creating Web Pages With Multimedia, Social Media, & Attracting Vistors (Dave Hallmon)Document89 pagesCOAP2000 Fall 1 2012 Week 7 Lesson Creating Web Pages With Multimedia, Social Media, & Attracting Vistors (Dave Hallmon)Dave HallmonNo ratings yet
- PHD Policies ProceduresDocument16 pagesPHD Policies ProceduresDave HallmonNo ratings yet
- COAP2000 Fall 1 2012 Week 5 Lesson Creating Pages With Image Maps & Forms (Dave Hallmon)Document70 pagesCOAP2000 Fall 1 2012 Week 5 Lesson Creating Pages With Image Maps & Forms (Dave Hallmon)Dave HallmonNo ratings yet
- Coap2000 Fall 1 2012 Week 4 Lesson When Missing Week 3 Tables, Embedded & Extenal CSS, Template Index (Dave Hallmon)Document52 pagesCoap2000 Fall 1 2012 Week 4 Lesson When Missing Week 3 Tables, Embedded & Extenal CSS, Template Index (Dave Hallmon)Dave HallmonNo ratings yet
- Mann-Whitney Learning HeirarchyDocument1 pageMann-Whitney Learning HeirarchyDave HallmonNo ratings yet
- Coap2000 Fall 1 2012 Week 1 Lesson Introduction To HTML & The Web Development Cycle (Dave Hallmon)Document48 pagesCoap2000 Fall 1 2012 Week 1 Lesson Introduction To HTML & The Web Development Cycle (Dave Hallmon)Dave HallmonNo ratings yet
- Mann WhitneyIPADocument2 pagesMann WhitneyIPADave HallmonNo ratings yet
- UMC Florida Annual Conference Filed ComplaintDocument36 pagesUMC Florida Annual Conference Filed ComplaintCasey Feindt100% (1)
- Making An Appointment PaperDocument12 pagesMaking An Appointment PaperNabila PramestiNo ratings yet
- 797B Commissioning Guidebook 07 (Procesos)Document65 pages797B Commissioning Guidebook 07 (Procesos)wilmerNo ratings yet
- 01 Lab ManualDocument5 pages01 Lab ManualM Waqar ZahidNo ratings yet
- Food Sub Inspector Question PaperDocument12 pagesFood Sub Inspector Question PaperGoutam shitNo ratings yet
- Smartrac - Iolineug - r5Document66 pagesSmartrac - Iolineug - r5Darwin Elvis Giron HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Chenab Railway Bridge Project ReportDocument50 pagesChenab Railway Bridge Project ReportPreet Chahal100% (1)
- On-Chip ESD Protection Design For IcsDocument14 pagesOn-Chip ESD Protection Design For IcsMK BricksNo ratings yet
- Admission Notice 2023-24Document2 pagesAdmission Notice 2023-24Galav PareekNo ratings yet
- Nozzle F Factor CalculationsDocument5 pagesNozzle F Factor CalculationsSivateja NallamothuNo ratings yet
- Crio - Copy Business Operations - Case Study AssignmentDocument3 pagesCrio - Copy Business Operations - Case Study Assignmentvaishnawnikhil3No ratings yet
- Procedure For NC and CapaDocument2 pagesProcedure For NC and CapaSAKTHIVEL ANo ratings yet
- CV. Anderson Hario Pangestiaji (English Version)Document5 pagesCV. Anderson Hario Pangestiaji (English Version)Anderson PangestiajiNo ratings yet
- DesignWS P1 PDFDocument673 pagesDesignWS P1 PDFcaubehamchoi6328No ratings yet
- PQ of Vial Washer Ensures Removal of ContaminantsDocument25 pagesPQ of Vial Washer Ensures Removal of ContaminantsJuan DanielNo ratings yet
- Ecma L1221BR3 PD02 05172016Document2 pagesEcma L1221BR3 PD02 05172016Anil JindalNo ratings yet
- Job Interview CV TipsDocument2 pagesJob Interview CV TipsCarlos Moraga Copier100% (1)
- Final Reflective Essay by Georgi ShopovDocument7 pagesFinal Reflective Essay by Georgi ShopovMd Siddique UllahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-The Hospitality & Travel Marketing SystemDocument14 pagesChapter 3-The Hospitality & Travel Marketing SystemCharis AbadNo ratings yet
- PWC Annual ReportDocument46 pagesPWC Annual ReportAigulNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument27 pagesMathsBA21412No ratings yet
- Research Chapter 1Document7 pagesResearch Chapter 1Aryando Mocali TampubolonNo ratings yet
- Base Is OkDocument84 pagesBase Is OkajaydevmalikNo ratings yet
- BS en 1044-1999 - Brazing Filler MetalsDocument26 pagesBS en 1044-1999 - Brazing Filler MetalsBorn ToSinNo ratings yet
- Epri ManualDocument62 pagesEpri Manualdrjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- User Manual - Rev3Document31 pagesUser Manual - Rev3SyahdiNo ratings yet
- The Act of Proclamation of The Independence of The Filipino PeopleDocument33 pagesThe Act of Proclamation of The Independence of The Filipino PeopleJULIANA RAE CONTRERASNo ratings yet
- Microscopes Open Up An Entire World That You Can't See With The Naked EyeDocument4 pagesMicroscopes Open Up An Entire World That You Can't See With The Naked EyeLouie Jane EleccionNo ratings yet
- JE Creation Using F0911MBFDocument10 pagesJE Creation Using F0911MBFShekar RoyalNo ratings yet
- A Secret Baby by The Bratva by Lexi AsherDocument184 pagesA Secret Baby by The Bratva by Lexi Asheralisa sanchez100% (1)